Glycolysis Quiz
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
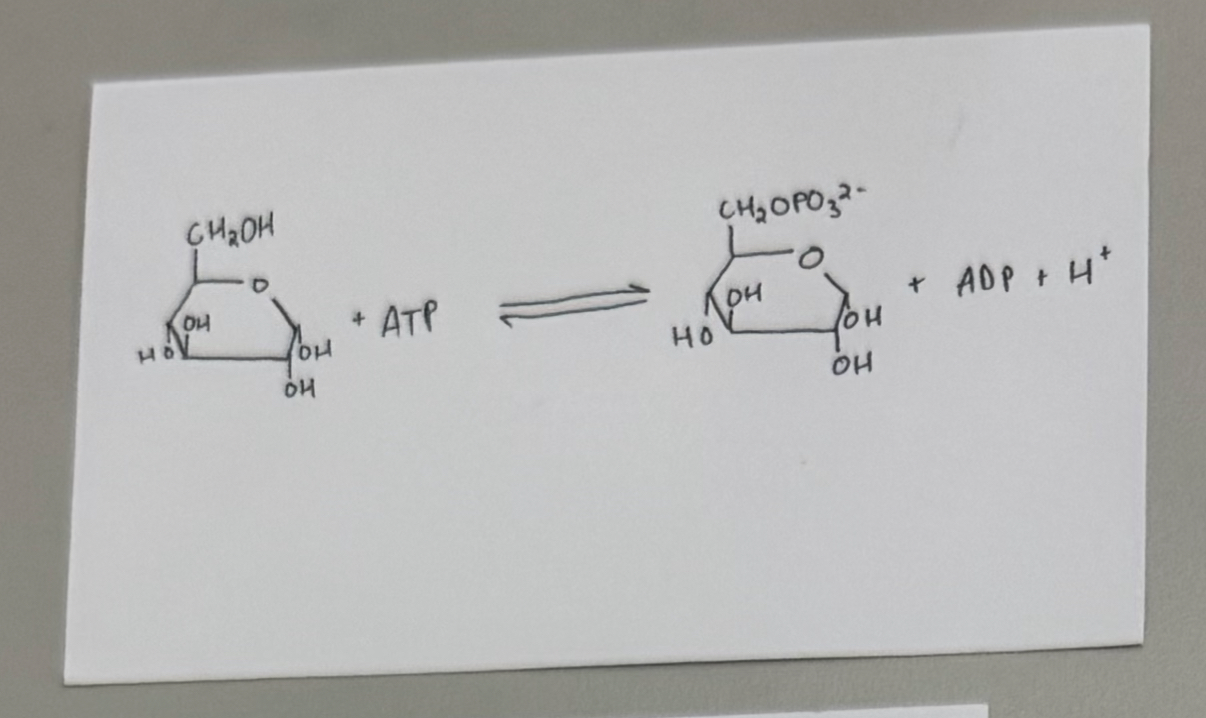
reaction #1 - Hexokinase Catalyzed Reaction
enzyme: hexokinase
purpose:
adds 1st phosphate group
traps glucose in the cell
glucose — > glucose 6-phosphate (G-6P)
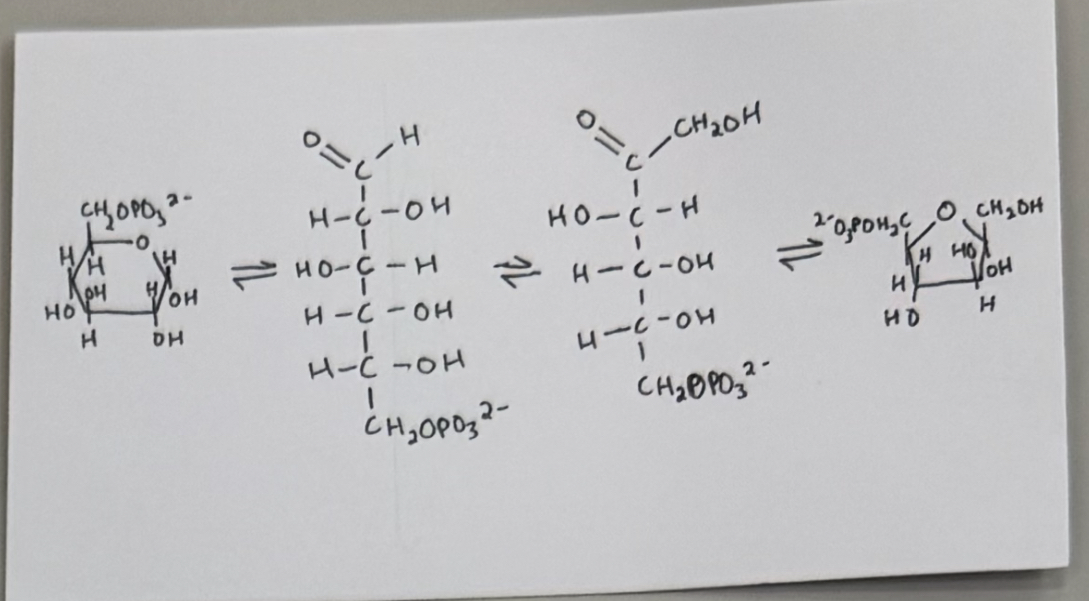
reaction #2 - phosphoglucose isomerase catalyzed reaction (aldose into ketose)
enzyme: phosphoglucose isomerase
purpose:
move carbonyll group to ensure that each product of aldol cleavage (in rxn #4) contains 3 carbons (2,3-carbon molecules)
glucose 6-phosphate (G-6P) ——> fructose 6-phosphate (F-6P)
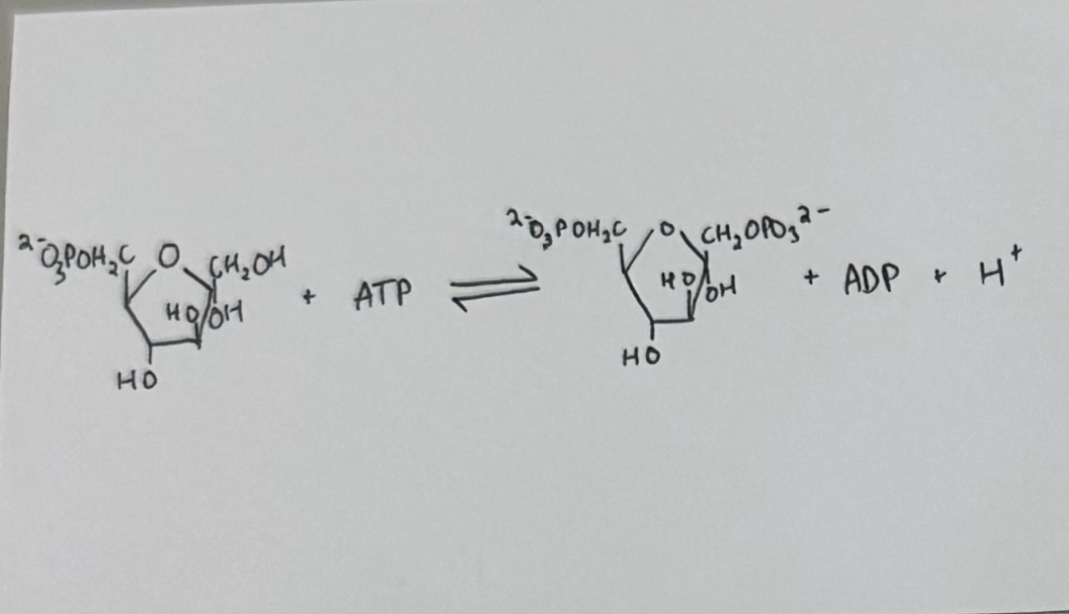
reaction #3 - phophofructokinas catalyzed reaction
enzyme: phosphofructokinase (PFK)
purpose:
adds 2nd phosphate group, so both products in aldolase cleavage reaction have a phosphate group and are isomers of each other.
