Unit 5: Cellular Respiration
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Endergonic Reaction
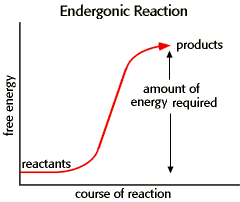
Energy is absorbed → more product than reactant
Requires energy
EX: Photosynthesis because it needs energy from the sun
Exergonic Reaction
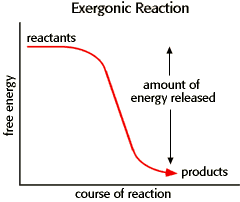
Energy is released → More reactant than product
EX: Cellular respiration because it releases ATP
Equation
C6H1260 = 6CO2+6H20+ATP+Heat
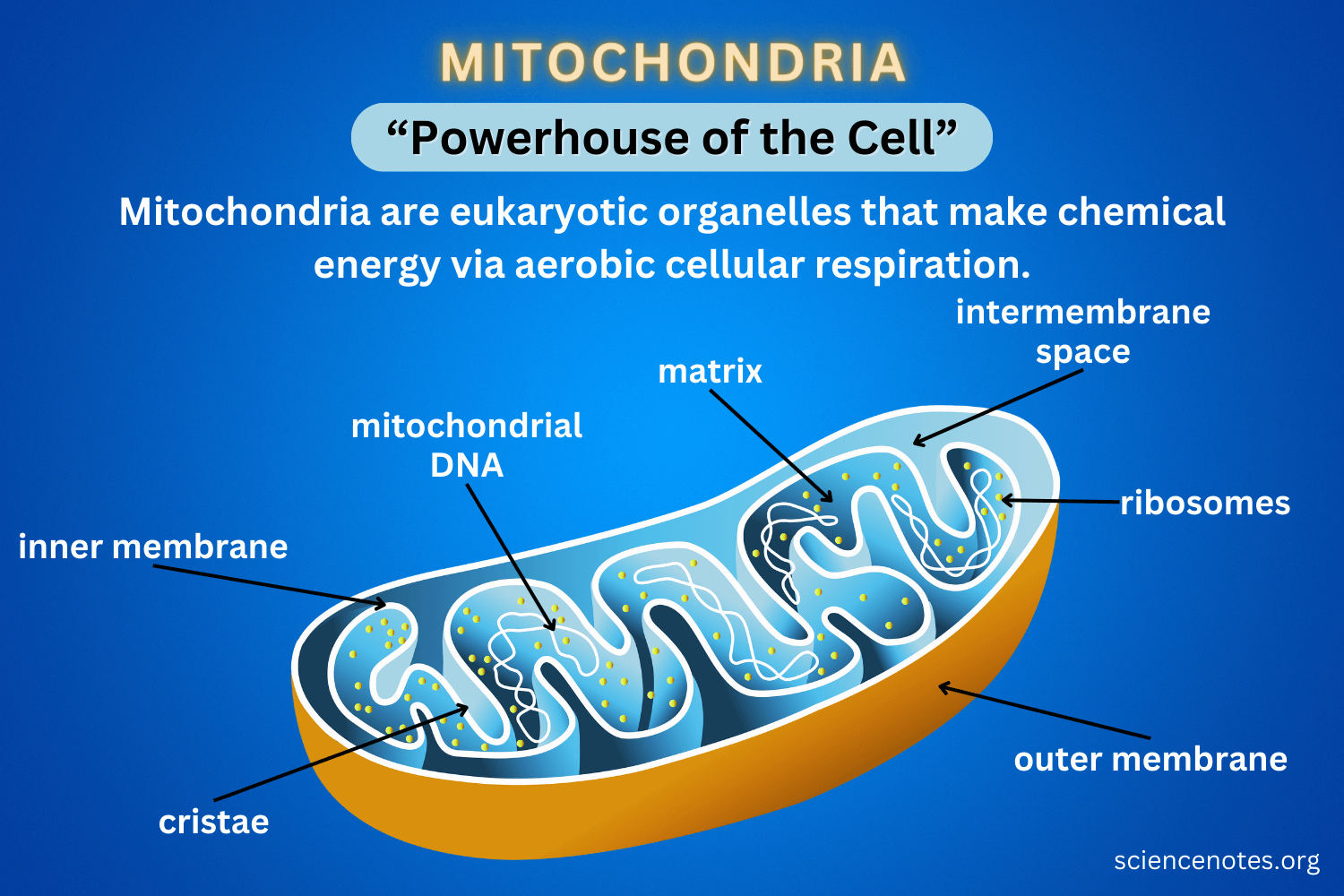
Mitochondria
Outermembrane - membrane enclosing the entire mitochondira
Innermembrane - membrane within mitochondria
Cristae - folds of innermembrane “finger like structure”
Intermembrane space - space beteen outer and innter membrane
Matrix - “maze-like” space ithin inner membrane space
Cellular Respiration
A controlled breakdown of food over many steps
Only 40% of food energy is captured by ATP → Most is lost as heat
Oxidation
A subtance loses electrons
LEO - Lose electrons is oxidation
Reduction
A substance gains electrons
GER - Gain electrons is reduction
Redox
Series of oxidation-reduction reactions
NAD+ and FAD
Electron carries that pick up electrons and prtons as glucose breaks apart
