Bacteria past Questions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
distinguish between facultative anaerobic and obligate anaerobic
FA can grow in the presence or absence of oxygen
OA can’t tolerate oxygen and die in its presence
FA rely on aerobic respiration
OA rely on fermentation or anaerobic respiration
FA - E coli
OA - Clostridium botulinum
what role does the human microbiota play in the immune system?
provides a first line of defense against invading pathogens
it produces substances that inhibit pathogens
contributes to the integrity of the intestinal barrier which prevents pathogens from invading the body
an example of a disease that develops as a result of the disruption of the microbiota?
CDI - clostridium difficile infection
causes inflammation of the colon (colitis)
primary trigger is antibiotic use
what is the bacterial capsule?
protective outer layer composed of polysaccharides that surrounds the cell wall of some bacteria
why is the bacterial capsule considered to be a virulence factor
inhibit the ability of immune cells by providing a physical barrier and prevents direct contact
can enhance the bacterium to adhere to host tissues which is needed for the spread of infection
describe two mechanisms of acquired antibiotic resistance in bacteria and an example of each
Enzymatic degradation - some bacteria produced enzymes that inactivate or modify antibiotics which render them ineffective. This occurs through gene transfer or mutation
Example = Beta-lactamases
Altered target sites - bacteria can acquire mutations or genetic changes that alter the target sites where antibiotics exert their effects which prevents the drug from binding effectively
Example = MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
distinguish between thermophilic, mesophilic and psychrophilic bacterial cells
thermophilic bacteria thrive at elevated temperatures (45-80)
Their enzymes and membrane lipids remain stable at high temp
Found in geothermal environments such as hot springs
Mesophilic bacteria grow best at moderate temperatures (20-45)
Can thrive in many environments including human and animal bodies, soil and surface waters
Psychrophilic bacteria grow best at low temperatures (0-20)
contain antifreeze proteins and membranes that remain fluid at low temp
Found in cold environments including polar ice capes and deep sea waters
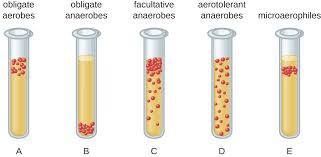
define aerotolerant bacteria growth
type of anaerobic bacteria that can tolerate the presence of oxygen but no not need it for growth
rely on fermentation processes to metabolize substrates and produce energy
define microaerophilic bacteria growth
group of microorganisms that require a reduced level of oxygen for growth, between 2% to 10% oxygen concentration
high concentrations are toxic to them
what is a bacterial endospore? Example of endospore-forming bacterial species
highly resistant, dormant structure formed by some bacteria to survive harsh environmental conditions
they can withstand extreme temperatures, radiation and chemical disinfectants which allow them to endure unfavorable conditions and resume growth when the environment becomes favorable again
Examples - Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus anthracis
distinguish between sterilization and disinfection
sterilization is the process of completely eliminating all microorganisms which includes bacteria. fungi, viruses and spores
methods of sterilization is autoclaving, radiation and chemical agents
Disinfection is the process of reducing pathogenic microorganisms
methods of disinfection is heat, ultraviolet and chemical disinfectants
describe the bacterial structure fimbriae in relation to virulence factor
hair like appendages found on the surface of many bacteria
some are involved in adhesion to host cells
increase the pathogenicity of bacteria
describe filtration as a method of sterilization
a process by which microorganisms are removed from a substance based on their size
passage of liquid or gas through a screen-like material with pores small enough to retain microorganisms