L39: urinalysis
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
what urinalysis component corresponds to concentrating ability?
USG measurement
what urinalysis component corresponds to proximal tubule reabsorption?
dipstick analysis
what urinalysis component corresponds to tubular damage?
detection of casts
what urinalysis component corresponds to urinary tract inflammation?
presence of pyuria
what urinalysis component corresponds to glomerular (barrier) dysfunction?
significant protienuria (albuminuria)
why do we want fresh urine for a urinalysis?
cells deteroriate and start to form crystals wehn sample left for too long
what are the core components for a urinalysis?
visual
USG
dipstick
sediment
what are the collection methods for a urinalysis?
free catch
cystocentesis
catherization
which collection method would you expect to see bacteria in urine sample analysis?
free catch; expect to see bacteria
which collection method is most sterile for urinalysis; what does presence of bacteria mean?
cystocentesis
if have bacteria indicative of infection
while catherization is a sterile method of urine collection, from what part of the urinary tract will the bacteria be from if in a sample?
bacteria from bladder and upper urinary tract
what does it mean if urine color is colorless?
dilute urine
what does it mean if urine color is light yellow?
normal
what does it mean if urine color is dark yellow?
normal, concentrated; would want USG
what does it mean if urine color is red and clear?
hemoglobinuria
myoglobinuria
what does it mean if urine is red and cloudy?
hematuria
what does it mean if urine is orange to brown?
bilirubin
what does it mean if urine is coffee brown?
myoglobinuria
how else can urine appear if myoglobinuria is present?
red clear urine
what does it mean if urine clarity is clear?
expected, solutes dissolved
what does it mean if urine clarity is hazy to cloudy?
suspended particles present (cells, crystals)
USG by refractometry measures…
solute concentration proportional to the light refraction of dissolved solutes or solids
what 4 reagent strips are not accurate for urine chemical assays by dipstick?
leukocytes
nitrites
ubobilinogen
specific gravity
why are leukocytes not accurate in urinary dipstick tests?
often yields false positives
what type of urine do carnivores typically have?
acidic
what type of urine do herbivores typically have?
alkaline (UNLESS MILK DIET)
what values are a red flag in dilute urine?
+1/+2 protein and +1 bacteria
what USG is telling you it is dilute urine?
1.005-1.015
what change in pH can occur in a delayed analysis?
alkalinuria as bacteria through urea metabolism increase pH longer they are present in sample
what are the categories in which proteinuria can occur?
pre-renal
glomerular
tubular
post-renal
in dogs what is protein level is normal?
some can have trace to 1+
what proteins are detected best by urinaysis?
albumin = best
globulins will also be detected
what issue can result with proteinuria testing with alkaline urine?
false positives in alkaline urine
what does a positive for proteinuria in a urinalysis test indicate about the kidneys?
glomerular, tubular, or mucosal damage due to inflammation
pre-renal cause of proteinuria
small proteins (hemoglobin and myoglobin dimers) pass through glomerulus
*NOTHING WRONG WITH KIDNEYS
what is the only proteinuria that causes hypoalbuminemia?
glomerular
glomerular proteinuria
glomerulus is not working and allowing large proteins such as albumin and globulins to pass through
glomerular proteinuria can be quantified by…
UPC test to determine issue of kidney area
will also be seen on bloodwork
tubular proteinuria
small globulins not reabsorbed by proximal tubules
what is tubular proteinuria often associated with?
acute renal diseases (toxins and hypoxia)
what is important to note about tubular proteinuria?
DOES NOT PRODUCE HYPOALBUMINEMIA
what toxin is often associated with tubular proteinuria?
ethylene glycol
where is hemorrhagic or inflammatory proteinuria taking place in the body?
bladder only
hemorrhagic or inflammatory proteinuria
albumin and globulins are present in the urine due to damage or inflammation in the urinary trac
what conditions cause pre-renal proteinuria?
hemoglobinuria with IMHA
myoglobinuria
Bence Jones (lymphoid neoplasms)
what conditions cause glomerular proteinuria?