Aerobic respiration
Requires oxygen
Anaerobic Respiration
Does not require oxygen
Glycolysis
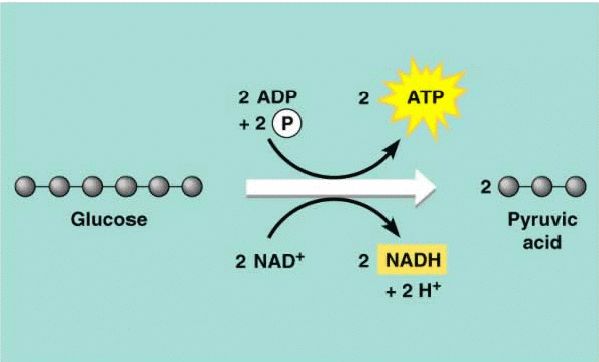
Breakdown of glucose *focusing on carbons
Glucose/Carbon is broken down into 2 pyruvate
From breaking down Carbon, electrons are released and picked up by 2NAD+, forming 2NADH
Remaining energy released from breaking of carbon, is stored in ADP and its third phosphorus, forming 2 ATPS.
Products: ATP, NADH
Pyruvate Oxidation
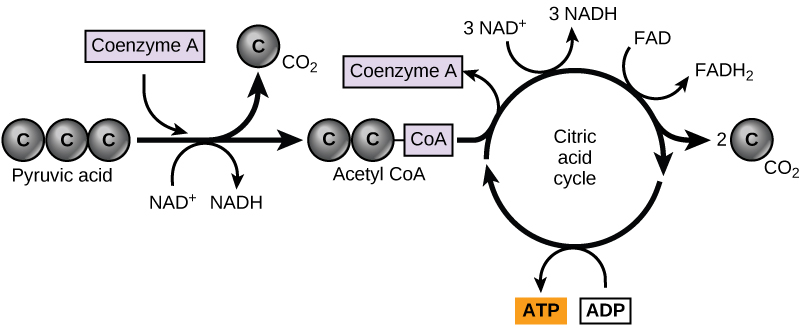
Pyruvate break off the last carbon on the chain becoming acedic acids
Through the bonds being broken, electrons released and picked up by NAD+
Broken off carbons leave into the cytoplasm and attaching to oxygen, forming CO2
Coenzyme A (CoA) attaches to remaining acedic acids, turning them into Acetyl-CoA
Kreb Cycle
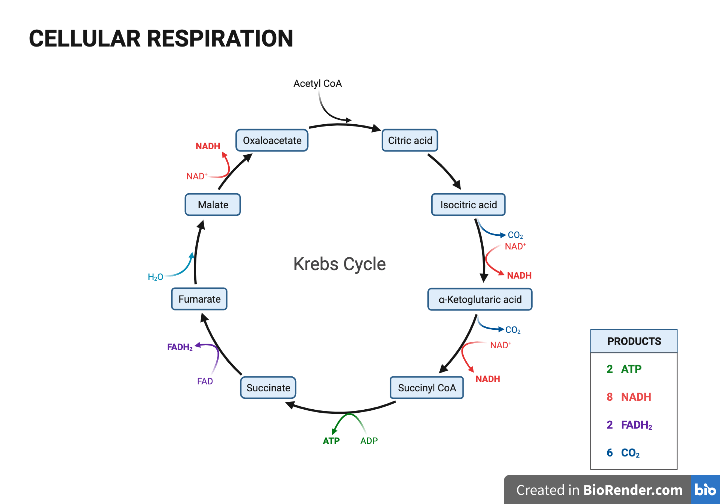
Acetyl CoA repeatedly broken down, releasing electrons, which are picked up by FAD and NAD
Acetyl CoA when broken down releases enough energy to be stored in ADP and its third phosphate
Creating 2 ATP
The broken down carbon leaves the cytoplasm and connects to O2, creating 4CO2.
Products: CO2, FADH, NADH, ATP
Oxidative Phosphorylation
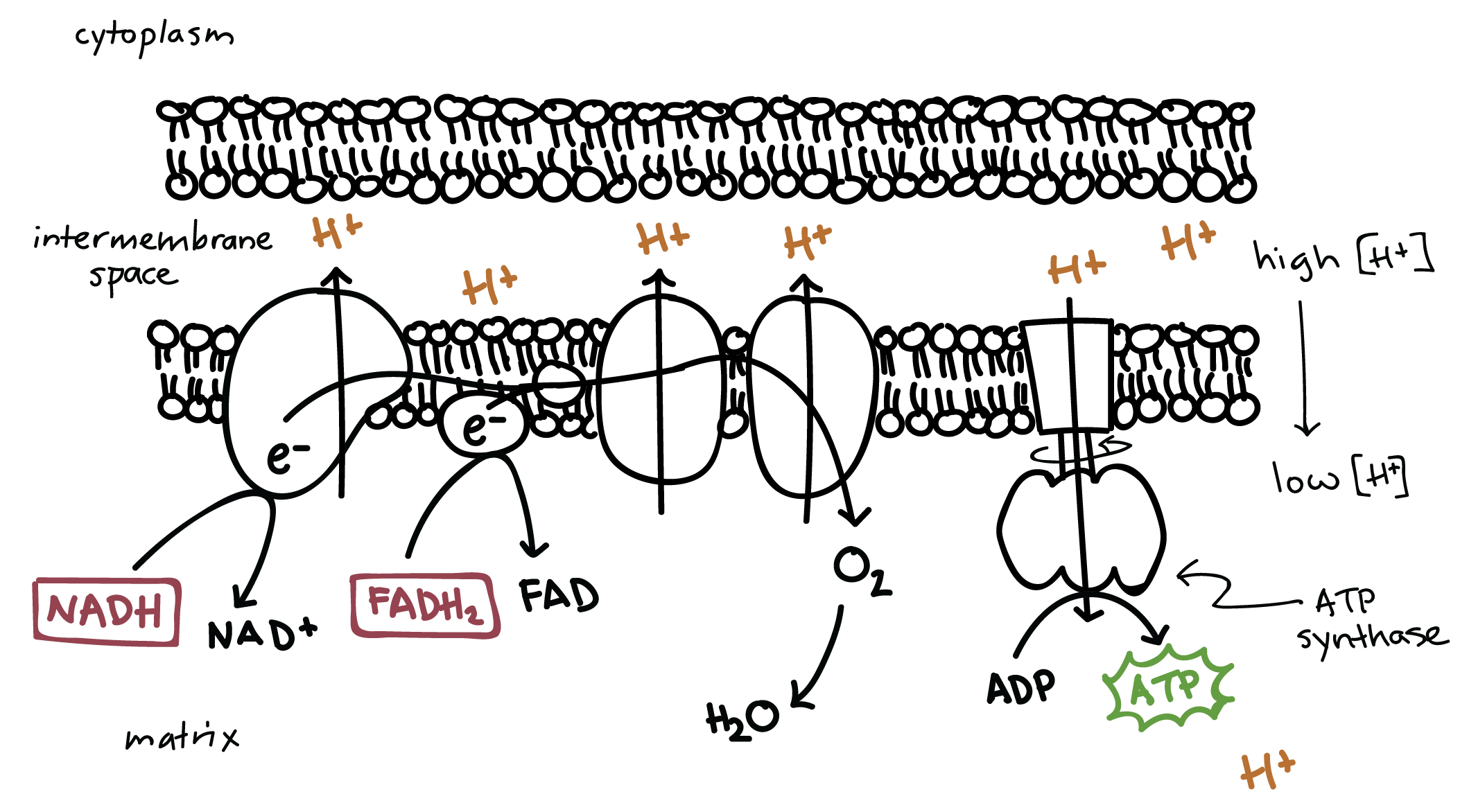
NADH and FADH release their electrons into the electron transport chain
As electrons move across the electron transport chain, hydrogen is pumped into the intermembrane → creating a proton gradient
Oxygen acts as a final acceptor as its extremely electronegative and attracts electrons through the chain
High concentration gradient of hydrogen flows through ATP synthase, creating an energy that is stored with ADP and P, forming ATP.
Products: H20, 32-34 ATP
Fermentation Process
Occurs when there is no oxygen present, making glycolysis repeat over and over
Lactic Acid Fermentation
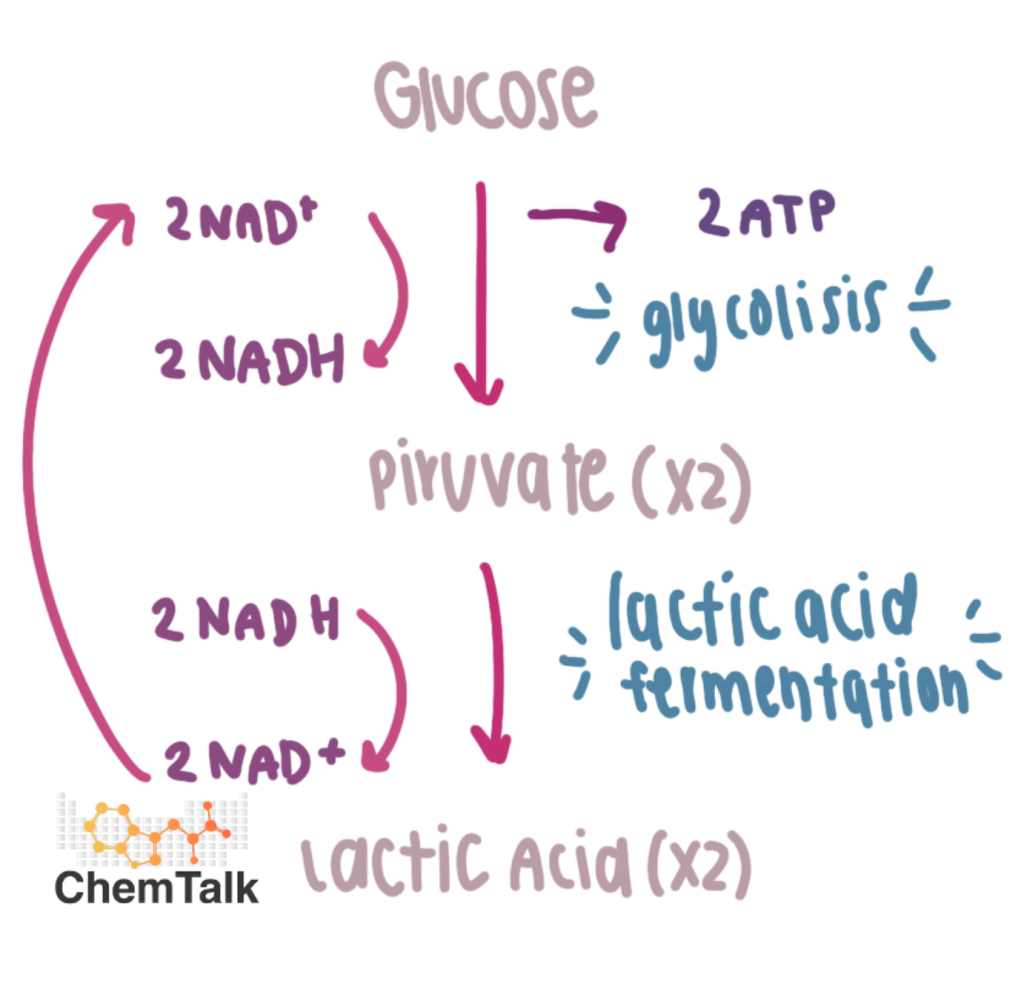
Cheese, Yogurt, Muscles
Glucose bonds break, creating pyruvates (2x), and releasing electrons → electrons stored in NAD+
Because NADH cant drop off electrons, it releases electrons on to the pyruvates
Turning pyruvates into lactic acid
→NAD+ gets recycled
Alcohol Fermentation
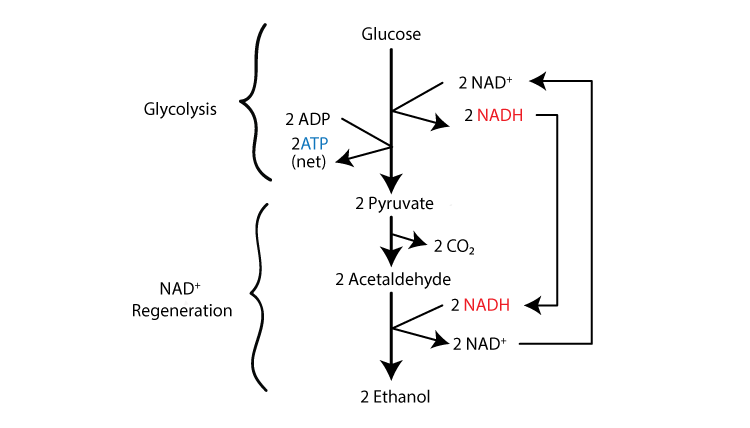
Bread, beer, wine
Glucose bonds break, creating 2 pyruvates, and released electrons
→ Stored in NAD+
→ Left over energy stored in ADP and P, creating 2ATP
Two pyruvates chop off the last carbon
Released carbon attracts Oyxgen, creating CO23.
Acetaldehyde is formed, picking up electrons and hydrogens, forming into 2 Ethanols
Universal process
Glycolysis is universal because it’s simple, doesn’t require oxygen, happens in all cells, and is essential for producing energy