Year 8 term 4 semester exam cards
5.0(4)Studied by 38 people
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Last updated 12:00 AM on 11/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
igneous rocks
a rock formed by cooled molten material.
2
New cards
metamorphic rock
a rock formed from a sedimentary, igneous or other metamorphic rocks that have under gone increased temperatures and pressure over a long period of time.
3
New cards
sedimentary rock
rock made from compressed sediment
4
New cards
mineral
a naturally occurring, inorganic substance present in the solid state, made of a specific chemical formula in a definite crystal structure.
5
New cards
rock
an inorganic, solid, and natural substance without any specific atomic structure or chemical composition.
6
New cards
what is the rock cycle?
is the process of how rocks become other types of rocks over huge periods of time
7
New cards
ore
an ore is a mineral with a large amount of useful metal in it.
8
New cards
what are the 2 ways minerals can form?
through the crystallization of magma, or the crystallization of materials dissolved in solution.
9
New cards
properties of a mineral
hardness, luster, cleavage, and streak
10
New cards
hardness
how easily a mineral can be scratched
11
New cards
luster
the shininess of a surface of a mineral
12
New cards
cleavage
the tendency of a mineral to break into a number of smooth planes
13
New cards
streak
the color of a powdered or crushed mineral.
14
New cards
properties of a rock
weight and density, color, layers, crystals and grain.
15
New cards
intrusive igneous rock
is an igneous rock found and formed deep within the earth by magma.
16
New cards
extrusive igneous rock
is an igneous rock found and formed on the surface of the earth by lava.
17
New cards
difference between intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks.
Intrusive rocks tend to have larger crystals, this is because the magma takes longer to cool, so the crystals have more time to form. Extrusive rocks tend to have smaller crystals, This is because the lava cools much more rapidly so the crystals have less time to form.
18
New cards
layers of the earth in order.
crust, mantle, outer core, inner core
19
New cards
lithosphere
is the solid, outer part of the Earth, made of the crust and upper most solid mantle.
20
New cards
Asthenosphere
is the denser, weaker layer beneath the lithospheric mantle made up of the partly molten section of the upper mantle.
21
New cards
kinds of tectonic plates boundries
transform, divergent, and convergent.
22
New cards
transformative boundries
when two tectonic plates slid past each other in opposite directions.
23
New cards
Divergent boundaries
when two plates spread apart from each other.
24
New cards
convergent boundaries
when a two tectonic plates go against each other and one goes
25
New cards
continental drift
is the idea that continents are continually moving and have significantly changed positions over millions of years.
26
New cards
sea-floor spreading
that the middle of the ocean is spreading apart, moving very slowly in opposite directions.
27
New cards
energy
energy is a massless entity that causes things to happen. It is the ability of an object to do work.
28
New cards
kinetic energy
is the energy of moving things
29
New cards
potential energy
energy that is stored and could be used
30
New cards
types of kinetic energy
mechanical, electrical, light, thermal, sound (remember M.E.L.T.S)
31
New cards
types of potential energy
gravitational potential energy, chemical potential energy, elastic potential energy
32
New cards
Law of conservation of energy
energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be transformed of transferred.
33
New cards
conduction
passing kinetic energy from one substance to another by direct contact
34
New cards
convection
is the transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid (gas or liquid) between areas of different temperatures
35
New cards
radiation
the transfer of heat across space or through another substance without touching it in the forms of waves/rays.
36
New cards
magma
molten rock underground
37
New cards
lava
molten rock exposed at the earths surface
38
New cards
what causes seismic waves?
