Joints
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
joint or articulation
any point where two bones meet, whether or not the bones are movable at that interface
synostosis
bony joint
an immobile joint formed when the gap between two bones ossifies
examples of synostosis
Left and right frontal and mandibular bones in infants
Ilium, ischium, pubis fuse to form hip bone in adult
Attachment of first rib and sternum with old age
Parietal bones along sagittal suture with old age
synarthrosis
fibrous joint
adjacent bones are bound by collagen fibers that emerge from one bone and penetrate into the other

sutures
immobile or slightly mobile fibrous joints in which short collagen fibers bind the bones of the skull to each other
serrate suture
interlocking wavy lines
ex: coronal, sagittal, and lambdoid sutures
lap (squamous) suture
overlapping beveled edges
ex: temporal and parietal bones
plane (butt) suture
straight, non-overlapping edges
ex: palatine processes of the maxillae
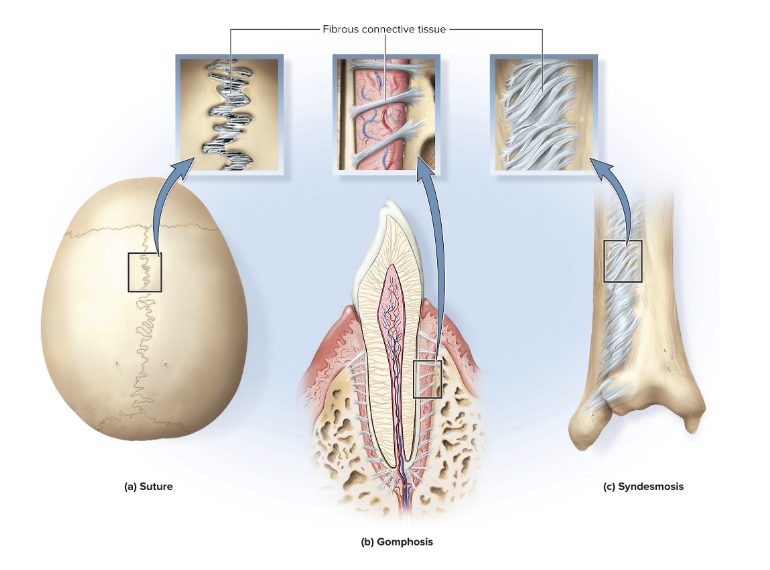
gomphosis
attachment of a tooth to its socket
held in place by fibrous periodontal ligament
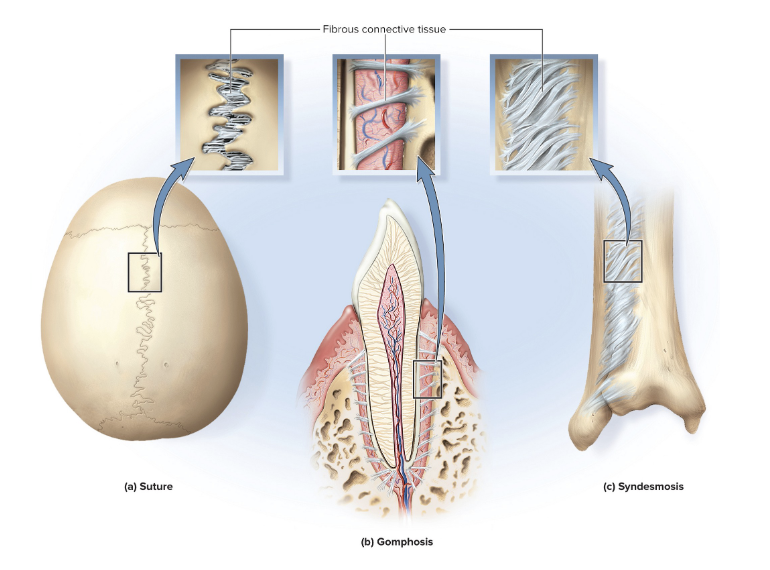
syndesmosis
fibrous joint at which two bones are bound by long collagen fibers
amphiarthrosis
cartilaginous joint
two bones are linked by cartilage
synchondrosis
bones joined by hyaline cartilage
examples of synchondrosis
first rib attachment to sternum
epiphyseal plate cartilage
