FNR201 - Lecture cards
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
172 Terms
What is research
systematic process of collecting and analyzing informaiton
process of discovering or uncovering new knowledge
fundamental basic research principles
encomapsses facts or understanding that are not ends in themselves but are compontnets in total process
based on assumptions
Good research is
based on the work of others
identify current state of knowledge
identify knowledge gaps
research agenda
activity that can be replicated
this is a mark of credible research
can help to form a basis for further work in the same area
generalizable to other settings
stand up in different but related settings
some may be difficult to generalize
based in logical rationale and tied to theory
fit into bigger pitcure
places findings into current state of knowledge
Doable
feasible (not to complicated or expensive to actually run
clear questions with a clear timeframe
able to generate new questions
give oppurtunity for further studies
Incremental
makes small contribution to larger body of knowledge
why do research?
improves understanding
allows for interpretation
determines the strength of relationships between two variables
allows for in-depth analysis (qualitative)
4 goals of research
description
explanation
prediction
control
Methodology
set of rules and procedures for how research is to be conducted
this is the experimental design of a study
methods
specific data collection and analysis techniques
analysis procedures and techniques for gathering the evidence to be used
this is more specific about what is used and what is being measured
Positivist approach to research
emphasis on control of physical and social environments
want results to operate like the natural world
used in physical sciences
quantitative and experimental knowledge
uses deduction
taking questions and finding answers
Instrumental approach
Positive approach assumptions
all behaviour is naturally determines
humans are part of the natural world
nature is orderly and regular
all objective phenomena are eventually knowable
nothing is self - evident
truth is relative
knowledge comes from experience
Interpretive approach
aims to examine how people make sense of their lives and how the social world operates
naturalistic qualitative knowledge
emphasized that humans are always in the process of becoming
values are relative and thus change over time
concerned with issues of dependability and transferability
critical approach
examines societal structures and power relations present in our world
based on reflective knowledge
values are absolute
certain values are correct while others are not
assumes all behaviour is influenced by power issues
goal is to achieve or promote social justice
Descriptive research
what is happening
census
public opinion polls
market research
Explanatory research
why does x change y
why does soluble fibre intake (x) lower cholesterol levels (y)?
Pure/basic research
goal to expand knowledge and test theories
values knowledge for its own sake
not trying to promote particular theories
value free research
Applied research
goal of the research is to solve a problem
changing health care practices
focuses on variables that can be changed by intervention to achieve desired goals
Quantitative research
quantify observations about human nature
emphasis on precice measurements and the testing of hypothesis and data analysis
single reality
large samples
deductive (hypothesis testing)
objective reality
tests theory
outcome oriented
positivist
statistical analysis
Quanlitative research
understanding how participants experience and explain their own world
ephasiz on verbal descriptions and explinations of human behaviour
multiple realities
small samples
inductive (observations → hypothesis)
reality is socially constructed
develops theory
process oriented
rich descriptions
control is not important
interpretive results
critical analysis
questions asked in quantitative research
what is the relationship between obesity and tv viewing
what is the relationship between breakfast programs and cognitive funciton
what is the relationship between exercise and fat mass
qualitative questions asked
what is is like to be overweight and obsese
how do teachers deal with students who do not follow instructions
what is it like for international students to study abroad
Deduction
top down approach
concerned with testing hypothesis
quantitative
theoretical → conceptual → operational
Induction
bottom up approach
exploratory
qualitative
operational → conceptual → theoretical
Units of analysis
individuals
focus of surveys and experiemnts
individuallevel variables
Aggregates
properties of groups (a population)
differences in health in different ethnic/national groups (epidemiology)
may not be able to apply results to each individual but this is the distribution of scores in general
What data is at the very bottom of the pyramid
expert opinions
no one cares that you are en expert
Dependent variable
effect of cause and effect relationship
influenced by other variabeles
Independent variable
influences other variables
cause in cause and effect
Control variable
variable that could influence the releationship between independent and dependent
intervening, conditional and confounding
grouped seperately cause it might have alternate effect
Intervening variable
variable that links an independent and dependent variable
represents an explination of how the independent variable influences the dependent variable
on the causal pathway
conditional variable
variable that accounts fo rthe change in the relationship between independent and dependent when the general conditions change
Confounding variable
has a possible influence on both the independent x and dependent variable y
accounts for the relationship between x and y
affects the two variables independently
can make it seem like there is a relationship where there is none in reality
defining dependent and independent variables
dependent
left alone
measured
varied at unknowl rate
effect
Independent
intentionally manipulated
controlled varied at known rate
cause
Operationalization
key is that variables must be measurable
reliable
repeatable
valid
are you measuring what you think you are measuring
Example for operalization ***
seniors appetite
should not measure meals consumed per day
cannot get valid measures because there is no setpoint for measuring meals vs appetite
Research process
identify a topic of interest
gather background information
set research questions
choose a design and methodology
develop necessary tools and methods
access sample to collect data
organize and analyze data
interpret results and define conclusions
transfer knowledge
planning research questions qual vs quant
quantitative
hypothesis and objectives
qualitative
aims and objectives
parts of planning research questions
aim: broad statement of desired outcome
hypothesis: propositon about the relationship between the tested variables
objective: steps necessary to answer the research question
What is epidemiology
research discipline involved with distribution and determinants of health related states or events in populations
distribution of health related determinants of health and disease
how often related events occur in diff groups of people
why variations in patterns of health and disease exist in different populations
application of the analysis to control health issues in populations
Epidemiology word
study upon populations
epi (among)
Demos (people)
Ology (study)
epidemiology importance
understanding the cause of disease in populations
prevention and control of disease in pops
guide health care policy and planning (policy makers)
guide management of health and disease in individuals
uses of epidemiology
monitor health care use
assess pop requirements for health care
evaluating organization of health are services
improving patientcare
generation hypothesis
monitoring regionla variations in provision of services
investigating the impact of inequality
population
large groups of ppl in defined setting
relatively unselected group of ppl
general population, hospitalzed poplation, uni pop
subpopulation - shares specific characteristics (age, race, presence of disease etc)
sample
research (epidimiologic research, clinical research) carried out in samples
selected subset of the population
representative samples
Epidemiology
concerned about populations
intersted in characteristics of a defined population
for practical reasons it is done in samples
two questions of epidemiological research
are the conclusions of the research corrects for people in the sample?
