Higher Chemistry Definitions
1/83
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Lattice
A regular repeating structure
Malleable
The ability to be rolled into sheets
Ductile
The ability to be stretched
Physical properties
Properties which do not involve the substance in chemical reactions
LDF
The electrostatic attraction between a temporary and
Instantaneous dipole and induce dipole
Covalent Bond
The electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and
The positively charged nuclei of the two atoms which are sharing these electrons.
First Ionisation Energy
The first ionisation energy of an element is the energy required to remove one electron from every atom in a mole of free atoms
Second Ionisation Energy
The second ionisation energy is the energy required to remove a second electron from every atom in a mote of free atoms once a first electron has already been removed

Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a measure of the attraction an atom which is involved in a covalent bond has for the shared electrons of the bond
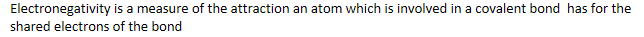
Period/Row
H

orizontal line of elements on the periodic table
Column/Group
Vertical column of elements in the periodic table having same # of outer electron and similar chemical properties
Covalent Bond
The electrostatic attraction between positive nuclei and negatively charged pair of electrons shared between them
Ionic
The electrostatic attraction between a positive and negative ion

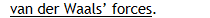
Van der Waals’ forces.
Any intermolecular forces acting to attract one molecule to another molecule
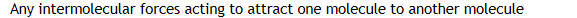
Polar Molecule
Is a molecule which has a permanent slightly positive charge on one side and a permanent slightly negative charge on the other. Polar molecules have permanent dipoles
Hydrogen Bond
Is an unusually strong permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions which will be found between any molecules containing O-H, N-H or F-H covalent bonds.
Permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions
Are intermolecular forces of attraction between polar molecules.
Viscosity
Is another term for thickness of a liquid
Miscible
Liquids which dissolve in each other
Immiscible
Liquids which do not dissolve in each other and form two separate layers
Oxidation
Is a process in which electrons are lost
(OIL RIG)
Reduction
Is a process in which electrons are gained
(OIL RIG)
Redox Reaction
Are ions which appear unchanged on both sides of an equation, they do not take part in a reaction.
Oxidising Agent
Is a chemical which acts on another substance to oxidise it.
Reducing Agent
Is a chemical which acts on another substance to reduce it.
Displacement Reaction
Is a redox reaction in which one element is replaced by another in a compound.
Concordant
Results are titres that are very close together.
(Within about 0.2 cm3)
Redox Titration
The concentration of an oxidising or reducing agent is determined by measured how much is required to react completely with another substance.
Functional Group
is that part of a molecule which gives the substance its characteristic properties
Homologous Series
Is a family of compounds with the same general formula and similar chemical properties.
Isomer
Are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulae
Distilation
Is a method of separating miscible liquids which have different boiling points by evaporation followed by condensation.
Distillate
The liquid which has been separated from the mixture as a result of distillation
Condensation Reaction
Occurs when two molecules are joined together with the loss of a small molecule- usually water.
Hydrolysis
Is a reaction in which a molecule is split up by the chemical action of water.

