BIOLOGY EXAM
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
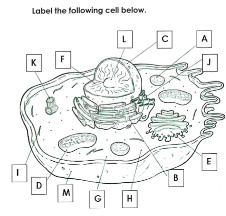
What is A
Lysosome
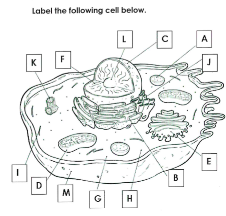
What is B
Rough ER
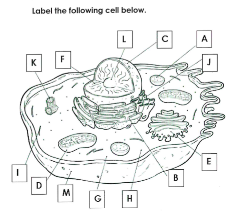
What is C
Nucleus
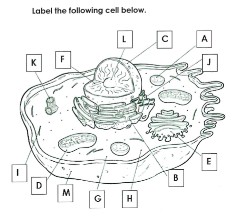
What is D
Mitchondria
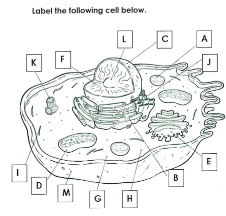
What is E
Golgi apparatus
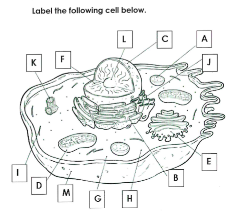
What is F
Chromatin
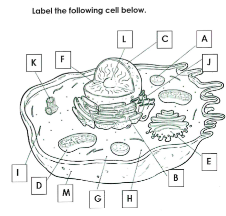
What is G
cytoplasm
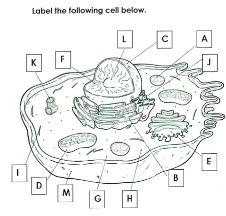
What is H
Ribosomes
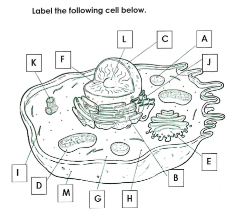
What is I
cytoskelton
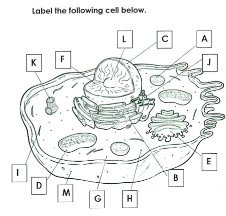
What is J
Smooth ER
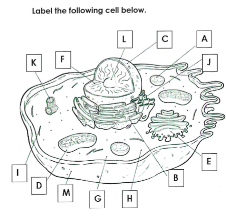
What is K
Centrioles
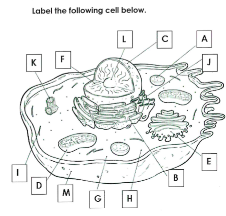
What is L
Nucleolus
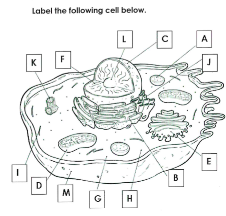
What is M
Cell membrane
Define Homeostasis
maintain stability and ability to fuction even though there are constant changes happening
The three components of a homeostatic mechanism
Sensor Control centre Effector
What do Ribosomes do
site of protein Synthesis
What does Mitchondria do
site of cellular respiration makes ATP
Why the plasma membrane is fluid mosaic
Made of phosolipid bilayer that moves like water
What does it mean if a membrane is selectively permeable
Allows only certain molecules to pass through
Tonocity
The strength of a solution in relationship to osmosis and determines movement of water into or out of cells.
hypotonic
haveing lower concentration of solutes compared to another ( coloured water compared to egg)
hypertonic
higher concentration of solutes compared to another (corn syrup compared to egg)
isotonic
equal concentration of solutes
faciliated diffusion
carrier protiens embedded in the cell membrane carry some molecules across
passive transport
Osmosis
The diffusion of water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration passive transport
passive transport
Movement of substances in and out of cell doese’t use energy
active transport
movement of materials up the concentration gradient low to high uses ATP
exocytosis
when waste and cell products leave the cell
pinocytosis
cell drinking
phagocytosis
cell eating
endocytosis
cell membrane forms a pouch around particles closeing them in a vessicle inside the cell
why bulk transport happens
some molecules are to large to cross the cell membrane and use bulk transport to transport across
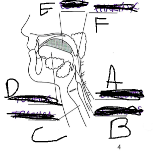
What is A
Epiglottis
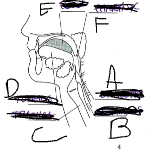
What is B
Esophagus
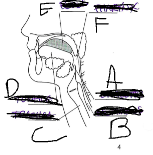
What is C
Trachea
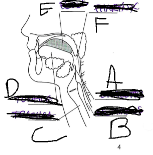
What is D
Tounge
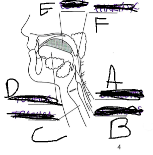
What is E
Bolus
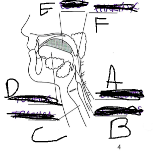
What is F
Pharynx
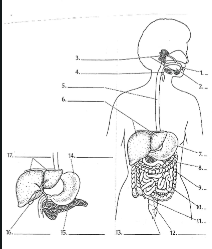
1
Mouth
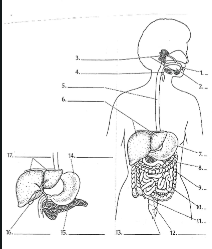
2
Tounge
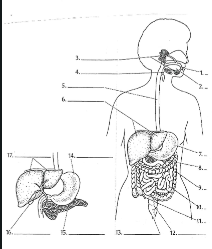
3
salivary glands
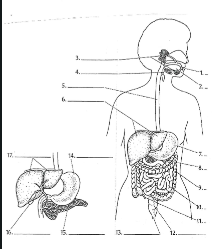
4
Epiglottis
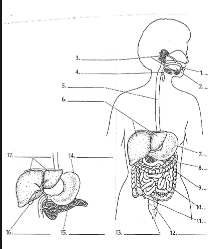
5
Esophagus
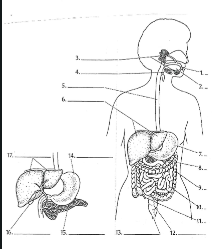
6
Liver
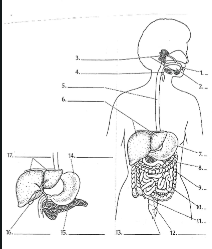
7
Stomach
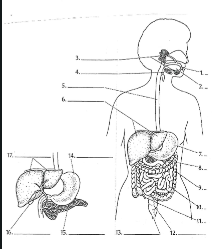
8
Pancreas
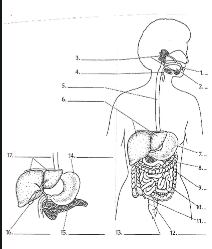
9
Large Intestine
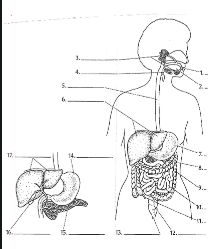
10
small intestine
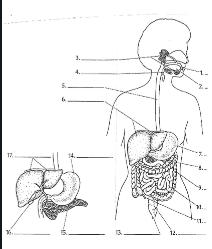
11
Appendix
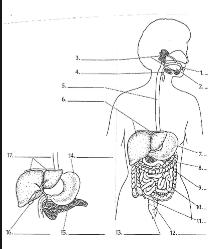
12
Rectum
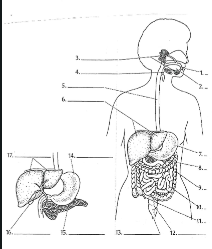
13
Anus
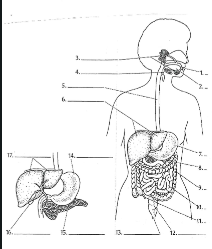
14
Stomach
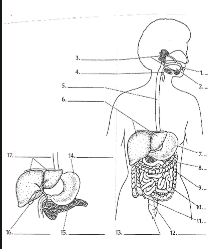
15
Pancreas
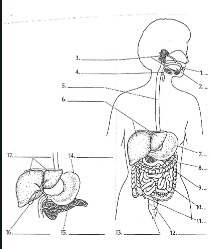
16
Gall bladder
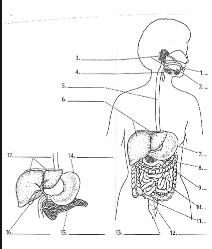
17
Liver
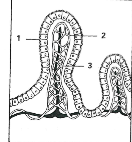
1
Epithelium
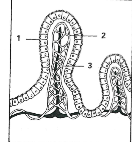
2
Capilaries
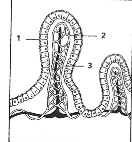
3
Lacteal
Ingestion
eating food
Digestion involves breakdown of food in two ways what are they
Mechanical and Chemical
What is the entrance of the esophagus to the stomach marked by and what does sit prevent
Cardiac Sphincter Blocks stomach acids from coming up into esophagus
if something is Gastric what organ/part of the digestive tract is it referring to
Stomach
How does a person get a Gastric Ulcer
The HCI penetrates the mucus lining of the stomach and burns the wall and breaks it down
Where is majority of digestion completed
The small intestine
what enzyme digest protien and where does it take place
pepsin in the stomach (protease ,pancreas and small intestine)
What chemical process does bile assist with which organ secretes Bile
emsulsification of fats(lipids) The gall bladder secretes bile
Where is salivary amylase found what does it break down
It is found in the mouth and it breaks down Startch (Carbs) to Maltose
Which acid is present in the stomach which aids in chemical digestion
Hydrochloric Acid
Where Chemical digestion of lipids takes place
Small intestine
where does most water get absorbed along the alimentary canal
The large intestine
what is the primary function of the villi in the small intestine
absorption of nutrients
which type of substances are considered lipids give some examples
Fats oils ,waxes, Cholestorel
which macronutrient provides quickest form of energy
CarboHydrates
Function of pancreas
produce bicarbonate ions and digestive enzymes
name the accessory glands
Pancreas
Liver
gall Bladder
salivary glands
how is salivary amylase and pancreatic amylase simalar
they are both enzymes that break down startch (carbs)
what is the medical term for poop what is another word for defecation
Feces, Egested
What is the name of the iron-containing protein molecule whose job is to
carry oxygen and carbon dioxide around the body?
