FSC316
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/235
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:44 AM on 4/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
236 Terms
1
New cards
what is forensic toxicology?
the application of toxicological principles (i.e., the harmful effects that chemicals, substances, or situations have) to cases before the court
2
New cards
what is a chemical?
any substance that is produced in a reaction that involves changes to atoms or molecules
3
New cards
what are organic chemicals?
carbon containing
4
New cards
what are the types of chemicals?
1. poisons/environmental chemicals (hydrogen sulphide, cyanide, etc.)
2. chemicals of abuse (depressants, hallucinogens, etc.)
5
New cards
what is chemical trauma?
trauma caused directly or indirectly by the application of chemical agents to tissues
6
New cards
what is direct chemical trauma?
* direct destruction of tissues (e.g., tattoo removal with chemical produce or hole in the mouth caused by drug use)
* mechanisms (red/ox, corrosion)
* alveolar destruction
* mechanisms (red/ox, corrosion)
* alveolar destruction
7
New cards
what is indirect chemical trauma?
* infection
* introduction via the route (needle or inhalation)
* introduction via the agent (aspergillosis infection from inhaled cocaine)
* asphyxia
* alveolar destruction
* aortic dissection
* introduction via the route (needle or inhalation)
* introduction via the agent (aspergillosis infection from inhaled cocaine)
* asphyxia
* alveolar destruction
* aortic dissection
8
New cards
what is asphyxia and how can it happen?
it is the loss of oxygen due to:
* suffocation = blockage of airway (failure of O2 to reach blood → choking, environmental)
* strangulation = blockage of blood vessels (failure of blood supply to reach brain by occlusions of neck vessels → hanging)
* suffocation = blockage of airway (failure of O2 to reach blood → choking, environmental)
* strangulation = blockage of blood vessels (failure of blood supply to reach brain by occlusions of neck vessels → hanging)
9
New cards
how can chemicals lead to asphyxia?
strangulation route = blockage of blood vessels (rare for suffocation to occur due to chemicals)
10
New cards
what is alveolar destruction?
destruction of alveoli due to chemical use.
* can lead to Hemosiderosis (lots of iron to blood)
* can lead to thick fibrous tissue in lungs (inability to exchange blood effectively + less elasticity (can’t open/close))
* can lead to Hemosiderosis (lots of iron to blood)
* can lead to thick fibrous tissue in lungs (inability to exchange blood effectively + less elasticity (can’t open/close))
11
New cards
what is aortic dissection and what is it’s forensic significance?
* Vessels layers separate
* Can be caused by stimulant use OR blunt force trauma
* Forensic significance: in MVA, was it the collision or drug use that led to aortic dissection?
* Important for cause and mechanism of death
* Can be caused by stimulant use OR blunt force trauma
* Forensic significance: in MVA, was it the collision or drug use that led to aortic dissection?
* Important for cause and mechanism of death
12
New cards
what factors determine the severity of chemical trauma?
* chemical agent (strong bases >>)
* time or timing of exposure (length, developmental window)
* tissue exposed/penetrated
* delivery method (IV, inhaled, ingested → IV is quickest)
* quantity and concentration
* time or timing of exposure (length, developmental window)
* tissue exposed/penetrated
* delivery method (IV, inhaled, ingested → IV is quickest)
* quantity and concentration
13
New cards
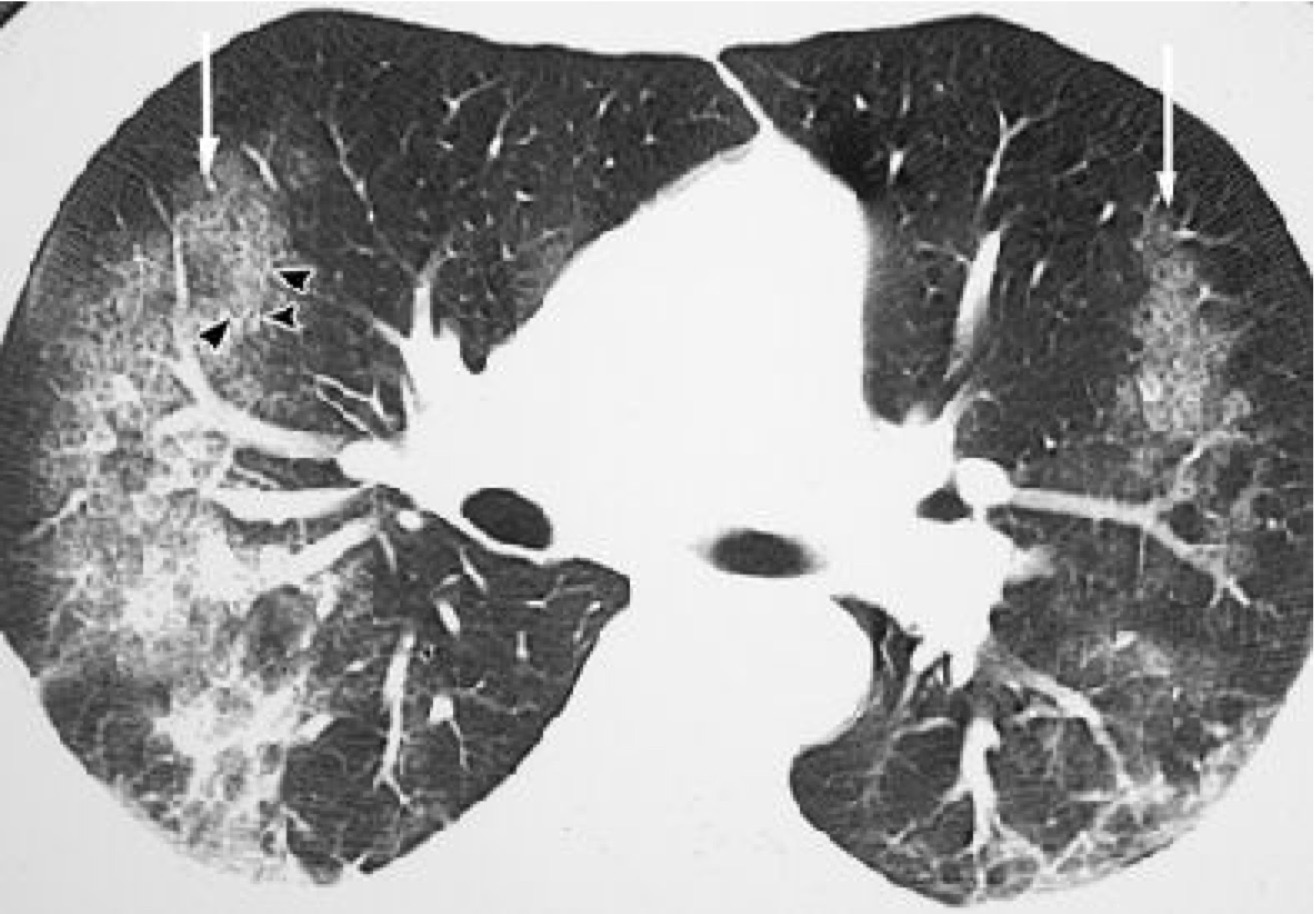
what is wrong with this image?
