Psychology 2 - Lesson 8: Social Perception
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Psychology 2 Lesson 8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Lesson 8: Social Perception
Lesson 8: Social Perception
CRB True or false? Social perception is the initial information we have about other people to try and understand their intentions.
True. Social perception is the initial information we have about other people to try and understand their intentions.
CRB Chris took a large group of fellow architects aside and led a conversation about his vision for the project, and he nominated himself as the Lead Architect. Later that week, Chris was shocked when people deviated from this plan and nominated another person as Lead Architect, since he thought that everyone agreed with his plans. Which of the following terms best describes this phenomenon?
(A) Self-Serving Bias
(B) Projection Bias
(C) False Consensus
(D) Optimism Bias
(C) False Consensus
In this scenario, Chris assumed that everybody agreed with his actions (in this case, both pulling everyone aside and nominating himself Lead Architect). This would best be described as a False Consensus.
CRB Recently, a local high school was told that they could no longer have the local minister lead the graduating class in prayer during the official graduation ceremony. Previously, the administration had assumed everybody was okay with this, since the whole administration were Christians. Which of the following terms best describes this phenomenon?
(A) Self-Serving Bias
(B) Projection Bias
(C) False Consensus
(D) Optimism Bias
(B) Projection Bias
In this scenario, the administration were all Christians, and they projected their faith and positive views of prayer onto the larger school community. This is best described as Projection Bias.
CRB Wait, Projection Bias and False Consensus sound very similar. Can you explain the difference between these two examples?
In the False Consensus example, Chris had assumed that everyone else agreed with his Actions. In the Projection Bias example, however, the administration was assuming that others had the same Beliefs that they did. This is a subtle, yet key, distinction!
True or False. Stereotyping is strictly defined as overgeneralizing a group of people that are perceived as a minority.
False. Stereotyping is loosely defined as overgeneralizing any group of people from anything like race to one's shoe size.
How might stereotyping be advantageous? Provide an example.
We can use it to make quick decisions, saving both time and energy.
An example could be seeing a baby bear in the woods, stereotyping that approaching this baby bear could be dangerous since mama bears often protect their nearby babies, and using that stereotype to run to safety and avoid any trouble.
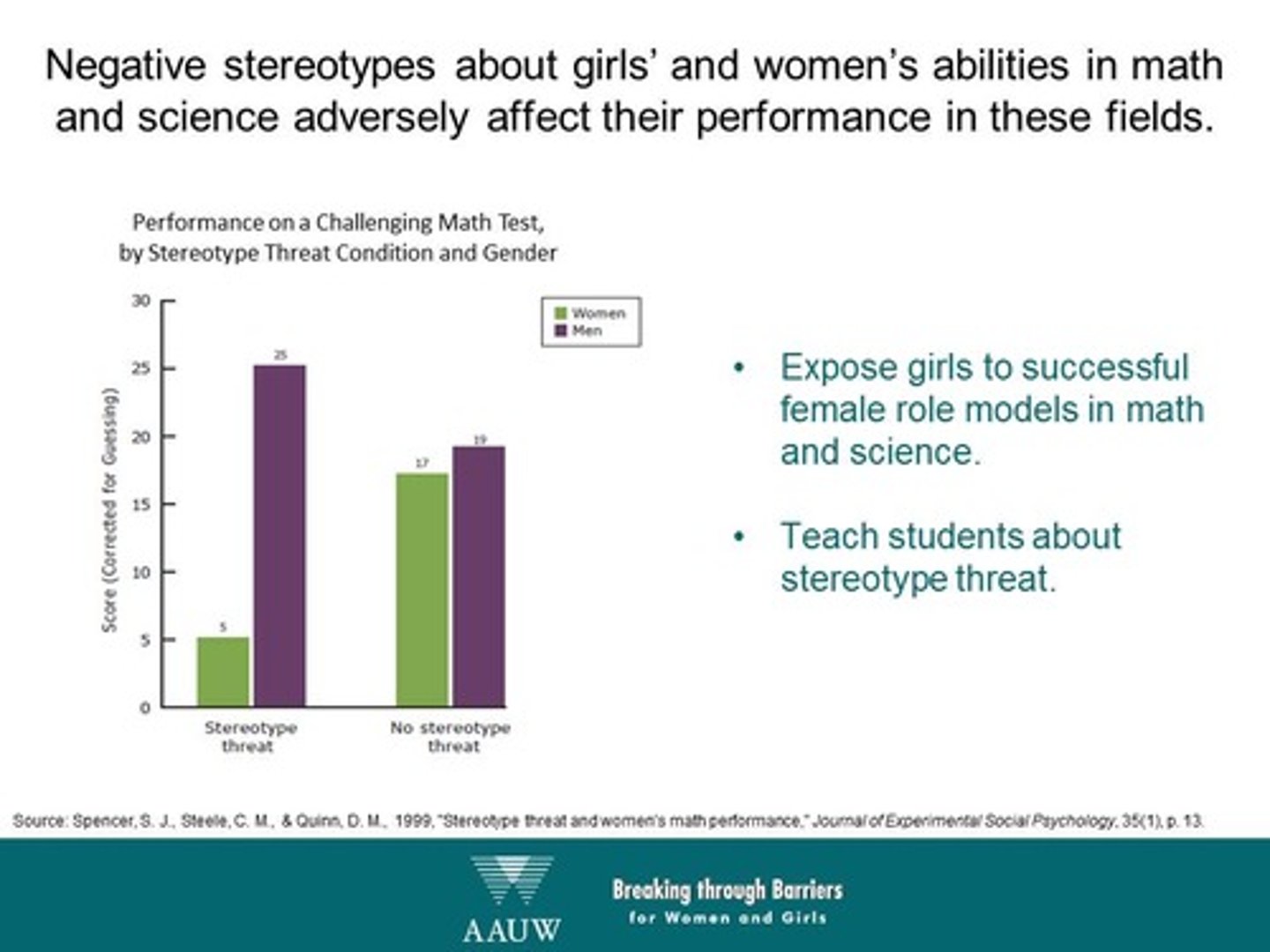
