UIUC MCB 150 Exam 1
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Cell Theory
all organisms are made of cells, all existing cells are produced by other living cells, the cell is the most basic unit of life
Prokaryotes
Cells that do not contain nuclei, bacteria and archaea
-singular circular chromosome
-no membrane bound organelles
-nucleolus
Archaea
Domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls that do not contain peptidoglycan
-live in harsh environments
Eukaryotes
Cells that contain nuclei
-multiple linear chromosomes in the nucleus
-extensive cytoskeleton
Central Dogma
DNA-transcription-RNA-translation-protein
Bacteria
Domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls containing peptidoglycan
Covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
Polar: uneven sharing
Nonpolar: even sharing
Ionic bonds
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Macromolecules
any large molecules made up of smaller molecules (monomers) joined together into a polymer
Condensation reactions
a chemical reaction in which two or more molecules combine to produce water or another simple molecule
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
Nucleoid
A dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell.
Plasmids
small circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the bacterial chromosome
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
-Prokaryotes have less extensive cytoskeleton
Cell wall
a fibrous layer found outside the plasma membrane of most bacteria and archaea and eukaryotes
flagellum
A long, hairlike structure that grows out of a cell and enables the cell to move.
fimbria
A short, hairlike appendage of a prokaryotic cell that helps it adhere to the substrate or to other cells.
Archaea are more closely related to _____ than _____.
Eukaryotes, bacterial
Nucleus
-contains chromosomes
-double membraned
-contains sites where the RNA are processed into their functional form
nuclear envelope
Double membrane perforated with pores that control the flow of materials in and out of the nucleus.
Nucleoulus
the area in the nucleus of a cell where ribosomes are produced