* this is an example of “crack lung”
* there is a mass area of whitened, damaged, scarred tissue in the lungs
* the white areas should not be there
* there is a mass area of whitened, damaged, scarred tissue in the lungs
* the white areas should not be there
14
New cards
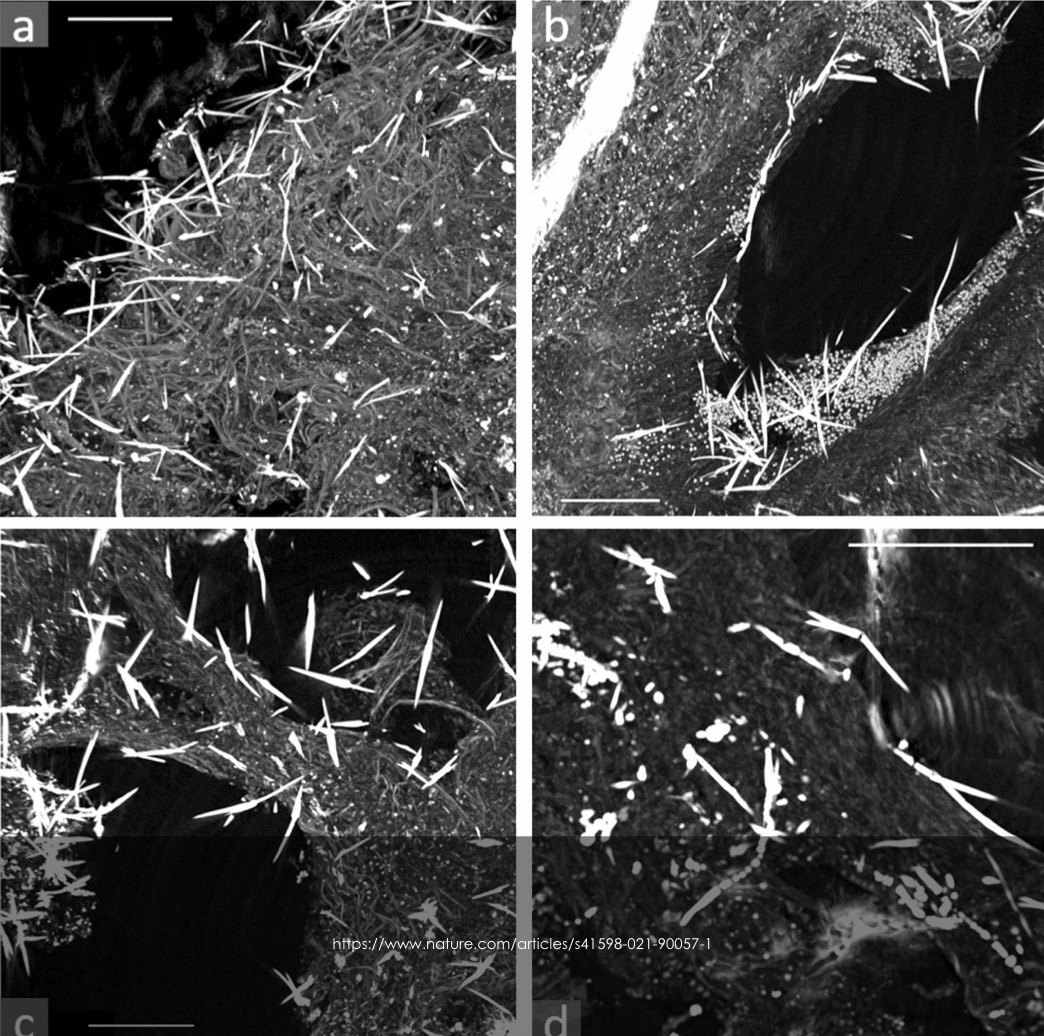
This image is a CT scan of someone’s lungs. Describe what you see.
* lungs were exposed to a chemical agent = asbestos
* asbestos are very easy to breathe in and they become invaginated in the tissues, so they cannot get out
* the image shows a build-up of asbestos in the mucous tissue of the lungs
* asbestos are very easy to breathe in and they become invaginated in the tissues, so they cannot get out
* the image shows a build-up of asbestos in the mucous tissue of the lungs
15
New cards
how can the timing of chemical use impact severity of trauma?
* acute
* depression of function (drug acting on brainstem will affect respiration, heart rate, and balance → fentanyl)
* chronic
* receptor sensitivity changes = tolerance
* cell death leads to structural loss, and loss of function (alcohol neuropathy)
* depression of function (drug acting on brainstem will affect respiration, heart rate, and balance → fentanyl)
* chronic
* receptor sensitivity changes = tolerance
* cell death leads to structural loss, and loss of function (alcohol neuropathy)
16
New cards
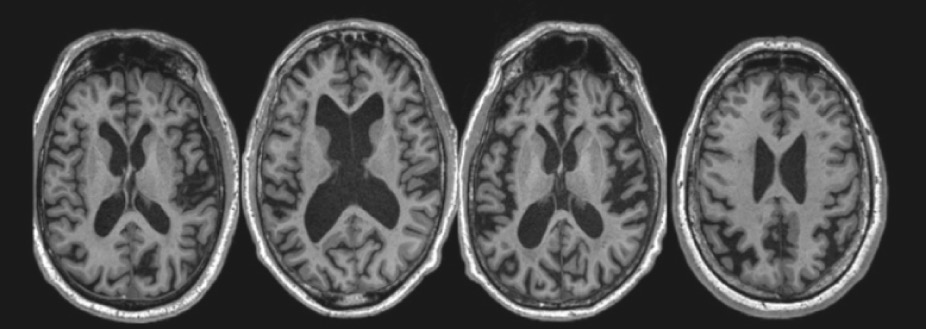
this is the development of an individual's brain. Explain whether this is healthy or unhealthy and why.