if conclusions are true, does the sample fairly represent the population of interest?
generalizability: can these findings be applied to the broader population of interest?
3 explanations of research findings
bias (systematic error)
chance (random error)
truth (observation is correct)
Bias (systematic error)
process at any stage of the research tending to produce results that depart systematically from true values
any stage of the research process can be susceptible to this error
many types of biases (selection bias, measurement bias, confounding bias, outcome assessor bias)
qual will have more bias typically
less generalizable
Examples of Bias
participants (mothers postpartum)
intervention: higher intensity exercise (a) vs lower intensity exercise (b)
outcome: weight loss at 6 months
finding: women A more successful than those in B for weight los
If A was healthier participants and b was less healthy
if there was different conditions in the gyms
Descriptive epidemiology
examines patterns and trends
studying populations wihtout trying to change them
reliance on existing data
uses surveys of large groups of people to collect information
CCHS
NPHS
NHANES - us
Descriptive studies
population characteristics
age, gender, race, SES etc
Population trends
epidemic of childhood obesity
trend increasing
Geographic factors
international comparisons
rural-urban comparisons
local comparisons
Temporal trends
longterm trends (increasing childhood obesity)
seasonal variations (distribution of suicide with rates peakingin february
cyclic variation - time series analysis of seasonal variations
point epidemics
Frequency of events
incidence and prevalence
point epidemic
an epidemic in which several cases of a disease occur within a few days or hours due to exposure to a common source of infection
legionnaires disease
mystery illnness killing seniors in nursing home (env contamination) which got into the nursing homes water system
Incidence
rate at which new events occur in a population during a specified period
number of new events in a defined population over a specified time / number of disease free people in a population at the strt of the time period
New cases/ population of area
Prevalence
number of instances of a given disease or other condition in a given population at a designated time
number of existing cases in a defined population at a given time / number of people in the defined population at the same point in time
point prevalence
measured at a single point in time for each person
eg. rate of obesity in one school at one measuring time
period prevalence
measured during a specified period of time
Correlational studies (descriptive)
compares disease frequency between different groups
mortality/morbidity rates in different countries
does not explain relationships or determine associations
cross-sectional studies
describes the frequency of particular attribute in a defines population or sample at a given point in time
provides a snapshot of the health experience for that population
measurement of prevalence or distribution of an attribute
contrasting prevalence rates can identify which populations have higher risk of disease
helpful in measuring secular trends
used as a basis for longterm followups
advantages and limits of cross sectional
advantage
quick and easy
can measure multiple exposures and outcomes at one time
useful for measuring the burden of disease
Limitations
problems with the direction of causality
recall bias
not efficient for rare diseases
not suitable for diseases with short durations
low response rates could bias prevalence estimates
Case series
describe groups with similar conditions
could describe postpartum obsessive compulsive disorder
usually suggests future study hypotheses
Analytical epidemiology
causation or etiology
to test hypothesized cause and effect relationship between suspected risk factor and a disease or condition
analytical research designs
observational
case control
cohort
experimental
clinical trials
case-control studies
group of patients who have particular outcome and a control group who do not have the outcome are compared
measure the frequency of an exposure in both groups to see if it is more or less common in one group than the other
steps for case control studies
define objective criteria for case diagnosis → selecting cases and controls → estimating exposure status
cases: clinical trials, hospital records
controls: population controls, hospital controls, relatives/friends
Advantages and disadvantages of case control
advantages
relatively quick
more efficient for rare diseases than cross sectional studies
can test multiple exposure hypothesis on single disease
Disadvantages
temporal sequence between exposure and outcome may be difficult to establish
which came first?
