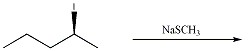Organic Chem summer test 2
1/170
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 5, 6, and 7 Pearson
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
________ are isomers which have the same bonding sequence but differ in the orientation of their atoms in space.
Stereoisomers
What is the structural relationship between the two molecule shown below?
constitutional isomers
How many enantiomers are there of the molecule shown below?
1
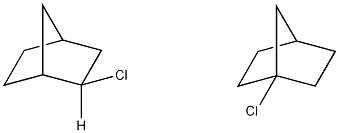
Which of the following terms best describes the pair of compounds shown: enantiomers, diastereomers, or the same compound?
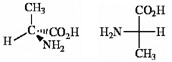
the same compound
Which of the following terms best describes the pair of compounds shown: enantiomers, diastereomers, or the same compound?
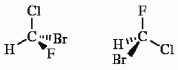
the same compound
Which of the following terms best describes the pair of compounds shown: enantiomers, diastereomers, or the same compound?

enantiomers
Is the molecule shown below chiral or achiral?
(CH3)3CCH(CH3)2
achiral
How many asymmetric carbon atoms are present in the following compound?

1
How many asymmetric carbon atoms are present in the following compound?
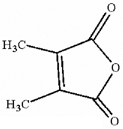
0
How many asymmetric carbons are present in the compound below?
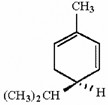
1
How many asymmetric carbons are present in the compound below?

0
How many asymmetric carbons are present in the compound below?
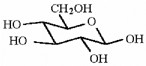
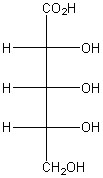
5
How many asymmetric carbon atoms are present in the molecule shown?
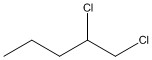
1
How many asymmetric carbon atoms are present in the molecule shown?
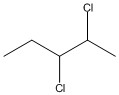
2
Is the mirror image of the following molecule an enantiomer or is it superimposable with it?

superimposable
Which of the following terms best describes the pair of compounds shown: enantiomers, diastereomers, or the same compound?
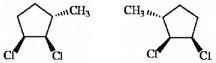
enantiomers
Which of the statements below correctly describes an achiral molecule?
The molecule has a nonsuperimposable mirror image. |
The molecule might be a meso form. |
The molecule exhibits optical activity when it interacts with plane-polarized light. |
The molecule has an enantiomer. |
None of the above |
The molecule might be a meso form.
Choose each chiral molecule among those shown below.
.jpg) | .jpg) | .jpg) |
.jpg)
Is the molecule shown below chiral or achiral?
CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH3
achiral
Is the molecule shown below chiral or achiral?
achiral
Is the molecule shown below chiral or achiral?
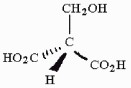
achiral
Is the molecule shown below chiral or achiral?
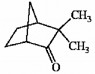
chiral
How many asymmetric carbons are present in the compound below?
3-ethyl-2,2,4-trimethylpentane
1
Which of the following terms best describes the pair of compounds shown: enantiomers, diastereomers, or the same compound?
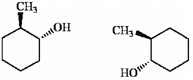
enantiomers
Is the molecule shown below chiral or achiral?

achiral
Does the molecule shown below contain asymmetric carbon atoms?
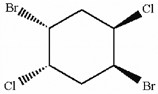
yes
Is this molecule chiral?