* unhealthy → looks like alcoholic person
* a lot of open black scapes (sinuses)
* ventricles are much bigger than normal
* less white matter (less communication in the brain)
* structural loss → loss of function
* a lot of open black scapes (sinuses)
* ventricles are much bigger than normal
* less white matter (less communication in the brain)
* structural loss → loss of function
17
New cards
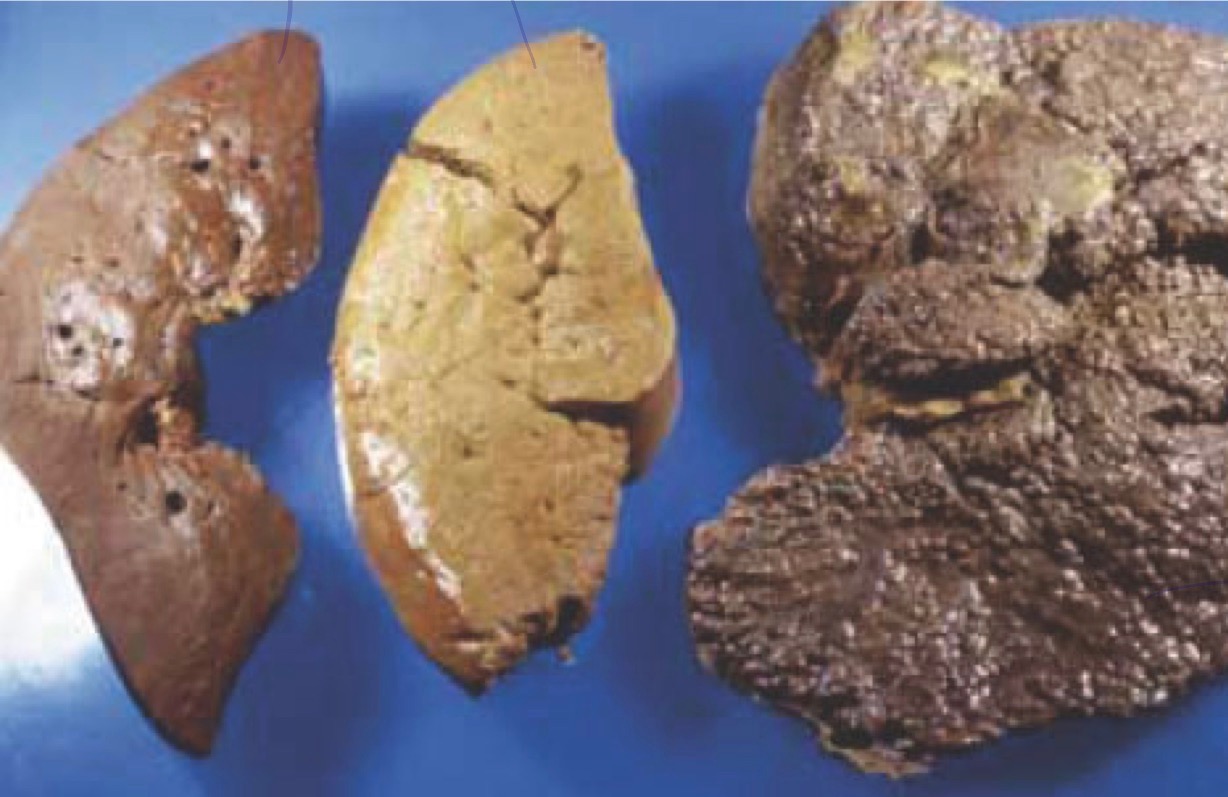

how can the timing of alcohol affect the liver?
* middle liver = medium-term abuse (fatty liver/statosis) = reversible with lifestyle changes + drugs
* right liver = long term abuse (cirrhotic liver) = irreversible
* healthy tissue replaced with fibrous/scar tissue
* right liver = long term abuse (cirrhotic liver) = irreversible
* healthy tissue replaced with fibrous/scar tissue
18
New cards
what is fetal alcohol syndrome?
* pregnant woman drinks during developmental window
* developmental window = period of time during development with rapid differentiation occurs
* prior to 8th week in utero
* rapid development + organ formation
* sensitive to birth defects → very likely to lead to incompatible with life
* after the 8th week in utero
* neurological impairment possible
* 3rd trimester fetus can redirect blood supply and spare brain
* prenatal growth restriction (not growing to healthy sizes and masses)
* developmental window = period of time during development with rapid differentiation occurs
* prior to 8th week in utero
* rapid development + organ formation
* sensitive to birth defects → very likely to lead to incompatible with life
* after the 8th week in utero
* neurological impairment possible
* 3rd trimester fetus can redirect blood supply and spare brain
* prenatal growth restriction (not growing to healthy sizes and masses)
19
New cards
what are some features of fetal alcohol syndrome?
* flat midface
* short nose
* indistinct philtrum
* low nasal bridge
* short nose
* indistinct philtrum
* low nasal bridge
20
New cards
what can fetal alcohol syndrome lead to?
learning disorders: dyslexia, visual/auditory/verbal processing disorder, ADHD
21
New cards
how can the delivery method impact the severity of the chemical trauma?
IV drug injection (overdose likely due to direct exposure -- infection can occur)
pulmonary delivery (inhaling) -- affects respiratory centers → lung edema → death
pulmonary delivery (inhaling) -- affects respiratory centers → lung edema → death
22
New cards
how can the quantity and concentration of the drug impact the severity of the chemical trauma?
1. pharmacokinetics = dose → concentration vs time
2. pharmacodynamics = effect vs concentration
1. effective dose - desired therapeutic, recreational effect
2. overdose - effect is too strong, or effect is on wrong tissues
3. PK-PD = dose → effect vs time
23
New cards
what are the signs of an overdose and what do those indicate?
signs: nausea, tremors, drowsiness, changes in heart rate, changes in eye movement
indicates: seizure activity, respiratory distress, cardiac dysrhythmia, coma
indicates: seizure activity, respiratory distress, cardiac dysrhythmia, coma
24
New cards
what is the integumentary system?
1. skin (keratinized/external) or unkeratinized/internal (e.g., mucous membranes: GI, vagina, bladder)
2. appendages to skin (e.g., hair, nails, sweat glands)
25
New cards
what are the functions of the integumentary system?
* barriers to pathogens
* heat regulation + cooling
* water distribution/movement
* heat regulation + cooling
* water distribution/movement
26
New cards
what are the 3 layers of the skin?
1. epidermis (protection of pathogens and regulation of water and movement)
2. dermis (responsible for cushioning and protecting the body)
3. hypodermis (subcutis) (protection and cushioning, heat regulation, connecting to muscles and bones)
27
New cards
what are the 5 layers of the epidermis?
superficial to deep:
1. stratum corneum
2. stratum lucidum
3. stratum granulosum
4. stratum spinosum
5. stratum basale
1. stratum corneum
2. stratum lucidum
3. stratum granulosum
4. stratum spinosum
5. stratum basale
28
New cards
what are the 3 layers of the dermis?
superficial to deep:
1. papillary dermis
2. reticular dermis
3. adipose tissue layer
1. papillary dermis
2. reticular dermis
3. adipose tissue layer
29
New cards
what is a burn?