Endoplasmic Reticulum
A system of membranes that is found in a cell's cytoplasm and that assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
-Dotted with ribosomes
-Involved in synthesizing plasma membrane proteins, secreted proteins, and proteins located in the ER, Golgi Apparatus, and lysosomes
-Proteins move into the interior, "lumen", undergo folding and other types of processing
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
-lacks ribosomes
-Involved in synthesizing lipids and removing toxic molecules
-Contains enzymes that catalyze reactions involving lipids
-functions as a reservoir for calcium ions
Golgi apparatus
-A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
-Cis: closest to nucleus, receives
Lysosomes
-cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
-Imports H+ to lower pH
endomembrane system
A network of membranes inside and around a eukaryotic cell, related either through direct physical contact or by the transfer of membranous vesicles.
Vacuoles
Used for bulk storage of water, pigments, oils, or other substances
Peroxisomes
small membrane enclosed organelles filled with enzymes
-oxidizes fatty acids and other compounds rendering them harmless
Mitochondria
An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur.
-form a series of cristae in the inner membrane
>site of electron transport chain and ATP synthase
Mitochondrial DNA
A small amount of DNA that is located in the mitochondria of cells. Mitochondrial DNA is inherited only through the mother.
Chloroplasts
organelles that capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in a process called photosynthesis
-double membraned
-thylakoid: a membrane bound network of flattened saclike structures inside a plant chloroplast
extracellular matrix
The substance in which animal tissue cells are embedded, consisting of protein and polysaccharides.
Microfilaments
Long, thin fibers that function in the movement and support of the cell
Microtubules
intracellular highways for transporting vesicles and organelles
-also required for cellular locomotion via flagella and cilia