COMMITTED STEP
fructose 6-phosphate (F-6P) ——> fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (F-1,6BP)
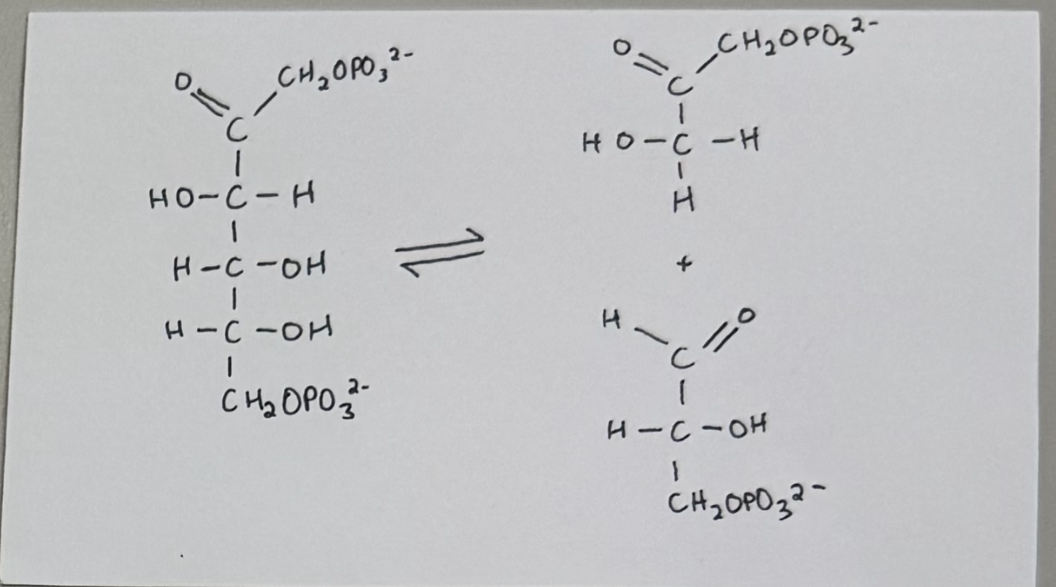
reaction #4 - aldolase catalyzed reaction
enzyme: aldolase
purpose:
cleave a 6-carbon molecule between C3 & C4 into 2, rapidly convertible 3-carbon isomers
fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (F-1,6BP) ——> Dihydroxacetone phosphate (DHAP) & glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP)
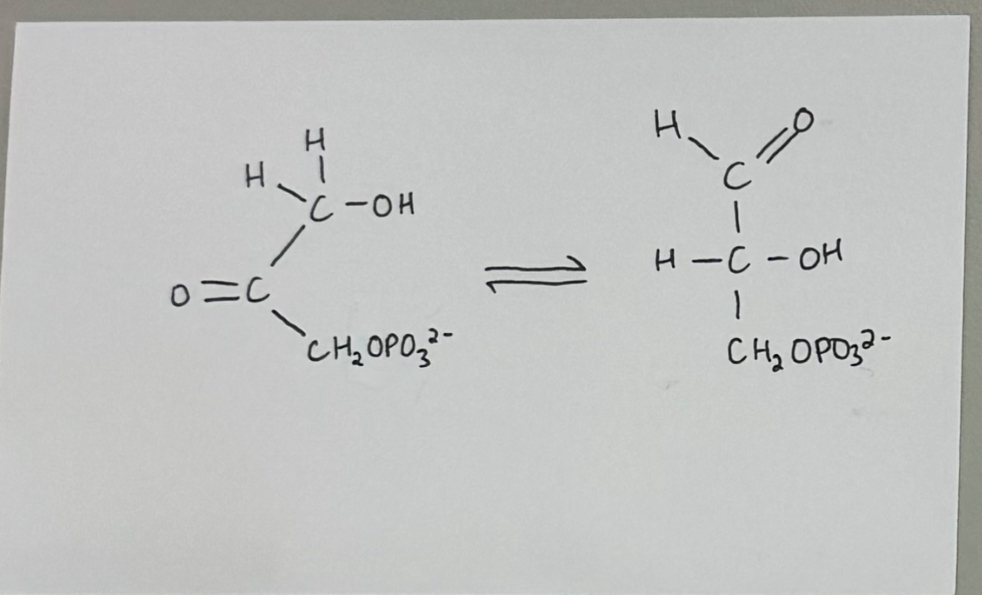
reaction #5 - triose phosphate isomerase catalyzed reaction
enzyme: triose phosphate isomerase
purpose:
GAP (starting point) & DHAP (not used)
enzyme converts DHAP to GAP to maintain supply (most catalytically efficient enzyme in glycolysis)
Dihydroxacetone phosphate (DHAP) ——> glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP)
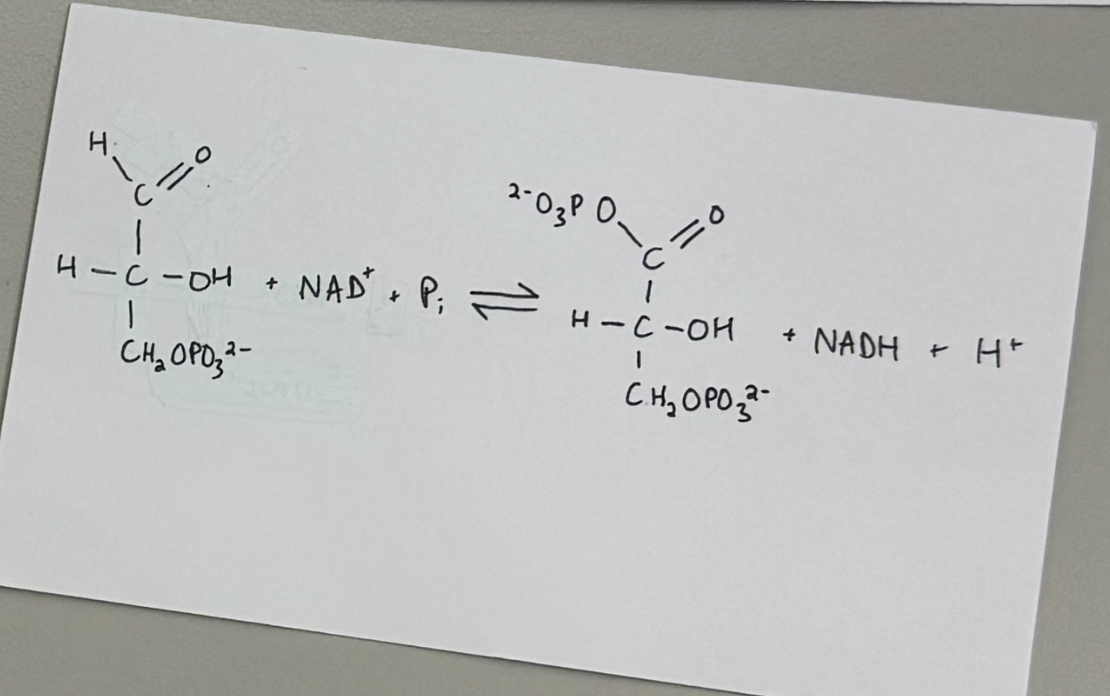
reaction #6 - glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase catalyzed reaction
enzyme: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
purpose:
make a high phosphoryl transfer potential (PTP) compounds
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP) ——> 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG)
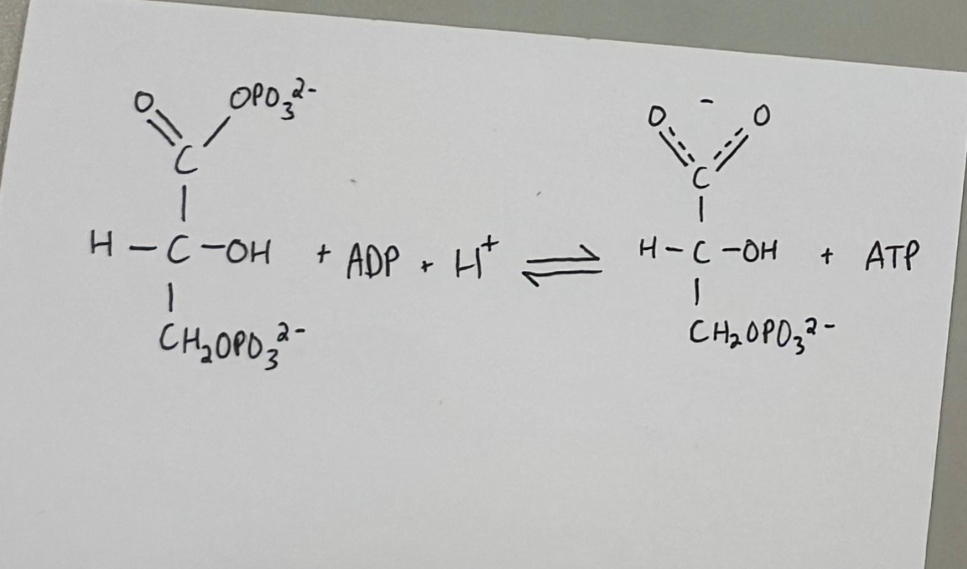