symphysis
two bones joined by fibrocartilage
examples of symphysis
pubic symphysis joined by interpubic disc
bodies of vertebrae joined by intervertebral discs
diarthrosis
synovial joint
joint in which two bones are separated by a joint cavity
articular cartilage
layer of hyaline cartilage, 2-3 mm thick
covering the facing surfaces of two bones
joint cavity
separates articular surfaces
synovial fluid
slippery lubricant in joint cavity
rich in albumin and hyaluronic acid
viscous, slippery texture
function of synovial fluid
nourishes articular cartilage and removes waste
makes movement of joints almost synovial free
joint capsule
connective tissue that encloses the cavity and retains the fluid
synovial membrane
composed mainly of fibroblast-like cells that secrete synovial fluid and marcophages that remove debris from the cavity
articular disc
pad crosses the entire joint capsule
examples of articular disc
jaw, joints of the clavicle, between the ulna and carpal bones
meniscus
crescent-moon pad does not cross joint entirely
found in knee
function of meniscus
absorb shock and pressure, stabilize joint
tendon
strip of collagenous tissue attaching muscle to bone
ligament
strip of collagenous tissue attaching one bone to another
bursa
fibrous sac filled with synovial fluid
function of bursa
cushions muscles, helps tendons slide more easily, modifies direction of tendon pull
tendon sheath