No
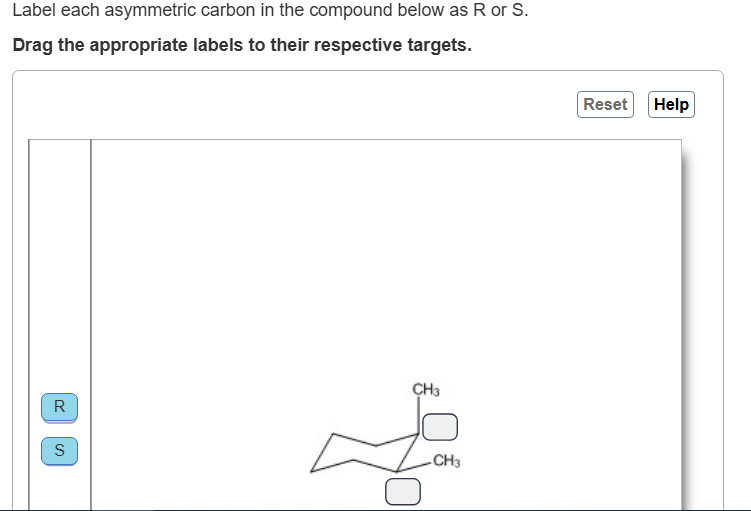
Top R
Bottom S
Which of the following configurations corresponds to the structure below?
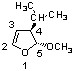
4-R
5-R
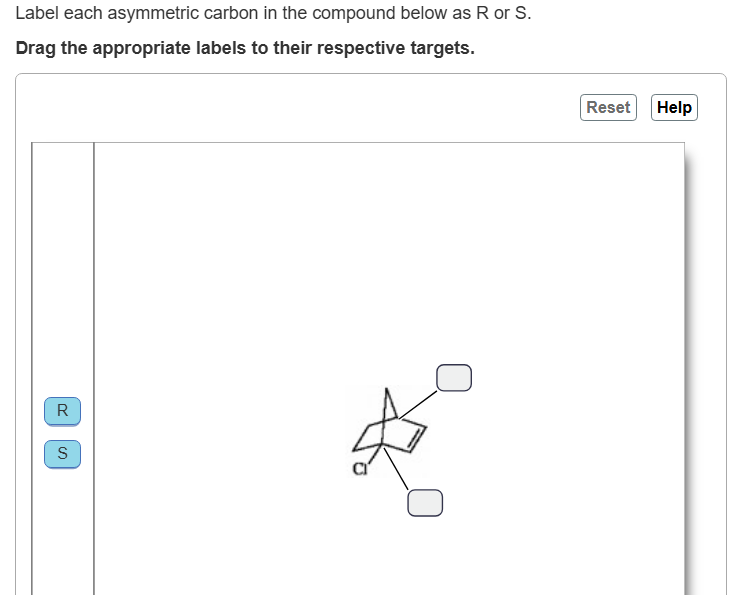
top S
Bottom S
Compounds that rotate the plane of polarized light clockwise are called ________.
dextrorotatory
Which of the following statements is (are) true for the compound (RR)-2-butanol?
This compound is optically active. |
This compound is chiral. |
This compound has an enantiomer. |
Which of the following statements correctly pertains to a pair of enantiomers?
They rotate the plane of polarized light by exactly the same amount and in opposite directions.
If (SS)-glyceraldehyde has a specific rotation of -8.7°, what is the specific rotation of (RR)-glyceraldehyde?
+8.7°
Predict the specific rotation of the compound shown.
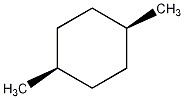
Zero; the compound is achiral.
Given that glucose has a specific rotation of +52.8°. Predict the concentration of a glucose aqueous solution contained in a 10 cm long polarimetry tube if a rotation of +15.8° was observed.
0.299 g/mL
A student measured the optical activity of an unknown sugar at two different concentrations. The results of his measurements are shown below. Given that the sample cell had a path length of 10.0 cm, calculate the specific rotation for the unknown sugar. (Hint: Consider each measurement of plane polarized light has a true reading and a "ghost" reading 180° from the true reading).
concentration | observed rotation |
2.00 g sugar in 10.0 mL water | +159.1∘ |
5.00 g sugar in 10.0 mL water | +127.8∘ |
-105∘ |
A newly isolated natural product was shown to be optically active. If a solution of 2.0 g in 10 mL of ethanol in a 50 cm tube gives a rotation of +2.57°, what is the specific rotation of this natural product?
+2.57°
A mixture of equal amounts of two enantiomers ________.
statements "is called a racemic mixture" and "is optically inactive" are correct
If a mixture contains 75% of one compound and 25% of its enantiomer, what is the e.e. of the mixture?
50
Calculate the e.e. of a mixture containing 8.0 g of (-)-glyceraldehyde and 2.0 g of (+)-glyceraldehyde.
60
A mixture of two enantiomers with a composition of 65.0% R has an observed rotation of -25.3° in a 10.0 cm polarimeter tube. If the mixture has a concentration of 2.038 g/mL at 25°C, what is the predicted [α]25D of an optically pure sample of the S enantiomer?
+41.3°
(-)-Lactic acid has a specific rotation of -3.8°. What is the specific rotation of a solution containing 7.5 g of (-)-lactic acid and 2.5 g of (+)-lactic acid?
-1.9°
Can the molecule shown below be properly described as a meso compound?