injury caused by the application of any force or energy that releases heat
30
New cards
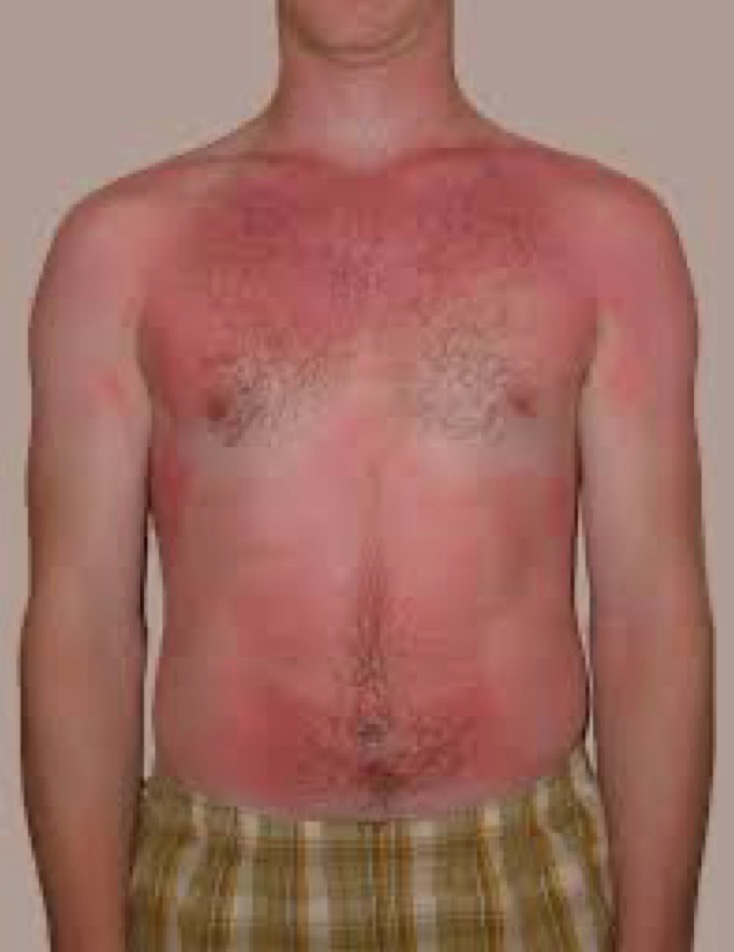
what erythema
redness of skin or mucous membranes due to increased blood flow
31
New cards
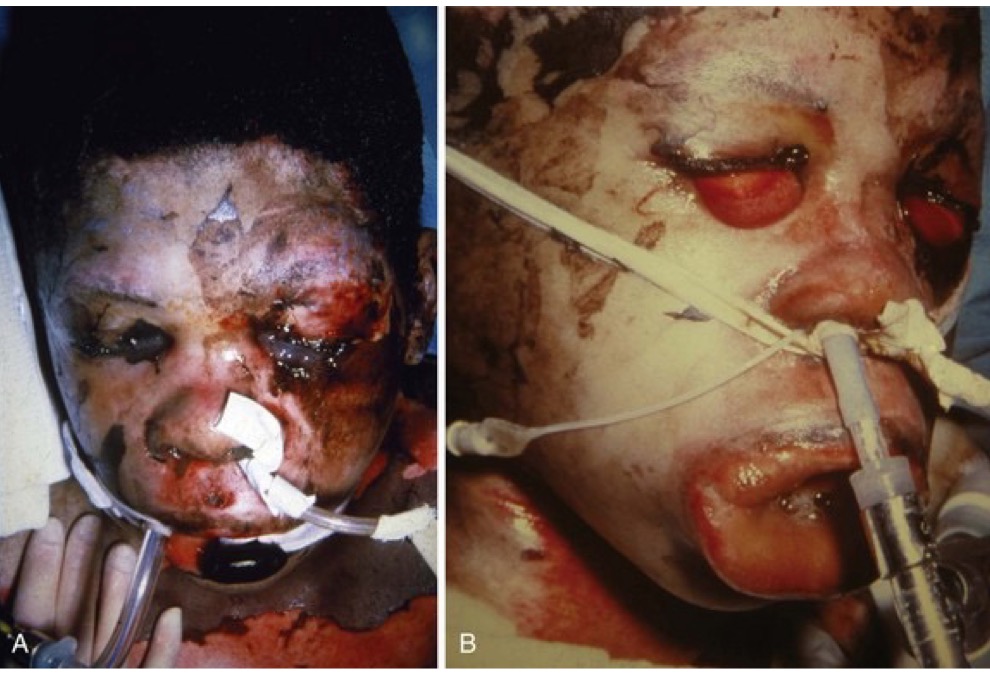
what is edema?
swelling caused by loss of fluid from small blood vessels into tissues
32
New cards
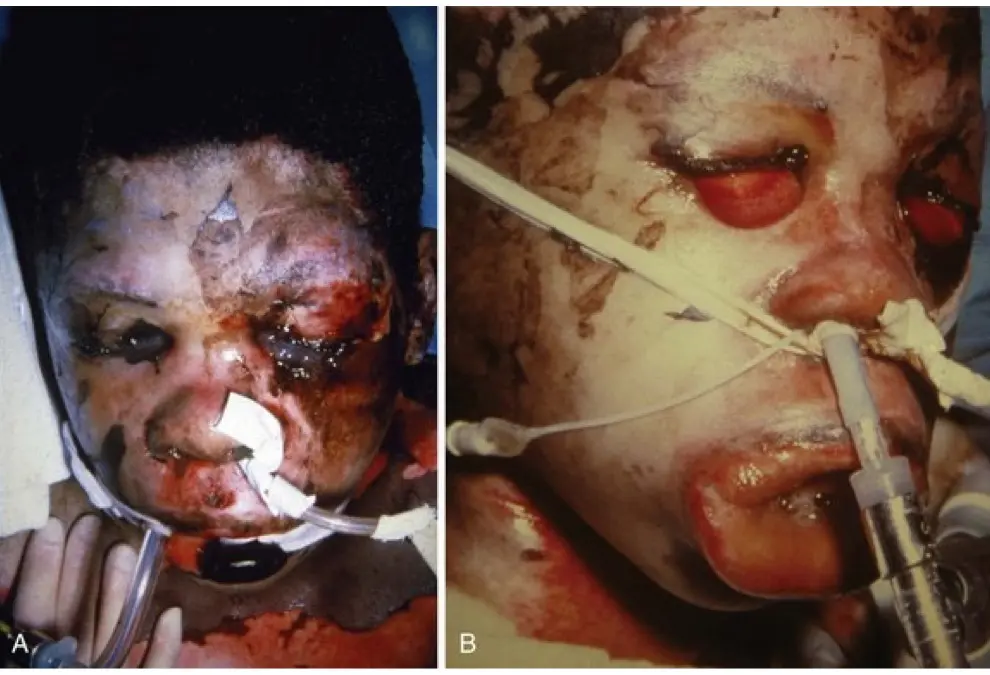
what is hyperemia?
