P1 LESSON 1 Introduction to Pre-stressed Concrete
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Reinforced Concrete
uses concrete to resist compression and
to hold the steel bars in place, and
uses steel to resist all of the tension
Concrete
strong in compression but weak in tension
Steel
strong in tension (as well as compression)
Prestressing
a method in which compression force is applied to the reinforced concrete section.
Reinforced Concrete
Tensile strength of concrete is neglected (i.e. zero)
___ beam always crack under service load
Prestressing
reduce the tensile stress in the section to the point that the tensile stress is below the cracking stress. Thus, the concrete does not crack!
Yes
It is then possible to treat concrete as an elastic material??
Internal Prestressing Forces
External Forces (from DL, LL, etc...)
The concrete can be visualized to have 2 force systems
Pre-stressed Concrete
Internal stresses are induced to counteract external stresses.
Pre stressing
permanent acting forces in concrete to resist elastic forces under loads
1904
Freyssinet attempted to introduce permanent acting forces in concrete to resist elastic forces under loads and was named “Pre stressing”
Reinforced Concrete (RC)
Cracked with deflection under dead load and full service load
Prestressed Concrete (PC)
Uncracked with likely camber under dead load and prestress
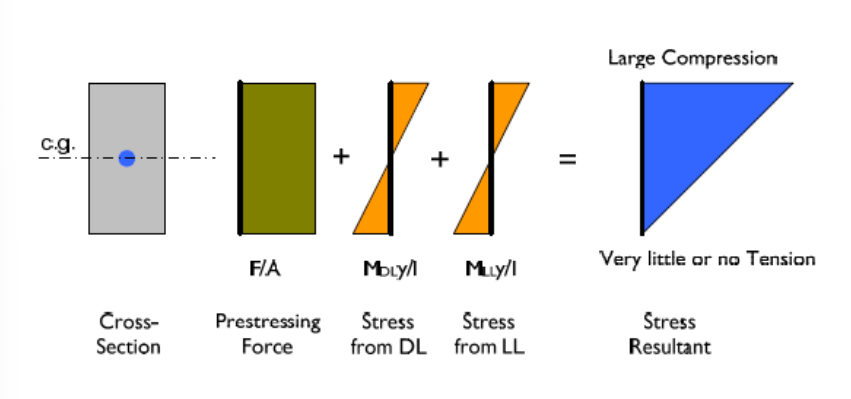
Stress in concrete section (simple case)
when the prestressing force is applied at the c.g. of the section
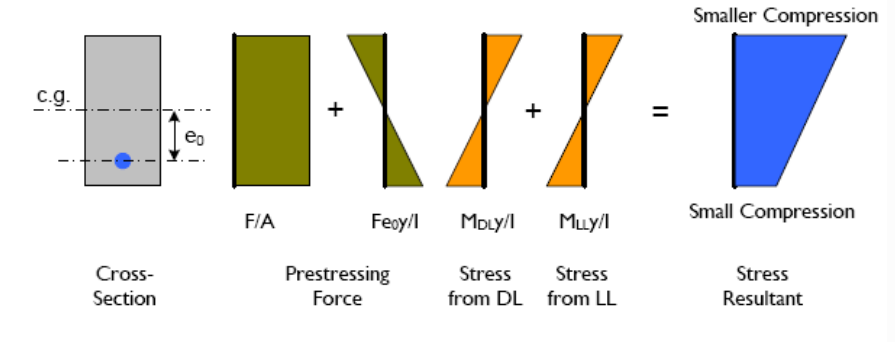
Stress in concrete section (typical case)
when the prestressing force is applied eccentrically with respect to the c.g. of the section
No
does the concept of prestressed concrete is new?
1886
a patent was granted for tightening steel tie rods in concrete blocks. This is analogous to modern day segmental constructions.
low strength of steel at that time
Early attempts were not very successful due to?
Since we cannot prestress at high stress level, the prestress losses due to creep and shrinkage of concrete quickly reduce the effectiveness of prestressing.
Early attempts were not very successful due to? (another reason)
Eugene Freyssinet (1879-1962)
first to propose that we should use very high strength steel which permit high elongation of steel.
Eugene Freyssinet
First prestressed concrete bridge in 1941 in France
First prestressed concrete bridge in US: Walnut Lane Bridge in Pennsylvania. Built in 1949. 47 meter span.
Bridges
Slabs in buildings
Water Tank
Concrete Pile
Thin Shell Structures
Offshore Platform
Nuclear Power Plant
Repair and Rehabilitations
Applications of Prestressed Concrete
Pretensioning
Posttensioning
External
Internal
Linear
Circular
End-Anchored
Non End-Anchored
Bonded
Unbonded Tendon
Precast
Cast-In-Place
Composite
Partial
Full Prestressing
Classification and Types of Prestressing
Pretensioning
the tendons are tensioned against some abutments before the concrete is place.
After the concrete hardened, the tension force is released.
The tendon tries to shrink back to the initial length but the concrete resists it through the bond between them, thus, compression force is induced in concrete.
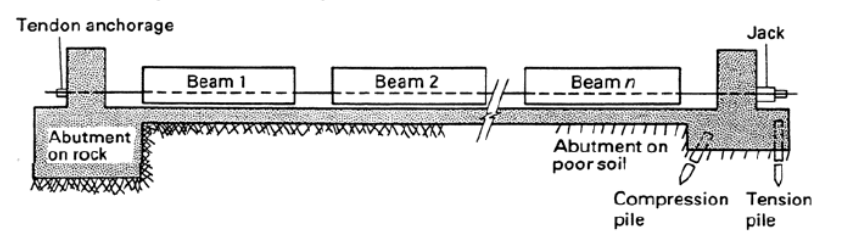
___ is usually done with precast members.
Posttensioning
the tendons are tensioned after the concrete has hardened.
Commonly, metal or plastic ducts are placed inside the concrete before casting.
After the concrete hardened and had enough strength, the tendon was placed inside the duct, stressed, and anchored against concrete. Grout may be injected into the duct later.
This can be done either as precast or cast-in-place.
External Prestressing
Prestressing may be done outside
Internal Prestressing
Prestressing may be done inside
Linear Prestressing
Prestressing can be done in a straight structure such as beams
Circular Prestressing
Prestressing can be done in a around a circular structures, such as tank or silo.
Bonded Tendon
The tendon may be ___ to concrete (pretensioning or posttensioning with grouting)
helps prevent corrosion of tendon.
Unbonded Tendon
The tendon may be __ concrete (posttensioning without grouting).
allows readjustment of prestressing force at later times.
Non-End-Anchored tendons
In Pretensioning, tendons transfer the prestress through the bond actions along the tendon
End-Anchored tendons
In Posttensioning, tendons are anchored at their ends using mechanical devices to transfer the prestress to concrete; (Grouting or not is irrelevant)
Full Prestressing
Prestressing tendon may be used in combination with regular reinforcing steel.
Thus, it is something between ___ prestressed concrete (PC) and reinforced concrete (RC).
The goal is to allow some tension and cracking under full service load while ensuring sufficient ultimate strength.
Partial Prestressing
use to control camber and deflection, increase ductility, and save costs.
Uncracked under dead load; cracked under full service load
Takes full advantage of high strength concrete and high strength steel
Need less materials
Smaller and lighter structure
No cracks
Use the entire section to resist the load
Better corrosion resistance
Good for water tanks and nuclear plant
Very effective for deflection control
Better shear resistance
Advantages of PC
Initial Loading
Service Loading
Stages of Loading
Initial (Immediately after Transfer of Prestress)
Full prestress force
No MLL (may or may not have MDL depending on construction type)
Service
Prestress loss has occurred
MDL+MLL
Bulkheads
high-strength steel tendons are pulled between two end abutments
Anchoring of tendons against the end abutments
Placing of jacks
Applying tension to the tendons
Casting of concrete
Cutting of the tendons
Various stages of the pre-tensioning operation are summarized as follow
Improving the performance of the building under various service condition.
Allow to carry a greater load or span a greater distance then ordinary reinforce concrete.
It permits steel to be used at stresses several times larger than those permitted for reinforcing bars
Pre-tensioned Concrete
Large reduction in traditional reinforcement requirements as tendons cannot distress in accidents
Tendons can be easily "woven" allowing a more efficient design approach.
Higher ultimate strength due to bond generated between the strand and concrete
Strong against compression
Post-tensioned Concrete