*TYPICALLY CHRONIC
glomerulonephritis
glomerular amyloidosis
what conditions cause tubular proteinuria?
acute tubular toxicity
what conditions cause hemorrhagic or inflammatory proteinuria?
hematuria
pyuria
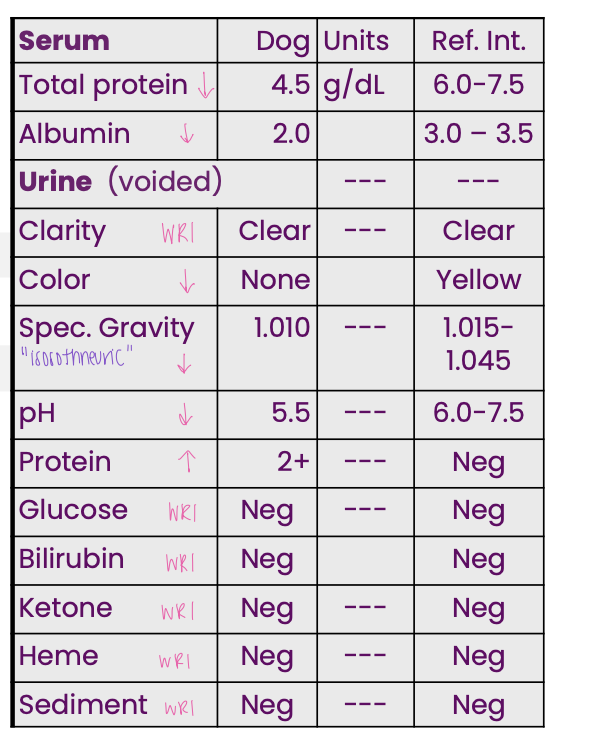
A dog presented for not eating or
drinking; it was dehydrated.
Evaluate serum and USG first.
This dog’s proteinuria is most likely…
glomerular proteinuria
what does UPC need to be?
urine sediment needs to be inactive ( no RBC, bacteria, or WBC present)
what causes need to excluded of proteinuria to trust UPC and what does it tell you?
excluded: pre-renal, tubular, hemorrhagic
tells you: severity of glomerular proteinuria
what physiological process are we expecting when examining urine for glucose?
expect negative reaction as filtered glucose should be reabsorbed by proximal tubule
what plasma glucose level is expected in renal glucosuria?
plasma glucose is WRI
what is the mechanism for renal glucosuria?
glucose enters ultrafiltrate
tubular disease or defect
defective glucose reabsorption
osmotic diuresis
glucose in tubular fluid reduces H20 resorption by tubules leading to polyuria
what ketone in urine does chemical assay detect?
acetoacetate
what ketone does urinalysis not detect and why is that an issue?
beta-hydroxybutyrate; issue because this is elevated in DKA
why are hepatocytes formed in urine?
ketone bodies from fatty acid metabolism
what ketone bodies are formed in urine?
acetoacetate
beta-hydroxybutyrate
acetone
ketonuria
excess catabolism of fatty acids by hepatocytes leads to formation of ketones
what promotes ketonuria?
decreased insulin activity and increased glucagon activity
when is it common to see ketonuria?
diabetes mellitys
bovine ketosis
what electrolyte changes happen with ketonuria?
hyponatremia
hypokalema
hemeturia
RBC in urine sediment
alkaline
USG less than 1.015 (very dilute)
what is the appearance of hemeturia?
plasma= clear
intact RBC
hemoglobinuria
free hemoglobin in sediment; expect patient to have anemia
hemoglobinuria appearance
lysed RBC
plasma = red
myoglobinuria
free myoglobin in sediment; expect evidence of muscle damage in history
what do we expect to be elevated in myoglobinuria?
muscle enzymes (CK)
appearance of myoglobinuria
plasma = clear (no hemolysis)
nothing to do with RBC!
