B6- Inheritance, Variation and evolution
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what is DNA
it is the chemical that all of the genetic material in a cell is made up from.
it contains coded information to put an organism together and make it work.
it determines inherited characteristics
what is a gene
a small section of DNA found on a chromosome.
each gene codes for a particular sequence of amino acids which are put together to make a specific protein
what is a genome
the entire set of genetic material in an organism
why is understanding the human genome important for sience and medicine
identify genes that are linked to different types of disease.
knowing what genes are linked to inherited diseases could help develop effective treatment.
they can trace the migration of certain populations all over the world.
how does sexual reproduction work
sexual reproduction is where genetic info from two organisms is combined to produce offspring which are genetically different.
the mother and father produce gametes by meiosis - sperm & egg
each gamete contains 23 chromosomes - half normal number
the egg and sperm fuse together to form a cell with the full number of chromosomes
how does asexual reproduction work
theres only one parent so the offspring are genetically identical to the parent
happens by mitosis - an ordinary cell makes a new cell by dividing in two
the new cell has exactly the same genetic material - a clone
bacteria,some plants and some animals reproduce asexually
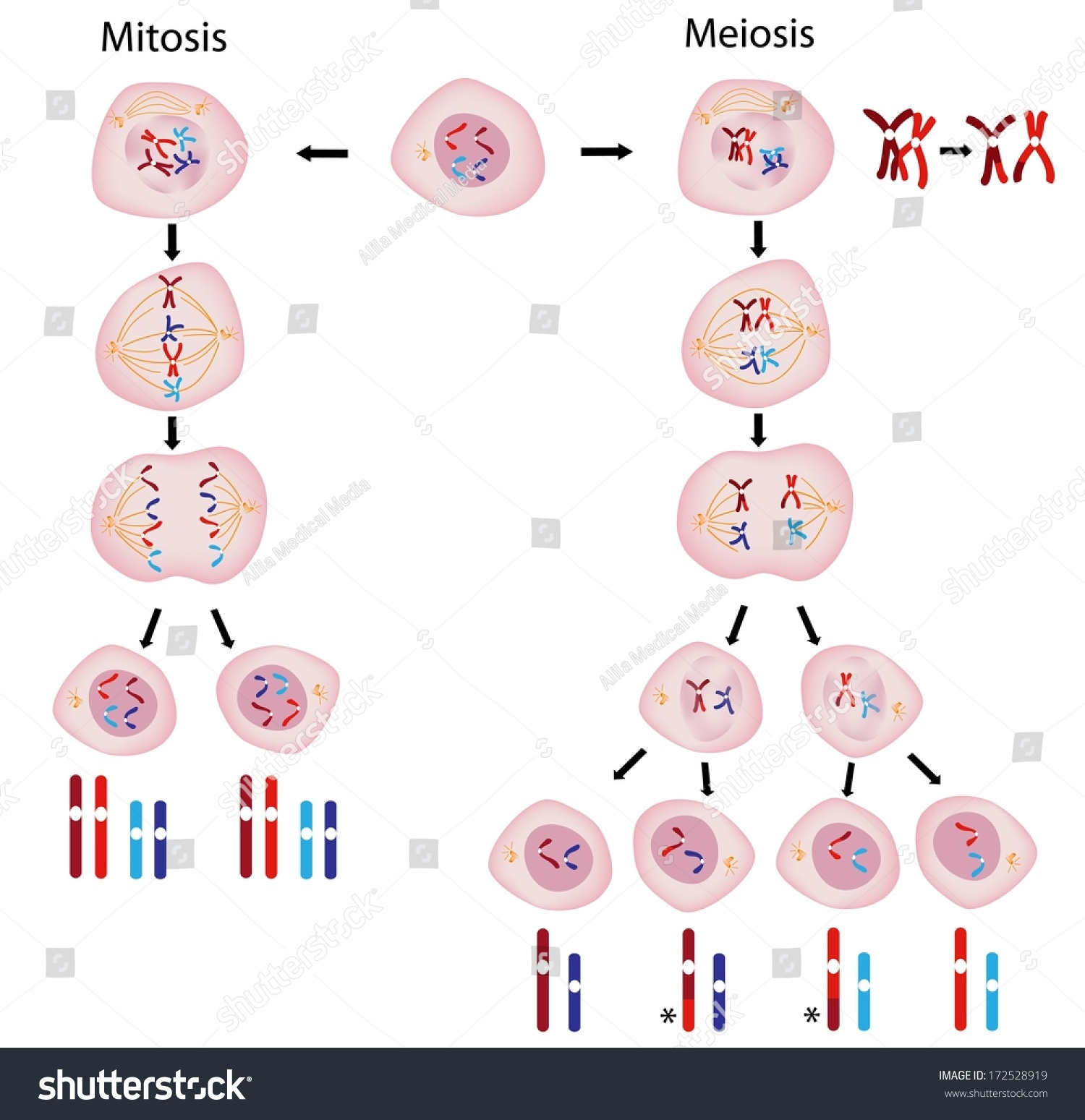
describe meiosis
before the cell divides it replicates its genetic information and the chromosomes arrange themselves into pairs
in the first division the chromosome pairs line up int he center of the cell
the pairs are then pulled apart so each new cell only has one coppy of each chromosome
this is repeated in the second division
4 gametes are produced, each with only a single set of chromosomes.
