notes 3 - b cells and antibodies
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
maturations of B cells
what happens in the bone marrow:
where to b cells begin
what processes do they go through
where do b cells end as
in the bone marrow b cells begin as early pro-b cells - here they go through receptor formation to develop into pro/pre-b cells - the pro-b cells go through the negative selection/ self tolerance selection process to develop into immature b cell
maturations of B cells
what happens in the spleen:
B-cells that move to the spleen are T1 cells
T1 cells move transition to T2 cells, fully Mature B-cells
Where do mature primary B cells migrate to?
what do they express on the surface?
what does the mature b cell recirculate between?
what do they help respond to?
what is the half life of a mature b cells?
Mature, primary B cells migrate to the lymph nodes/lymphoid tissues
Express high levels of IgM/IgD on their surfaces as BCR
Recirculate between blood and lymphoid organs
Help to respond to antigens with T-cell help by producing antibodies
Half-life of approximately 4.5 months in periphery
why do b cells have to go through these maturation process?
it needs to be able to respond to the pathogens (diverse) but also doesn’t attack itself (autoimmunity?)
If an immature cell does not recognize/bind an antigen, it dies - why?
where do nieve b cells circulate through and to?
why does this increase the likelihood og encountering an antigen?
Antigen recognition by mature B cells provides a survival signal
b-cells receptors
b cell receptor expression
allelic exclusion
Why would you want a B-cell that is only able to produce 1 antibody for 1 antigen?
b cell activation
what does the activation of the b-cell involve and how is the response brought about ?
thymus-dependent (TD) antigen activation
what are the steps for this process
thymus independent (TI) b-cell activation
when antigens bind to BCR (b cell receptor) and PRR or other receptors is the response weaker or stronger?
whats the difference between TI-1 and TI-2? give examples of each
when antigens bind to BCR (b cell receptor) and PRR or other receptors the response weaker
b - cell proliferation
what does b-cell activation results in
after this result, which is activated by what and produces a clone of identical cells
*not stuck in the membrane
plasma cells
BCR / antibody structure
antibody structure (AB)
Fab VS Fc
antigen binding
idiotype vs isotype of antibody
avidity vs affinity of anitbody
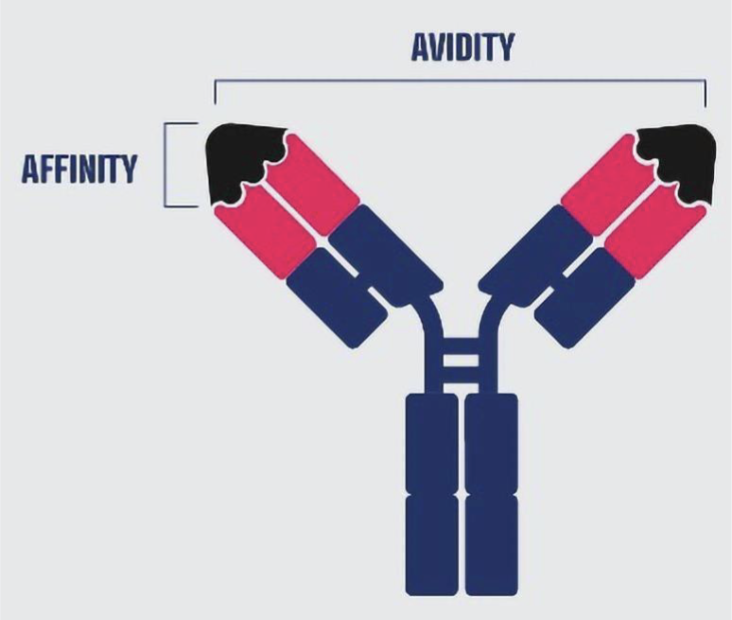
why have both avidity and affinity?
diversity of antibodys
multiple gene segements
recombination
somatic hypermutation
recombination vs hypermutation