Hydrocarbon
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
containing carbon and hydrogen and other possible elements
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Aliphatic
straight chain and branched, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons,
Aromatic
hydrocarbons containing benzene and related compounds
Cyclic hydrocarbons
any ring structures
Heterocyclic aromatics
ring structures containing at least one atom that is not carbon
Saturated hydrocarbon
containing the maximum number of hydrogens
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
having double or triple bonds (less than max. hydrogens)
Alkane
saturated HC's straight chained, branched or cyclic.
Alkene
unsaturated HC's (only double bonds) straight chained, branched or cyclic
Alkyne
unsaturated HC's having at least one triple bond.
Functional group
elements within a molecule that are chemically reactive
Alcohol
OH
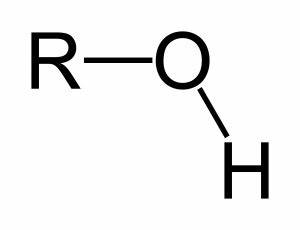
Ether
R-O-R
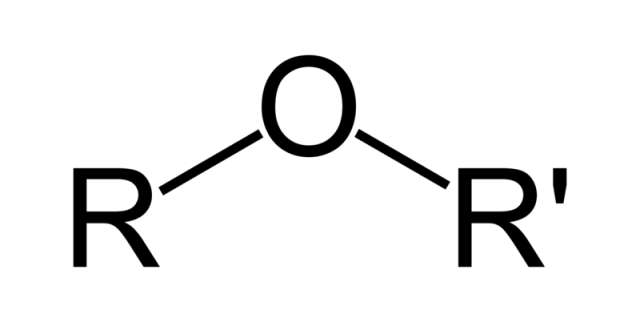
Aldehyde
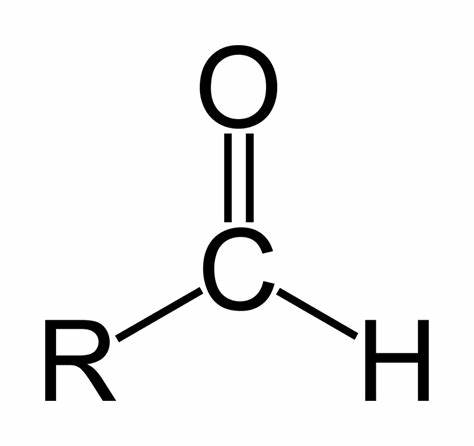
Ketone
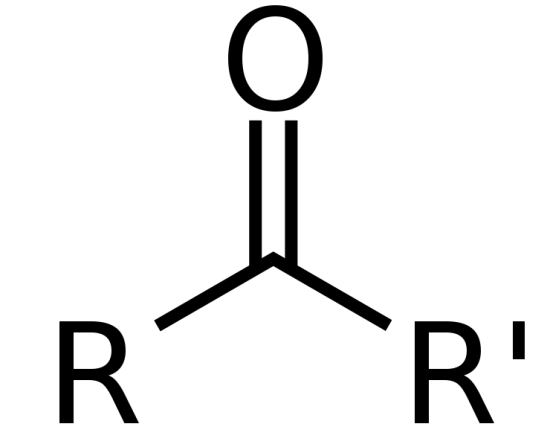
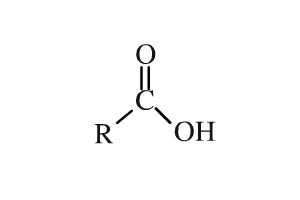
