4.6: Place
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/31
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
1
New cards
what is a distribution channel
route taken from the producer to the customer
2
New cards
methods of distribution
- retailer
- wholsaler
- agent
- wholsaler
- agent
3
New cards
retailers
- bulk breaking
- sell in locations convenient to customers
- add value to products by providing other services
- sell in locations convenient to customers
- add value to products by providing other services
4
New cards
features of common retailers
- independents
- supermarkets
- department stores
- chain stores
- hypermarkets
- kiosks
- market traders
- online retailers
- supermarkets
- department stores
- chain stores
- hypermarkets
- kiosks
- market traders
- online retailers
5
New cards
independents
relatively small outlets owned by sole traders
6
New cards
supermarkets
- large stores selling many product lines
- cheaper than independents as they can afford to buy in bulk from manufacturers
- located on cheap land with readily available parking
- cheaper than independents as they can afford to buy in bulk from manufacturers
- located on cheap land with readily available parking
7
New cards
department stores
- large stores split into distinct selling departments
- aim to provide good quality products with customer service
- aim to provide good quality products with customer service
8
New cards
chain stores
one owner opens multiple stores selling the same range of goods in many different locations regulated by the same central office with standardised:
* products
* pricing
* store front
* store layout
* staff uniform
* staff training and wages
they specialise in all sorts of product lines by bulk buying direct from manufacturers for low cost of sales
* products
* pricing
* store front
* store layout
* staff uniform
* staff training and wages
they specialise in all sorts of product lines by bulk buying direct from manufacturers for low cost of sales
9
New cards
hypermarkets
* very large
* located on the outskirts of town
* sell a wide range of goods
* fewer staff
* wide product range
* cheaper than supermarkets
* located on the outskirts of town
* sell a wide range of goods
* fewer staff
* wide product range
* cheaper than supermarkets
10
New cards
kiosks
* small
* limited range of foods
* fast food, confectionary, newspapers
* low set up costs
* minimal overheads
* price depends on location
* limited range of foods
* fast food, confectionary, newspapers
* low set up costs
* minimal overheads
* price depends on location
11
New cards
market traders
* small time businesses selling goods from market stalls
* common
* low overheads
* cheaper than retailers
* some move from one market to another
* common
* low overheads
* cheaper than retailers
* some move from one market to another
12
New cards
online retailers
buy goods from manufacturers and sell them online
13
New cards
2 types of e-commerce
* business to consumers
* business to business
* business to business
14
New cards
business to consumers (B2C)
* ordered online and delivered
* click and collect
* click and collect
15
New cards
business to business (B2B)
* businesses selling to other businesses
* cheapest supplier
* cheapest supplier
16
New cards
B2C - benefits to consumers
* cheap due to low costs
* 24/7
* variety and choice
* can shop from anywhere
* 24/7
* variety and choice
* can shop from anywhere
17
New cards
B2B - benefits to businesses
* no costs of operating stores
* low start up costs