Reversible Reaction
Is a reaction that can go in both the forward direction and in the reverse direction.
Enzymes
Are proteins which acts a biological catalyst
Essential Amino Acids
Are amino acids that cannot be synthesised by the human body and must be present in the diet.
Volatile Molecule
One that easily evaporates
Denaturing
Is the word used to describe the change that happens when the intermolecular bonds holding a protein chain into a certain shape are broken.
Aldehyde
Is a molecule containing a primary carbonyl group. (The carbonyl group is connected to no more than one carbon atom).
Ketone
Is a molecule containing a secondary carbonyl group. (The carbonyl group is connected to two carbon atoms).
Rancid
word used to describe the foul smelling products produced when edible oils react with oxygen from the air.
Antioxidants
Are molecules that reduce the rate of oxidation reactions by donating electron(s) to an oxidising agent. They are, themselves, reducing agents.
Saponification
Is the process of making soap by hydrolysing edible oil using an alkaline solution
A Detergent
Is a cleaning product having molecules that have both hydrophilic (polar) and hydrophobic (non-polar)parts.
Hard Water
Is water containing relatively high concentrations of Ca2+(aq) or Mg2+(aq) ions.
Soft Water
Is water with very low concentrations of Ca2+(aq) or Mg2+(aq) ions.
Scum
Is an insoluble precipitate formed when Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions react with soap.
Soap less Detergents
Are substances that do not form scum in hard water. An example of a soap less detergent is shown
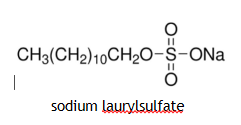
Emulsion
Contains small droplets of one liquid dispersed in another liquid.
Essential Oils
Are concentrated extracts of the volatile, non-water soluble aroma compounds from plants.
Free Radicals
Are atoms or fragments of a molecule with unpaired electrons and, as a result, are highly reactive.
Initiation Reaction
Is one in which two free radicals are formed by breaking the bond in a molecule. This step requires an input of energy- (UV light or sometimes heat)
Propagation Reaction
Is one in which a free radical reacts with a molecule to form a new free radical. A new molecule is formed too in this step.
Termination Reaction
Is one in which two radicals meet and form a stable molecule. The unpaired electrons from each radical come together to form a covalent bond.
Free-radical Scavenger
Is a molecule which can react with free radicals to form a stable molecule, stopping a chain reaction.
Gram Formula Mass (GFM)
The mass in grams of 1 mole of a substance
Limiting Reactant
Is the one which is completely used up in a chemical reaction (This will be the most expensive chemical in the reaction)
Excess Reactants
Are ones that are not used up completely in a chemical reaction (These will be the cheaper chemicals in the reaction)
Percentage Yield
Is a measure of the efficiency with which the reactants have been converted into the final product.
Atom Economy
Measures the potential amount of waste through the production of by-products for any reaction.
(An atom economy of 100% indicates that no by-products are produced)
Molar Volume
Is the volume (measured in litres) 1 mole of that gas occupies at a certain temperature and pressure.
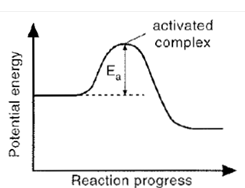
Activated Complex
Is the unstable arrangement of atoms formed- at the maximum of the potential energy barrier.
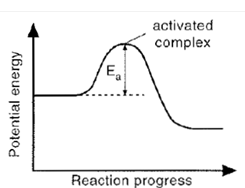
Activation Energy
Is the additional potential energy which has to be achieved by colliding molecules to form an activated complex.
Enthalpy
Is a measure of the chemical energy stored, within substances.
Exothermic Reaction
Reaction is a chemical change that gives out heat energy.
Endothermic Reaction
Reaction is a chemical change that takes in heat energy.

Enthalpy Change
For a reaction is difference between the final total enthalpy of the products and the original total enthalpy of the reactants. The symbol for enthalpy change is ∆ H and the units are kilojoules (kJ).
Enthalpy of Combustion
Is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance burns completely in oxygen, all reactants and products being in their standard states at 25 0C and one atmosphere
Hess’s Law
States that the overall enthalpy change in a reaction, or sequence of reactions, depends only on the reactants and products and not on the route taken.
Bond Enthalpy
Is the energy required to break one mole of bonds and form two separate atoms, all species being in the gaseous state.
Mean Bond Enthalpy
Is the average energy required to break one mole of bonds, which can occur in a variety of environments, to form two separate atoms, all species being in the gaseous state.
Hydroxyl Group
Alcohols
Functional group is -OH
General Formula is CnH2n+1OH
Carbonyl Group
Carboxyl Group
Ester Link
Gives a fruity smell
Functional Group is -COO
General Formula
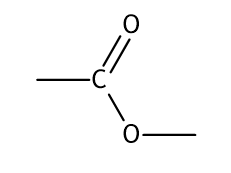
Aldehyde