BIOLOGY Q1 EXAM
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What is biology?
Study of life
What might a biologist do?
~Study the diversity of life
~Research diseases
~Develop technologies
~Improve agriculture
~Preserve the environment
What are the eight characteristics of life?
~Made of one or more cells
~Displays organization
~Grows and develops
~Reproduces
~Responds to stimuli
~Requires energy
~Maintains homeostasis
~Adaptations evolve over time
What does Made of one or more cells mean?
cells are the basic unit of structure and functions in all living things. Can be unicellular (one cell) or multicellular ( many cells)
What does displays organizations mean?
they are arranged in an orderly Way
How are Single cells organized?
They contain organized functional structures.
How are Multicellular organized?
cells organized into tissues, Tissues are organized into organs, and Organ systems work together to support an organism
what does Growth mean?
The addition of mass to an organism, often in the form of new cells and structures.
What does development.mean?
The process of natural changes over the lifetime of an organism
What does Reproduces mean?
the production of offspring
What does Responds to stimuli mean?
Anything that is part of the internal or external environments and triggers a reaction by the organism is called a stimulus.
The reaction to a stimulus is a response.
A stimulus is like a cause, and a response is like an effect.
What does Requires Energy mean?
Living things get their energy from food. (either sun or consuming other organisms)
What does Maintains homeostasis mean?
What does Adaptations evolve over time mean?
An adaptation is any inherited characteristic that results from changes to a species over time.
Adaptations enable species to survive and pass on their genes to the next generation.
Adaptations are usually developed in response to an environmental factor.
What is the difference between growth and development?
Growth is number development is natural changes
What is an example of homeostasis?
sweating
What is an observation?
a direct method of gathering information in an orderly way.
What is an inference?
The process of combining what you know with what you have learned to draw logical conclusions
What are examples of observations and inferences?
Observations are gathering information, and inferences use what you know to draw conclusions.
What is a hypothesis?
a testable explanation of a situation.
What is an experiment?
They investigate a phenomenon in a controlled setting to test a hypothesis.
What is an independent variable in an experiment?
The tested factor that might affect the outcome of the experiment
What is a dependent variable?
results from or depends on changes to the independent variable.
What is a control group?
The group used for comparison.
What is an experimental group?
A group exposed to the factor being tested.
What is quantitative data?
collected as numbers, such as measurements of time, temperature, length, mass, etc. (numbers )
What is qualitative data?
descriptions of what our senses detect
Who invented the microscope?
Robert hooke
What is a microscope used for?
Seeing things the human eye can't
Which scientists are responsible for early discoveries in microbiology?
Leewenhoek, schwann, virchow
What did Leewenhoek discovered?
He discovered single celled living organism
What did Schwann discovered?
He reported that animal tissue also contained cells
What did Virchow discovered?
He discovered all cells are produced from the division of existing cells.
What is a cell?
The basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
What is cell theory?
~All living organisms are composed of one of more cells.
~Cells are the basic unit of structure and organization of all living organisms.
~Cells arise only from previously existing cells, with cells passing copies of their genetic material on to their daughter cells.
What is the difference between a compound light microscope and an electron microscope?
A compound uses a series of glass lenses and visible light to magnify images and can magnify up to ~1000x actual size.
Electrons create an image by illuminating a sample with a beam of electrons and collecting electrons that reflect back from the sample, which can be magnified up to 500,000 times actual size.
How can you calculate magnification on a compound light microscope?
Objective times eyepiece
What are things all cells have in common?
A plasma membrane
What are the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) are cells without a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. ( smaller and simpler)
Eukaryotic cells ( plants and animals, and fungi) contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles (like mitochondria, ER, and chloroplasts).
What is selective permeability?
meaning they allow some substances to pass through while keeping others out.
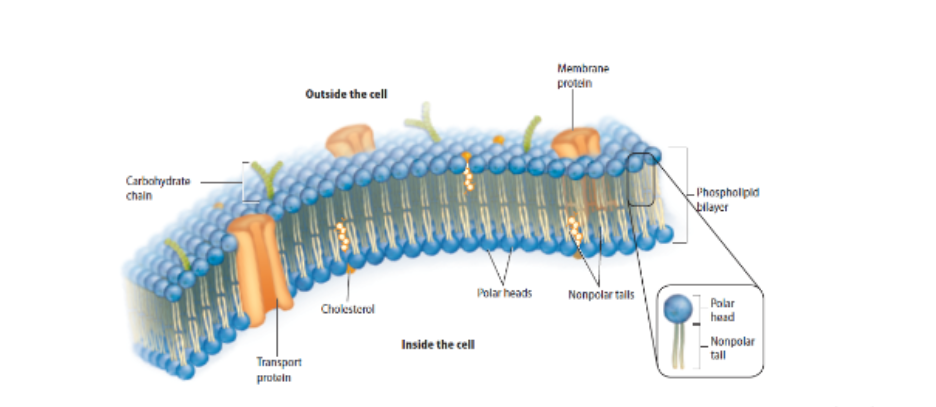
What is the plasma membrane made of?
phospholipid bilayer
what is the phospholipid bilayer?
two layers of phospholipids are arranged to allow the membrane to exist in a watery environment.