elongated cylindrical bursa wrapped around a tendon
found in hand and foot
range of motion
the degrees through which a joint can move
types of axis rotations
multiaxial, biaxial, monoaxial
multiaxial joints
joint has three degrees of freedom
biaxial joints
movement in two planes
ball-and-socket joints
smooth, hemispherical head fits within cup-like socket
ball-and-socket examples
shoulder joint and hip
condylar joints
oval convex surface of one bone fits into a complementary-shaped depression on the other
condylar examples
radiocarpal joint, metacarpophalangeal joints
saddle joints
both bones have an articular surface that is shaped like a saddle, concave and convex
saddle examples
trapeziometacarpal, sternoclavicular joint
plane joints
flat articular surfaces, bones slide over each other
plane examples
between
carpal bones of wrist
tarsal bones of ankle
articular processes of vertebrae
hinge joints
one bone with convex surface fits into a concave depression of another bone
hinge examples
elbow, knee, finger joints, toes
pivot joints
a bone spins on its longitudinal axis
pivot examples
atlantoaxial joint (C1 nd C2), radioulnar joint at the elbow
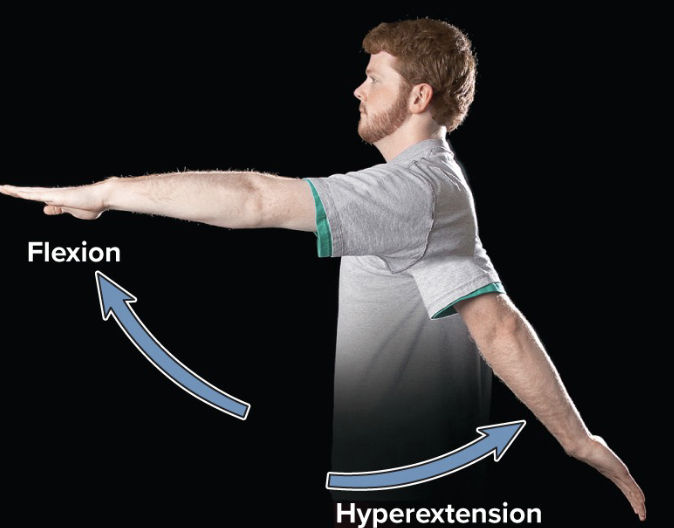
flexion
movement that decreases joint angle
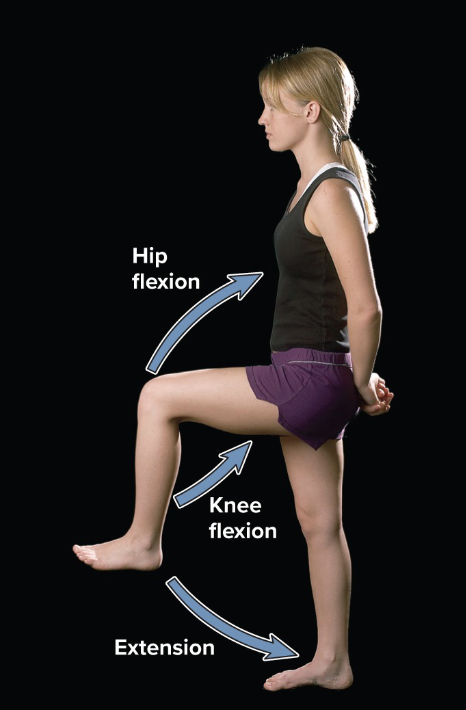
extension
movement that straightens a joint and returns a body part to the zero position
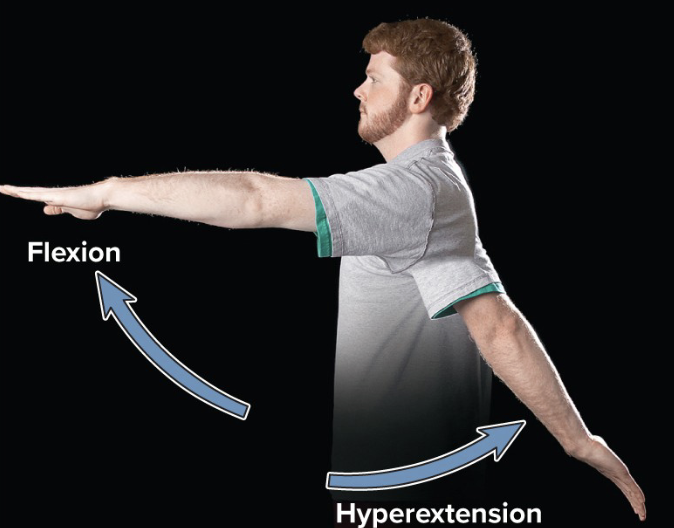
hyperextension