they are caused by a sudden movement of materials within the earth
39
New cards
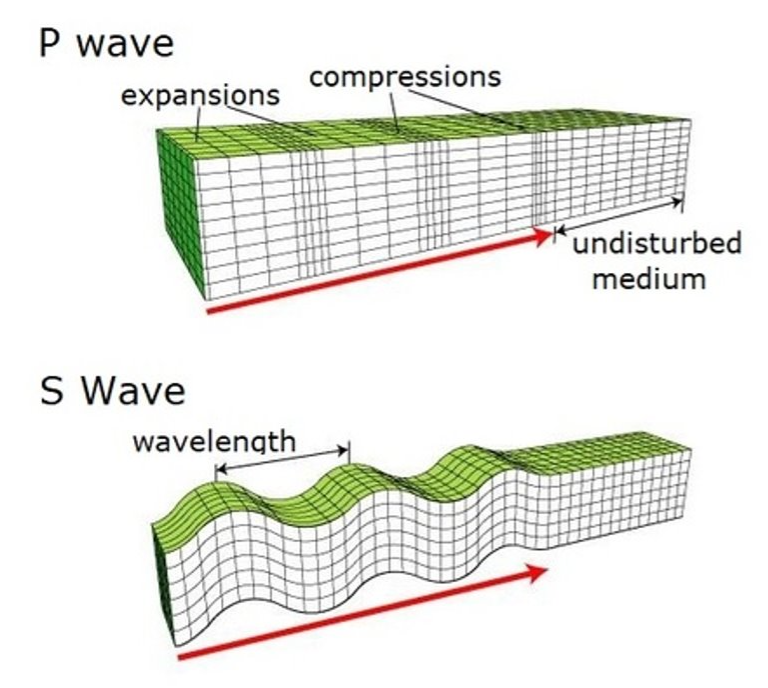
P-waves (primary waves)
they are the fasted wave that travels through the inside of the Earth through solid and liquid. It reaches the seismic station first and moves the rock in a push-pull compressional wave.
40
New cards
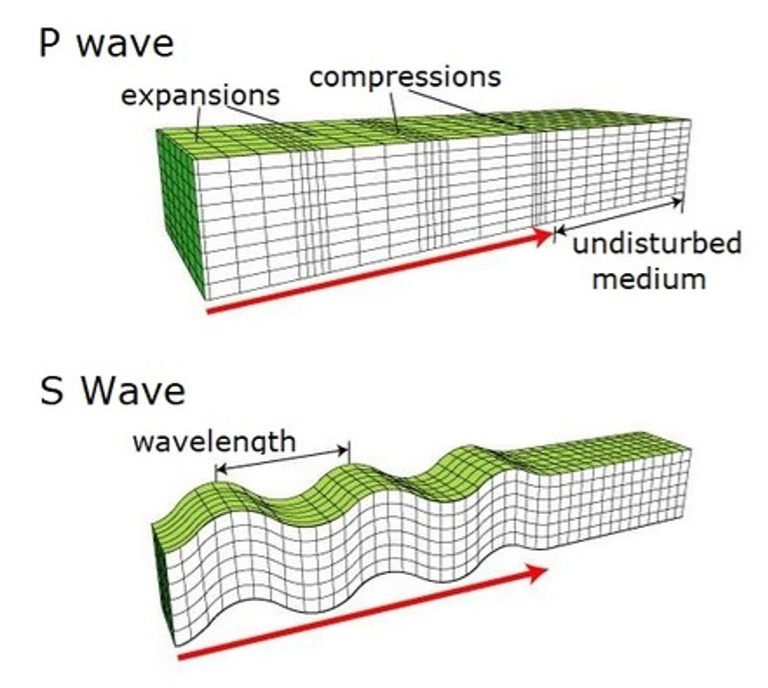
S-waves (secondary waves)
they travel through the inside of the earth through solids only, it reaches the seismic station second. It moves rock up and down perpendicular to the wave.
41
New cards
what are fossils
is an organism preserved in a rock.
42
New cards
how do fossils form
fossils form when an organism dies, and it gets covered by sediment then over millions of years, as the sediment builds up, it compacts and cements turning it into a sedimentary rock, which preserves the organism from weathering and predators.
43
New cards
how do you date fossils
You can date them by using comparative dating, this compares the different layers of the Earths sediments, bottom being the oldest and top being the youngest. Another way to date fossils is using radioactive dating, you do this by measuring the amount of radioactivity left in rocks
44
New cards
pangea
Pangea was a super-continent, and the idea that the all the continents were once connected.
45
New cards
order of pangea
Permian, Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous, Present day.
46
New cards
effect of transformative plates
earthquakes
47
New cards
effect of convergent plates
trenches, volcanoes, and mountains
48
New cards
effect of divergent plates
rift valleys, and ocean floor spreading
49
New cards
rift
is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart