Theories of Personality Exam 3 Dr. Dimos
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Freud Key Word
FORCES
Emphasized unconscious forces (instincts, drives, psychic energy) controlling behavior
Freudian Basic Assumptions
Psychic Determinism (there is a psychic meaning underlying all thoughts, feelings, and behaviors; freudian slips)
Influence of the Unconscious Mind (all thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are determined by unconscious forces)
Personality is a Closed System
There is a limited amount of energy
Energy can be blocked but does not “just go away,” instead gets expressed in some other manner, along a path of least resistance
The mind functions to achieve a state of homeostasis
Freud's Instincts and Psychic Energy
Life instinct (libido): drives people toward the preservation and reproduction of the organism
Death instinct: the destructive, dark motivational force to use psychic energy to get what you want (sex)
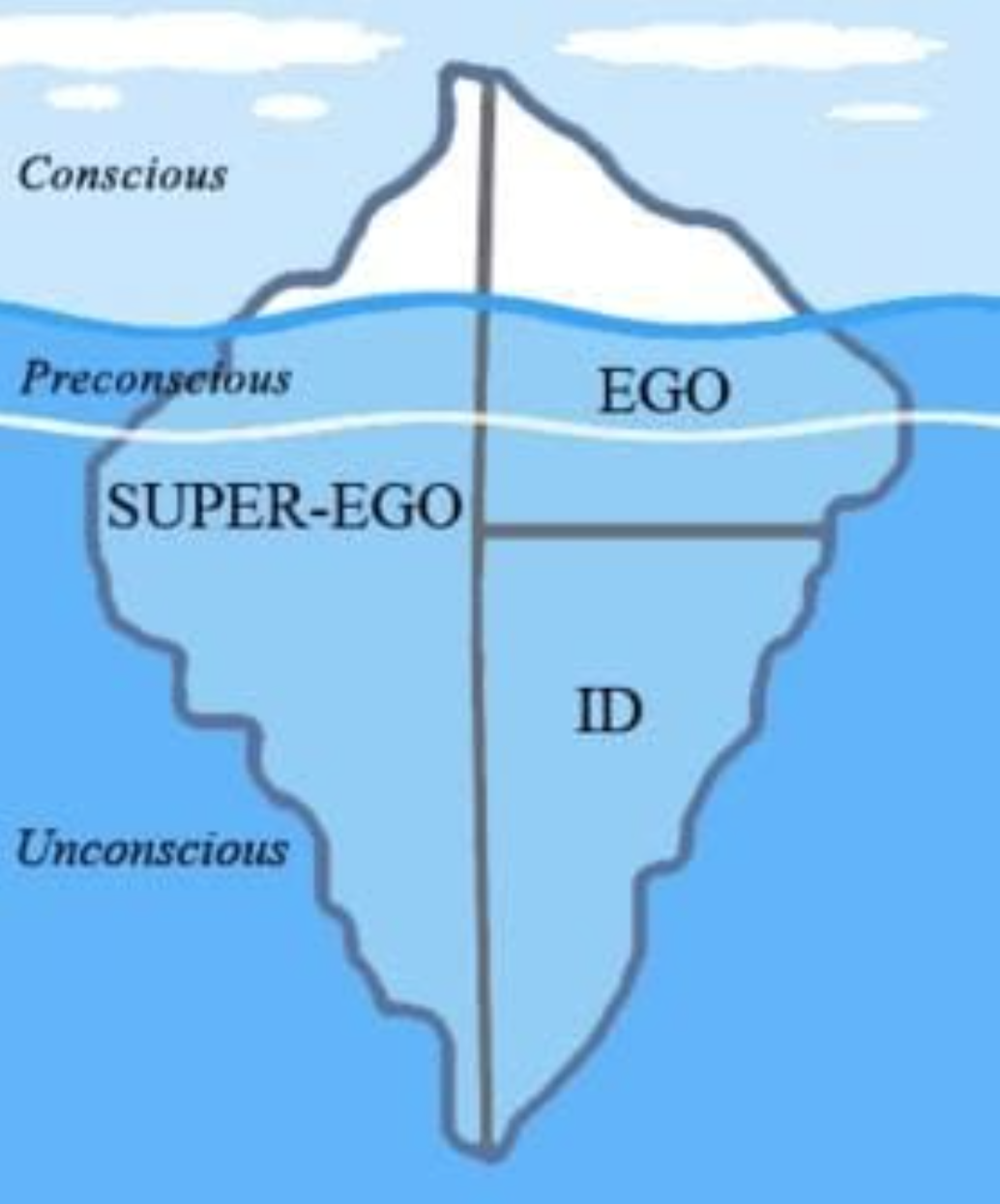
Freud's 3 Regions of the Mind
Unconscious mental contents are parts of the mind we are unaware and cannot become aware of except under special circumstances
Preconscious level could be aware if attended to
Conscious level includes thoughts we are aware of
The Id
The core of personality
Operates on the pleasure principle
Present at birth, gets pushed into unconscious region in early life
Source of psychic energy and instincts
The Ego
Develops in response to the demands of the real world
Operates on reality principles
Functions to meet the demands of the id within the confines of reality and morality
The Superego
The Moral Authority of Personality
Develops as the internalized voice of society; a conscience
Freud attempted to understand the properties of the unconscious by analyzing a variety of psychological phenomena:
Psychoses
Dreams
Slips of the tongue
Works of art
Neuroses
Rituals
Psychodynamic Perspective Overview
Purpose: assist the ego to deal with the conscious and unconscious threats of anxiety
Healthy use vs Unhealthy use
Selective use in conscious awareness can serve as an effective temporary strategy
Excessive unconscious activation can result in the development of psychopathology
Key to the Freudian Personality Structure: Balance
Freud's Ego Defense Mechanisms
Sublimation: finding a social appropriate outlet
Undoing: making up for your guilt indirectly
Projection: YOU have the problem!
Repression: most basic
Reaction Formation: expressing the opposite feeling
Rationalization: talking yourself into it
Regression: becoming child-like
Denial: distant reality to make it more comfortable (most common)
Displacement: kicking the dog after a big argument (hurt people, hurt people)
Theory of Psychosexual Stages of Development
Development occurs in a series of distinct steps/stages
In each stage, we look for successful resolution which propels us to the next stage, or we can get “fixated” by either indulging or repressing the desire
On April, Peter Learned Growth
Oral Stage of Development
0-18 months (0-2 yo)
Focus: Pleasure centers on the mouth (sucking, biting).
Key Task: Weaning from breast feeding; developing trust and a sense of security.
Successful: the emergence of the ego and the development of delay of gratification
Unsuccessful: ego too weak to control oral impulses (chewing gum/nails/kissing)
Anal Stage of development
2-3 yo
Focus: Pleasure shifts to the anus (withholding and expelling feces).
Key Task: Toilet training; learning self-control and obedience.
Successful: superego emerges
Unsuccessful: associate bowel movements with losing something (anal retentive; rigid and controlling) or a prize/gift to others (anal sadistic: messy/careless)
Phallic Stage of Development
3-7 yo
Focus: Pleasure focuses on the genitals.
Key Task: Resolving the Oedipus or Electra complex; identifying with same-sex parent.
Oedipus complex: boys wanting to kill father (jelousy) to get to mother
Castration anxiety: boys fear of losing genital; realization that girls don't have a penis
Successful resolution: hostility towards father leads to increased castration anxiety and eventual abandonment of oedipus complex
Unsuccessful: stays a mama's boy; don't develop appropriate male interests
Latency Stage of Development
7-11 yo
Focus: Suppression of sexual impulses; emphasis on social and intellectual development; realization of libido; decrease in sexual urges and interest
Key Task: Developing social and cognitive skills; forming relationships outside the family
Genital Stage of Development
11 yo+
Focus: Reawakening of sexual interests (resurgence of libido); directed towards mature, adult relationships.
Key Task: Establishing intimate relationships; contributing to society.