Before taking an math exam, girls are informed that typically girls will perform worse on math-related exams. Will the girls perform better or worse than if they had not been informed of this? This is an example of:
(A) Minority Challenge
(B) Stereotype Threat
(C) Self-concept
(D) Front-stage Self
(B) Stereotype Threat
This is an example of Stereotype threat, and the girls will perform worse once they are aware of the stereotype.

What could be done to enhance the girl's performance once they've become aware of this stereotype?
Teach them about stereotype threat.
Match each of the following:
(A) Stereotyping
(B) Prejudice
(C) Discrimination
(1) Behavioral
(2) Affective
(3) Cognition
(A) Stereotyping -> (3) Cognition
(B) Prejudice -> (2) Affective
(C) Discrimination -> (1) Behavioral
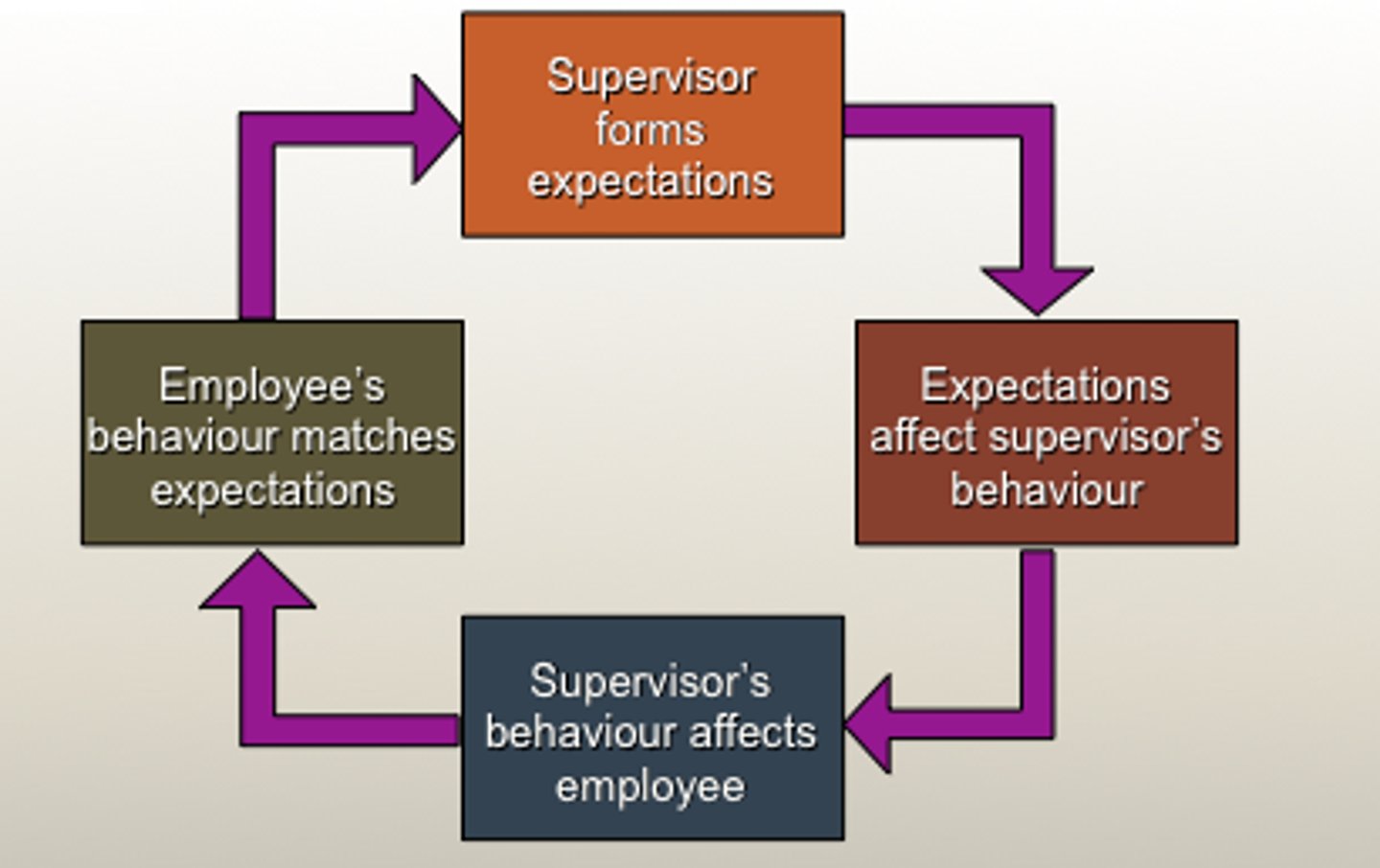
Describe how the Self-fulfilling prophecy may apply to a child who believes that teachers are jerks.
The child believes teachers are jerks (stereotype) -> The child feels anger toward his teachers (prejudice) -> The child is mean to his teachers (discrimination) -> He thinks his teachers don't like him and that they are being rude to him -> This reinforces the child's beliefs that teachers are jerks and the cycle continues.
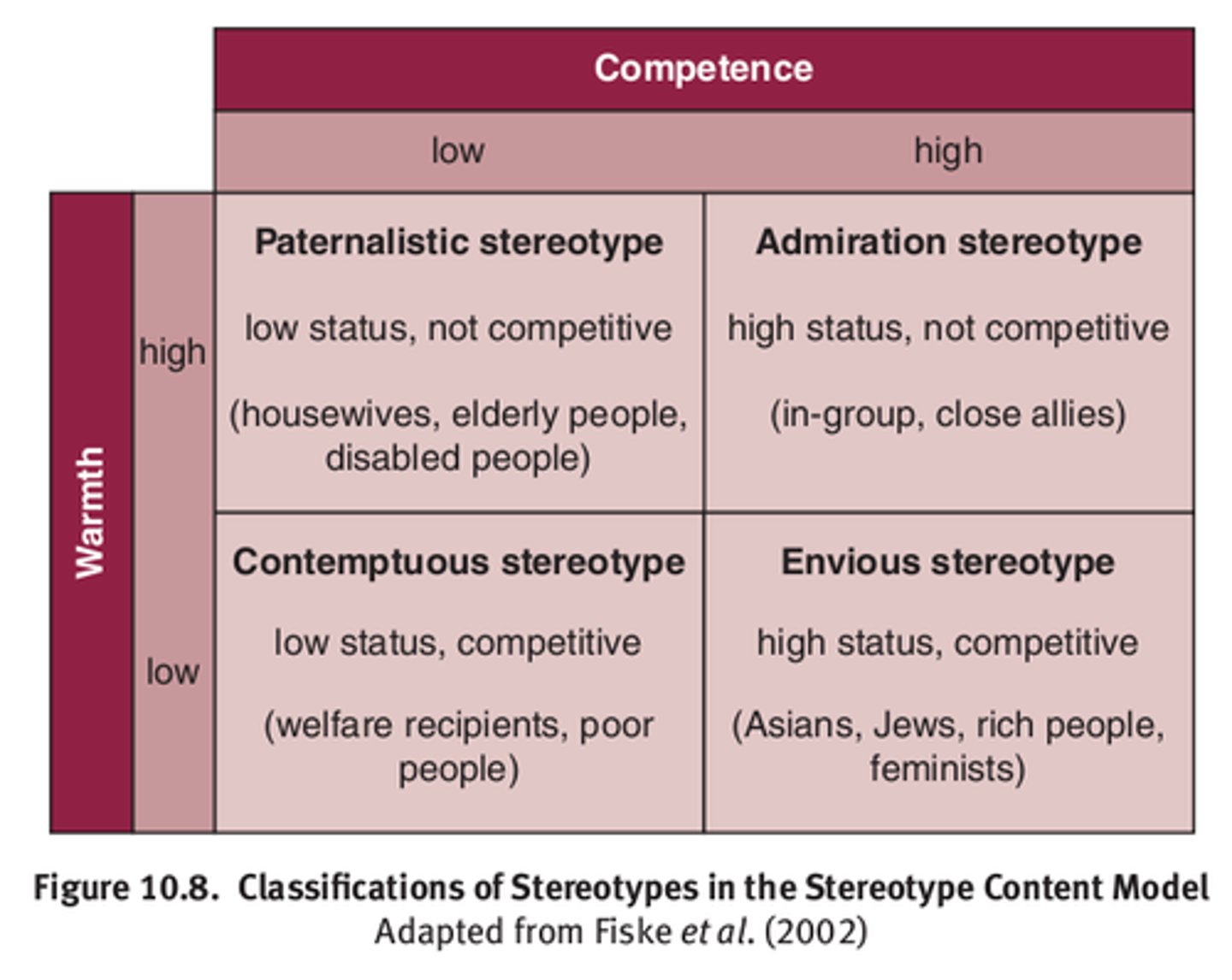
CRB Which of the following are the two dimensions used to classify stereotypes in the Stereotype Content Model?
