genetic inheritance
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
trait
characteristics of an organism
e.g. eye colour
phenotype
appearance of an organism
e.g. green eyes
genotype
genetic composition of the individual
e.g. YY, Yy, yy
gene
region of DNA influencing a trait
e.g. gene for eye colour
allele
alternative version of the same gene
e.g. Y or y
locus
specific place on a chromosome occupied by a gene
homozygous
an organism possessing 2 of the same alleles at a locus
heterozygous
an organism possessing 2 different alleles at a locus
variant
refers to a variation in genetics
ranked on a scale

how are genetic conditions “on a scale”
mendelian (monogenic) - affects only 1 gene
polygenic - affects multiple genes
what are the 3 laws of inheritance
principle of segregation
principle of uniformity (dominance)
principle of independent assortment
what is the principle of segregation
during the formation of gametes, genes segregate randomly so that each gamete receives one or the other with equal likelihood
what is the difference between predicted genotypes & phenotypes
For example:
genotypes = RR : Rr : rr
phenotype = rounded : wrinkled
what is the principle of uniformity
when 2 genes responsible for a single character are present, one is dominant to the other, which is recessive
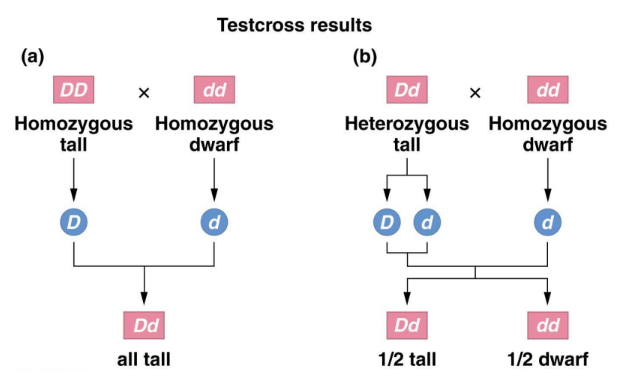
what is a testcross
a test to determine if individuals are homozygous or heterozygous for a trait
dominant phenotype & homozygous recessive
what is the principle of independent assortment
each pair of alleles segregates independently of other alleles during gamete formation
what is the difference between autosomal & sex-linked
forms of inheritance based on location
sex-linked = X or Y chromosomes
autosomal = other 22 chromosomes
what are carriers
individuals who are heterozygous for a variant
what is a pedigree
a representation of a family tree that outline inheritance of characteristics
what is a proband
a affected individual who first brings a family’s genetic condition to the attention of a professional
what is a consultand
an individual seeking genetic evaluation
may be unaffected
commonly also the proband
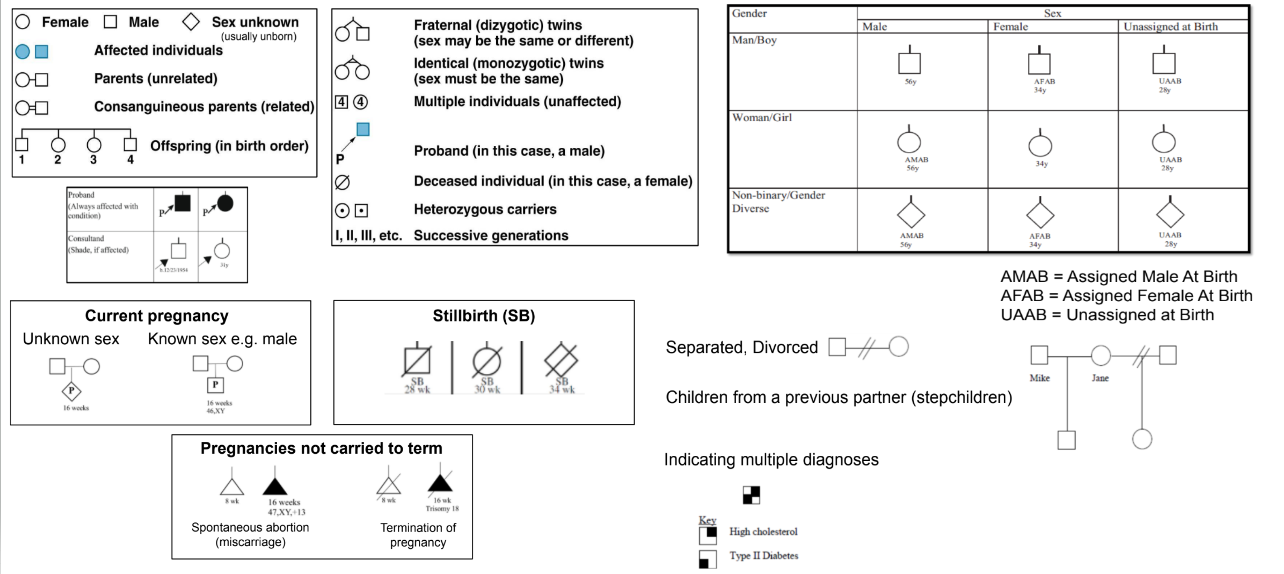
what are some symbols for pedigrees
what is autosomal recessive inheritance
expressed only in homozygous
both genes mutated to express disease
parents are usually asymptomatic carriers
can skip generations
↑incidence of parental consanguinity
subsequent children = 25% of being affected
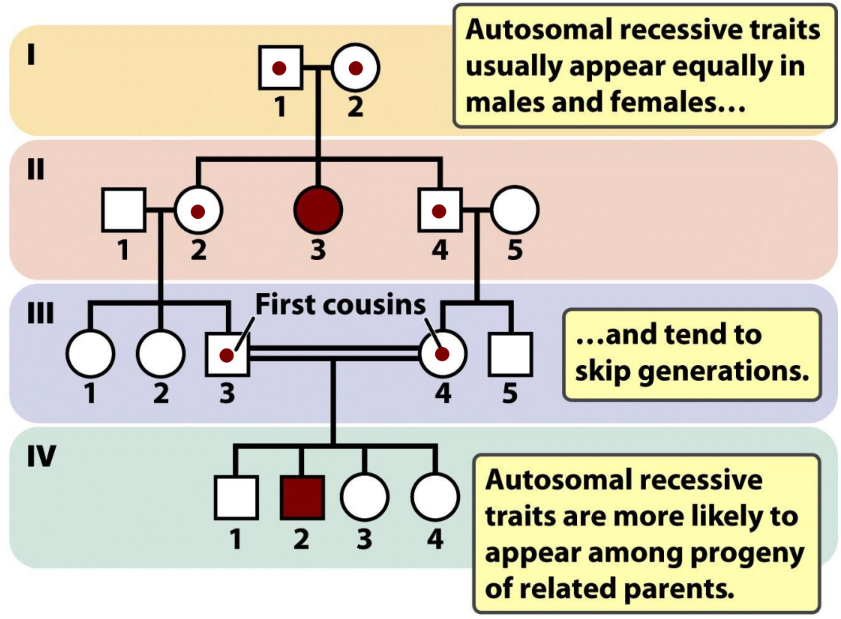
what is consanguinity
refers to a mating couple being related
increases chance of couple both carrying a disease-causing variant
more often for rare diseases in the family
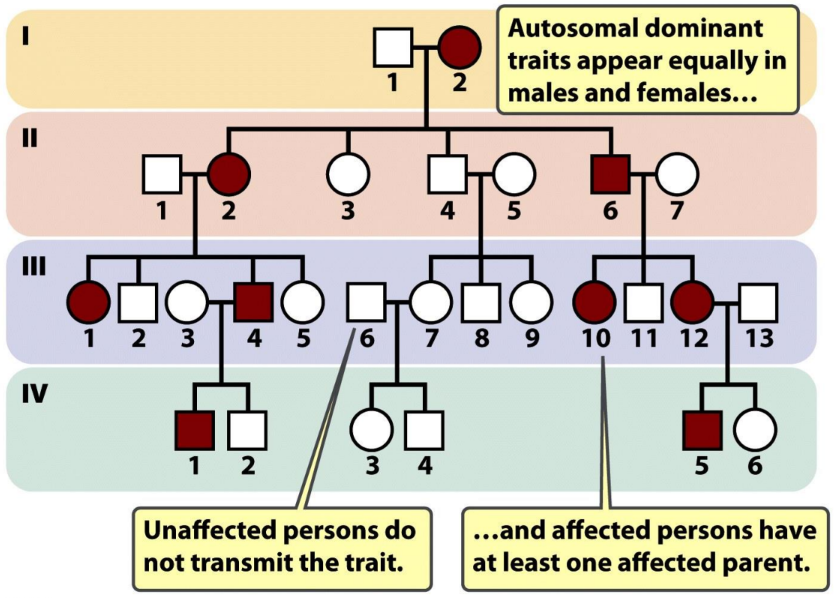
what is autosomal dominant inheritance
an affected person usually has at least 1 affected parent
affects either sex
usually doesn’t skip generations
1 affected & 1 unaffected parent = 50% of being affected
NOTE: affected = heterozygous
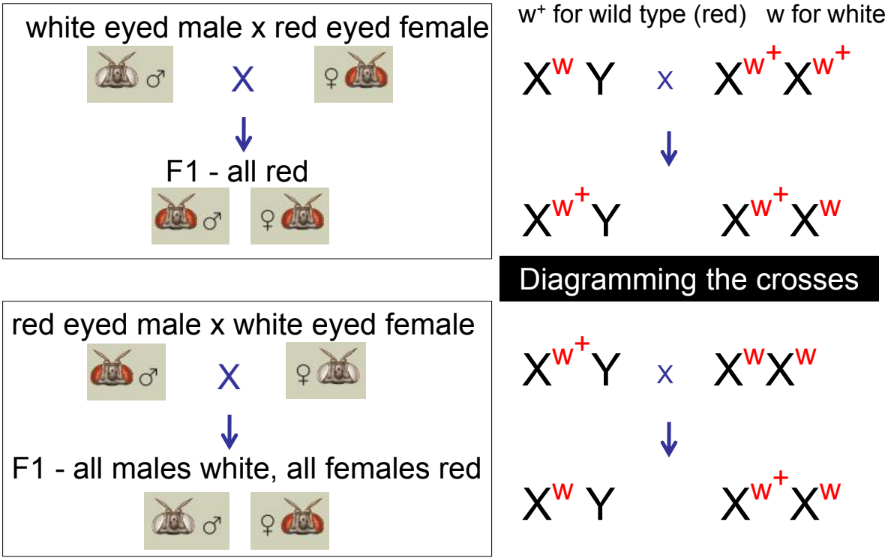
what is a reciprocal cross
a pair of crosses between a male of one strain and a female of another, and vice versa.
e.g. male = blue eyes & female = green eyes
male = green eyes & female = blue eyes
what is hemizygous
having only 1 copy of a gene rather than 2 copies
e.g. XY is hemizygous
what is some nomenclature for genetics
{letter} + = wildtype (most common allele in natural population)
{letter} = variant
{capital letter} = dominant
{lower case letter} = recessive
X-linked inheritance representation
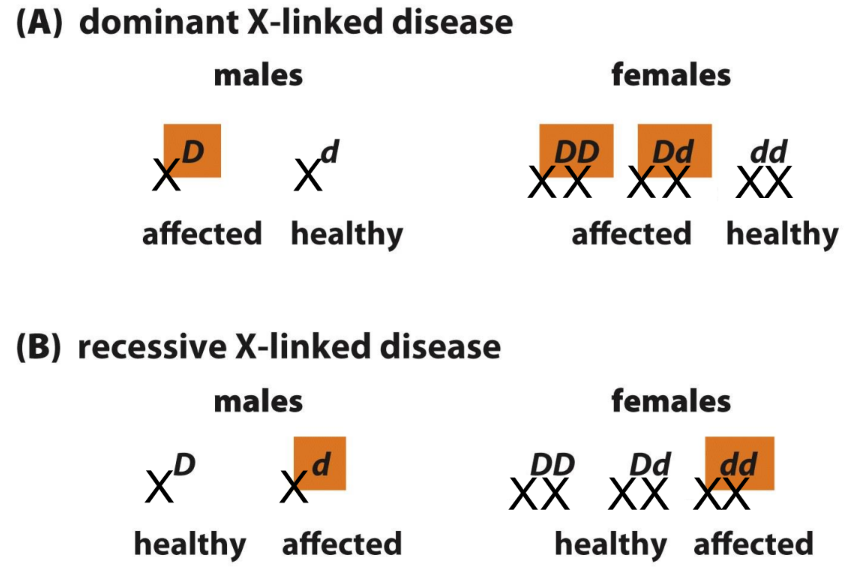
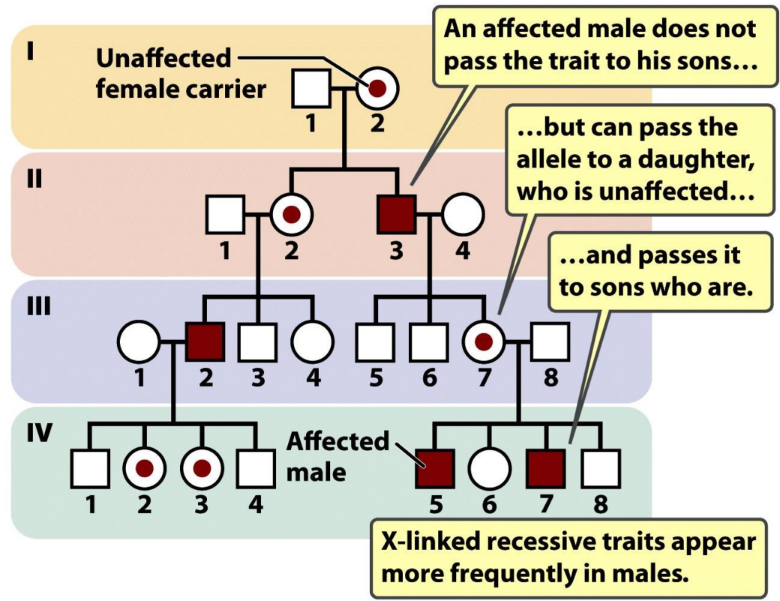
what is some information about X-linked recessive inheritance
affects mainly males
usually born to unaffected parents
mother is normally asymptomatic carrier
can occur due to a non-random X-inactivation
no male-to-male transmission
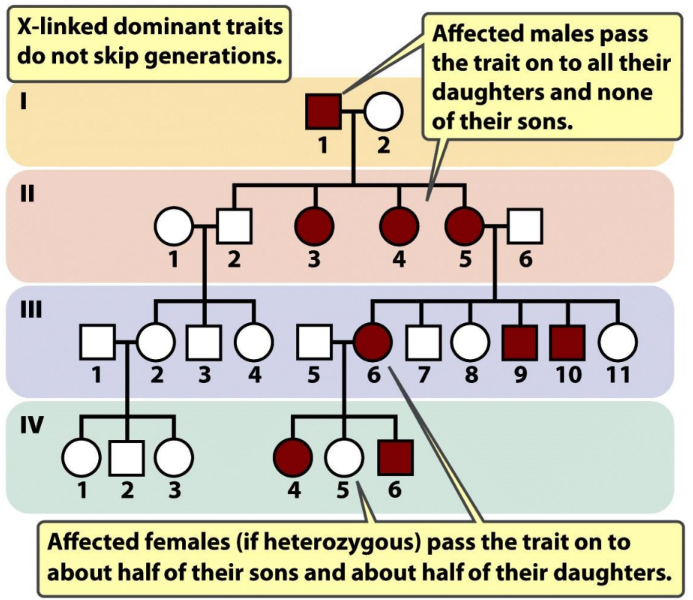
what is some information about X-linked dominant inheritance
affects either sex (more females affected)
at least 1 parent affected
females are often more mildly affected (X inactivation)
child of affected female has 50% chance of affected
affected male can transmit to daughters not sons
usually rare diseases (new mutations or germ-line mutations)
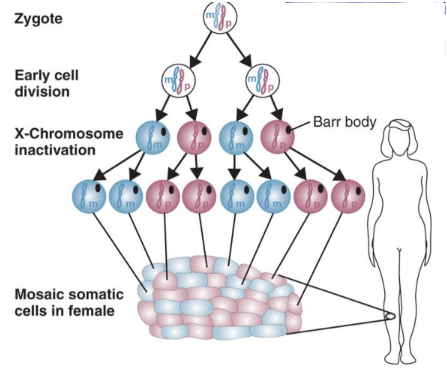
what is X chromosome inactivation
in females (XX), one X chromosome in each cell is inactivated.
mosaics
ensures females will produce X-linked gene products in similar quantities to males → dosage compensation
what is the sum rule of probability
the probability of either of 2 mutually excusive events occurring is the sum of their individual probabilities
e.g. Pr(A or B) = Pr(A) + Pr(B)
what is the product rule of probability
the probability of independent events occurring together is the product of the probabilities of the individual events
e.g. Pr(A and B) = Pr(A) x Pr(B)