Virtualization
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards cover virtualization concepts, before/after scenarios, hardware independence, encapsulation, platform components, hypervisor types, VM definitions, benefits, isolation, and a practical example.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
One
For most of the history of the microcomputer, a single computer has been able to run a single operating system at any _____ time.
Virtualization
But because of emerging platforms, a single computer is now capable of running multiple OS simultaneously through the concept of this.
Virtualization
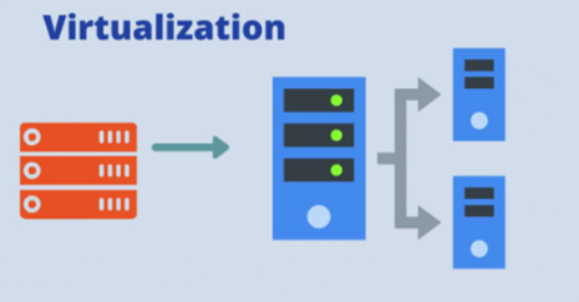
A technology that creates virtual, simulated environments from a single physical machine, allowing multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on shared hardware.
One OS image per machine
software and hardware tightly coupled
conflicts when running multiple apps
underutilized resources
inflexible and costly infrastructure.
Before virtualization, what were common issues?
After Virtualization
Hardware-independence of the operating system and applications
VMs can be provisioned to any system
Can manage OS and applications as a single unit by encapsulating them into virtual machines
Virtualization
Means that multiple operating systems can be installed and run simultaneously on a single computer
Virtualization
Because multiple operating systems can share the same physical hardware, _________ can improve resource use, reduce costs associated with physical maintenance, and boost security through isolated systems.
multiple servers
Without virtualization, you’d need _______ ______ to run Windows, Linux, and another Linux server for testing.
Hardware independence
Virtualization provides….
Guest VM sees the same hardware regardless of the host hardware
Isolation
Virtualization provides….
VM’s operating system is isolated from the host operating system
Encapsulation
Virtualization provides….
___________ of an entire VM (OS + applications + state) into a single portable file.
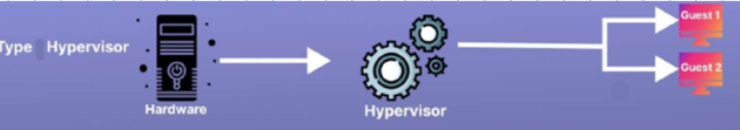
physical hardware → Hypervisor → VM/VM
Virtual Platform Components:
Computer
Virtual Platform Components:
Known as the hardware layer. It is the physical machine (or host) that provides the resources, such as CPU and memory for the virtual environment
Hypervisor / VMM (Virtual Machine Monitor)
Virtual Platform Components:
Known as the software layer. It manages the virtual machine environment and facilitates interaction with the host hardware and network.
It manages resources (CPU, RAM, storage, network) and allocates them to each virtual machine (VM) as if the VM were a completely independent system.
Guest Operating Systems (or Virtual Machines [VM])
Virtual Platform Components:
Operating systems installed under the virtual environment.
The number of operating systems is generally only restricted by hardware capacity. The hypervisor may also restrict the type of operating systems that can be installed.
Type 1 Hypervisor (Bare-metal Hypervisor)
Types of Hypervisors:
Type 2 Hypervisor (Hosted Hypervisor)
Types of Hypervisors:

Type 1 Hypervisor (Bare-metal Hypervisor)
Bare-metal hypervisor that runs directly on host hardware without an underlying OS; used in enterprise/cloud environments
Type 1 Hypervisor (Bare-metal Hypervisor)
(e.g., VMware vSphere, Hyper-V, Xen).
Type 2 Hypervisor (Hosted Hypervisor)
Hosted hypervisor that runs on top of an existing OS; suitable for personal or small-scale virtualization
Type 2 Hypervisor (Hosted Hypervisor)
(e.g., Oracle VirtualBox, VMware Workstation, Parallels).
Define a virtual machine (VM).
A software-based emulation of a physical computer that runs its own guest OS and applications under a hypervisor.
Resource Efficiency
Cost Savings
Flexibility
Isolation
Scalability
Disaster Recovery
What are the benefits of virtualization? RCFISD
Each VM’s OS is isolated from the host OS and other VMs, enhancing security and stability.
What does isolation mean in virtualization?
Applications can be moved and run on different host hardware via VMs without modification.
What is meant by hardware independence for applications?
VMs share the physical CPU, memory, storage, and network resources provided by the host hardware, increasing utilization.
How do multiple VMs share resources?
A single server with 64 GB RAM and 16 cores can host multiple VMs like Windows Server(16gb 4c), Ubuntu(16gb 4c), and Linux Mint(8gb 2c) with allocated RAM/cores.
What is an example of a virtualization resource distribution?
Easier backup, transfer, and deployment of the entire VM package.
What does encapsulating a VM into a single file enable?
Windows 1.0
is the first Microsoft windows operating system