(A) Warmth and Prejudice
(B) Prejudice and Contentness
(C) Warmth and Competence
(D) Prejudice and Groups
(C) Warmth and Competence
The two dimensions used to classify Stereotypes in the Stereotype Content Model are Warmth and Competence.
Compare Warmth and Competence in the Stereotype Content Model.
Warmth refers to groups that are either not in direct competition (high warmth) or are competing (low warmth).
Competence refers to if a group has high status in society (high competence) or lower status (low competency).
CRB Draw out the four possible groupings of the Stereotype Content model, and label their type of stereotyping as either:
- Paternalistic
- Admiration
- Envious
- Contemptuous
What personality type is more predisposed to engage in prejudice?
(A) Submissive
(B) Neurotic
(C) Authoritarian
(D) Oppressed
(C) Authoritarian
The Authoritarian Personality Type is more predisposed to engage in prejudice.
Which of the following individuals best exemplifies the Authoritarian Personality Type?
(A) Jack is obedient to his superiors.
(B) Jill sees her supervisors as jerks.
(C) Mark never listens to his dad, but he will readily listen to his friends.
(D) Mary refuses to do anything anyone says.
(A) Jack is obedient to his superiors.
The Authoritarian Personality Type is characterized by being obedient to one's superiors yet being oppressive to those beneath them. They are also rigid and inflexible in their thoughts and ways. It is thought that these people had a harsh and very disciplined childhood.

What needs might prejudice serve for someone with an Authoritarian Personality?
It allows the person to avoid having to confront aspects about themselves that they don't like. It also allows them to see themselves as superior, protecting their ego.
CRB Another phenomenon related to prejudice is the Illusory Correlation, which holds that examples that are seen as distinctive will have more attention paid to them and are more likely to be seen as representative. Which of the following is NOT an example of the Illusory Correlation?
(A) After watching Alexander Ovechking lose in the hockey playoffs again, fans assume Russian Hockey players cave under pressure.
(B) Recalling a few Grey's Anatomy episodes with a plane crashes, casual viewers assume that disasters occur in every episode.
(C) People assume all American Idol winners are successful, remembering Carrie Underwood won her season.
(D) After watching Michael Jordan's famous Flu game, opposing fans assume that MJ was exaggerating his symptoms.
(D) After watching Michael Jordan's famous Flu game, opposing fans assume that MJ was exaggerating his symptoms.
The other three examples all rely on a small subset of a group being used to extrapolate some characteristic unto the whole group. This example is limited to Michael Jordan.
CRB True or false? Based on how the Illusory Correlation relies on a few distinct examples being representative of the whole (wrongly), it is most similar to the problem-solving approach of Algorithms.
False. Based on how the Illusory Correlation relies on a few distinct examples being representative of the whole (wrongly), it is most similar to the problem-solving approach of Heuristics.
CRB True or false? Attribute substitution occurs when individuals are making complex decisions, so they will only use Situational Attribution.
False. Attribute substitution occurs when individuals are making complex decisions, so they will substitute in a simpler solution or use a Heuristic.
Some theorists are skeptical of the Authoritarian Personality connection with Prejudice. The Frustration-aggression Hypothesis is an alternative theory for what leads people to exhibit Prejudice. How does this theory explain why one person might be more prejudice than another?
The Frustration-aggression Hypothesis suggests that as someone becomes frustrated they become more aggressive, which in turn will lead them to take out their aggression on easy prey like minority groups, who they may use as Scapegoats.