Successful: mature sexual relationships and expression
Unsuccessful: failure to establish emotional relationships in adulthood
Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial Development
Trust vs Mistrust (1 year)
Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt (2-3 years)
Initiative vs Guilt (4-5 years)
Industry vs Inferiority (6-12 years)
Identity vs Role Confusion (Adolescence)
Intimacy vs Isolation (Early Adulthood)
Generativity vs Stagnation (Adulthood)
Integrity vs Despair (Elderly)
Carl Jung
Neo-Freudian, analytic psychology; psychodynamic, personality as an open system
Libido: is all types of energy, not just sexual
Studies: dream studies/interpretation
Emphasis on people’s struggle with opposing forces
Fundamental personal tasks:
Life is a journey to know your true self
Own the acceptable and unacceptable parts of the self
Integrate various opposing faces of the psyche
Jung Key Word
JOURNEY
Believed life is a journey toward the Self and individuation
The Jungian “Open System”
Collective unconscious: holds past experiences of generations we "all dive into"; is universal
Archetypes: universal symbols we recognize and react to
Seen in fairy tales, dreams, myths, and some psychotic thoughts
We tend to instinctively recognize and react to archetypes
This recognition is evidence that they are buried in our collective unconscious
Jung and the Self
Complex - a collection of thoughts, feelings, and attitudes that center on a particular concept
Animus - masculine aspects of females
Anima - feminine aspects of males
Persona - predisposition to conform to social norms
Shadow - primitive aspects of personality
Self - central, unifying aspect of all aspects of the individual’s personality
Alfred Adler
Neo-Freudian, psychodynamic; ego and individual psychology
Theories based on social interest: the desire to relate to others and cooperate
Suggested we had more conscious control of the Self
A move towards ego psychology and individual psychology
Contributions: basic mistakes, style of life, inferiority/superiority complexes, childhood influences personality formation
Adler Key Word
ADVANCE
Focused on striving to overcome inferiority and move forward
and ARRIVAL
Birth Order Theory
Adler’s Basic Approach
How a person copes with inferiority becomes a distinctive aspect of his/her personality functioning
Our early wounds force us to compensate
Striving for superiority
Efforts to go beyond compensation to reach one’s full potential
One’s full potential is always met through social interest
“It is the feeling of inferiority, inadequacy, insecurity, which determines the goal of an individual’s existence”
Psychodynamic Theory of Personality Perspectives
Freudians: see an extremely aggressive woman as expressing penis envy
Jungians: aggression complex; warrior archetype
Adlerians: see such persons as in a normal developmental process compensating for stereotyped feminine role of weakness and inferiority
Psychodynamic ToP but with a continuing shift to a developmental and growth perspective
Adler’s Birth Order Theory
Parents and siblings matter
The Pampered child vs the Rejected child
Birth order effect has specific advantages and disadvantages to each situation and compensating that leads to striving for superiority
Modern Birth Order Theory
Based on Adler’s theories, but less deterministic
More related to availability of roles
Karen Horney
Neo-Freudian, psychodynamic
Studied the role of culture in the development of gender identity
Contributions: criticized Freud, stated that personality is molded by current fears and impulses rather than being determined solely by childhood experiences and instincts, neurotic trends
Social security: main driving force in her theory; emphasis on neurotic functioning and how people cope with childhood anxiety and feeling isolated and helpless
Responded to penis envy with womb envy (men are jealous that women can conceive children)
Horney Key Word
HOSTILITY
Centered on basic anxiety, insecurity, and neurotic responses to others
Horney's 3 ways to respond to basic anxiety
Moving toward: excessive interest in being accepted, needed, and approved
Moving against: person assumes that everyone is hostile and that life is a struggle against all
Moving away: person shrinks away from others in neurotic detachment
Harry Stack Sullivan
Theory of interpersonal relations
Turned off of psychodynamic approach to personality because of Freud’s sexual approach
Connection between mental illness and loneliness and disconnection and also noticed many trauma backgrounds
Theorized that the qualities of connection in childhood set momentum and trajectory to the way in which you would connect with others as adults, which is vital and influential on your mental health or betterment
Sullivan Key Word
SOCIAL
Personality is shaped through interpersonal relationships
Attachment theory
Bowlby's Attachment Behavioral System (ABS)
We have a fundamental need for attachment
Secure attachment starts in childhood
Securely attached children become adults with healthy self expression and boundaries
Separation distress is normal and healthy
Securely attached children grow into adolescents who feel safe enough to individuate and form healthy attachments to people outside of the family
Securely attached adolescents grow into adults with healthy boundaries (vulnerable enough to invest in intimate relationships, maintain an appropriate sense of self that is not defined by others, and does not see these two a paradox)
Carl Rogers
Humanistic
Contributions: founded person-centered therapy, theory that emphasizes the unique quality of humans especially their freedom and potential for personal growth, unconditional positive regard, fully functioning person
Rogers Key Word
REAL
Emphasized the real self, authenticity, and congruence
Rogers' View of the Person
Developed the idea that our most fundamental motivation is toward positive growth
Self-actualization:
An organism’s tendency to grow from a simple entity to a complex one
Move from fixity and rigidity to a process of change and freedom of expression
The ‘reality’ we observe is really a ‘private’ world of experience, the phenomenal field
Phenomenal field (subjective construction): space of perceptions that makes up our experience ("your truth")
Rogers and the Self
The Self = key structural aspect of phenomenological experience
Actual self: who we believe we are now
Ideal self: how we ideally see ourselves becoming in the future
“Feelings of Authenticity”
Individuals can realize a state in which their conscious experiences and goals are consistent with their inner, viscerally-felt values
Rogers' 2 basic ways in which humans best thrive
1. Need for Positive Regard: need to be accepted/respected
Unconditional Positive Regard: accepting others for who they are without passing judgment on them
Conditional Positive Regard: being accepting of others only when they meet your expectations
2. Congruence (genuineness):
Showing up with our whole selves to the present moment, whatever it is, with integrity, honesty, and courage
We can think of numbing out, checking out, or being fake as the opposite of congruence
Abraham Maslow
Humanist psychologist who developed a pyramid representing hierarchy of human needs
Deficiency Needs: Basic survival and psychological needs that arise from a lack of deprivation (show fear towards those with being needs)
Being Needs: Needs for personal development and fulfillment, not driven by a deficit (show condescension towards those with deficiency needs)
Maslow Key Word
MOUNTAIN
His hierarchy is literally a climb upward
Hierarchy of needs
Physiological needs (basic needs necessary for survival)
Safety (need for stability, order, and predictability— reduce daily uncertainty)
Belongingness and Love (establish and maintain meaningful relationships— receive social support from others)
Esteem (self-respect and respect of others— leadership ability)
Self-actualization (express one's ability to their full potential)
Self-actualization individuals
People have a deep feeling of identification, sympathy, and affection for human beings in general
Are there gender differences in personality?
Yes; but they are small, complex and nuanced and with many counter-examples
Those differences are changing over time
Descriptive not prescriptive
What causes gender differences of personality?
Really complex and multiple interacting factors that result in gender differences in personality
What are some stable differences between males and females in personality
SLOPES
Self-esteem and Confidence
Love
Overt physical aggression
Passive/indirect aggressiveness
Emotional expressiveness
Sexuality
Variations in Self-esteem and Confidence
Tend to be lower in women than in men
Women tend to underestimate their competence, men tend to overestimate
Variations in Love
Females report being in love more often and more intense feelings of love
Females have more pragmatic expectations and are more cautious
Men tend to fall in love more quickly
Variations in Overt Physical Aggression
Across various cultures and at an earlier age of onset, males tend to exhibit more acts of physical aggression than females
Variations in Passive/Indirect Aggression
Across various cultures, greater female aggression includes gossiping, name calling, and social rejection
Variations in Emotional Expressiveness
Females demonstrate more self-report expressions of emotions; no gender differences when using objective measures
Except for aggression, females display more facial and verbal emotional expression, experience their emotions more intensely, and express their emotions in a more socially acceptable manner
Variations in Sexuality
Males have more casual attitudes about sex and have more sex than females
Females seek intimacy for sex while males seek gratification for sex
Both report similar levels of sexual gratification
Viewing men as sexual deviants and women as sexually uninterested is dehumanizing to both
Men’s brains function in hemispheres, and women’s brains jump back and forth between them