Intermediate filaments
anchor organelles and intercellular junctions
Carbohydrates
Macromolecules=Polysaccharides
-used for energy sources, cell walls, cell identification and recognition
Carbohydrates formula
Cn(H2O)n
-subtract 1 H2O for every glycosidic bond
Hexose
6 carbon sugar
Pentose
5 carbon sugar
Triose
3 carbon sugar
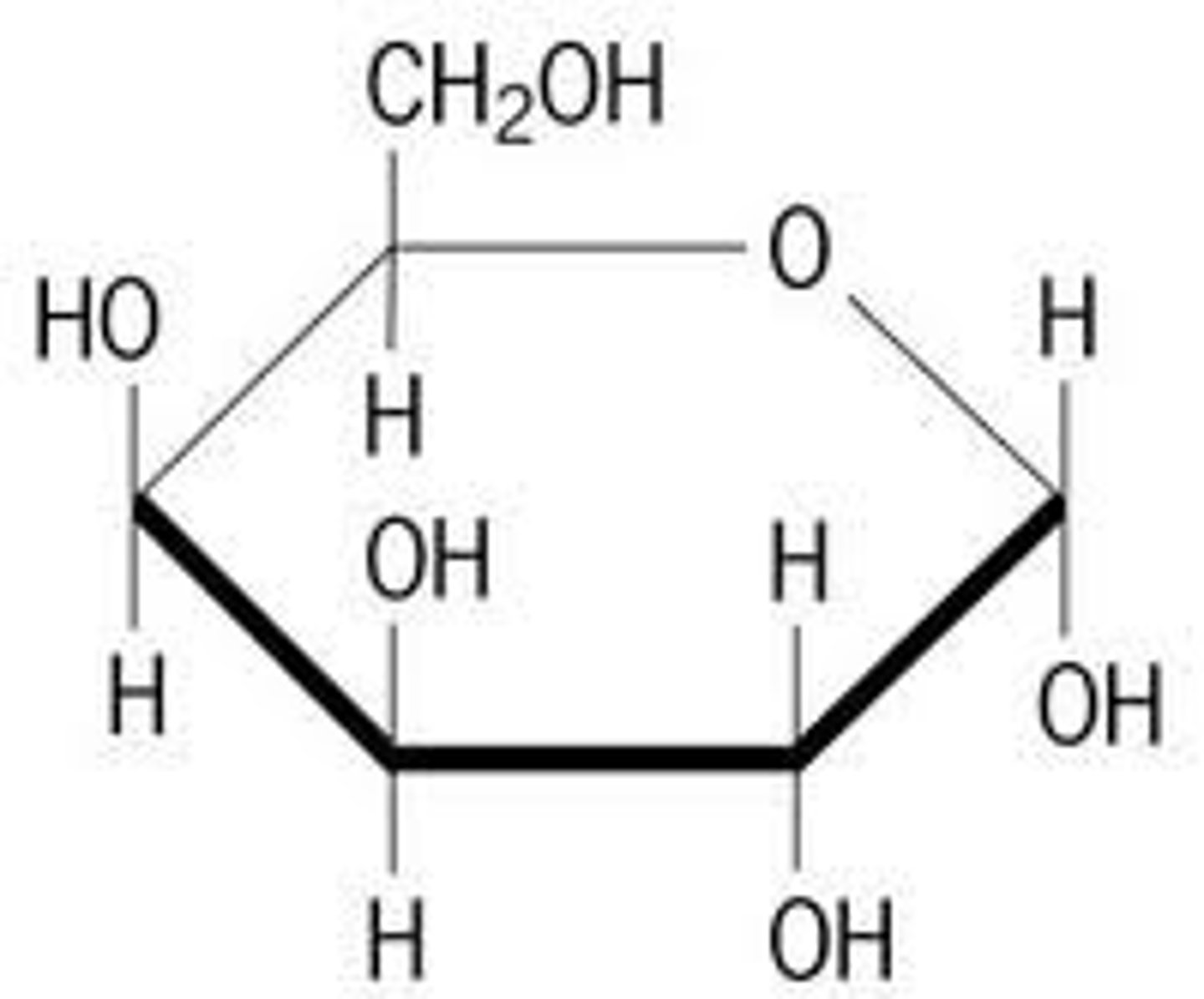
alpha Glucose
glucose where on C1 H on top, OH on bottom
beta glucose
glucose where on C1 OH on top, H on bottom
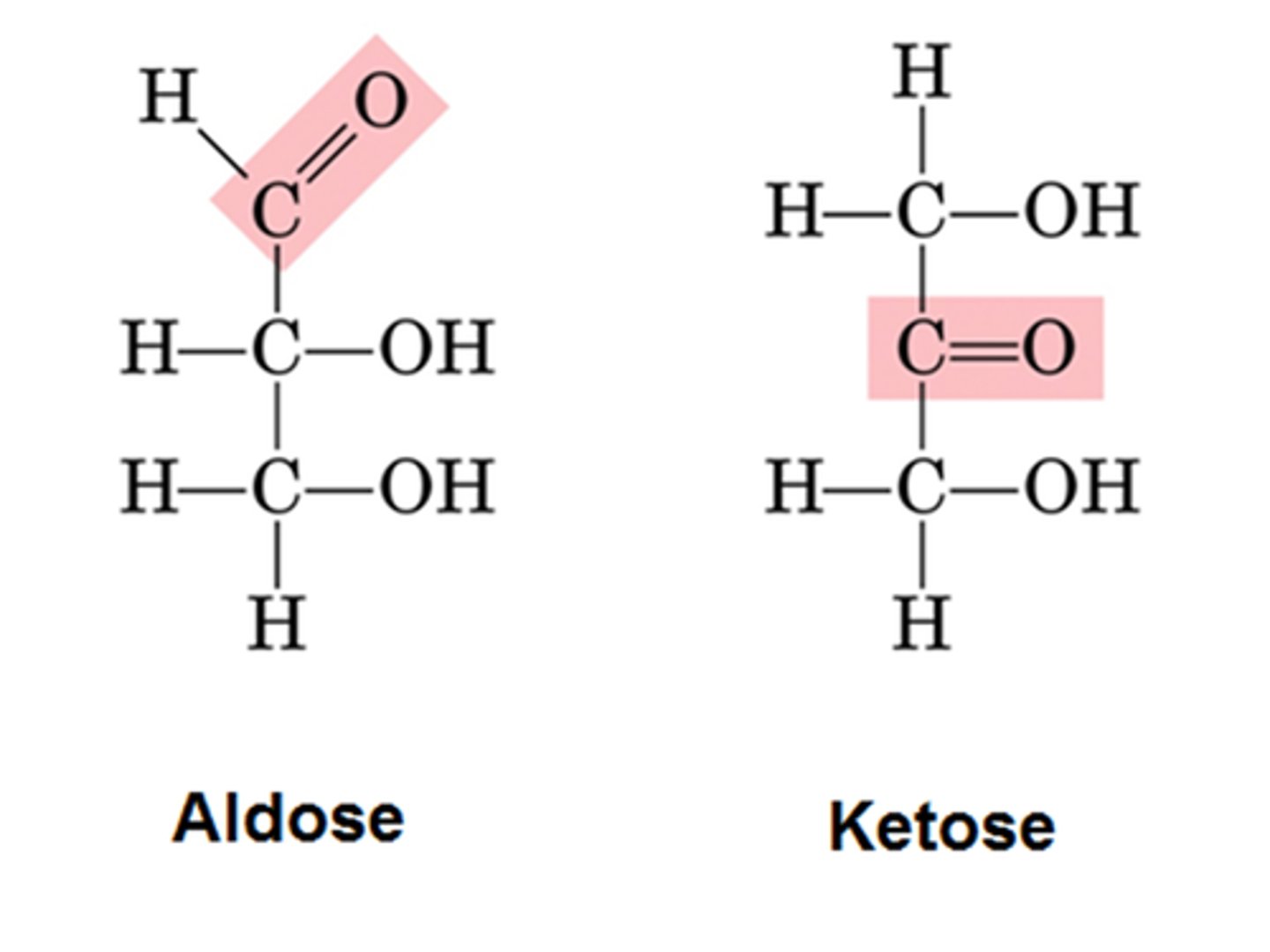
Aldose sugar
Carbonyl at the end of a monosaccharide
-same number of members in ring as carbons
-one carbon on outside of ring
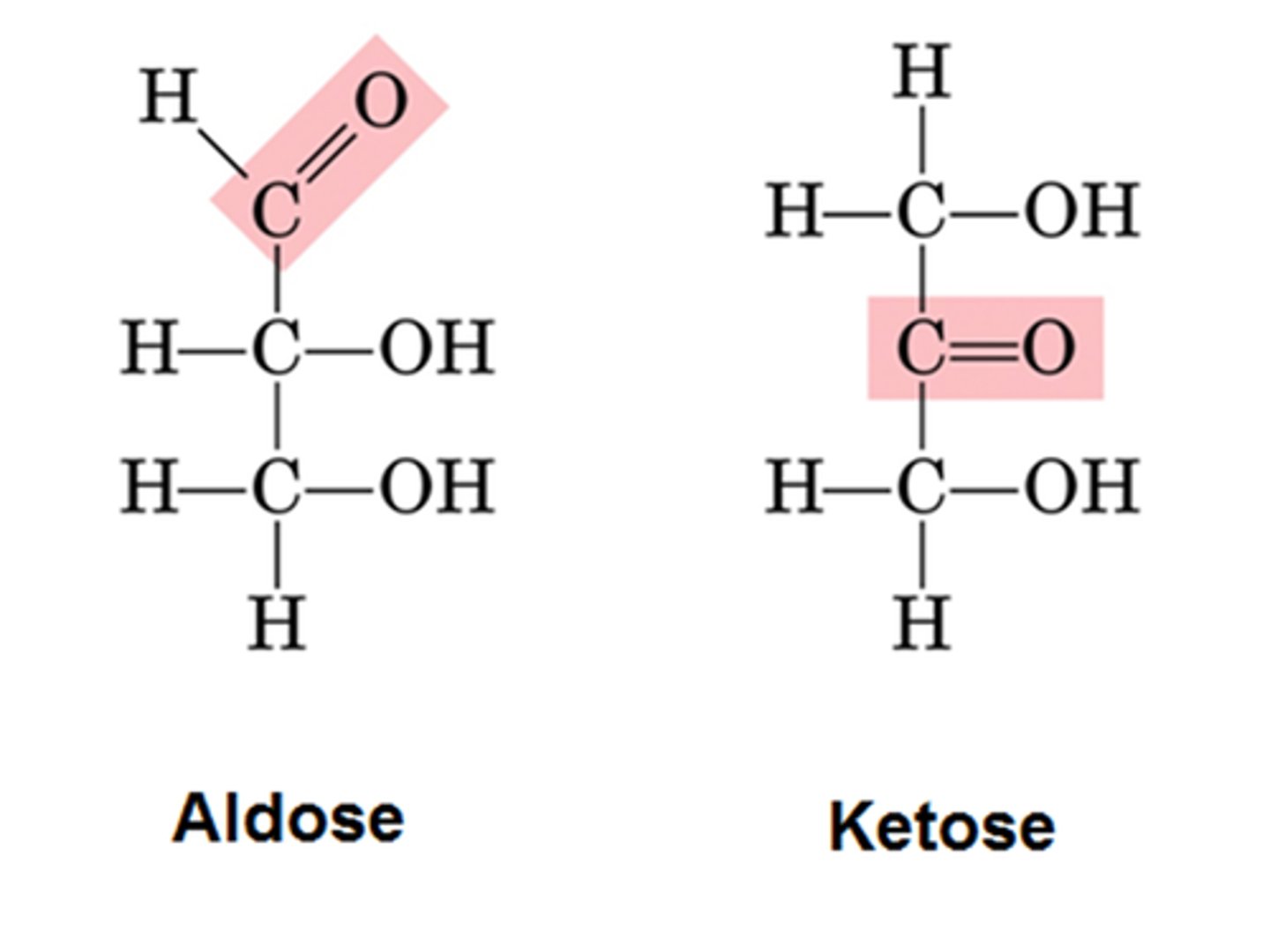
Ketose sugar
carbonyl group within carbon skeleton
-one less members in ring as carbons
-two carbons on outside of ring
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
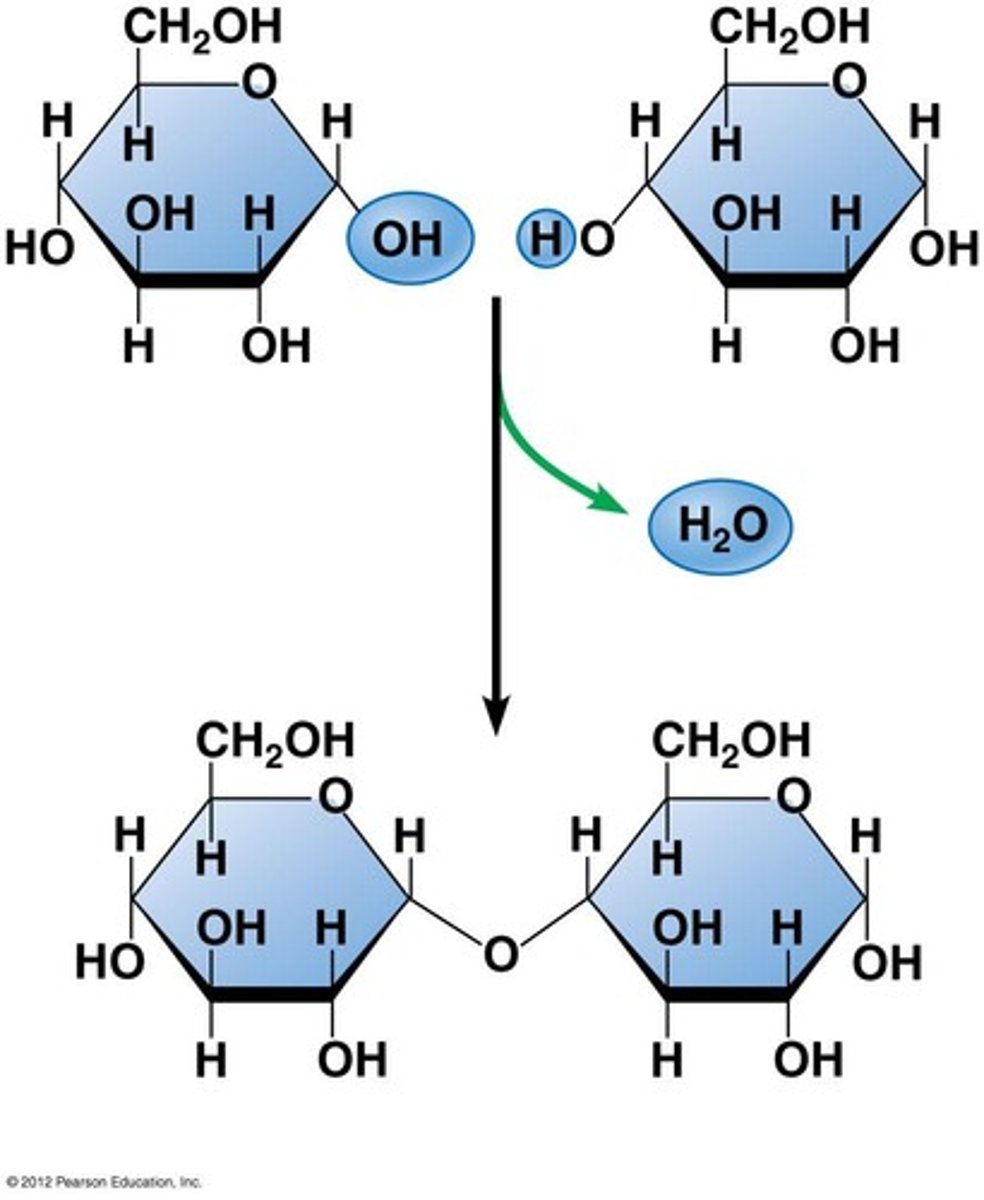
glycosidic linkage
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
-results in polysaccharides
glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch.
-Helical, highly branched
-Unbranched: a-1,4-glyocidic links
-Branched: a-1,6-glycocidic links
Starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose.
-helical, mixture of branched and unbranched (less than glycogen)
-Unbranched: a-1,4-glyocidic links
-Branched: a-1,6-glycocidic links
Cellulose
polysaccharide consisting of glucose monomers that reinforces plant-cell walls
-linear, unbranched polymer of glucose
-Unbranched: B-1,4-glycosidic links
phosphorylase
An enzyme that breaks down glycogen by catalyzing hydrolysis of the a-glycosidic linkages between the glucose residues.
Glucose
A simple sugar that is an important source of energy.
-Aldose
-monosaccharide
-Hexose
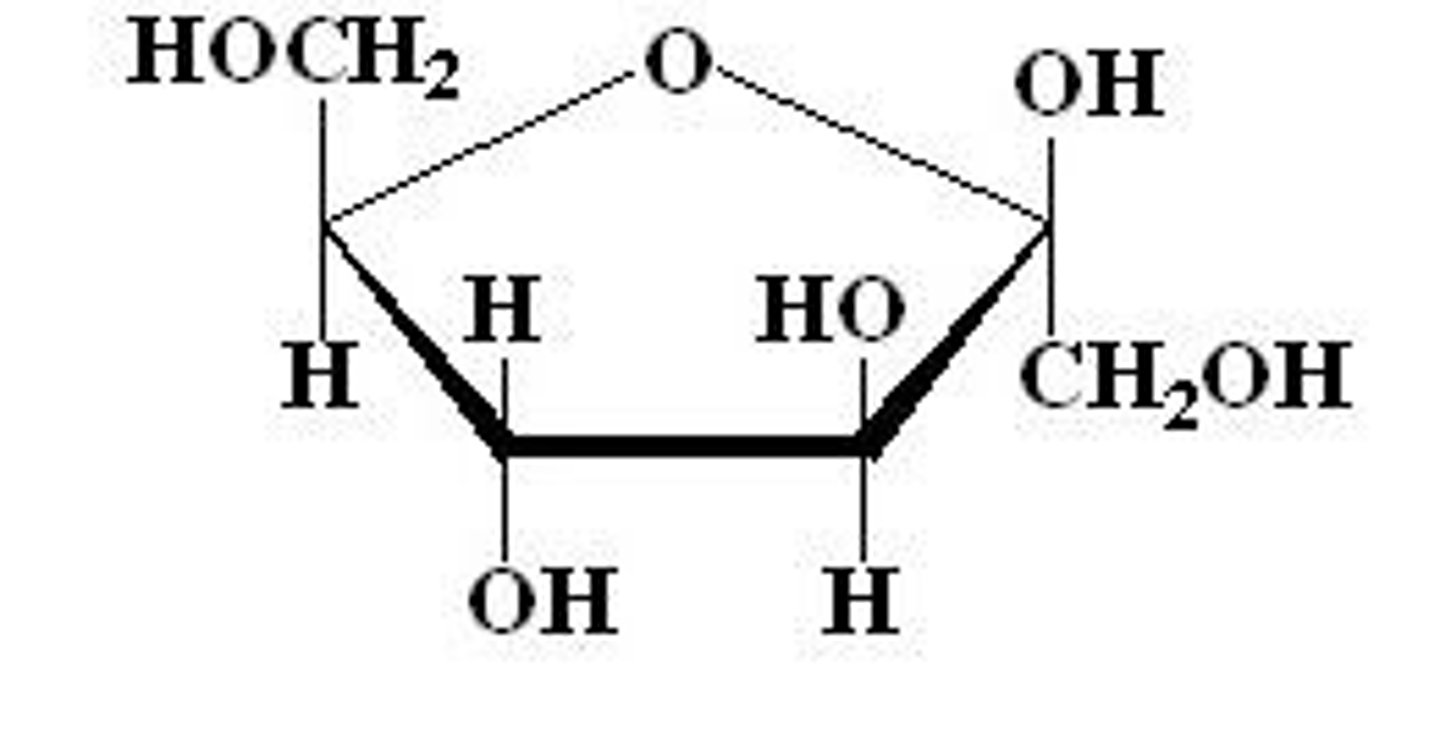
Fructose
-ketose
-Hexose
Galactose
-aldose
-Hexose
Glucose + fructose
sucrose
glucose + galactose
lactose
glucose + glucose
maltose
Amino group
(—NH2) a functional group composed of nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and to the carbon skeleton. Can act as a base in solution, accepting a hydrogen ion and acquiring a charge of +1.
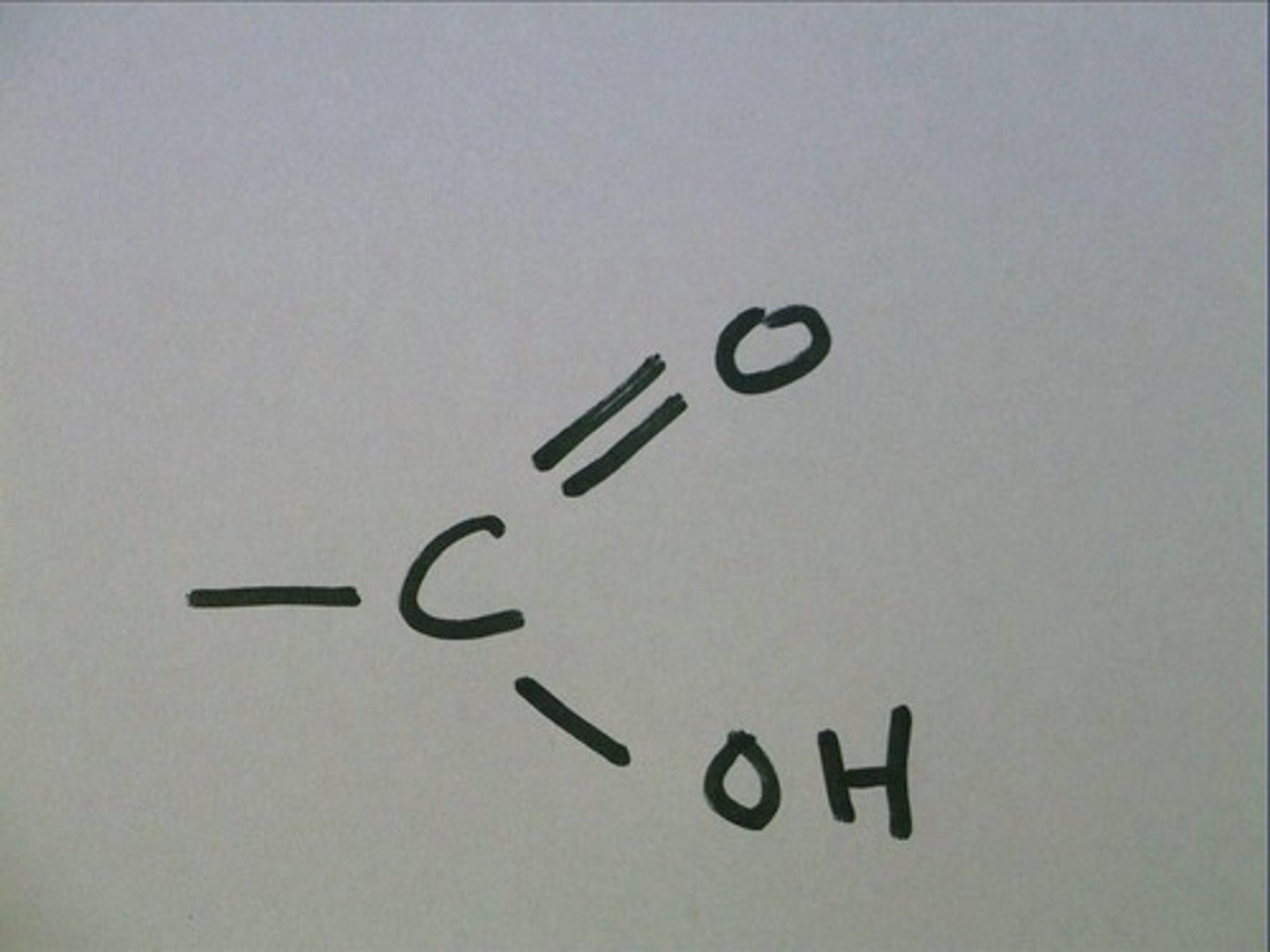
carboxyl group
-COOH
A functional group present in organic acids and consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group.
carbonyl group
a chemical group consisting of a carbon atom linked by a double bond to an oxygen atom
-at the end of Aldehydes
-inside ketones chains