what are the causes of bilirubiuria?
hemolytic icterus
hepatoobiliary disease
hemolytic icterus
bilirubin formation occurring faster and greater rate than bilirubin excretion into bile
hepatobiliary disease
issue with gallbladder leads to impaired bilirubin excretion where bilirubin is regurgitated into plasma
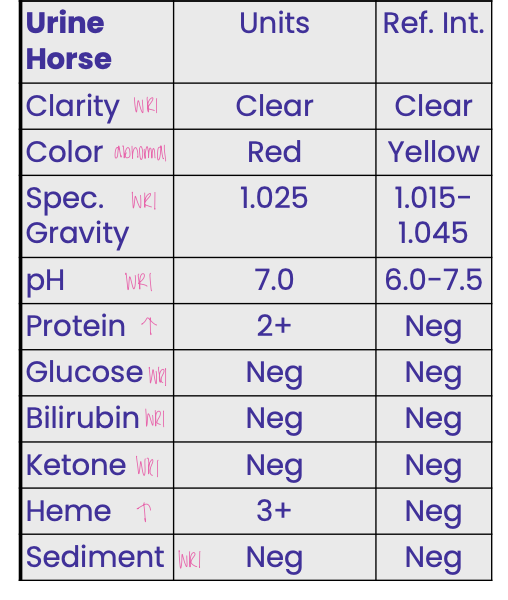
A 6-yr-old horse presented because it
passed red urine. Initial CBC results
revealed anemia (Hct 10 %) and
leukocytosis. The data indicate the
horse has
prerenal proteinuria and intravascular hemolytic disease
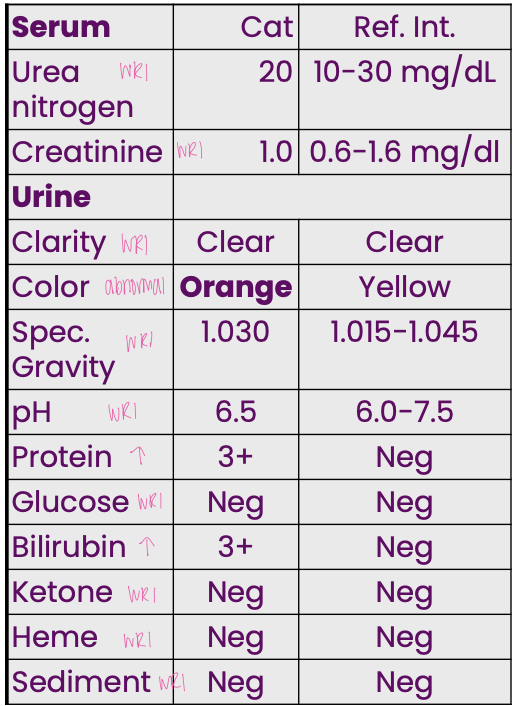
A 6-yr-old cat presented
with pale mucous
membranes, and
mmmm regenerative anemia. Based
on all information, what is
the most likely cause
extravascular hemolytic disorder
pyuria
leukocytes in urine
hematuria
erythrocytes in urine
bacteriuria
bacteria in urine
cylinduria
casts in urine
why might epithelial cells be present in urine?
can be normal, inflammatory, or neoplasia
crystalluria
crystals in urine
pyuria is often concurrent with…
hematuria
what area of the urinary tract are you suscpious of if you see leukocytes or erythrocytes from a voided collection?
genito-urinary tissues
what structures of the urinary tract are you suspicious of being the problem if you see leukocytes or erythrocytes in a sample from catheter?
urethra
bladder
kidneys
male (prostate)
what structures of the urinary tract are you suspicious of as the problem if you see leukocytes or erythrocytes in a sample from cytocentesis?
bladder
kidneys
male (prostate)
what happen to RBC in dilute (<1.015) or alkaline urine?