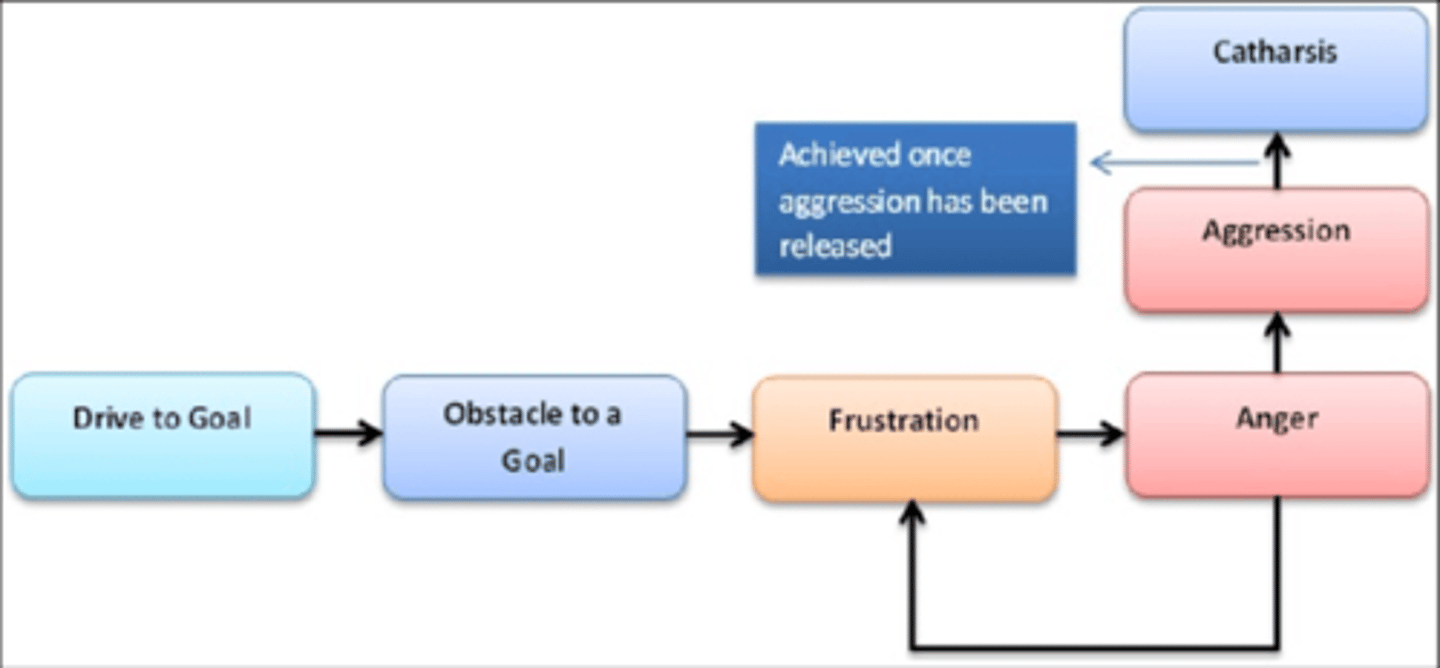
CRB After World War I, the German economy struggled greatly under the punishments from the Treaty of Versailles. Angry German citizens began blaming the Jews for these economic struggles. As a result, the Nazi party begain encouraging aggressive actions against the Jews. Would the Jews be considered Scapegoats in this example?
Yes, the Jews would be considered Scapegoats in this example. They are a minority group that received the blame for German frustrations (the poor economy), and ended up having aggressive actions taken against them.
How does the Hypothesis of Relative Deprivation suggest about what causes frustration?
You become frustrated when what you actually get is less than what you expected to get.
Compare Race and Ethnicity.
Race is a physical characteristic that has been deemed to put you in one group versus another. It can be seen as socially-constructed. Examples include Black, White, etc.
Ethnicity is the cultural group that you belong to. It may also relate to your country of origin. Examples include Jewish, Japanese-American, Irish, etc.
Jerry is extremely poor and worked his whole life as a custodian. He does, however, feel like he was able to choose his own destiny throughout his life. How do the terms Power, Social Class, and Prestige apply to Jerry?
Because Jerry feels like he is in control and he has power to do things, he has a high amount of Power from his perspective.
Jerry is poor, though, which means he is of a low social class [at least in a society where social class is based on income]
Jerry was a custodian, which is not a very prestigious job.
Jimmy is a wealthy land owner and has many slaves. How might Jimmy use the Just World Hypothesis to justify his position (Social Class)?
He might say that the slaves got what they deserved and he did too, which is why he is wealthy.
Which of the following do Stigmas share aspects of?
I.Stereotypes
II.Prejudices
III.Discrimination
(A) I only
(B) I and III only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Stigmas have some aspects of Stereotypes, Prejudices, and Discrimination.
Give an example of a Stigma.
- People with mental disorders are dangerous or crazy.