extension of a joint beyond the zero position

abduction
movement of a body part in the frontal plane away from the midline of the body
hyperabduction
raise arm over back or front of head
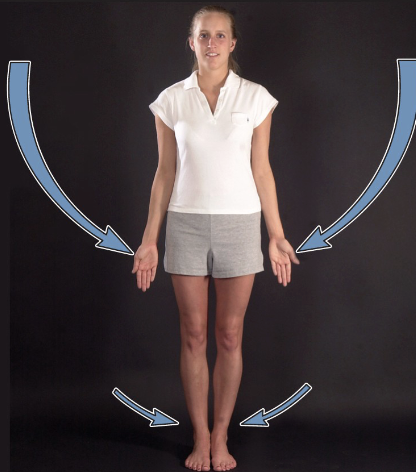
adduction
movement in the frontal plane back toward the midline
hyperadduction
crossing fingers, crossing ankles
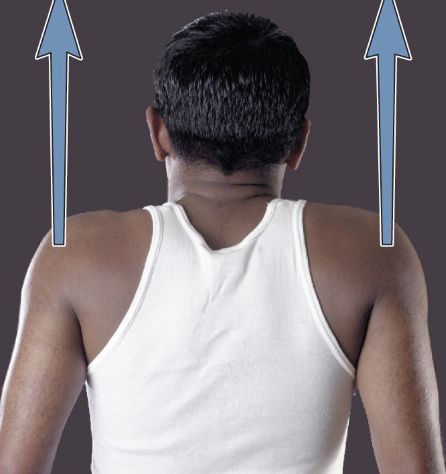
elevation
movement that raises a body part vertically in the frontal plane
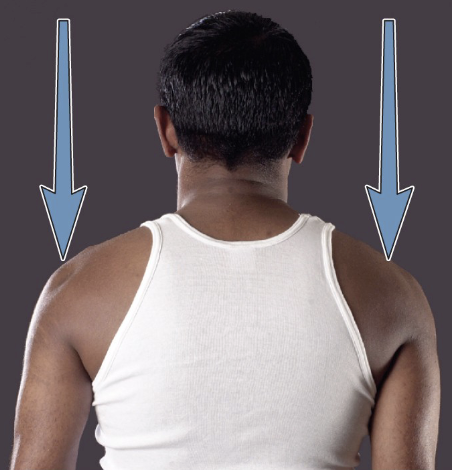
depression
movement that lowers a body part in the same plane

protraction
anterior movement of a body part in the transverse plane
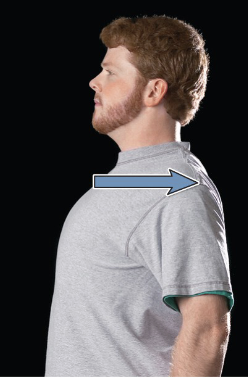
retraction
posterior movement of a body part in the transverse plane
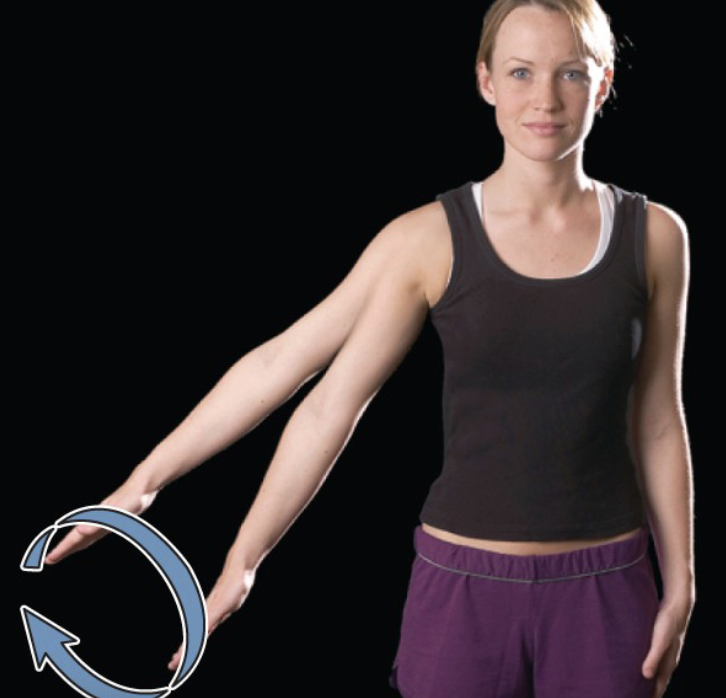

circumduction
one end of an appendage remains stationary while other end makes a circular motion
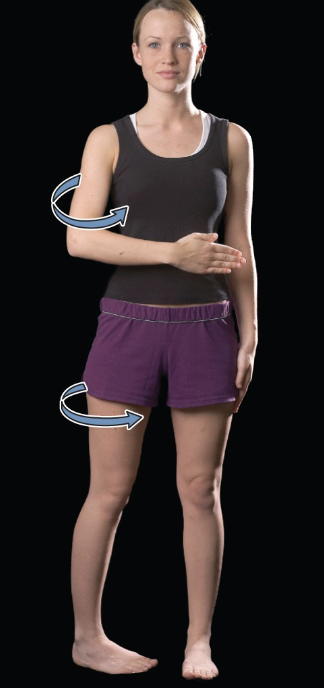
medial (internal) rotation
movement that turns the bone inward

lateral (external) rotation
movement that turns the bone outward
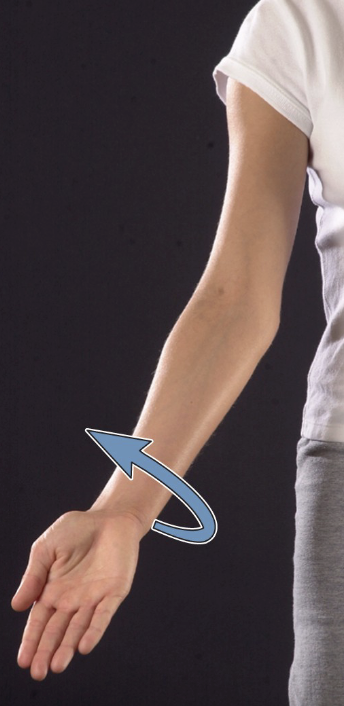
supination
forearm movement that turns palm to face anteriorly or upward

pronation
forearm movement that turns palm to face posteriorly or downward
osteoarthritis
wear-and-tear arthritis, resulting from years of joint wear
rheumatoid arthritis
autoimmune attacks against joint tissues
arthroplasty
replacement of diseased joint with artificial joint prosthesis