What is polarity?
Polar heads facing outside and nonpolar heads facing inside
Why does the Plasma Membrane have polar heads facing outward on each side of the bi-layer?
Polar heads facing outside and nonpolar tails facing inside the cell, allowing the membrane to keep the internal and external environments separate.
Polar or Nonpolar, which one likes to be around water?
Polar
What is the role of Transport Proteins?
What type of molecule would most likely use a transport protein channel?
Large
What is cholesterol used for in the cell membrane?
prevents the fatty acid tails of the phospholipid bilayer from sticking together.
What are carbohydrates used for?
define the cell’s characteristics
Explain the fluid mosaic model.
describes the phospholipids in the bilayer as a “sea” in which other components can float and move around. The different substances in the plasma membrane create a pattern or mosaic on the surface of the cell.
Know how to label the whole membrane.
What is diffusion?
It is the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration.
What is diffusion’s trend?
High to low
What is dynamic equilibrium?
When diffusion occurs over a long enough time, concentrations will become uniform. ( all mixed together)
What's the difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion uses transport proteins to move ions and small molecules across the plasma membrane.
What is passive transport? Does diffusion require energy?
Diffusion and facilitated diffusion are types of passive transport – they require no energy.
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
Where does water move toward through osmosis?
The more solute
What is an isotonic solution? Could you identify one?
The same concentration of water and solutes as the cytoplasm of the cell.
What is a hypertonic solution? Could you identify one?
a lower concentration of solutes than in the cytoplasm of the cell. As water moves into the cell, pressure increases. (swells)
What is a hypotonic solution? Could you identify one?
a higher concentration of solutes than in the cytoplasm of the cell. As water moves out of the cell, pressure decreases. (shrinks)
What is active transport?
Movement of particles across the cell membrane, against the concentration gradient, requires energy
What is an example of active transport?
Na+/K+ ATPase pumps
What is exocytosis?
The excretion of materials at the plasma membrane.
What is endocytosis?
the process by which a cell surrounds an object in the outside environment in a portion of the plasma membrane.
What is a catabolic reaction?
release energy by breaking down larger molecules.
What is an anabolic reaction?
use energy to build larger molecules.
What type of reaction is Photosynthesis?
Anabolic
What type of reaction is Cellular Respiration?
Catabolic
How are Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis related to one another?
The reactants of one are the products of another
What is the ATP molecule used for?
The most important biological molecule is that which provides chemical energy.
What is the arrangement of the ATP molecule?
Nucleotides made of an adenine base, a ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups
How do you release energy from the ATP molecule?
Break it by the second and third phosphate.
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O= C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is Chloroplast?
Organelles that capture light energy
What is a Thylakoid?
flattened saclike membranes
What are Grana?
Stacks of thylakoids
What is the Stroma?
The fluid-filled space outside the grana
What is the most common pigment found in plants?
Chlorophyll
What colors does it absorb? Reflect?
Chlorophyll absorbs red and blue light and reflects green.
How could leaves change color in Autumn?
Chlorophyll dies, so other pigments are more abundant and other colors of light are reflected.
What are the products of the first phase of photosynthesis?
ATP, NADPH
How does the plant make NAPDH?
Ferrodoxin transfers the electrons to the carrier molecule NADP+, forming the energy storage molecule NADPH.
How does the plant make ATP in phase one?
produced in conjunction with the electron transport system through chemiosmosis.
Where does the Calvin Cycle take place?
Stroma
How does CO2 get into the plant cells?
Open pores on the leaf
What happens in Step 1?
CO2 molecules combine with 5-carbon molecules to form 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA)
What happens in Step 2?
Chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH is transferred to the
3-PGA to form glyceraldehyde 3-phospate (G3P).
What can G3P turn into in step 3?
Some G3P molecules leave the cycle to be used for the production
of glucose and other organic compounds.
What two things are needed to convert G3P back into a 5-carbon molecule in Step 4?
Rubisco and ATP
Is photosynthesis anabolic or catabolic?
Anabolic
What are CAM plants, how and why are they different from normal plants?
Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) is found in desert plants & pineapple. Collect CO2 at night and store it in organic compounds. During the day, release CO2 from organic compounds for the light-dependent cycle of photosynthesis .they would lose too much water collecting Co2 during the day