what is the male and female genetic code
male: XY
female: XX
what does homozygous
if an organism has two alleles for a particular gene that are the same
what is heterozygous
if an organism has two alleles for a particular gene that are different
what is cystic fibrosis
a genetic disorder of the cell membrane. results in the body producing a lot of thick mucus in the air passage and in the pancreas.
the allele is a reccessive ‘f’
both parents must be a carrier of have the disorder
what is polydactyly
a genetic dissorer where a baby is born with extra fingers or toes.
it is caused by a dominant allele ‘D’ and can be inherited if one parent carries it
what is embryonic screening
during IVF it is possible to remove a cell from the embryo and analyse its genes to detect genetic dissorders
why are people against embryo screening
implies that people with dissorders are undesirable
expensive
it may become popular and every one does it to gain desirable characteristics.
why are people for embro screening
help stop suffering
treating the disorders costs the government money - tax
there are laws to stop it going too far
what is variation
variation is genetic and caused by a difference in genotype
what is a mutation
a rare, random change in an organisms DNA that can be inherited
most genetic variants have very little or no effect on the protein it codes for
some variants have small influence on the organisms phenotype - they alter the individuals characteristic
what is the theory of evolution
all of todays species have evolved from simple life forms that first started to develop over three billion years ago
survival of the fittest
charles darwin came up with the theory evolution by natural selection
the organisms with the most suitable characteristics for the environment would be sucessful competitors and more likley to survive
the succesful organisms are more likely to reproduce and pass on the successful characteristics.
over time the beneficial characteristics become more common and the species evolves
what is speciation
over a period of time the phenotype of organisms change so much because of natural selection that a completley new species is formed
populations of the same species change to become reproductively isolated - they cant interbreed to produce fertile off spring
why do species become extinct
the environment changes too quickly - destruction of habitat
new preditors kill them all - humans hunting
a new disease
they cant compete with another species for food
a catastrophic event kills them all
what is selective breeding
when humans artificially select the plants or animals that are going to breed so that the genes for particular characteristics remain in the population
how does selective breeding work
from existing stock, select the ones with the desired characteristics
breed them with eachother
select the best offspring and breed them together
continue this over several generations and the desirable trait gets stronger and stronger
what is the main dissadvantage to selective breeding
there is a reduce in the number of different alleles which can cause health problems from inbreeding.
if a new disease appears because there is not much variation in the population, if one gets killed the others are also likely.
what is genetic engineering
a useful gene is isolated from one organisms genome and is inserted into a vector
the vector is usually a virus or a bacterial plasmid
when the vector is introduced to the target organism the useful gene is inserted into its cells
examples of genetic engineering
bacteria modified to produce human insulin to treat diabetes
crops have been modified to improve the size and quality or make them disease resistant
sheep to produce substances like drugs in their milk to treat disease
3 ways that fossils form
gradual replacement
casts and impressions
preservation
how are fossils formed through gradual replacement
things like teeth, shells, bones - that dont decay easily can last a long time when buried
theyre eventually replaced by minerals as they decay, forming a rock like substance shaped like the original part
the surrounding sediments also turns to rock but the fossils stay distinct.
how are fossils formed through casts and impressions
fossils are formed when an organism is buried in soft material like clay which hardens around the organism as it decays and forms a cast
things like footprints can be pressed into the material when soft and leave an impression
how are fossils formed from preservation
in amber and tar pits there is no oxygen or moisture so decay microbes cant survive
why cant hypotheses abut how life began be proved
many early forms of life were soft bodied and soft tissue tends to decay completely
fossils formed millions of years ago may have been destroyed by geological activity
hoe does bacteria become antibiotic resistant
bacteria sometimes have random mutations in there DNA which can lead to changes in the bacteria’s characteristics meaning they are less affected by antibiotics
bacteria are rapid at reproducing so they can evolve quickly
if it is not impacted by the antibiotic it can live for longer and reproduce quicker which increases the population size.
what are the classification groups
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
what is the three domain system
ARCHAEA - primitive bacteria
Bacteria
Eukaryota - broad range of organisms : fungi, plans, animals, protists