- People with addictions are flawed.
- Women who have abortions are amoral.
Note: These are not true nor proven but are merely examples of Stigma found at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Social_stigma
Compare Social Stigma and Self Stigma.
Social Stigma - negative belief toward a group of people (i.e. "mentally ill are dangerous").
Self Stigma - when one internalizes the Stigma that has been placed upon them (i.e. "maybe I really am dangerous and need to be locked away").

How might Media, Society, Family, and Oneself respectively influence the spreading of a Stigma that women who are overweight are unintelligent?
Media may portray women that are overweight as being brainless in various situations.
Society may believe this and avoid giving intellectual jobs to women that are overweight.
One's Family may tell a girl that she needs to lose weight or study harder.
Oneself may believe the Stigma placed upon them, resulting in a Self-fulfilling Prophecy.
First Impressions are "Long, Strong, and Easy to Build Upon." What do each of these mean?
Long - First impressions last a long time.
Strong - First Impressions are hard to change or erase.
Easy to Build Upon - People tend to look for info that supports their first impression.

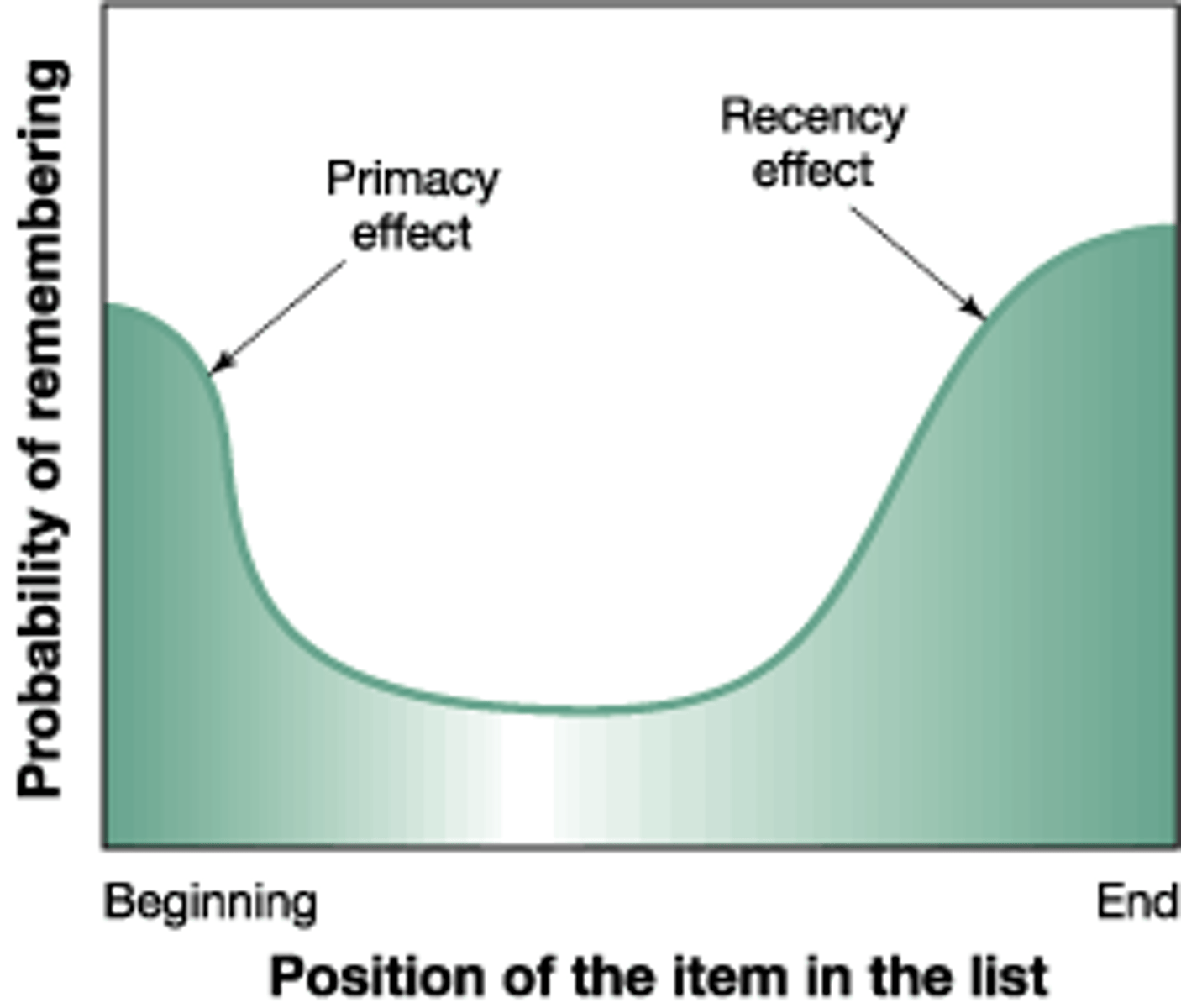
You are teaching a classroom full of students about psychology. At the beginning of the lecture, you teach the students about Freud, in the middle about Erikson, and at the end about Piaget. Which theorist(s) will the students remember the best?