excess of blood and fluid in vessels supplying an organ or tissue
33
New cards
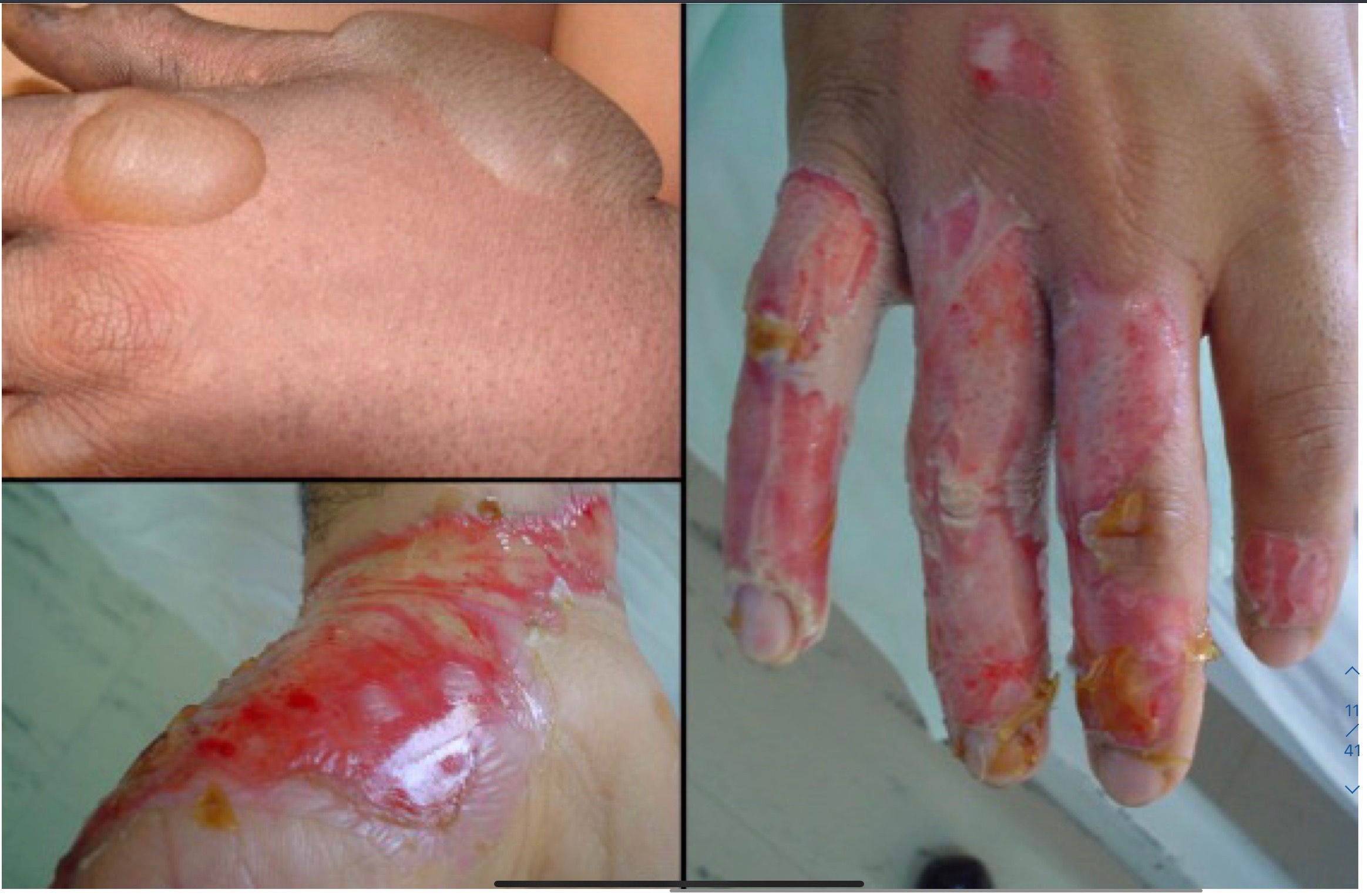
what is a blister and where is it formed?
fluid filled sac formed between epidermis and dermis
34
New cards
what are the 6 categories of burns based on the agent?
1. flame = skin in direct contact with flame
2. contact = skin in direct contact with a hot surface
3. radiant = skin exposure to heat wave (indirect)
4. scalding = skin exposed to hot liquid
5. microwave = skin contact with electromagnetic wave
6. chemical = skin contact with caustic chemical agents
35
New cards
what are the 4 categories of burns based on severity?
1. first degree = superficial epidermis, erythema and edema, pain (sensory neurons intact), no scars
2. second degree = epidermis and dermis, blistering, pain, no scars
3. third degree = burned area white, loss of sensation, severe scarring
4. fourth degree = incineration of tissue (black tissue), complete destruction of epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous tissue, can include bone
36
New cards
what are the factors that determine the severity of the burns?
* intensity - amount of heat transferred to skin (regardless of agent)
* duration (regardless of agent)
* underlying conditions (e.g., less adipose tissue)
* presence and type of clothing (can protect or adhere to burn)
* duration (regardless of agent)
* underlying conditions (e.g., less adipose tissue)
* presence and type of clothing (can protect or adhere to burn)
37
New cards
what factors determine the survivability of a burn?
* age (older = less skin to absorb the heat) -- rly young and old are always more vulnerable
* degree of burn
* percentage of body surface
* rule of 9 for adults (head x1, arms x1, torso x4, legs x2)
* rule of 5 for children (head x2, arms x2, torso x6, legs x3)
* degree of burn
* percentage of body surface
* rule of 9 for adults (head x1, arms x1, torso x4, legs x2)
* rule of 5 for children (head x2, arms x2, torso x6, legs x3)
38
New cards
what is the difference between ante/peri- versus post-mortem burns?
* soft tissue is difficult to distinguish and can share histological features
* bone can show fracture characteristics (longitudinal fractures) that are associated with pugilistic contracture (flexing of hands = fracture = looks like body parts are missing)
* bone can show fracture characteristics (longitudinal fractures) that are associated with pugilistic contracture (flexing of hands = fracture = looks like body parts are missing)
39
New cards
What is environmental trauma?
Morbidity and mortality due to tissue damage caused by environmental conditions, namely hypothermia, hyperthermia, drowning, and lightning
40
New cards
what is hypothermia?
core body temperature is below 35 degree C due to exposure to cold environments for prolonged periods of time + susceptibility
41
New cards
what factors determine the survivability of hypothermia?
* age
* sex
* body habitus
* water exposure (good conductor of heat compared to air - boiling water VS hand in oven)
* sex
* body habitus
* water exposure (good conductor of heat compared to air - boiling water VS hand in oven)
42
New cards
what are the physical symptoms of **mild** hypothermia?
* maximal shivering
* amnesia
* ataxia = difficulty performing tasks
* amnesia
* ataxia = difficulty performing tasks
43
New cards
what are the physical symptoms of **moderate** hypothermia?
* reduced consciousness
* shivering stops, dilated pupils
* cardiac arrhythmia
* coma
* shivering stops, dilated pupils
* cardiac arrhythmia
* coma
44
New cards
what are the physical symptoms of **severe** hypothermia?
* loss of voluntary movement + reflexes
* no response to pain
* hypotension, bradycardia (slow heart rate)
* no response to pain
* hypotension, bradycardia (slow heart rate)
45
New cards
how can hypothermia lead to morbidity and mortality?
