ISC - S2 - Questions
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
What are SOC 2 engagements?
examinations in which a third party evaluates and reports on a service organization’s system controls as it relates to the AICPA’s five Trust Services Criteria, which givers users reasonable assurance that the service organization’s controls listed in its system description are accurately depicted and effective
What are the five Trust Services Criteria?
Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy
SOC 2 engagements emphasize auditors to not only have an advanced understanding of information technology terminology, but also…
technical expertise in the way in which key components of the modern IT landscape function
What does Network Infrastructure refer to?
the hardware, software, layout, and topology of network resources that enable connectivity and communication between devices on a network
What Network Infrastructure Hardware is the device that brings internet into a home or office?
Modems
What is a Modem
a device that connects a network to an internet service provider’s network, usually through a cable connection
What is a Router
a device that manages network traffic by connecting devices to form a network
How does a Router work?
they read the source and destination fields in an information packet header to determine the most efficient path through the network for the packet to travel
How does a Gateway work?
It transforms data from one protocol into another so that information can flow between networks
What is an edge-enabled device?
a network device that allows computing, storage, and networking functions closer to the devices where the data or system request originates, rather than a distant central location
Which network device assigns IP addresses
Routers
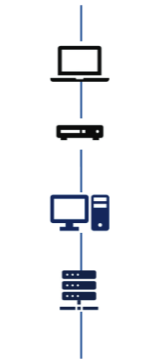
What type of topology is this?
Bus Topology (Linear)
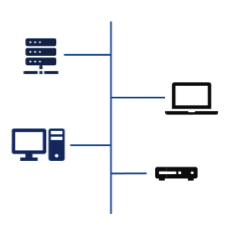
What type of topology is this?
Bus Topology (Tree)
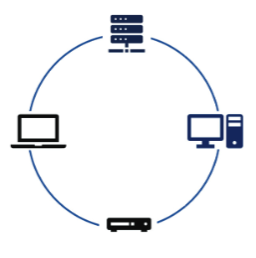
What type of topology is this?
Ring Topology
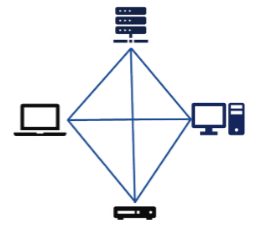
What type of topology is this?
Mesh Topology
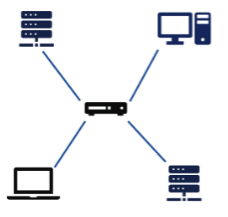
What type of topology is this?
Star Topology
What are the 7 layers of the OSI model?
Physical
Data Link
Network
Transport
Session
Presentation
Application
What is the purpose of Layer 1 (physical)
to convert the message sent from the data link layer into bits so it can be transmitted to other physical devices
What is the purpose of Layer 2 (data link)
to format data packets for transmission as determined by hardware and networking technology
What is the purpose of Layer 3 (Network)
to detect errors and add routing and address headers or footers to the data, such as source and destination IP addresses, so that the message reaches the correct devices
What is the purpose of Layer 4 (Transport)
to support and control the communication connections between devices by setting rules for how devices are referenced, the amount of data that can be transmitted, validating the data’s integrity, and determining whether data has been lost
What is the purpose of Layer 5 (Session)
to allow sessions between communicating devices to be established and maintained
What is the purpose of Layer 6 (Presentation)
to transform data received from the application layer into a format that other devices using the OSI model can interpret, such as standard formats for videos, images, and webpages. It also handles data encryption and decryption, as well as compression and decompression of data.
What is the purpose of Layer 7 (Application)
to serve as the interface between applications that a person uses and the network protocol needed to transmit a message
What does Network Infrastructure Architecture refer to?
the way an organization structures its network from a holistic design standpoint considering factors such as geographical layout, physical and logical layout, and network protocols used
What do Local-Area Networks (LANs) do?
provide network access to a limited geographic area such as a home or single-location office
What do Wide-Area Networks (WANs) do?
provide access to larger geographic areas such as cities, regions, or countries. WANs connect other networks such as LANs together to provide broad coverage
What is the largest example of a WAN?
The internet
What do Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WANs) do?
monitor the performance of WAN connections and manage traffic to optimize connectivity
What does a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) do?
separates a LAN from other untrusted networks such as the internet, which is set up by creating a physical or logical subnetwork outside of the LAN’s firewall
What does a Virtual Private Network (VPN) do?
provide remote and secure access to an existing network
What does software consist of?
the applications, procedures, or programs that provide instructions for a computer to execute
What is an operating system?
software that orchestrates the global functioning of a group of applications hardware and their performance by acting as an intermediary between these resources to allow a user to execute specific tasks
What does mobile technology refer to?
any wireless-enabled device that is connected, or has the ability to connect, to a private network or the internet
What is considered an extension of mobile technology?
Internet of Things devices
What is Cloud Computing?
A computing model that uses shared resources over the internet
What is it called when customers rent storage space, processing power, proprietary software or a combination of the three on remote servers from another company?
Cloud Computing
What is Infrastructure as a Service?
The CSP provides an entire virtual data center of resources and organizations can outsource servers, storage, hardware, networking services, and networking components to third-party providers, which is generally billed on a per-use basis
When evaluating CSP’s data security measures, what do you NOT have to look at?
Vertical Scalability
What is Platform as a Service?
The CSP provide proprietary tools or solutions remotely that are used to fulfill a specific business purpose
In a PaaS model, the tools facilitate the creation of programs and delivery of services, such as building an online platform to sell merchandise, advertise products, or build other websites, all of which run on…
the CSP’s hosted infrastructure
What is Software as a Service?
The CSP provides a business application or software that organizations use to perform specific functions or processes
In a SaaS model, how do customers typically purchase the service?
Licensing
What is a common service offered in conjunction with SaaS models?
Business Process as a Service
What is Business Process as a Service?
third parties use SaaS software to deliver specific business functions such as outsourced payroll, billing, or logistics services
What are the four types of Cloud Computing Deployment Models?
Public
Private
Hybrid
Community
What is a Public Cloud Computing Deployment Model
The cloud in this model is owned and managed by a CSP that makes the cloud services available to people or organziations who want to use or purchase them
What is a Private Cloud Computing Deployment Model
The cloud in this model is created for a single organization and is managed by the organization or a managed service vendor
Where can cloud infrastructure exist in a private network?
Either on or off the organization’s premises
The use of a private cloud is popular is ___ ___ industries
highly regulated
What is a Hybrid Cloud Computing Deployment Model
the cloud in this model is composed of two or more clouds, with at least one being a private cloud, that remain unique cloud entities but with technology in place that facilitates the portability of data and applications between each entity
What is a Community Cloud Computing Deployment Model
The cloud infrastructure is shared by multiple organizations to support a common interest, such as companies banding together for regulatory compliance or collaboration with industry peers
What is a CSP?
a third party that provides cloud computing services such as application delivery, hosting, or monitoring to customers and performs all maintenance and tech support on the hardware
What is multi-tenant when discussing CSPs
when CSPs service multiple cloud customers at once and use common resources and technology for all customers
information about CSPs may be found in ___ reports regarding compliance with regulations or standards
SOC 2
What are two advantages to using CSPs?
processing and storage can be rented in units of time, scaling up during peak usage times
redundancy and ability to recover from a disaster is improved
According to COSO, what are the five components for addressing an organization’s risk?
Governance and Culture
Strategy and Objective Setting
Performance
Review and Revision
Information, Communication, and Reporting
What is the Governance and Culture COSO Component?
Governance: Sets the company’s tone and reinforces the importance of having oversight of enterprise risk management
Culture: Related to the company’s target behaviors and values and involves understanding risks
What is the Strategy and Objective-Setting COSO Component?
a company’s risk appetite should be aligned with its strategy, and business objectives should be put in place to help achieve that level of appetite through identifying risk, assessing it, and responding to it
What is the Performance COSO Component?
requires that organizations prioritize their risks based on risk appetite so that business objectives are assessed, met, and reported to key stakeholders
What is the Review and Revision COSO Component?
involves reviewing a company’s performance over time and making revisions to functions when needed
What is the Information, Communication, and Reporting COSO Component?
recommends that a continual process be in place that supports sharing both internal and external information throughout the organization
How were the set of 20 COSO principles designed so that organizations of any industry, size, or type can implement them?
practical and customizable
According to COSO’s Enterprise Risk Management for Cloud Computing, an organization must integrate the governance of cloud computing into its…
overall risk management strategy
When outsourcing to a CSP, the ownership of risk…
remains with the organization
The COSO Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Framework can help organizations establish ideal ______ by applying eight components.
configurations for cloud options
What are the eight COSO ERM Framework Components for cloud configurations
Internal Environment
Objective Setting
Event Identification
Risk Assessment
Risk Response
Control Activities
Information and Communication
Monitoring
What are the risks that should be considered when evaluating CSPs and their services?
the rate of competitor adoption
being in the same risk ecosystem as the CSP and other tenants
transparency
reliability and performance
lack of application portability (vendor lock-in)
security and compliance
cyber attacks
data leakage
IT organizational change
CSP long term viability
What is an ERP
cross-functional systems that support different business functions and facilitate integration of information across departments
What advantage do ERPs have over multiple independently functioning systems?
data input is less intensive in an ERP system because a central repository is used
What is the relationship between an AIS and an ERP?
An AIS is a part of an ERP
What is an AIS?
collects, records, and stores accounting information, then compiles that information using accounting rules to report both financial and nonfinancial information to decision makers in an enterprise
What are the three main AIS subsystems
Transaction Processing System
Financial Reporting System
Management Reporting System
What does a TPS do?
converts economic events into financial transactions and distributes the information to support daily operations
What does an FRS do?
aggregates daily financial information from the TPS and other sources for infrequent events to enable timely regulatory and financial reporting
What does an MRS do?
provides internal financial information to solve day-to-day business problems
The three subsystems of an AIS collectively achieve the following five objectives:
Record valid transactions
Properly classify those transactions
Record the transactions at their correct value
Record the transactions in the correct accounting period
Properly present the transactions and related information in the financial statements
What are transaction cycles
core functions within an accounting department
In what cycle do loan payments occur?
Treasury Cycle
In what cycle would you find a Bill of Materials?
Production Cycle
In what cycle would you find a Sales Invoice?
Revenue Cycle
In what cycle would you find a Receiving Report?
Purchasing and Disbursement Cycle
Automation is an umbrella term used to describe the…
process of using technology to perform tasks without human intervention
What does Shared Services refer to?
seeking out redundant services, combining them, and then sharing those services within an organization
What is Robotic Process Automation?
a specific form of business process automation that refers to the use of programs to perform repetitive tasks that do not require skilled human labor
What does Natural Language Processing (NLP) Software involve?
the technology developed and used to encode, decode, and interpret human languages so that the technology can perform tasks, interact with other humans, or carry out comands on other technological devices
What is AI
an umbrella term used to describe systems that are created to perform complex tasks typically requiring human intelligence and judgement
What is Machine Learning
a subset of AI involving the use of algorithms and data sets supplied for somputers to learn and make decisions
What is an Artificial Neural Network?
a form of technology that is modeled after neurons that facilitate the function of human or animal memory
What does Processing Integrity refer to?
a system’s ability to initiate and complete transactions so that they are valid, accurate, completed timely, and authorized to meet a company’s objective
What are the 5 Trust Services Criteria?
Security
Availability
Processing Integrity
Confidentiality
Privacy
What is the goal of the Security TSC?
Identify transaction processing methods that compromise confidentiality, privacy, and availability, and that can be circumvented to allow unauthorized access
What is the goal of the Availability TSC?
Search for bottlenecks in the flow of data across the organization and identify other processes that prevent data from being available when needed
What is the goal of the Confidentiality TSC?
Evaluate employees and processes that handle transactions with confidential data to identify potential data leakage, mishandling, or other practices that expose confidential information
What is the goal of the Privacy TSC?
Analyze methods used to collect, store, use, and dispose of personal data that are being processed to identify the potential for data breaches or leakage
What is Blockchain?
a control system originally designed to govern the creation and distribution of Bitcoin
What is the value of blockchain
its resistance to alteration, multiparty transaction validation, and decentralized nature
What is system availability
when business data is accessible and IT systems are operating normally
The risk of normal business operations failing in part or as a whole must be evaluated and mitigated through ___
business resiliency programs
What is business resiliency?
the integration of system availability controls, disaster recovery plans, business continuity plans, and crisis management plans into a central set of procedures to consider whether a business can continue to operate or quickly return to operations without irreparable harm to its people, information, or assets