Bio term 2
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
CNS
central nervous system
PNS
peripheral nervous system
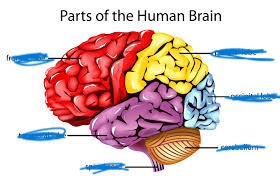
how many parts of the brain
6
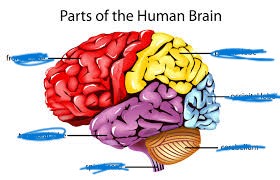
name the red
frontal lobe
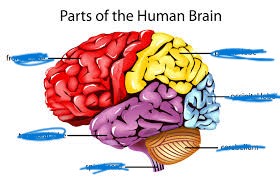
name the yellow
parietal lobe
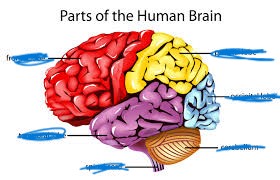
name the purple
temporal lobe
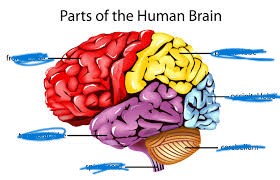
name the blue
occipital lobe
name the brown
cerebellum
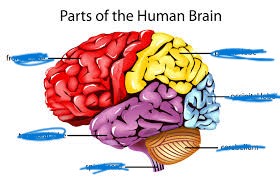
name the light purple
brain stem
name the 3 parts of the brain stem
mid brain
pons
medulla
what side of the brain is the side for creativity
right
what side of the brain is the side for thinking
left
what does the frontal lobe do
move, think and speak
what does the parietal lobe do
sensation
what does the temporal lobe do
understand and hear
what does the occipital lobe do
vision
what does the cerebellum
balance, coronation
what does the brain stem do
swallow, breath, heart rate, blood flow
how many parts are there in a neuron
6
what are the components in a neuron
dendrities
cell body/ soma
nucleus
axon
myelin sheath
axon terminals
what structure of the eye transmits messages from your eye to the brain
optic nerve
the pupil
the black part of your eye that allows light into the eye.
the Iris
the colored part of the eye that controls the amount of light in your eye
the cornea
the see through skin that covers your eye
the lens
a clear jelly substance that focuses light onto the retina.
the optic nerve
sends electric messages from the retina to the brain
what is the process to send a message
1 recognizes
2 sends message
3 processes
4 responds
stimuli
a event that triggers a response
Thermorespetors
detects temperature
pain receptors
pain
baroceptors
change in pressure
chemoeceptors
detects chemical connections
photoceptors
change in light
space between nerves
synaptic celf
neurotransmitters are
chemicals
GABA
calm/ relaxes
meletonin
sleep
oxytoein
love/ bellonging
dopamine
happiness
reflex action
a involuntary action in response to a stimuli
voluntary action
actions to a response to a external stimuli such as eating food/ chewing
involutary action
an action that just are natural and that you don’t have to think about such as keeping blood pumping to the heart.
how nerves communicate
1 stimuli
2 receptor
4 controller
5 effectors
6 response
what is the master gland
Pituitary gland
hormons control
reproduction
metabolism and energy balance
growth and development
body differences
general hemostasis: water nutrients and electrolyte balance in the blood.
endocrine system messages through
blood
the nervous system messages through
neurotransmitters
glands
is just a structure that secrets hormones
hormones are
proteins made of amino acids
hypothalamus
maintains homeostasis, including heart rate, temperature and blood pressure.
pituitary gland
is responsible for growth hormones
pineal gland
produces melatonin
thyroid
regulates energy and metabolism
parathyroid
produces hormones to help with calcium absorption
pancreas
manages blood sugar
adrenal
produces the hormone to help with stress
how many chemicals work in the body every minute.
50 different chemicals
what is the average body temp
37 degrees Celsius
pathogens
bacteria or virus
virus
not alive, genetic material
bacteria
alive, single cell
fungal
single or multicell, living
immune system
organs or tissues that can defend the body from infection
microrganism
microscopic organism
prokaryotic
no nucleus, no membrane
eukaryotic
nucleus, membrane - bond organisms
host
a larger organism that has a smaller organism inside
contagious
a disease that can spread from one person to the other
infection
the invasion and growth of microbes
viruses are surrounded by
protein coat, DNA/RNA envelope.
viruses replicate by
enters the host cell
makes it way into the cell and replicates
then this causes them to replicate into a lot more
the host cell releases dies and the virus particles release into the body
red blood cells
41% of blood
hemoglblobin
made of protein structure
carry oxygen around body
makes it red
plasma
made of water
proteins
yellow
in the bone marrow
55%
white blood cells
4% in the blood
fights pathogens
platelets
clots blood
how many lines of defense are there
3
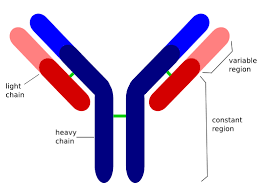
antigen
substance that is recognized as foreign
antibodies
specific to antigens
bind and neutralizes pathogens
memory
1st line
non-specific
innate
chemical or physical barrier
2nd line
non-specific
Innate
Inflammatory
consumes pathogens
internal
3rd line
specific
adaptive
kill pathogens with T-cells(destroys) and B-cells(antibodies)
internal
phagocytosis
recognition and adherence
engulfment
intrasellar killing of pathogen
memory
storage of B and T cells for future with Bacteria and Virus.