* low costs of transaction
* less paper needed
* payments can be made through online systems
* wider market
* 24/7
* choice when locating operations
* low start up costs
* low costs of transaction
* less paper needed
* payments can be made through online systems
* wider market
* 24/7
* choice when locating operations
18
New cards
disadvantages of e-commerce
* increased competition
* lack of human contact
* heavy dependency on delivery services
* technical problems
* security risk and malware
* poor aftersales
* customers without internet access and cards are excluded
* fake traders are difficult to identify
* lack of human contact
* heavy dependency on delivery services
* technical problems
* security risk and malware
* poor aftersales
* customers without internet access and cards are excluded
* fake traders are difficult to identify
19
New cards
other distribution methods
* direct selling
* wholesaling
* agents
* wholesaling
* agents
20
New cards
direct selling
producers market products directly to consumers
21
New cards
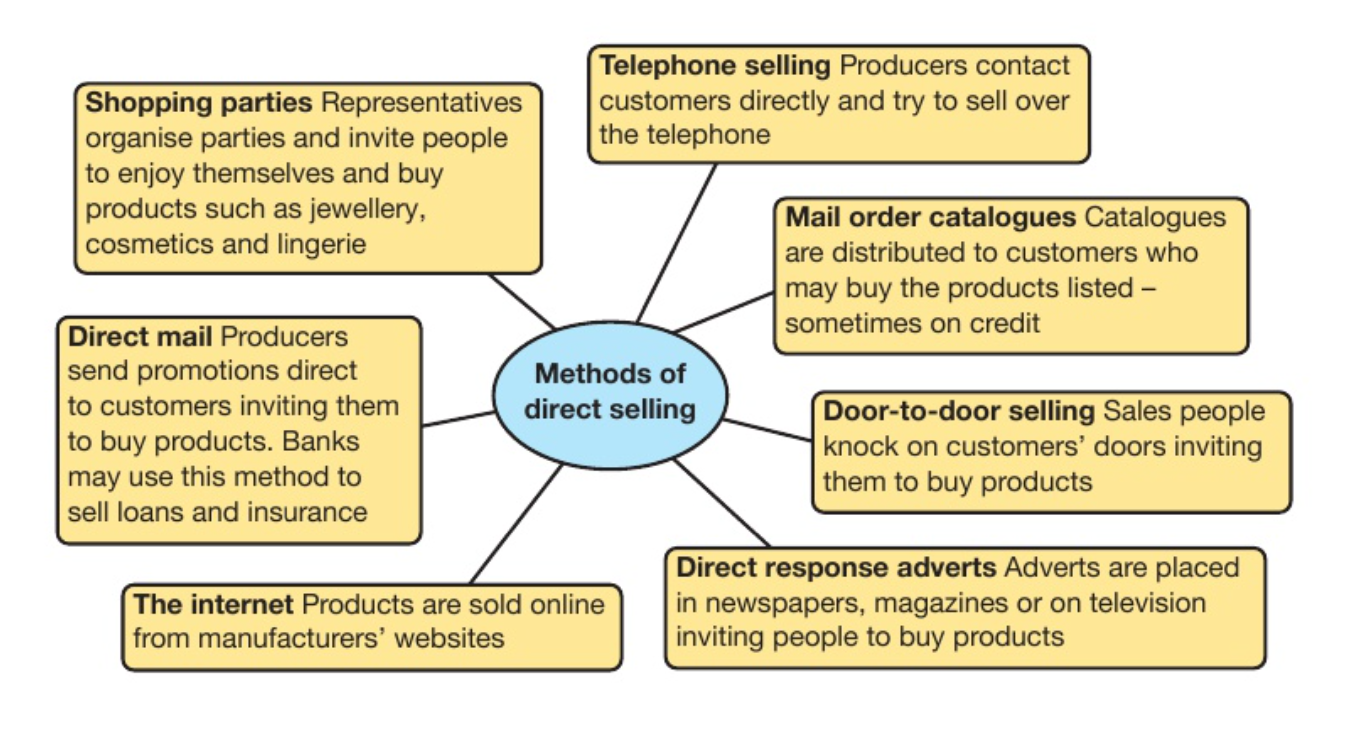
methods of direct selling
* shopping parties
* telephone selling
* mail order catalogues
* door to door selling
* direct response adverts
* direct mail
* internet
* telephone selling
* mail order catalogues
* door to door selling
* direct response adverts
* direct mail
* internet
22
New cards
wholesaling
buy from manufacturers and sell to retailers
* some break bulk, repack goods, redistribute smaller quantities, store goods and provide delivery services
* stocks goods produced by many manufacturers
* some break bulk, repack goods, redistribute smaller quantities, store goods and provide delivery services
* stocks goods produced by many manufacturers
23
New cards
wholesaling - cash and carry stores
customers come, buy goods, pay cash and take goods
24
New cards
agents
link buyers and sellers
25
New cards
when are manufacturers most likely to use agents
when exporting, as agents reduce risk by knowing the market
26
New cards
what to look at when choosing distribution channels
* nature of the product
* cost
* market
* control
* cost
* market
* control
27
New cards
nature of the product
different types of products require different distribution channels:
* services sold directly to customers
* fast-moving consumer goods
* high quality ‘exclusive’ products
* products needing demonstration
* services sold directly to customers
* fast-moving consumer goods
* high quality ‘exclusive’ products
* products needing demonstration
28
New cards
cost
* businesses choose the cheapest distribution channels
* prefer direct channels
* intermediary take share of the profit
* bulk buy = lower prices
* prefer direct channels
* intermediary take share of the profit
* bulk buy = lower prices
29
New cards
market
* when selling to mass markets - use intermediaries
* when targeting smaller markets - target customers directly
* overseas markets - use agents
* selling to other businesses - use direct channels
* when targeting smaller markets - target customers directly
* overseas markets - use agents
* selling to other businesses - use direct channels
30
New cards
control
some producers like to have complete control over distribution
31
New cards
large businesses
* more important
* greater quantities of produce
* benefitted from online selling
* greater quantities of produce
* benefitted from online selling
32
New cards
small businesses
* benefitted from online selling
* find it easier to sell to global markets
* find it easier to sell to global markets