HEMOGLOBIN
Oxygen and carbon dioxide gases are carried by white blood cells. State
if it is true or false and explain why.
FALSE, THEY ARE CARRIED BY RED BLOOD CELLS. WHITE BLOOD CELLS FIGHT INVADERS
Know which cells in your blood work to help clot and repair cuts in blood
vessels and skin. Explain how these cells do their job. Know the scientific and less scientific name for these cells.
PLATELETS (THROMBOCYTES) - THEY ARE VERY FRAGILE & ROUGH TISSUE FROM A CUT CAN RUPTURE THEM. THIS ALLOWS THE STICKY FLUID INSIDE THEM TO BE EXPOSED & THE CLUMP TOGETHER.
4. Simply explain the process some leukocytes use called phagocytosis.
THEY SURROUND, ENGULF, & DIGEST/ DESTROY THE INVADER.
What are the main functions of blood plasma?
-CARRY DISSOLVED NUTRIENTS
-PROVIDE BLOOD VOLOME FOR BLOOD PRESSURE. -CARRY IMMUNE CELLS.
6. What is the universal blood type donor?
O-
What is the universal platelet and plasma donor?
AB (+)
NO A OR B ANTIBODIES
What is the most common blood type?
O+
What is the universal recipient blood type?
AB+
Explain the difference between Rh positive and Rh negative.
A PERSON WITH THE RHESUS PROTEIN ON THEIR RED BLOOD IS RH+ A person who does not have it is RH -
Explain what sets your heart rate and where it is located.
THE SINOATRIAL NODE IN YOUR RIGHT ATRIUM.
Explain what pulmonary circulation is.
CIRCULATION OFBLOOD BETWEEN THE
HEART & LUNGS
Explain what systemic circulation is.
CIRCULATION OF BLOOD BETWEEN HEART
& REST OF BODY.
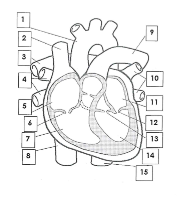
1
Aorta
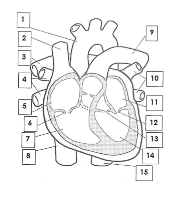
2
Superior vena cava
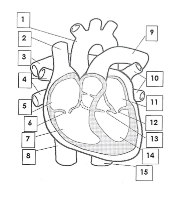
3
pulmonary artery
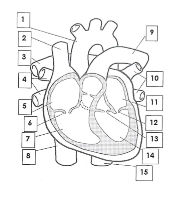
4
pulmonary veins
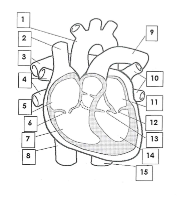
5
right atrium
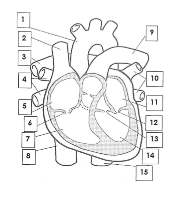
6
tricuspid valve
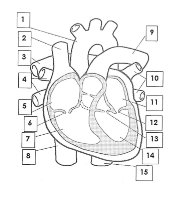
7
right ventricle
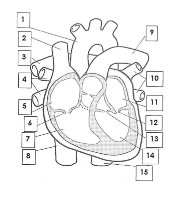
8
inferior vena cava
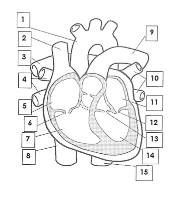
9
pulmonary artery
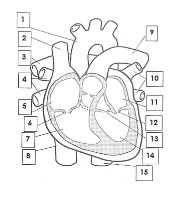
10
pulmonary vein