no
Is the molecule shown below chiral or achiral?

achiral
Which of the following terms best describes the pair of compounds shown: enantiomers, diastereomers, or the same compound?
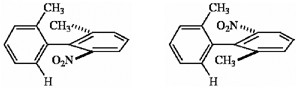
enantiomers
How many asymmetric carbons are present in the compound below?
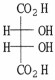
2
How many diastereomers are there of the molecule shown below?
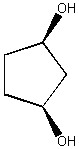
2
Stereoisomers which are not mirror image isomers are ________.
diastereomers
Which of the following terms best describes the stereochemical relationship of the two compounds shown below in Fischer notation?
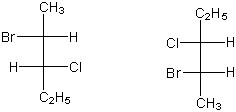
diastereomers
Which of the following terms correctly describe(s) the structural relationship between cis-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane and trans-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane?
both diastereomers and geometric isomers
Which of the following terms best describes the pair of compounds shown: enantiomers, diastereomers, or the same compound?
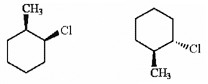
diastereomers
Which of the following terms best describes the pair of compounds shown: enantiomers, diastereomers, or the same compound?

the same compound
Which of the following statements is (are) true for the compound (3RR, 4RR)-3,4-dimethylhexane?
This compound is a diastereomer of (3RR, 4SS)-3,4-dimethylhexane. |
The enantiomer of this compound is (3SS, 4SS)-3,4-dimethylhexane. |
This compound is chiral. |
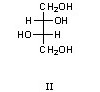
How many diastereomers are there of the molecule shown below?
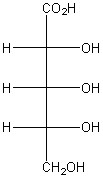
6
 |  |  |
The relationship between I and III is: ________.
diastereomers
 |  |  |
The relationship between I and II is: ________.
diastereomers
Which of the following terms best describes the pair of compounds shown: enantiomers, diastereomers, or the same compound?

diastereomers
Which of the following terms best describes the pair of compounds shown: enantiomers, diastereomers, or the same compound?
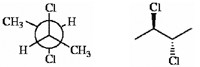
the same compound
Can the molecule shown below be properly described as a meso compound?
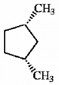
yes
How many enantiomers are there of the molecule shown below?
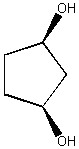
0
Which of the following statements is (are) true for the compound cis-1,2-dichlorocyclopropane?
None of the above
Draw the structure of the meso form of 1,3-dichlorocyclopentane. Take particular care to indicate three-dimensional stereochemical detail properly.