reaction #7 - phosphoglycerate kinase catalyzed reaction
enzyme: phosphoglycerate kinase
purpose:
ATP is generated via substrate level phosphorylation
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate —> 3-phosphoglycerate
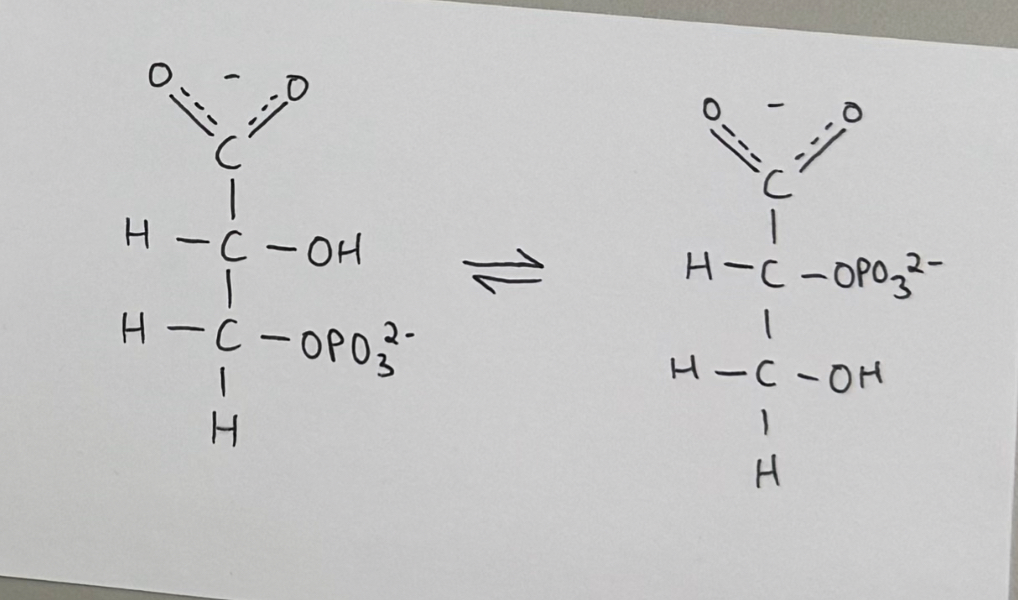
reaction #8 - phosphoglycerate mutase catalyzed rraction
enzyme: phosphoglycerate mutase
purpose:
working towards creating a high phosphoral transfer compound
3-phosphoglycerate ——> 2-phosphoglycerate
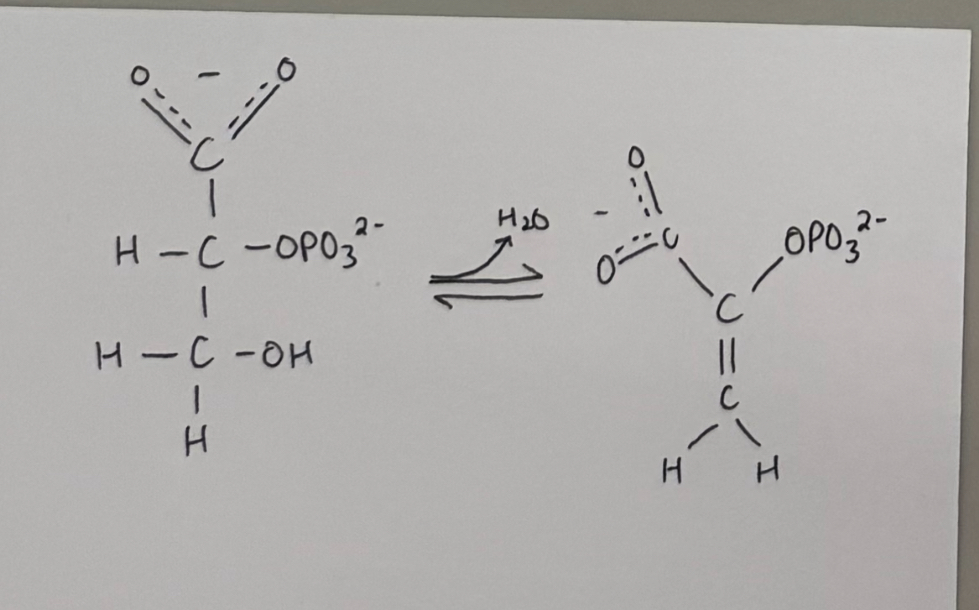
reaction #9 - enolase catalyzed reaction
enzyme: enolase
purpose:
make a high phosphoryl transfer potential (PTP) compound
2-phosphoglycerate ——> phosphoenolpyruvate
