Cognition: Selective Attention - Vision
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is a difference between attention in hearing and vision?
with vision can ‘point’ your eyes to what you wish to attend to
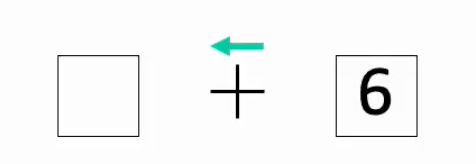
Posner et al. (1978; 1980) The attentional spotlight (of covert attention)
used endogenous cueing - probable stimulus location was indicated by arrow cue which was right 80% of time or neutral cue of asterisk
P must respond as fast as possible to stimulus while maintaining central fixation
choice ‘spatial’ RT - left/right from centre
choice ‘symbolic’ RT - letter or digit
RT always faster when location expected and slower when unexpected
What is the difference between endogenous and exogenous shifts?
endogenous is voluntary and top-down
exogenous is stimulus-driven and bottom-up
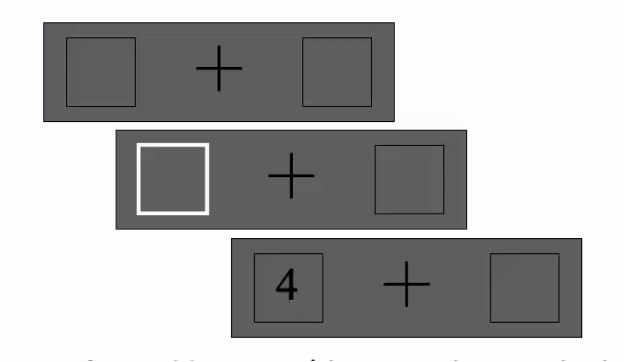
Study of endogenous and exogenous shifts
digit appears, then one square lights up (exogenous) - sudden and unexpected and did not relate to where digit would appear and just drew attention
RT was faster after sudden onset/change at stimulus location despite not predicting stimulus location
What is the difference in timings of exogenous and endogenous shifts?
exogenous attraction of attention is fast <200 msec
endogenous movement of attention takes several hundred msec
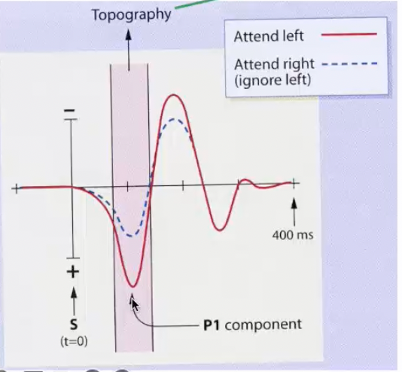
Magnun et al. (1993) - voluntary attention and early components of ERP
used ERP to measure activity
used cueing paradigm, stimulus could appear on top or bottom or left or right, Ps told to fixate of fixation cross and then cued to one of the locations
if stimulus appeared in attended location observed a big P1 and N1 with big amplitude
if stimulus appeared in unattended location observed smaller amplitude suggesting still perceived, but smaller
the divergence of waveform suggests that attention plays a role even at 200ms
Magnun et al. (1973) - ERP results
O’Connor et al. (2002) fMRI study of early selection in V1 and LGN
Ps fixated on central point when
series of digits appeared at fixation, and
high or low contrast checkerboards appear in left and right periphery
Ps either told to count digits at fixation or detect random luminance changes in left or right checkerboard
fMRI BOLD signal in LGN and V1, voxels that react to checkerboard luminance change is greater when attention directed to that side than to fixation
suggests that attention influences processing early on, at least some selection for certain regions in visual field occur early in processing
What are some similarities between visual selection and auditory attention?
is not all-or-none - there is a gradient of enhancement or suppression across the visual field
is an optional process - the size of the attended area is under voluntary control
Labarge (1983) - control of size of attended area
Ps asked to look at central letter or whole word but also had to respond to occasional probe displays such as 7 as T
those asked to look at central letter responded more slowly to probes the further they went from the centre - attention narrowed to central letter
this effect did not occur when asked to look at whole word - attentional spotlight widened, where probe appeared did not matter
Lavie (1995) effect of processing load on early selection
used Flanker task - Ps had to press certain keys for certain stimuli on midline e.g., right for little x, left for little z and told to ignore big letter above or below midline
if processing load low (2 letters) people slower with incongruent distractor for example big Z and little x relative to a congruent distractor for example big X and little x
when processing load high (more letters on midline), incongruity effect of big Z reduced as ps already have to find target from several irrelevant letters on midline
Inattentional blindness - Daniel Simon
ask Ps to attend closely to one coherent stream or visual events on screen, spatially overlapping with another stream
highly salient events such as a gorilla in unattended stream are missed by a large proportion of participants
the events of unattended stream do not appear to be processed to level of meaning
Summary of visual attention
Processing of information in the visual field to level or recognition and meaning is highly selective and limited
spotlight of visual attention can be moved voluntarily to locations or objects of interest away from fixation - it is attracted automatically and relatively fast to local transients in visual field and can be varied or zoomed
this selective filtering occurs early in the processing of visual information
processing of objects outside the spotlight is relatively shallow