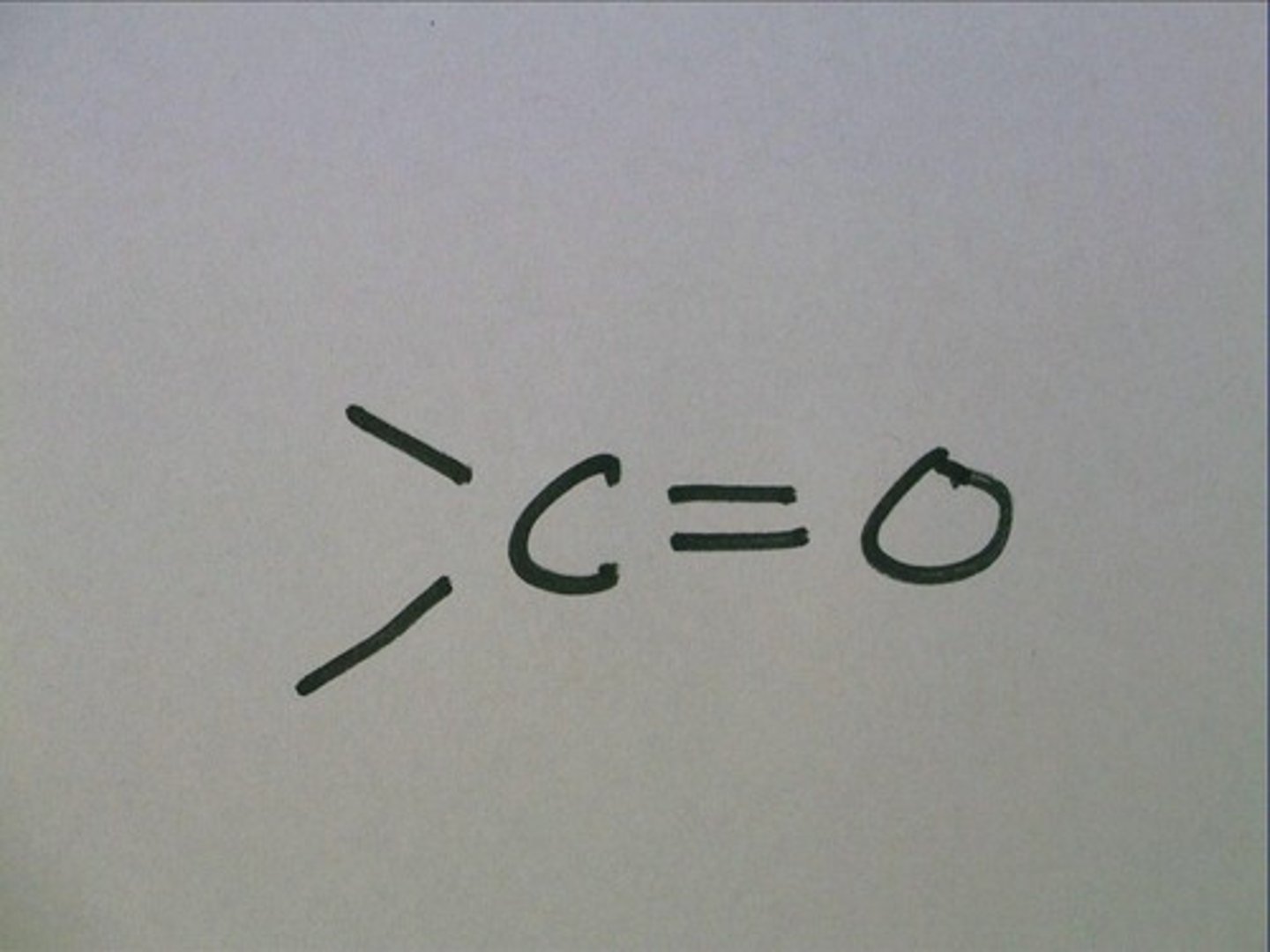
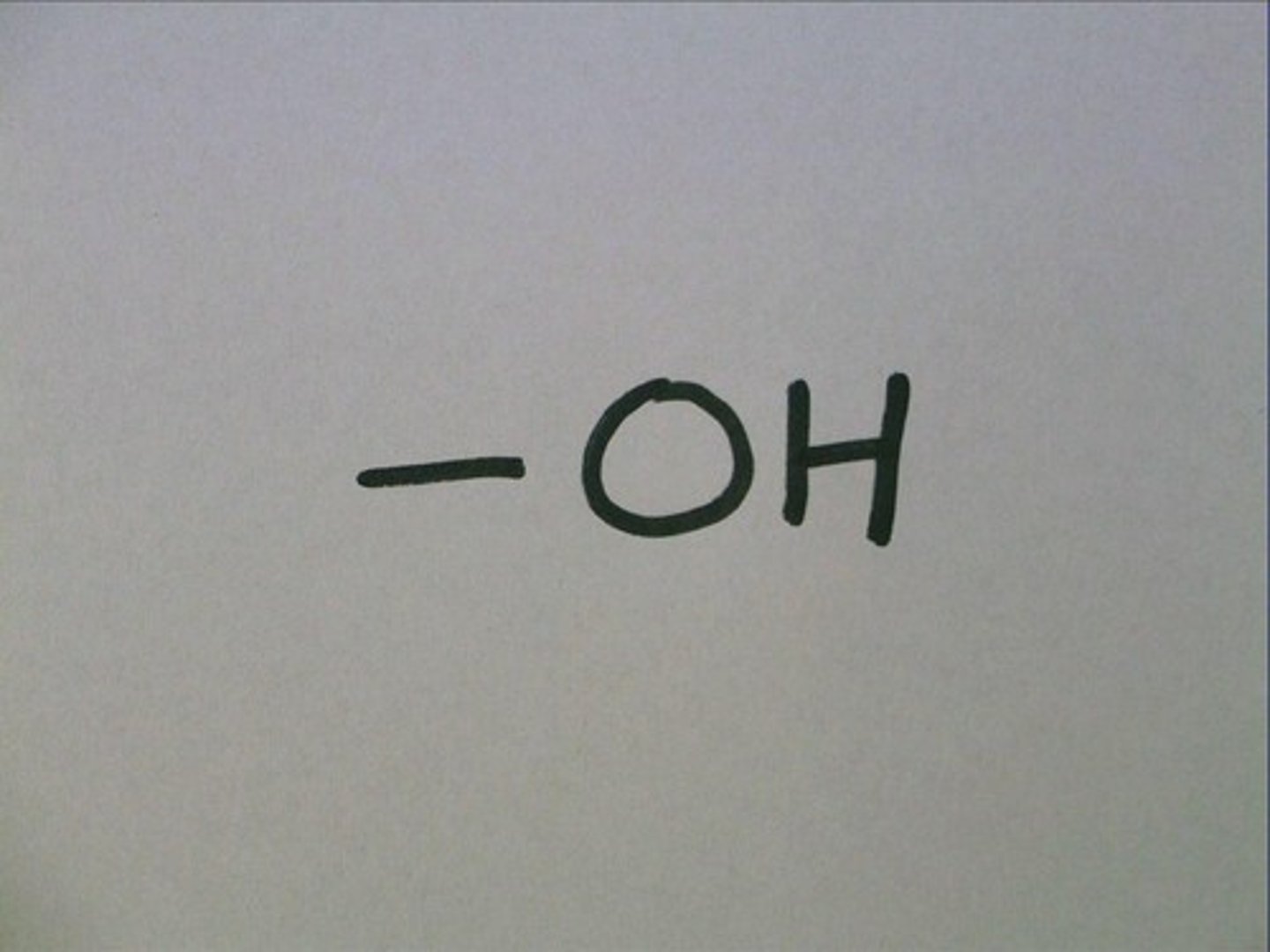
hydroxyl group
OH-
-highly polar, makes compounds more soluble
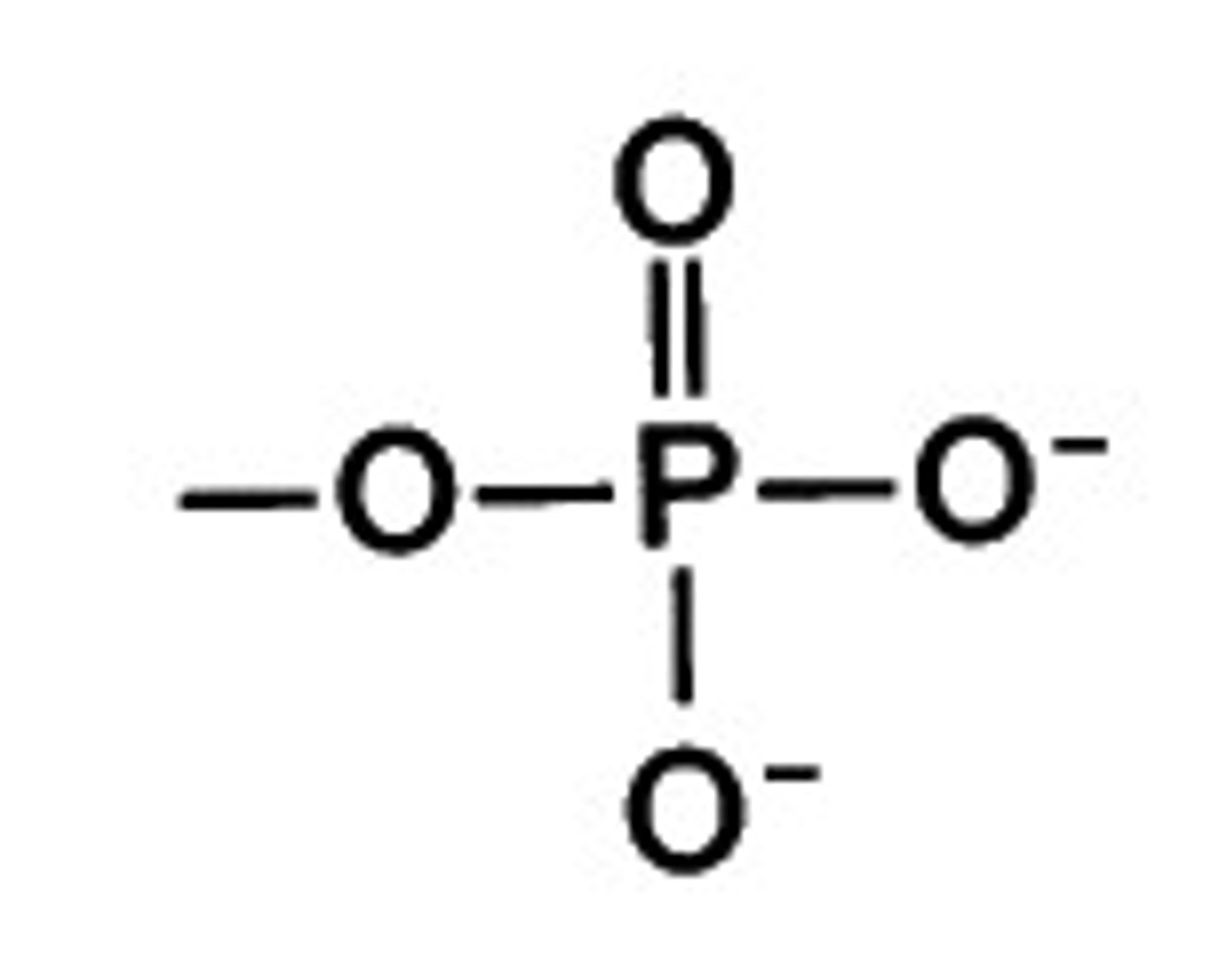
phosphate group
A functional group consisting of a phosphorus atom covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms
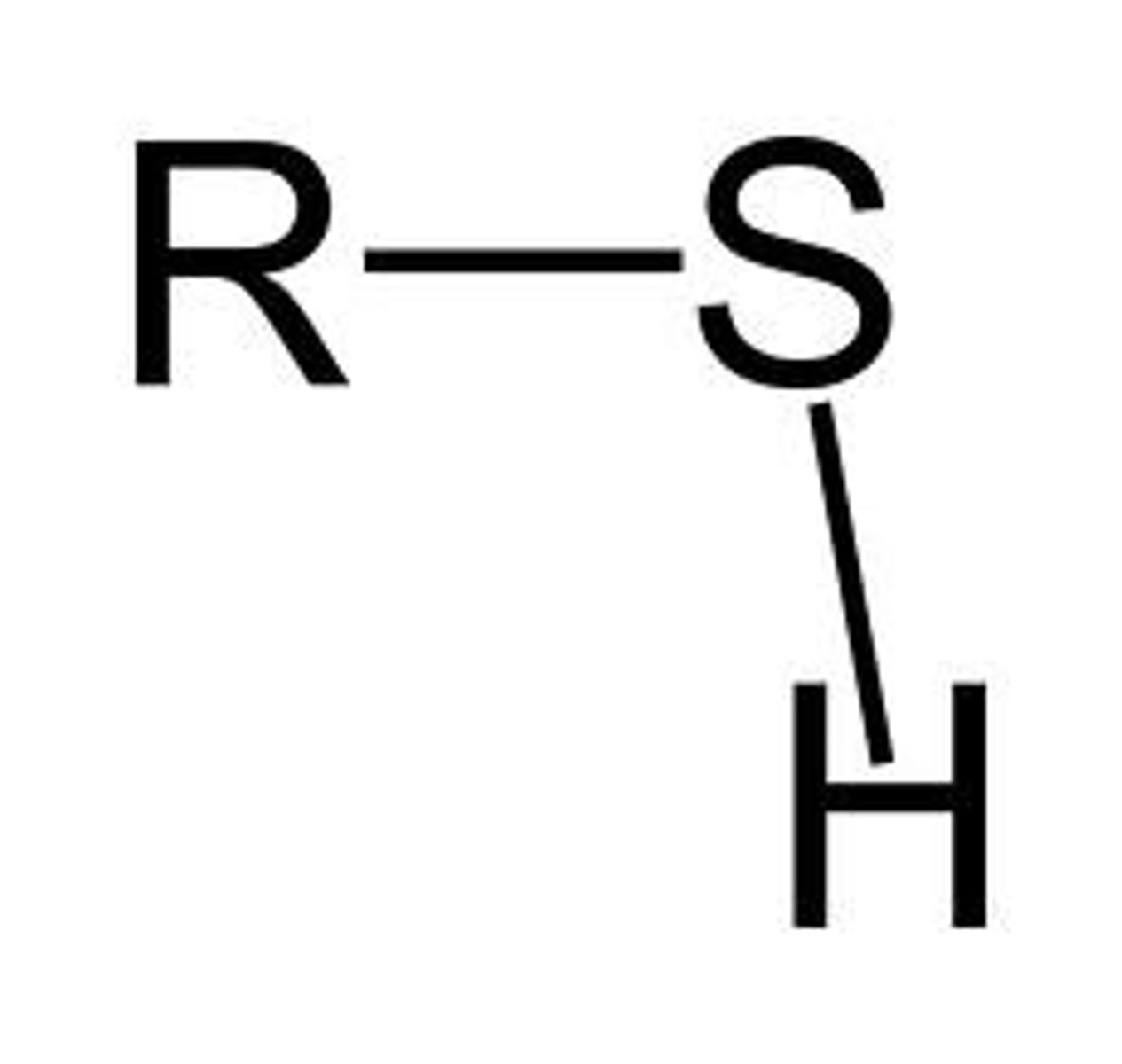
sulfhydryl group
A functional group consisting of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (—SH).
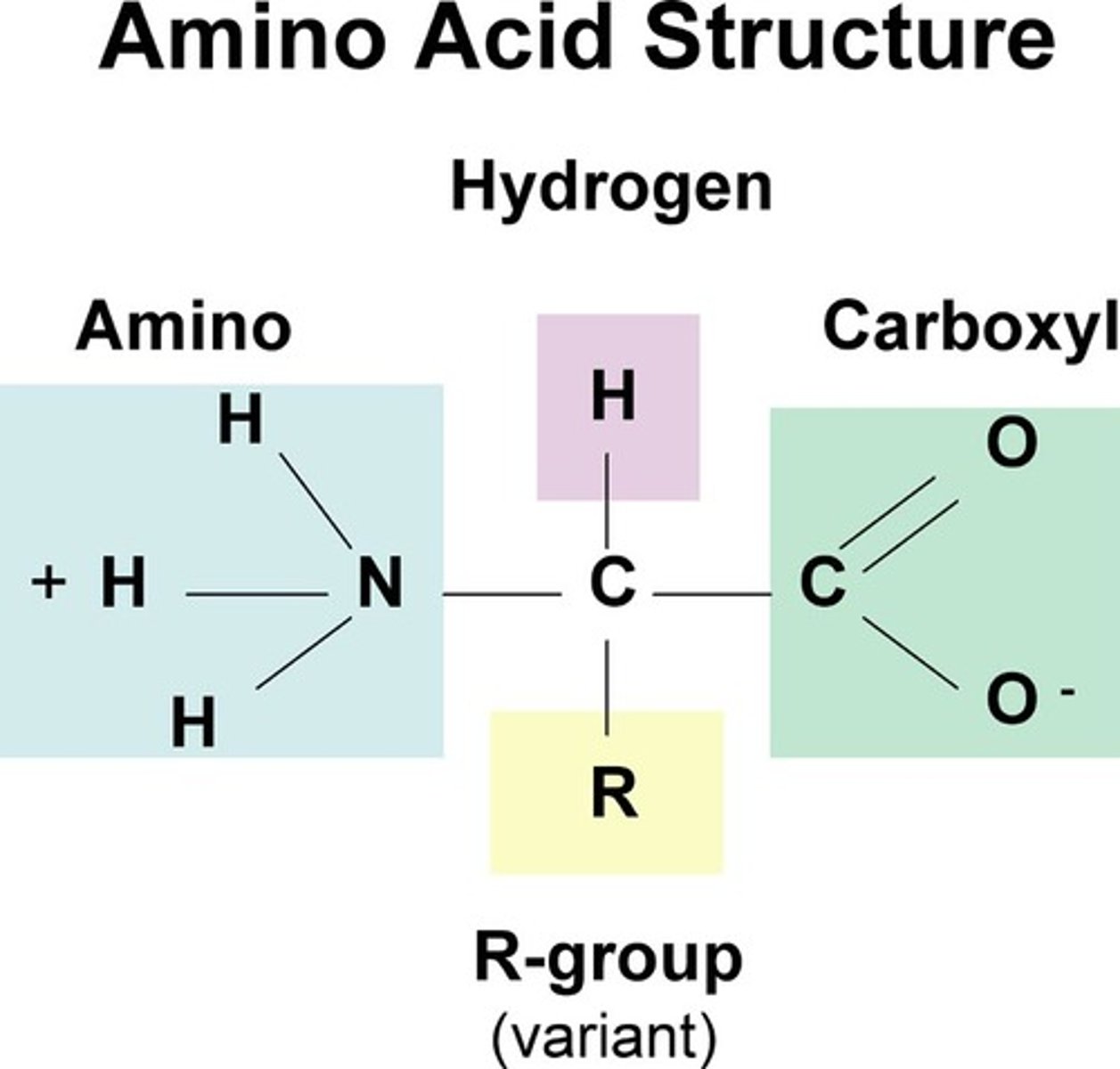
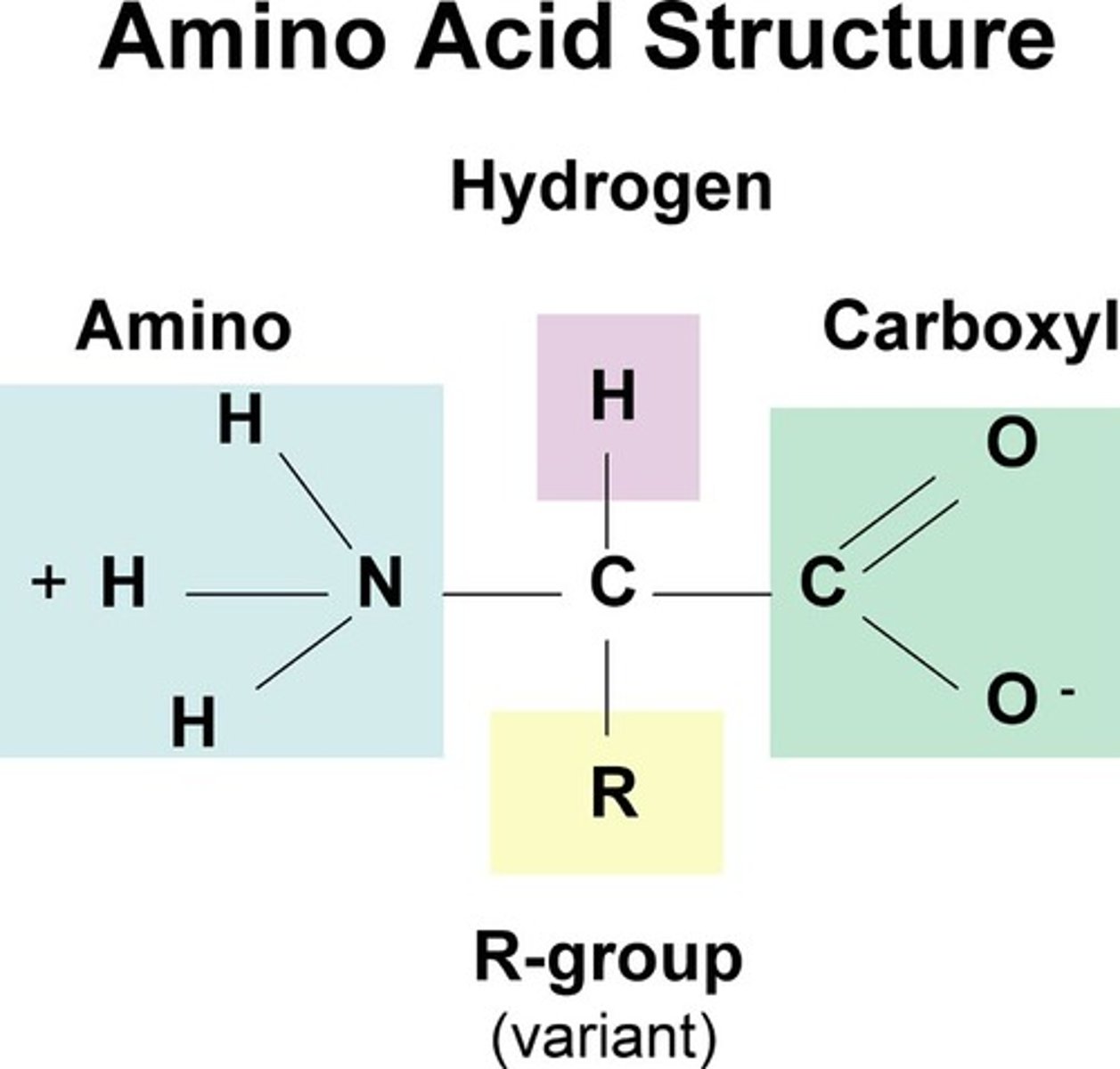
Amino Acids
a simple organic compound containing both a carboxyl (—COOH) and an amino (—NH2) group.