* depressed respiration
* muscle stiffness = falls
* ulcers and focal GI bleedings
* pneumonia
* kidney damage
* myocardial degeneration
* muscle stiffness = falls
* ulcers and focal GI bleedings
* pneumonia
* kidney damage
* myocardial degeneration
46
New cards
what is hyperthermia?
core body temperature above 40.5 degrees C
47
New cards
what are factors that determine the sensibility and severity of hyperthermia?
* age
* social determinants of health (SES, social support)
* pre-existing conditions
* alcoholism
* cerebral or cardiac atherosclerosis
* Rx drugs (e.g., antidepressants)
* obesity
* social determinants of health (SES, social support)
* pre-existing conditions
* alcoholism
* cerebral or cardiac atherosclerosis
* Rx drugs (e.g., antidepressants)
* obesity
48
New cards
what are the symptoms of **mild** hyperthermia?
* heat cramps
* heat exhaustion
* heat exhaustion
49
New cards
what are the symptoms of **severe/life-threatening** hyperthermia?
heat stroke
* life threatening without treatment
* mortality = 76% with treatment (forensically an issue when weather gets more severe - global warming)
* life threatening without treatment
* mortality = 76% with treatment (forensically an issue when weather gets more severe - global warming)
50
New cards
how can hyperthermia lead to mortality and morbidity?
* brain damage
* respiratory failure
* heart failure
* pancreas + kidney damage
* intestinal damage
* respiratory failure
* heart failure
* pancreas + kidney damage
* intestinal damage
51
New cards
define drowning
when oxygen is replaced with water in the body
52
New cards
what is the effect that the type of water can play on drowning?
freshwater (hypotonic = loss solute)
* passes more quickly through alveoli
* increases blood volume
saltwater (hypertonic = more solute)
* draws water into alveoli from blood
* decreases blood volume
* passes more quickly through alveoli
* increases blood volume
saltwater (hypertonic = more solute)
* draws water into alveoli from blood
* decreases blood volume
53
New cards
what can drowning lead to?
hypoxia
* results in damage to tissues (less oxygen reaches them)
* cerebral anoxia = oxygen not reaching brain
* death
* results in damage to tissues (less oxygen reaches them)
* cerebral anoxia = oxygen not reaching brain
* death
54
New cards
what are the gender differences in drowning?
* men more likely to drown
* more access to aquatic sites
* high risk behaviours
* alcohol consumption at sites
* more access to aquatic sites
* high risk behaviours
* alcohol consumption at sites
55
New cards
how does the temperature of the water impact drowning?
* cold water = slows down
* protective - “diving reflex”
* warm water = speeds up
* irreversible cerebral anoxia in 3-10 minutes
* heated water = speeds up the most
* hot tubs, whirlpool deaths
* often accompanied by alcohol/intoxication
* cerebra anoxia faster
* hypotension → faining/slipping under water (unnoticed)
* protective - “diving reflex”
* warm water = speeds up
* irreversible cerebral anoxia in 3-10 minutes
* heated water = speeds up the most
* hot tubs, whirlpool deaths
* often accompanied by alcohol/intoxication
* cerebra anoxia faster
* hypotension → faining/slipping under water (unnoticed)
56
New cards
what is near-drowning and how does it occur?
* significant morbidity
* survival for at least 24 hours post rescue
* due to
* sequelae of anoxia
* pulmonary edema
* blood in urine
* sepsis
* cerebral edema = death
* survival for at least 24 hours post rescue
* due to
* sequelae of anoxia
* pulmonary edema
* blood in urine
* sepsis
* cerebral edema = death
57
New cards
what is OHM’s law?
I = V/R
* I current (flow of electric charge)
* V voltage (electromotive force)
* R resistance (opposition to the flow of charge
\*high resistance = low current
* I current (flow of electric charge)
* V voltage (electromotive force)
* R resistance (opposition to the flow of charge
\*high resistance = low current
58
New cards
what factors determine the severity of electrocution?
* nature of current (AC (most electronics), DC, and flow)
* amount of current (A)
* voltage (V)
* path through the body
* time of exposure
* condition of circuit (wet, dry (more resistance), grounded to earth)
* resistance of body, clothing, ground, etc.
* amount of current (A)
* voltage (V)
* path through the body
* time of exposure
* condition of circuit (wet, dry (more resistance), grounded to earth)
* resistance of body, clothing, ground, etc.
59
New cards
how does a current flow?
follows shortest path (not path of least resistance)
* path varies with current entry and exit site
* morbidity will depend on path
* fatal paths usually cross brain or heart (interruption of electrical activity)
* path varies with current entry and exit site
* morbidity will depend on path
* fatal paths usually cross brain or heart (interruption of electrical activity)
60
New cards
How much current is sufficient for a cardiac arrest?
2A (2000mA)
(note: 100mA in a lightbulb)
(note: 100mA in a lightbulb)
61
New cards
What is the difference between low and high voltage on the severity of the electrocution?
Low voltage
*
*
62
New cards
what is force?
(F = ma) force is what sets an object in motion
63
New cards
what is kinetic energy?
(KE = 1/2mv^2) the energy an object has because it is in motion
64
New cards
true or false: mass has a greater contribution than speed
false
65
New cards
why are injuries important in forensics?
they tell you information about the situation, objects, and those involved
66
New cards
what are the types of blunt force injuries?
* abrasions = friction
* avulsions = something torn away
* fractures = broken
* contusions = bruise
* lacerations = torn tissue
* avulsions = something torn away
* fractures = broken
* contusions = bruise
* lacerations = torn tissue
67
New cards
what are the differences between raccoon eyes and black eye?
black eye is caused by blunt force trauma locally applied; raccoon eyes due to cranial fracture (circular + uniform black eyes)
both are contusions
both are contusions
68
New cards
what are the some information you can get from fractures?
OLD ACID
Open or closed
Location
Degree
Articular extension
Communication and pattern
Intrinsic bone quality
Displacement, angulation, rotation
Open or closed
Location
Degree
Articular extension
Communication and pattern
Intrinsic bone quality
Displacement, angulation, rotation
69
New cards
what is the difference between open and closed fractures?