RBC lyse
what type of change is crenation?
in vitro
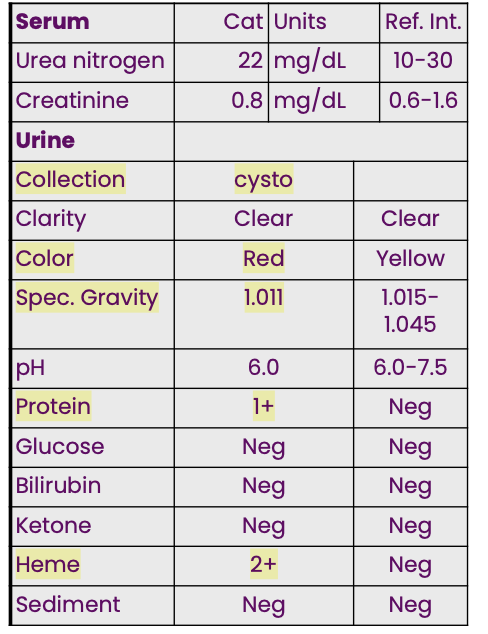
A 3-yr-old cat presented with
anorexia and polyuria. Initial CBC
detected a mild erythrocytosis. The
provided data indicate there is a
hemorrhage in urinary tract
what do you need to do if you have bacteria and no WBC?
culture
when in a cysto sample are we thinking red flag?
if +1 bacteria with no WBC tells you most likely contamination of the sample
casts
Cylindrical molds of renal tubules, made of mucoprotein ± cells
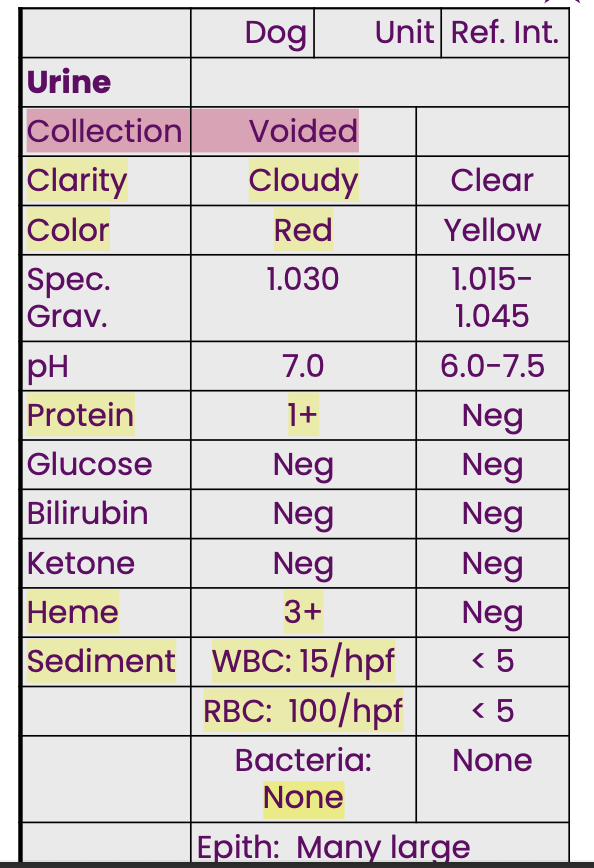
A male dog was presented
because it occasionally
passed red urine. The UA
data indicate there is
inflammation in the genital or urinary tissue
hyaline cast
pure Tamm–Horsfall protein, not
pathologic
casts are a clue for…
tubular injury or degeneratin
granular casts
fine or coarse; active tubular damage or epithelial degeneration
cellular casts
epithelial, leukocyte, erythrocyte
(cells trapped in protein; rare but significant)
waxy casts
advanced, chronic tubular degeneration
what type of epithelial cell in urine would you expect from distal urethra or genital tissues?
squamous
what type of epithelial cells would you expect in a urine sample from renal pelvis to urethra or genito-urinary tissues?
transitional