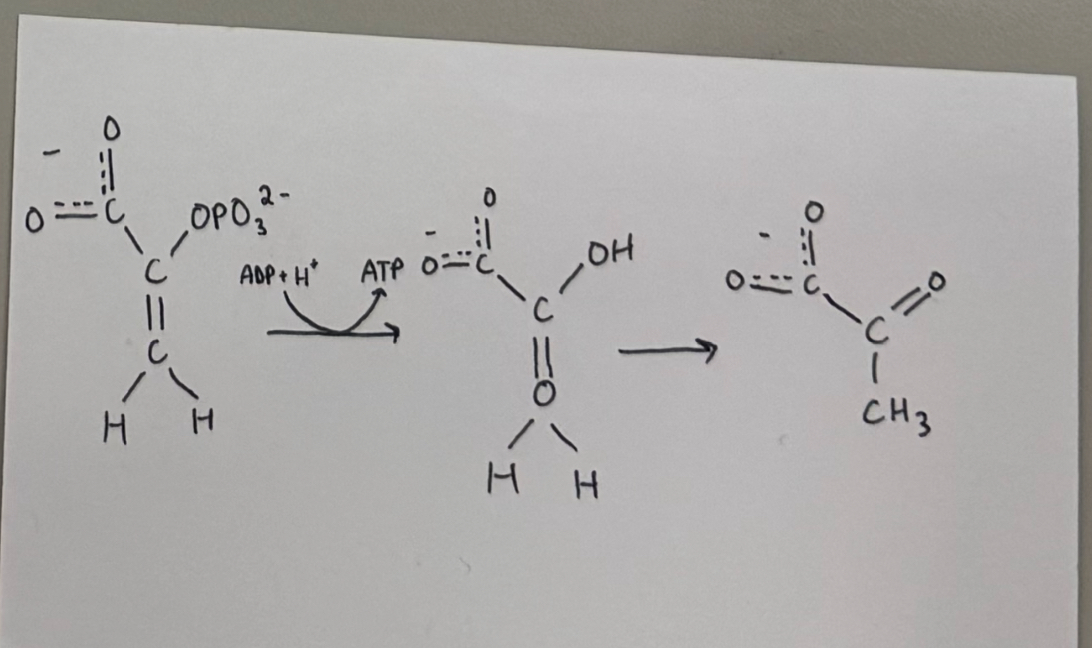
reaction #10 - pyruvate kinase catalyzed reaction
enzyme: pyruvate kinase
purpose:
ATP is generated via substrate-level phosphorylation
phosphoenolpyruvate ——-> pyruvate
What are the two stages of glycolysis?
Stage 1: Investment Stage, Stage 2: Payoff Stage
Stage 1: Investment stage
conversion of glucose to two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP), requires investment of two ATP (trapping and preparation)
Stage 2: Payoff
conversion of two molecules of GAP to two molecules of pyruvate, generates four molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH