8 - Attention + Concentration
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Defining Attention, EXAM
A process or feature of our brain - ability to use attention to focus on things which are important
A person’s ability to exert deliberate mental effort on what is most important on any given situation (Moran 2004) *EXAM
Defining Concentration
Individuals deliberate decision to concentrate attention on a specific thing
Defining Focus
A person’s ability to exert deliberate mental effort on what is most important on any given situation (Moran 2004) *EXAM
Selective Attention
Select where you put your attention
Focus on relevant environmental cues
Disregard irrelevant cues
Internal vs external
Alertness
maintaining attention over a long period of time
Switch on/off - different levels at different times
Regaining concentration when lost
Tiring
Situational Awareness
Awareness of what’s going on around you
Know what to focus on based on situational cues
Keep awareness while executing a skill
Shifting Attention
Shifting scope/focus of attention
Narrow / Broad
Internal / External
Information Processing Approach
Theoretical lens we use to understand attention and concentration in sport
Consider human thinking as steps - computer
Flexibility when allocating attention
3 Processes of Attention
Attentional selectivity
Attentional Capacity
Attentional Alertness
Selectivity
Spotlight used to focus on most important
Can fail:
*Fail to pinpoint
*Distraction
*Dividing attention
More skill developed - better selective attention
Automated
Capacity
Attention is limited, it’s a finite resource
2 types of attentional processing:
Controlled - give conscious attention
Automatic - process something without conscious attention
Alertness
Connected to our level of emotional arousal and attention
Too much emotion = narrow field of attention
Missing cues in other areas
Attentional Control Theory (Eysenck et al 2007)
Top down - goal directed processing (internal)
Bottom up - stimulus driven process (external)
Anxiety impairs TD attentional system, so influenced more by BU
Threatening stimuli
Wilson et al (2009) EXAM

Theory Summary

Attentional Focus
Nideffer (1976) - 2 dimensional theory
Width - broad vs narrow
Depth - internal vs external
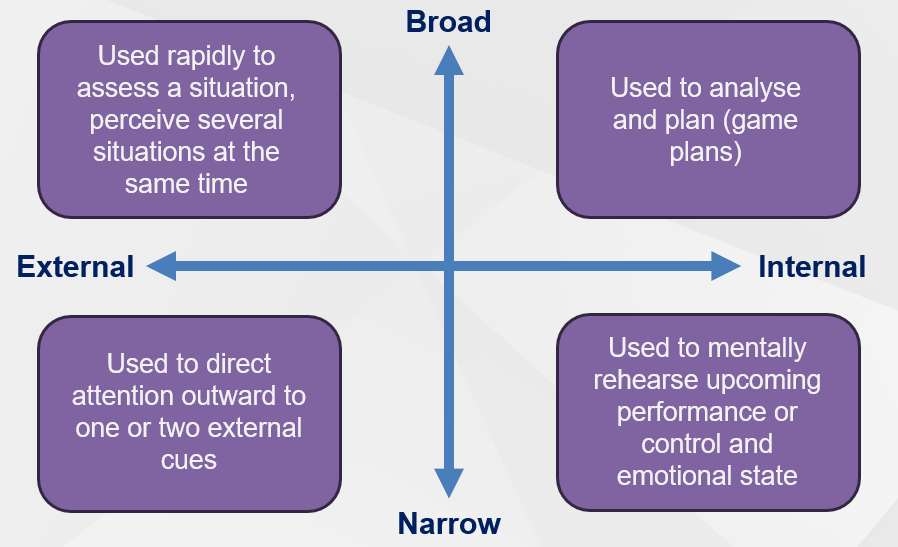
Attentional Focus - Width
Relates to broad or narrow focus of attention
Broad - athletes are aware of different stimuli at once
Narrow - athletes can exclude irrelevant info
Attentional Focus - Direction (Vertical)
Refers to the target of an individual’s attention
External - athlete focusing on stimuli external to them
Internal - concentrate on internal factors e.g. kinaesthetic
Attention Focus - Key Points
Use as a sport psychologist
Bring awareness to attention
Highlight attentional issues
Distraction
Internal - choking, overconfident, self doubt
External - weather, crowd
Outcome focus - position, score
Choking under pressure
Attentional process
Decrease in performance
The Choking Process (Hill et al + Weinberg & Gould)
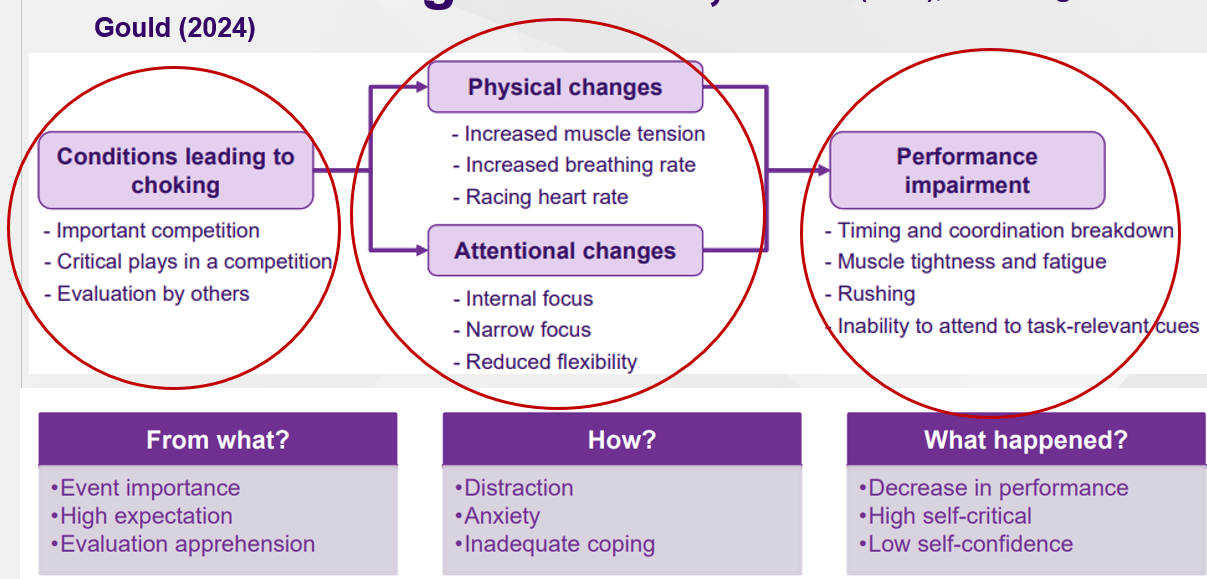
Improving attention
Self-talk
Mindfulness
Pre-performance routines
Attention Case Study - XC MTB