I. Freud
II. Erikson
III. Piaget
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) II and III Only
(C) I and III Only
We tend to remember information at the beginning (Primacy Bias) and information presented at the end (Recency Bias).
Jim meets a new girl at work and Jim thinks she is very attractive. He is later made her manager and is asked to evaluate her in several key indicators. How might the Halo Effect play into Jim's evaluation?
Because his overall impression of her is good, he will likely over-exaggerate how good she is in each individual area of work.
Compare the Halo Effect and the Devil Effect.
The Halo Effect occurs when you have an overall good impression of someone and it skews your evaluation of them toward the positive end of the spectrum.
The Devil Effect occurs when you have an overall bad impression of someone and it skews your evaluation of them toward the negative end of the spectrum.

"You reap what you sow" relates most closely to which term?
(A) Stereotype
(B) Self-fulfilling Prophecy
(C) Just World Hypothesis
(D) Relative Deprivation
(C) Just World Hypothesis
"You reap what you sow" is basically saying that good actions have good rewards and bad actions have consequences, which is the basic premise of the Just-world Hypothesis.
How does the Just World Hypothesis relate to Attribution Theory?
Just World Hypothesis would lead people to make internal attributions when evaluating situations.
CRB In Attribution theory, which of the following are types of Attribution?
I. Situational Attribution
II. Dependent Attribution
III. Dispositional Attribution
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) I and III only
(D) II and III only
(C) I and III only
The two types of Attribution seen in Attribution Theory are Situational and Dispositional Attribution.
CRB Compare Dispositional and Situational Attribution with the example of someone getting their credit card declined when buying gas.
Dispositional Attribution attributes behavior more to internal causes. Here, someone may say "Oh, this driver is really irresponsible and bad at managing money".
Situational Attribution would attribute behavior more to external cues. Here, someone would say "Wow, this driver must be down on his luck. Maybe he has had to pay a lot of medical bills lately for his kids".
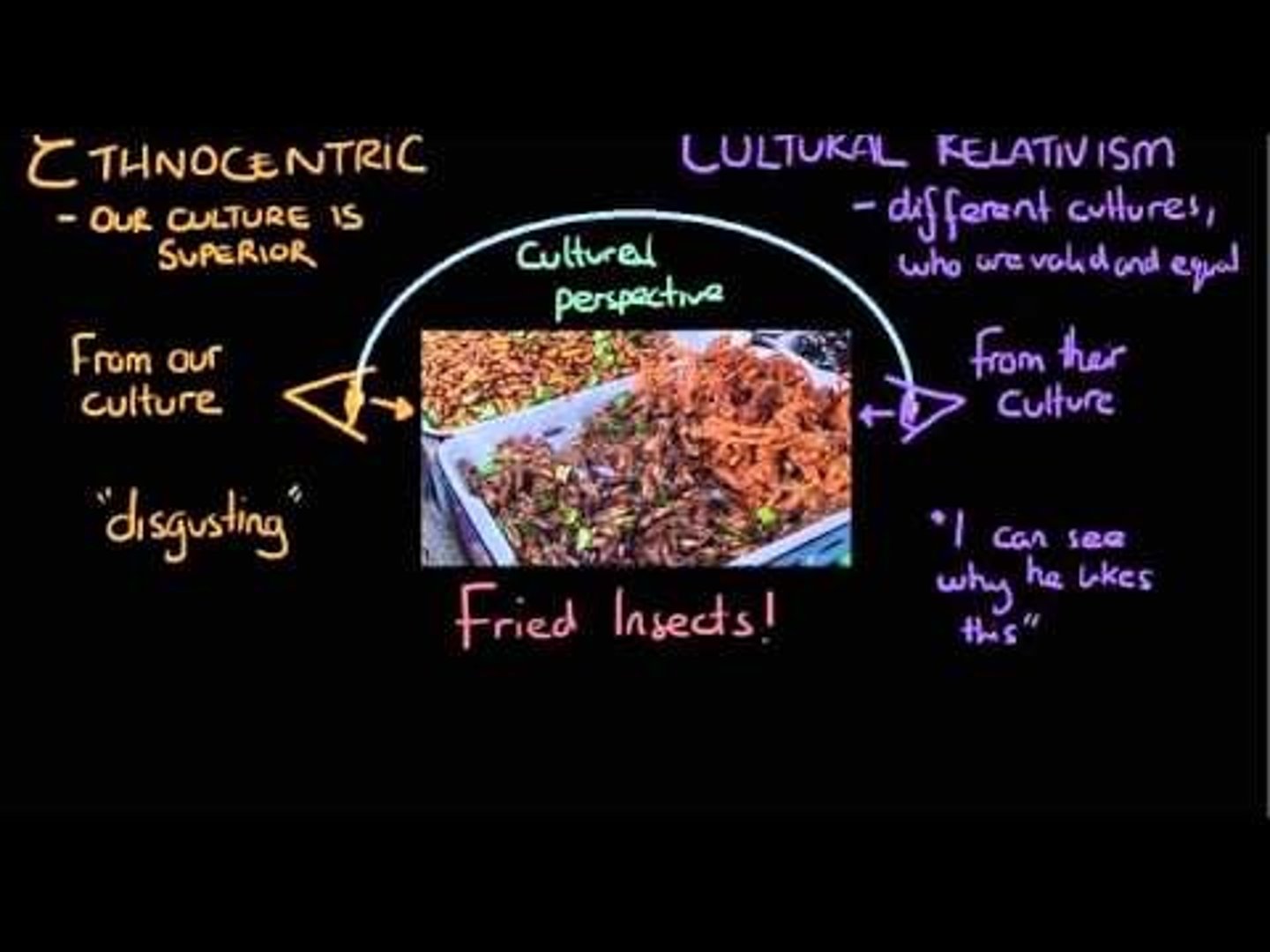
You go to Japan and a man bows to you. How might you view this gesture if you have a mindset based in Cultural Relativism? Ethnocentrism?
If you have a mindset based in Cultural Relativism, you might think, "How nice. What a great way to show respect. I might not do that, but I can at least appreciate it." You are seeing Japanese culture from the Japanese perspective.
If you have a mindset based in Ethnocentrism, however, you might think, "How strange. What a weird place this is." You are seeing Japanese culture from your own perspective/lens, which you see as superior.
You hang out with a group of nerds. What might the in-group be in this case? What about the out-group?