Acid
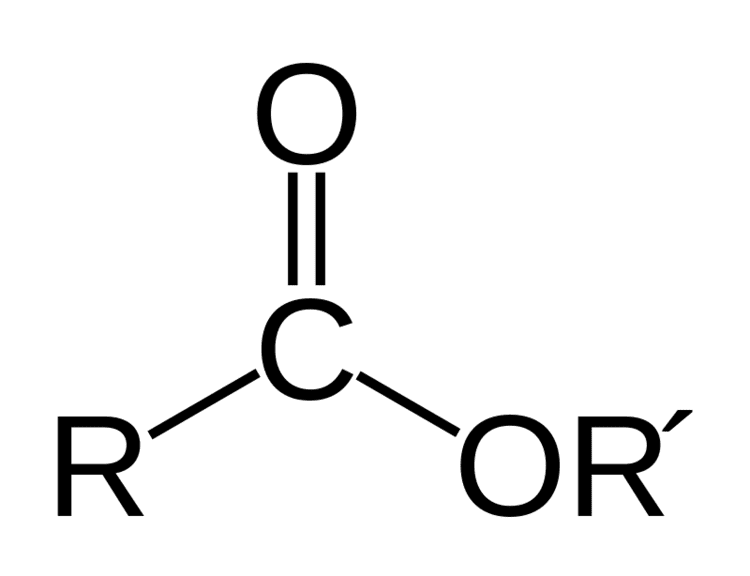
Ester
Nitrile(Cyano)

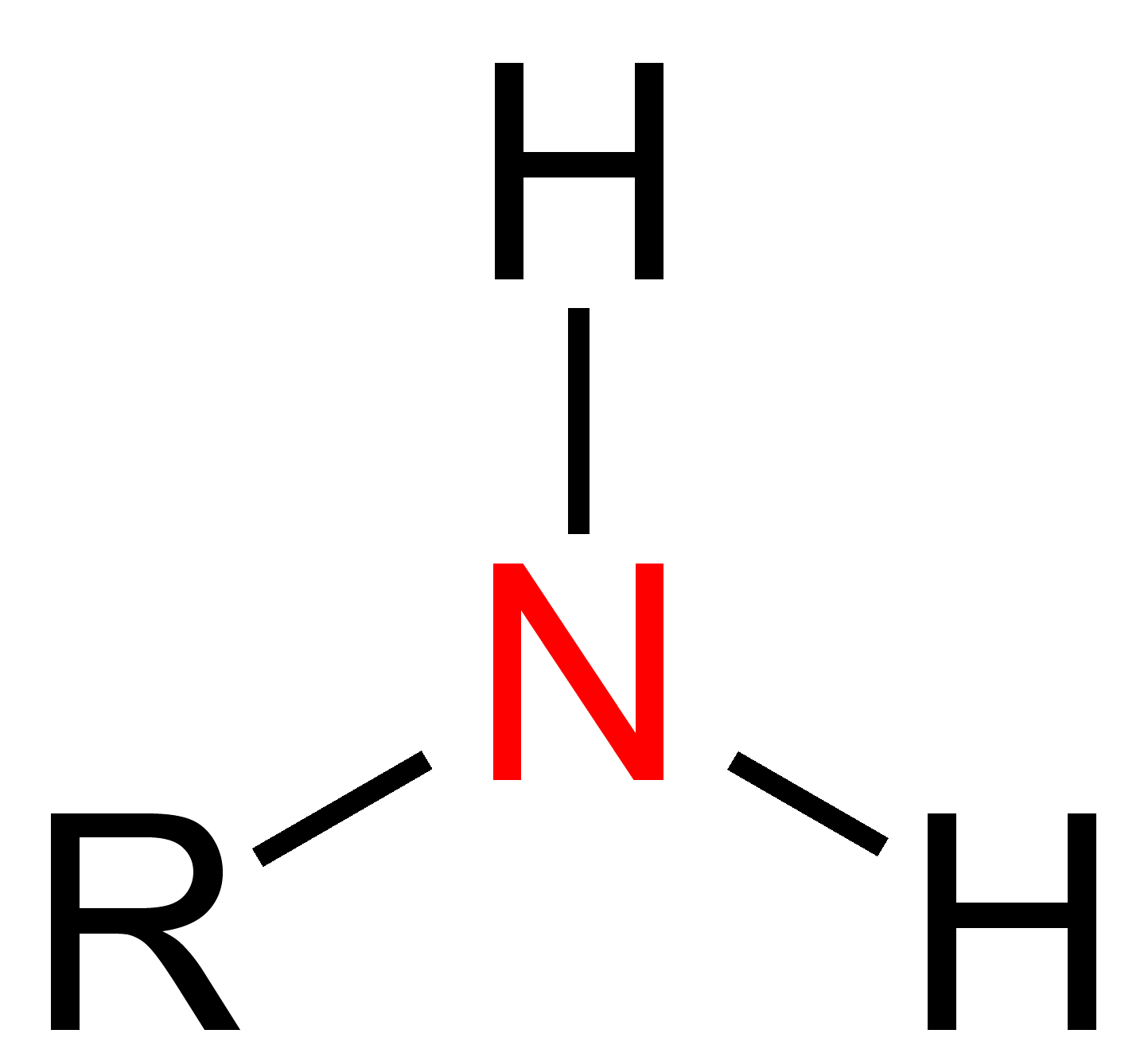
Amine
Amide
R-C-NH2
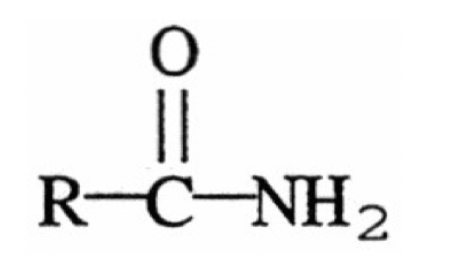
Covalent Bonding Lewis Dot Structures
shared electron pairs
Coordinate covalent bond
a covalent bond having an electron pair coming from one of the two atoms making the bond.
Hybridized Orbitals
modification of electron orbitals to accommodate the spatial orientation of the bonding and non-bonding electron pairs
sp3 hybrid orbitals
hybridization leading to the tetrahedral shape
sp2 hybrid orbitals
hybridization leading to a trigonal planar shape
sp hybrid orbitals
hybridization leading to a linear shape
sigma bonds
covalent bonds defined by the bonding pair being located between the nuclei
pi bonds
covalent bonds defined by the bonding pair being located above and below the plane of the nuclei
MO theory
An alternate theory to valence bond theory. The molecular orbital is considered as atomic orbitals applied to the bonds between two atoms.
Lewis Acid (electrophile)
electron pair acceptor
Lewis Base (nucleophile)
electron pair donor