Can the molecule shown below be properly described as a meso compound?
(CH3)2CHCH2CH3
No
Which of the following is classified as a vinylic halide?
CH3CH=CHCl
The flame retardant below has been found to be an androgen agonist and may have a contribution to an increasing rate of occurrence of prostate cancer (J. Med. Chem. 2006, 7366). What is the correct term that describes the relative position of the bromides in this structure?
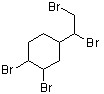
vicinal
What general classification is given to the molecule below?
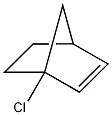
tertiary chloride
Provide the name of the bromoalkane shown below.
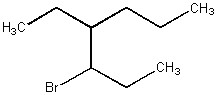
3-bromo-4-ethylheptane
Provide an acceptable name for CHCl3.
trichloromethane
Provide an acceptable name for CH3CH2CH2C(CH3)2I.
2-iodo-2-methylpentane
Provide an acceptable name for the compound shown below.
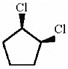
cis-1,2-dichlorocyclopentane
Provide the structure of isopropyl iodide.
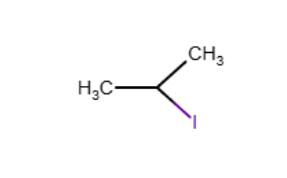
Which of the following is a secondary halide?
(CH3)3CCHClCH3 |
Which of the following is a tertiary halide?
(CH3)2CClCH2CH3 |
Which of the following is a geminal dihalide?
3,3-dichloropentane
Which of the following is a vicinal dihalide?
cis-1,2-dibromocyclopentane
Which of the following is a secondary alkyl halide?
isopropyl chloride
Which of the following is a primary alkyl halide?
isobutyl chloride
The following structure is a proteasome inhibitor that may find application in treating cervical cancer (J. Med. Chem. 2011, 449). The halides in this structure may be classified as ________ and ________.

vicinal & aryl
Which of the following alkyl halides has the smallest molecular dipole moment?
CF4
Among the following alkyl halides, choose the one with the lowest boiling point.
tt-butyl chloride
When water is shaken with dichloromethane, a two-phase system results. Which compound forms the upper phase?
water
Provide the structure of the major organic product in the reaction below.
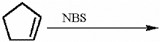
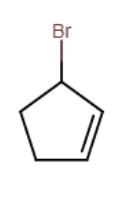
Consider the reaction of (CH3)3CO- with iodomethane. Will the reaction rate increase, decrease, or remain the same if the concentration of iodomethane is increased?
will increase
What type of intermediate is present in the SN2 reaction of cyanide with bromoethane?
This reaction has no intermediate.
Which of the following species is the least nucleophilic?
BF3
Which of the following compounds is the most nucleophilic?
CH3SH
Arrange the following species in order of decreasing nucleophilicity:
CH3CH2S- > CH3CH2O- > (CH3)3CO- >(CH3)3COH
Rank the species below in order of decreasing nucleophilicity in hydroxylic solvents:
CH3S- > HO- > CH3CO2 - >H2O.
Which of the following factors is favorable for nucleophilicity but not basicity?
highly polarizable
Which of the following solvents could be described as polar and protic?
ethanol
Which of the following compounds will undergo an SN2 reaction most readily?
(CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH2I
Which of the following alkyl chlorides will undergo SN2 reaction most readily?
1-chloro-4-methylpentane
Arrange the following substrates in order of their decreasing SN2 reactivity with NaCN:
Bromoethane > 1-chloro-3,3-dimethylpentane > 1-chloro-2,2-dimethylpentane > 2-bromo-2-methylpentane
List the following bromides in order of their decreasing reactivity as substrates in SN2 reactions:
PhCH₂Br > PhCH(CH₃)Br > PhBr
List the following alkyl halides in order of their decreasing reactivity as substrates in SN2 reactions:
1-iodobutane > 2-iodobutane > 2-chlorobutane
Which of the following statements describe a favorable attribute of a leaving group?
The leaving group should be highly polarizable. |
The departed leaving group should have low basicity |
Which of the following alkyl halides reacts most rapidly via an SN2 reaction with NaCN?
1-iodohexane
SN2 reactions take place with ________ of stereochemistry at the center undergoing substitution.
inversion
Provide the major organic product of the reaction below.