The in-group is your nerd friend group. The out-group consists of everyone else who doesn't belong to your friend group.
Describe how In-group Favoritism compares to Out-group Derogation?
In-group Favoritism - we are friendly and positive to the in-group and neutral to the out-group.
Out-group Derogation - You are nice to the in-group but mean and rude and negative to the out-group.
African Americans Adam and Sarah Smith are trying to rent a new apartment. They don't get approved by the landlord. Then a white couple, Jack and Jill Jones, with the same income and credit history as the Smiths, apply for the apartment and get approved. This is an example of which type of Discrimination?
(A) Unintentional Discrimination
(B) Side-effect Discrimination
(C) Individual Discrimination
(D) Institutional Discrimination
(C) Individual Discrimination
This is an example of Individual Discrimination because a single individual, the landlord is doing the discriminating. If this was a widespread problem within a real estate company, at that point we would refer to it as Institutional Discrimination. This is actually a common problem across apartment complexes. Very sad.
Check out this article to read more about present day Institutional Discrimination: https://www.usnews.com/news/blogs/at-the-edge/2015/05/06/institutional-racism-is-our-way-of-life
CRB In response to these various forms of discrimination, there have been efforts to limit discrimination by using these previously discriminated-against factors to benefit under-represented groups. Which term best describes this phenomenon?
(A) Reverse Discrimination
(B) Affirmative Action
(C) Stereotype Threat
(D) Anti-Discrimination
(B) Affirmative Action
Affirmative Action is best described as attempts to limit discrimination by considering previously discriminated-against factors to benefit current or past victims of discrimination.
CRB True or false? Affirmative Action attempts can prevent the most qualified people from receiving these jobs or spots in schools if they are part of the majority group, a phenomenon called "Reverse Discrimination".
True. Affirmative Action attempts can prevent the most qualified people from receiving these jobs or spots in schools if they are part of the majority group, a phenomenon called "Reverse Discrimination".
Compare the two types of Unintentional Discrimination: Side-effect Discrimination and Past-in-present Discrimination. Give an example of each.
In Side-effect Discrimination, discrimination in one setting leads to Unintentional Discrimination in another setting. For instance, a couple is discriminated against and unable to move into an apartment in a nice neighborhood and end up living in a poorer neighborhood, where they are unintentionally discriminated against by the government in that they received worse educations for their children in that area.
In Past-in-present discrimination, discrimination in the past leads to Unintentional Discrimination in the present. For instance, an all-black hospital becomes a all-races hospital, yet the doctors continue to unintentionally treat the blacks differently than the whites who go there.