open fractures = broken end of bone passes through skin
closed fracture = skin is not lacerated
closed fracture = skin is not lacerated
70
New cards
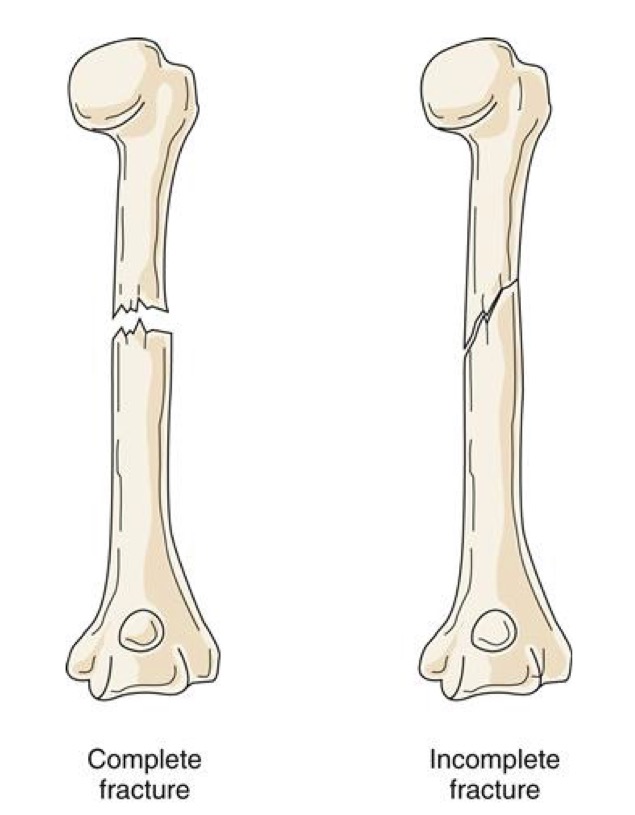
what are the degrees of fractures?
complete fractures: transect the bone, separation of bone segments
incomplete fractures: bone bends and tears but is not transected
incomplete fractures: bone bends and tears but is not transected
71
New cards
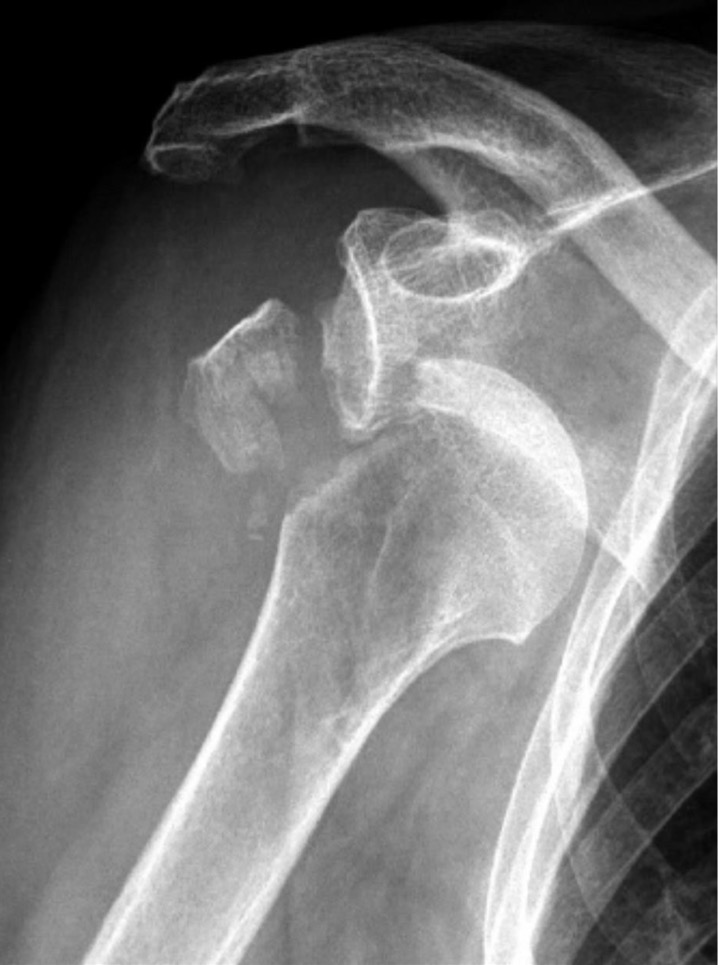
what is articular extension?
fracture enters joint space (e.g., rotator cuff injury with articular extension)
72
New cards
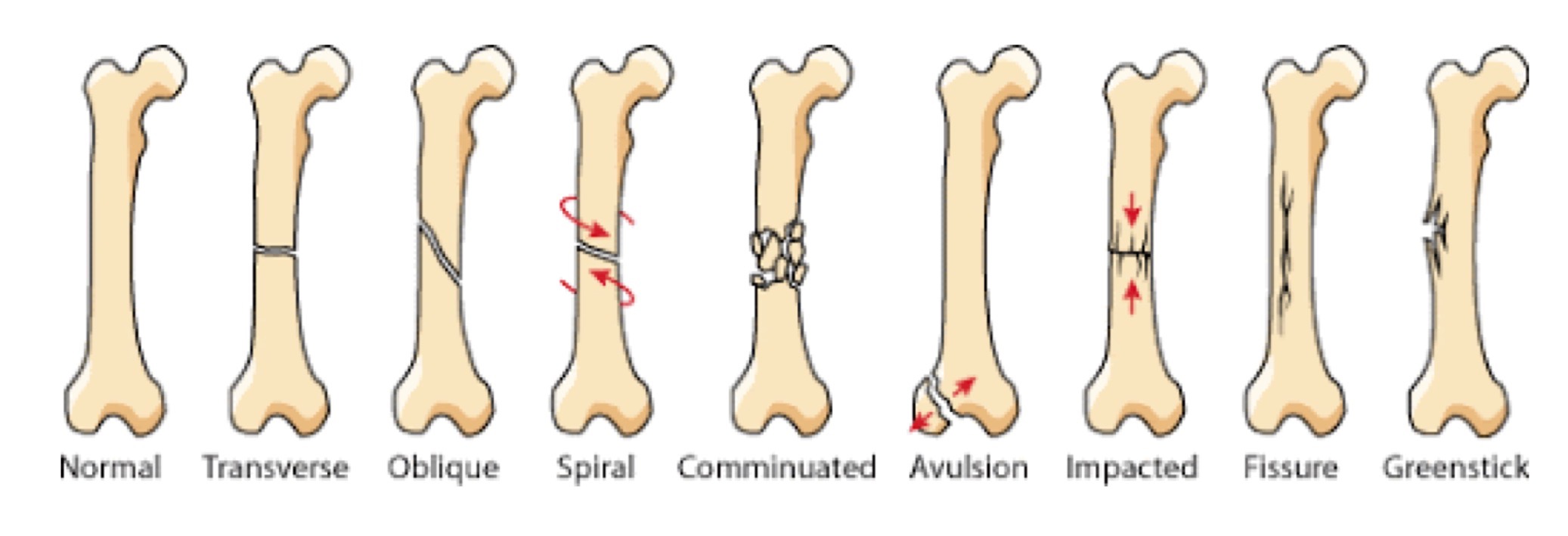
list the patterns and comminution of the following fractures:
normal
transferse
oblique
spiral
comminuated
avulsion
impacted
fissure
greenstick
transferse
oblique
spiral
comminuated
avulsion
impacted
fissure
greenstick
73
New cards
what is intrinsic bone quality?
underlying conditions that predispose bones to fracture (like osteoporosis/osteopenia, osteogenesis imperfecta)
must test for and rule out conditions where there is a suspicion of child or elder abuse
must test for and rule out conditions where there is a suspicion of child or elder abuse
74
New cards
What is displacement, angulation, and rotation of a fracture?
