Circle Theorems
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
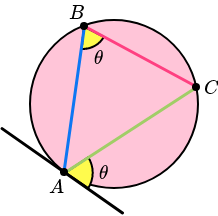
Alternate segment theorem
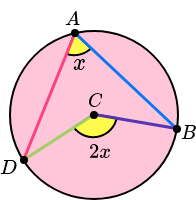
The angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference
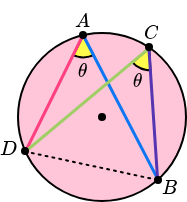
Angles in the same segment are equal.
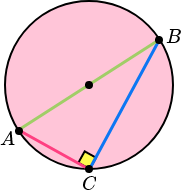
The angle in a semicircle is 90 degrees.
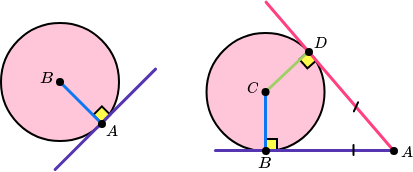
The angle between a tangent and a radius is 90 degrees. Tangents which meet at the same point are equal in length.
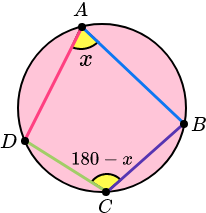
The opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral total 180 degrees.
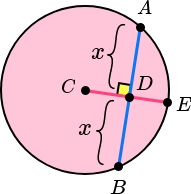
The perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord
Central Angle
Angle with its vertex at the center of a circle
Central Angles Sum
Total sum of central angles in a circle is 360 degrees
Arc
A portion of a circle defined by two endpoints
Semicircle
An arc with a measure equal to 180 degrees
Minor Arc
An arc with a measure less than 180 degrees
Major Arc
An arc with a measure greater than 180 degrees
Adjacent Arcs
Arcs in a circle sharing exactly one common point
Arc Length
Distance between two endpoints along an arc in linear units
Sector Area
Ratio of the area of a sector to the area of the whole circle
Inscribed Angle
Angle with its vertex on a circle and sides containing chords
Intercepted Arc
Arc with endpoints on the sides of an inscribed angle
Congruent Arcs
Arcs with the same measure in the same or congruent circles
Inscribed Polygon
Polygon where each side is tangent to a circle circumscribed around it
Tangent
A line that intersects a circle at exactly one point
Common Tangent
Line, ray, or segment tangent to two circles in the same plane
Two-Tangent Theorem
If two segments from the same exterior point are tangent to a circle, they are congruent
Circumscribed Polygon
Polygon with each side tangent to a circle inscribed within it
A Tangent
It is a straight line that touches the circumference of the circle at only one point.
Congruent
To have the same shape and size