-monomers of proteins
-Amino acids amino group connects to incoming carboxyl group
R group (side chain)
part of amino acid that determines the molecule's physical and chemical properties
Peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
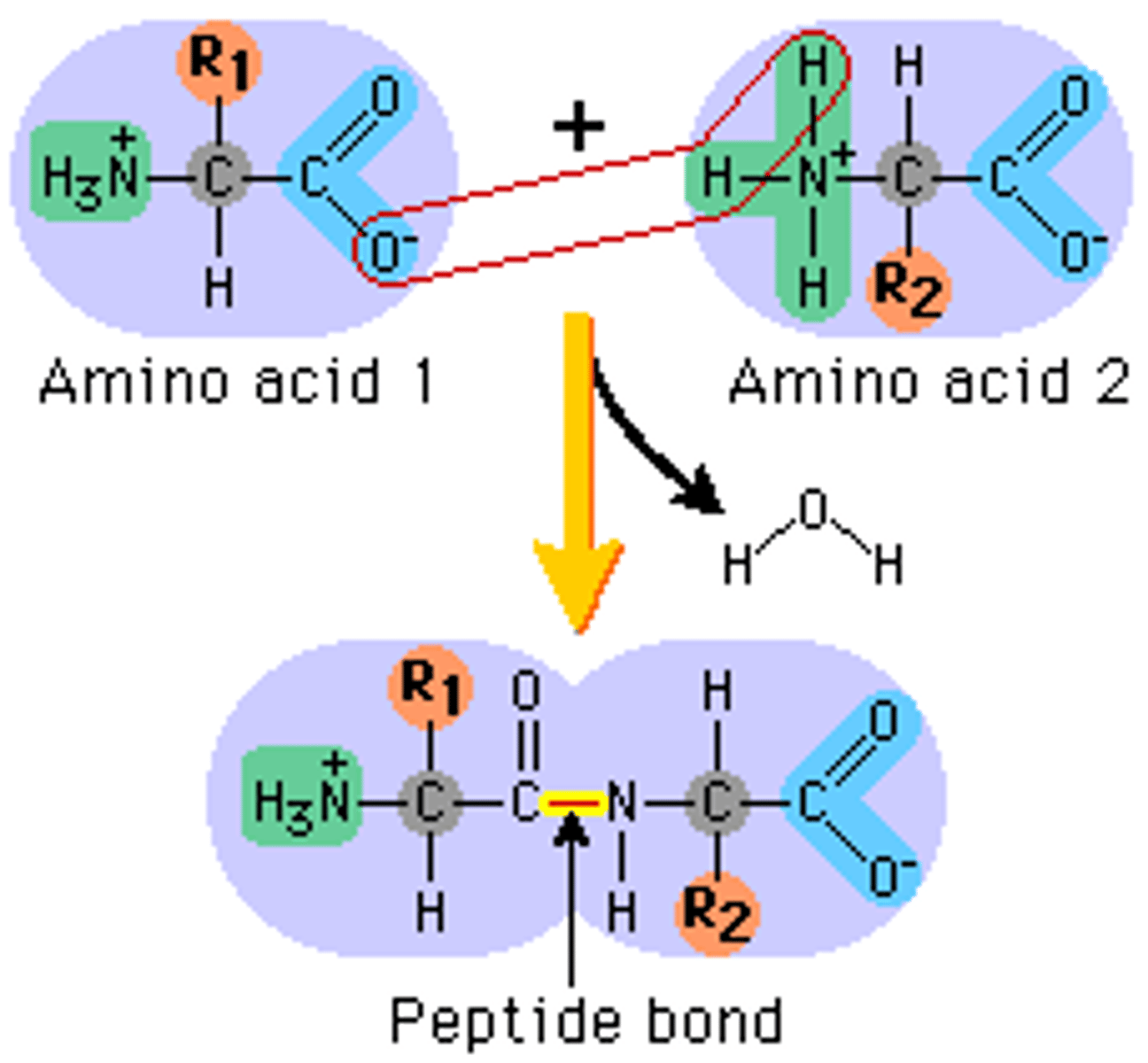
disulfide bonds (sulfhydryl)
Strong chemical side bonds formed when the sulfur atoms in two adjacent protein chains are joined together.
primary structure of protein
the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain
secondary structure of protein
local structure of alpha helix or beta pleated sheets; stabilized by peptide-linkage hydrogen bonds (no R-group interactions at this level)
tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
native conformation of a protein
the most stable three dimensional structure
quaternary structure of a protein
protein structure is a protein consisting of more than one folded amino acid chain
Dipeptide
Two amino acids bonded together
Oligopeptide
4-9 amino acids
Polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
Stabilizing forces in protein
-Hydrogen bonds
-Hydrophobic clusters
-Ionic bonds
-Van der Waals Interactions
-Disulfide linkages
Heterodimer
a protein composed of two polypeptide chains differing in composition in the order, number, or kind of their amino acid residues
homodimer
two of the same polypeptides
amylose
unbranched starch
amylopectin
branched starch
The surface area-to-volume ratio of a cell
Accounts for the size limit of cells
activation energy (Ea)
The amount of energy required to produce the transition state of a chemical reaction. If the activation energy for a reaction is very high, the reaction occurs very slowly. Enzymes (and other catalysts) increase reaction rates by reducing activation energy.
transition state
a high-energy intermediate state of the reactants during a chemical reaction that must be achieved for the reaction to proceed
Substrates
the reactants of enzyme-catalyzed reactions
Catalyst (enzyme)
a molecule that influences the rate of chemical reactions but is not consumed in the reaction
induced fit
Brings chemical groups of the active site into positions that enhance their ability to catalyze the chemical reaction.
Enzyme
a substance produced by a living organism that acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction.
-lower Ea
Cofactors
Any nonprotein molecule or ion that is required for the proper functioning of an enzyme. Cofactors can be permanently bound to the active site or may bind loosely with the substrate during catalysis
coenzyme
If the cofactor is an organic molecule.
prosthetic group
A non-protein, but organic, molecule (such as vitamin) that is covalently bound to an enzyme as part of the active site.