Displacement – bone moved away from natural position
Angulation – bone moved away and shifted by a discernable angle
Rotation – bone rotated along axis (with or without displacement or angulation)
Angulation – bone moved away and shifted by a discernable angle
Rotation – bone rotated along axis (with or without displacement or angulation)
75
New cards
what is the difference between a laceration vs a stab?
Stab is deeper than it is wide
76
New cards
What can projectile injuries show?
Entry and exit wounds can show direction = position of those involved
77
New cards
What are mixed force injuries?
Injuries resulting from trauma inflicted by more than one type of force or energy
* chop wounds = shard and blunt
* crush wounds = blunt and sharp
* pneumothorax = blunt and sharp
* chop wounds = shard and blunt
* crush wounds = blunt and sharp
* pneumothorax = blunt and sharp
78
New cards
what is patterns of injury?
Tells us information about the circumstances/sequence of events
79
New cards
What are patterned injuries?
Tell us information about the object when the imprint of the object is stamped onto the skin
80
New cards
what is the difference between “patterned injuries” and “injury patterns”?
* patterned injuries = tell us information about the object
* injury patterns = tells us about the circumstances
* injury patterns = tells us about the circumstances
81
New cards
What are defensive wounds?
* damage to the hands, forearms, feet, inner thighs
* tells us the victim was conscious
* tells us the victim was conscious
82
New cards
What do you need to consider with MVCs?
* bumper height
* compression and avulsion injuries in almost 60% of MVC pedestrian deaths
* directionality of damage → directionality of impact
* compression and avulsion injuries in almost 60% of MVC pedestrian deaths
* directionality of damage → directionality of impact
83
New cards
what is inguinal stretching?
* MVC
* blunt force trauma
* from behind or oblique collision
* inguinal ligament overstretched, pulls skin and fascia (bleeding into tissues)
* blunt force trauma
* from behind or oblique collision
* inguinal ligament overstretched, pulls skin and fascia (bleeding into tissues)
84
New cards
Where are IV drug injection sites usually?
* when veins in arms cannot be used, they will use veins of legs and feet
* harder to find in thigh and leg
* often feet, between toes
* popliteal area uncommon because it’s hard to reach
* harder to find in thigh and leg
* often feet, between toes
* popliteal area uncommon because it’s hard to reach
85
New cards
what is dismemberment?
* sharp post-mortem trauma
* tool marks remain on bone
* often done to hide identification of body or body disposal
e.g., striation means something was going back and forth (like a saw)
* tool marks remain on bone
* often done to hide identification of body or body disposal
e.g., striation means something was going back and forth (like a saw)
86
New cards
What is a pelvic ring fracture?
separation of pelvic bones (SI joint or pubic symphysis)
* causes external over-rotation
* causes external over-rotation
87
New cards
what can lead to sudden natural death?
* undiagnosed/untreated pelvic neoplasia (can be due to stigma)
* STIs
* HIV = cervical cancer
* HPV = infection → sepsis
* UTIs
* sepsis
* STIs
* HIV = cervical cancer
* HPV = infection → sepsis
* UTIs
* sepsis
88
New cards
What is prostate cancer?
* older men
* hardens prostate = reduction in urinary outflow
* rule out = enlarging of prostate and urinary outflow reduction
* hardens prostate = reduction in urinary outflow
* rule out = enlarging of prostate and urinary outflow reduction
89
New cards
What is ovarian cancer?
* most difficult to diagnose
* needs different imaging techniques
* most commonly originates in epithelial layers of ovary
* older women
* frequently metastases
* needs different imaging techniques
* most commonly originates in epithelial layers of ovary
* older women
* frequently metastases
90
New cards
what is cervical cancer?
* cancer of cervix and uterus
* one source is HIV
* higher rates in highly religious people and antivaxxers
* one source is HIV
* higher rates in highly religious people and antivaxxers
91
New cards
What are complications of pregnancy?
* assault
* vulnerable population for violence
* sudden natural death
* hemorrhage (ectopic - fetus growing in a place other than the uterus)
* infection and sepsis
* complications of abortion
* obstetric fistula (obstructed labour)
* vulnerable population for violence
* sudden natural death
* hemorrhage (ectopic - fetus growing in a place other than the uterus)
* infection and sepsis
* complications of abortion
* obstetric fistula (obstructed labour)
92
New cards
what are the 3 types of death?
1. somatic
1. heart and lungs stop working = whole systems failing
2. neurologic
1. brain death = irrecoverable
3. cellular
93
New cards
what are the 3 types of cellular deaths?
* apoptosis = preprogrammed cell death
* necrosis = cellular and tissue localized death due to external causes
* autolytic = enzymatic non-programmed self-destruction after somatic death
* necrosis = cellular and tissue localized death due to external causes
* autolytic = enzymatic non-programmed self-destruction after somatic death
94
New cards
what are the 2 phases of decomposition?
1. intrinsic (internal)
1. cellular
2. autolysis
3. bacterial
2. extrinsic (external)
1. can be physically seen
2. changes to soft tissue
3. used to determine post-mortem internal/time since death
95
New cards
what is autolysis
* “cell death”
* cellular processes that keep native enzymatic activity in check stops
* leads to lack of O2 and nutrients to cells
* cellular processes that keep native enzymatic activity in check stops
* leads to lack of O2 and nutrients to cells
96
New cards
what are the 4 extrinsic stages of the decomposition process?
1. fresh
1. autolysis
2. mortis triad
2. early decomposition
1. bloating
2. skin slippage
3. purging
3. advanced decomposition
1. compression/deflation
2. initial skeletonization
4. skeletonization/mummification
1. skeletal elements more than 75% exposed OR
2. skin becomes mummified
97
New cards
what is the mortis triad?
1. livor mortis (pooling/settling of blood to the lower point (fixed lividity)
2. algor mortis (cooling or warming of body)
3. rigor mortis (stiggin of the body post-mortem)
98
New cards
how can algor mortis be used to estimate PMI?
in a climate-controlled environment, it will change 2 degrees F/hr
very variable (if hotter could be higher rate)
very variable (if hotter could be higher rate)
99
New cards
how long will rigor mortis be seen for?
appear the first 30 min → 2 hours after death
* completely fixed at 12 hours
* starts relaxing 24-36 hours post mortem
* completely fixed at 12 hours
* starts relaxing 24-36 hours post mortem
100
New cards
what is the megyesi scale?
scale used to measure decomposition after the first 72 hours
* examines: head + neck, torso, limbs (upper + lower togethers)
* lowest possible score = 3 (fresh in all 3 areas)
* highest score = 35 for skeletonized
* examines: head + neck, torso, limbs (upper + lower togethers)
* lowest possible score = 3 (fresh in all 3 areas)
* highest score = 35 for skeletonized