Chaperones
help proteins fold correctly
competetive inhibition
Inhibitor molecule attaches to the active site and the substrates are unable to bind temporarily
allosteric regulation
The binding of a regulatory molecule to a protein at one site that affects the function of the protein at a different site.
nucleic acids
polymers that are made up of monomers called nucleotides
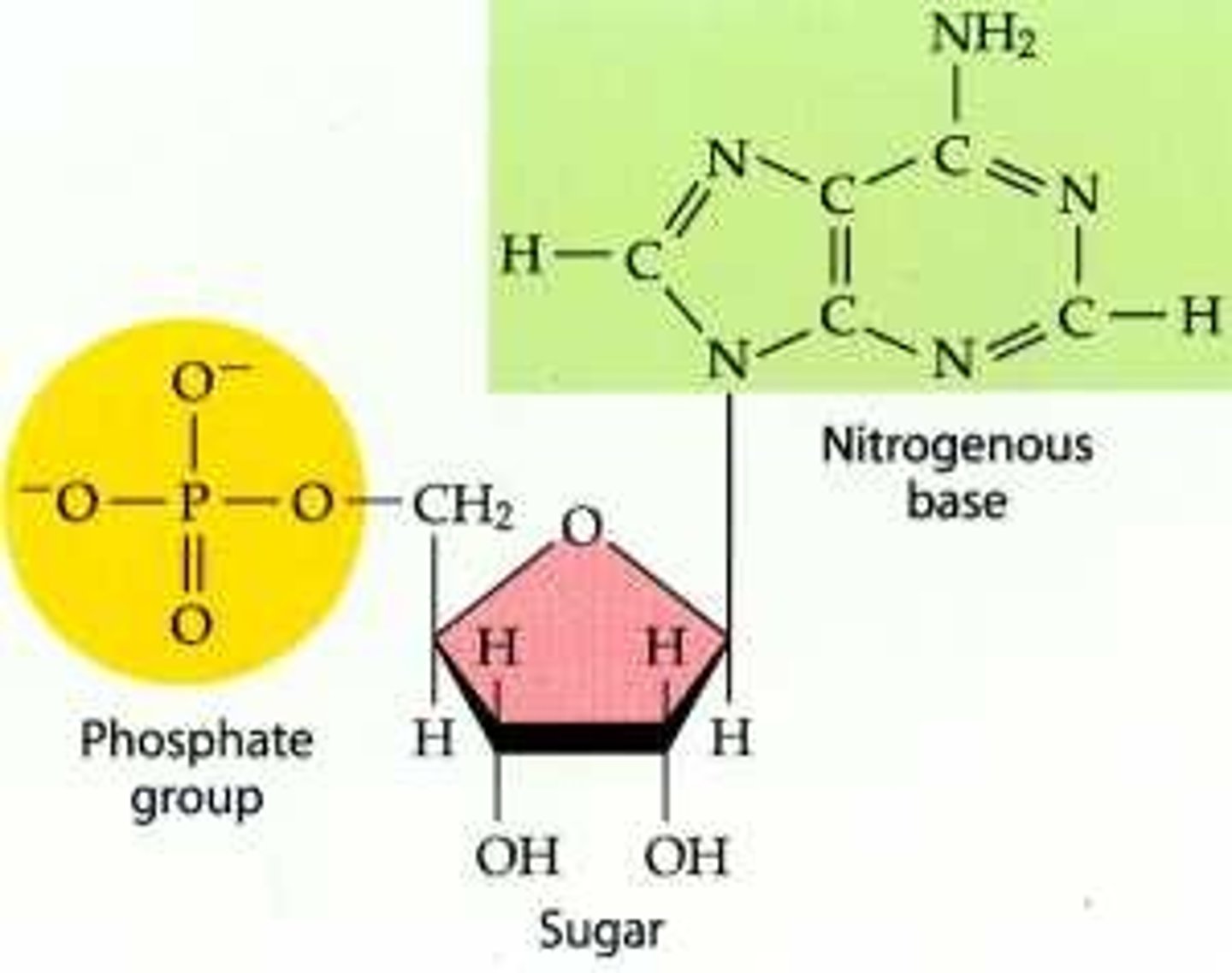
nucleic acids are made of
5 carbon sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
purines
Adenine and Guanine (double ring)
Pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil(single ring)
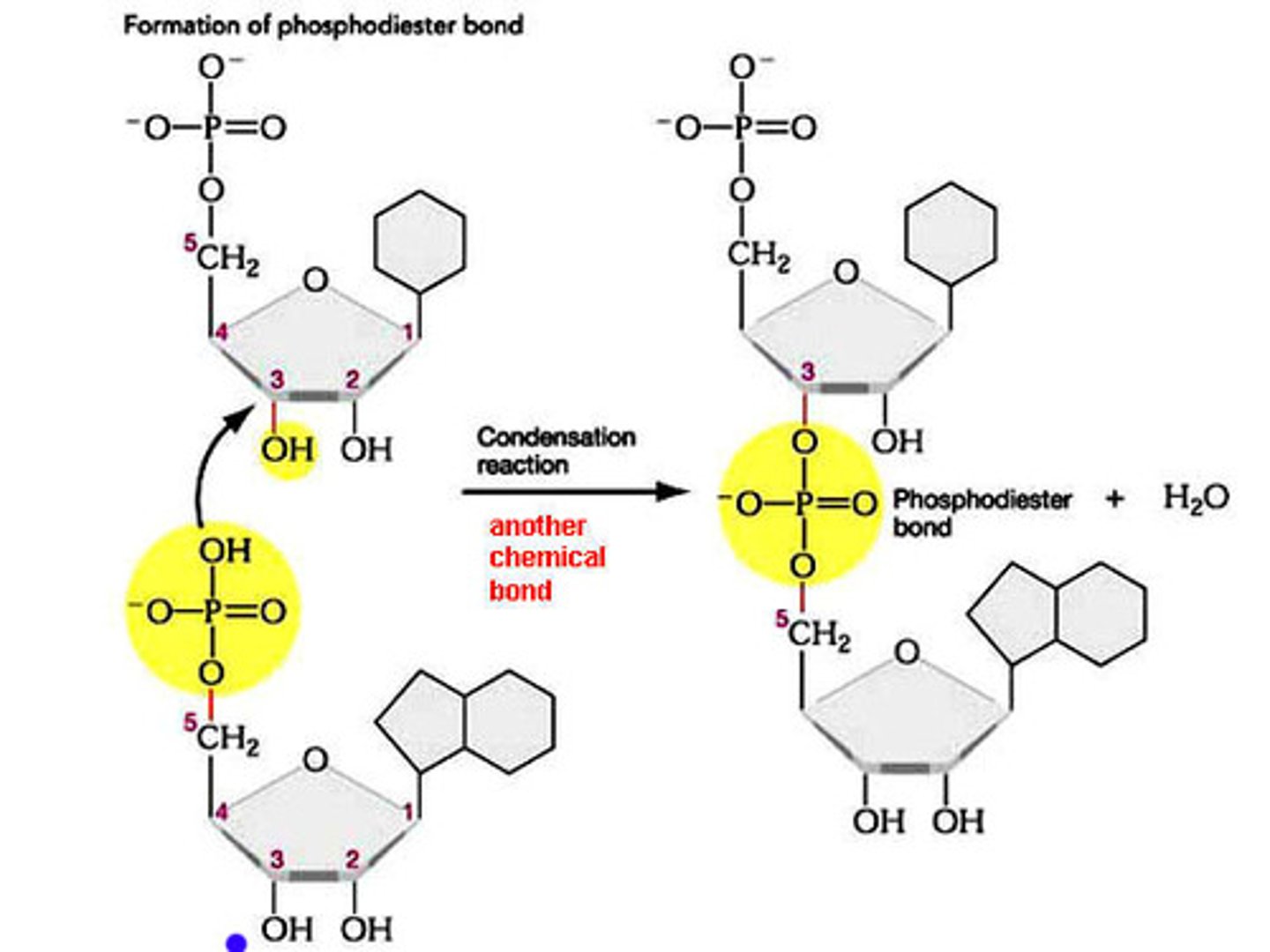
phosphodiester linkage
covalent bonds that join adjacent nucleotides between the -OH group of the 3' carbon of one nucleotide and the phosphate on the 5' carbon of the next
Lipid
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
-do not dissolve in water.