may be hard to obtain information about past exposures
selection of appropriate group may be difficult
Cohort studies
follow a designated group of individuals for a given period of time
study group is measured at baseline for characteristics then followed over tiem to assess the dvelopment of new events
study health related events incidence in populations
explore and generation of hypothesses
examination of natural prognosis of disease
Cohort studies advantages and disadvantages
advantages
direct measure of incidence of disease in exposed and unexposed groups
time relationship between exposure and disease can be studied
investigation of multiple outcomes can occur
natural history of disease can be investigated
Disadvantages
time consuming
expensive
outcome assessment can be influenced by knowledge exposure
information bias
too much dependence on quality of records for historical cohorts
Clinical trials
begin with 2 or more experimental conditions
follow up of groups to specified endpoints or time points
common measure: HR (hazards ratio)
Common measures in analytical epidemiological studies
RR (cohort studies)
OR (case control studies)
RR - Math
incidence of cases in the exposed /
incidence of cases in the unexposed
A/(A+B) /
C/ (C+D)
Number of new cases in those expoed vs those not exposed
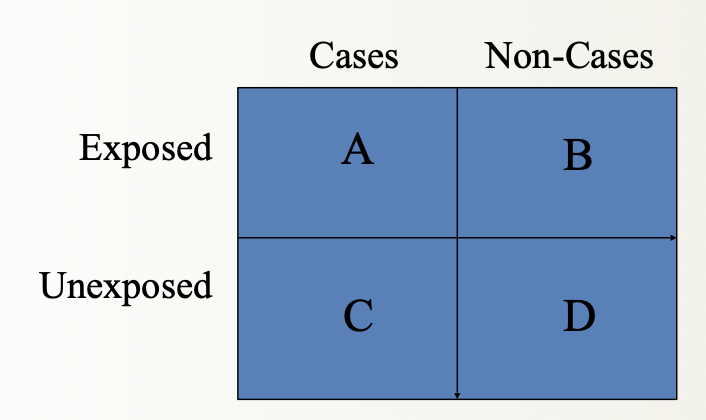
RR description
measures the odds of an outcome occuring in one group compared to another
ratio of probabilities
used in cohort studeis to measure incidence
How much more (or less) likely is the oucome in group A compared to group B
Odds ratio definition
odds of an outcome occuring in one group compared to another
a ratio of odds
used in case control studies when the outcome is rare
what are the odds of the outcome in group A relative to group B
Interpretation of odds ratio
way to compare whether the probability of a certian event is the same for two groups
an odds ratio of 1 implies thta the event is equally likely in both groups
if it is above one it means that the event is more likely in the first group
<1 means that the event is less likely in the first group compared to the second group
OR math
odds of exposure for cases /
odds of exposure for controls
A/C /
B/D
AD/
BC
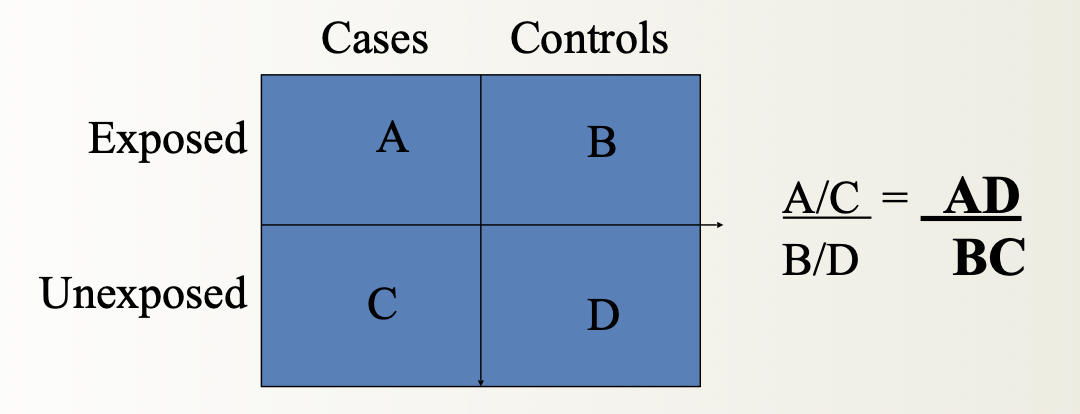
Critical appraisal
discipline for increasing the effectiveness of your reading
useful tools for
systematically evaluating scientific literature
sifting the good from the bad when results are conflicting
breaking down barriers between research and practice
filtering out original research
critical apprasal of quantitative research
ask yourself about
message
what were findings
what is the bottom line of this research
Validity
did trial address clearly focussed issue or question
how was sample selected? power analysis?
were groups similar at baseline?
Generalizability
can these be applied to a laeger populaitons?
were all possible outcomes considered?
do benefits outweigh th ecosts/harms?
also condiser the declaration of outside interests, ethics and use of literature review
Appraisal of reviews
message
does review set out to answer a specific question
validity
have authors sought out the correct studies
was there explicit inclusion and exclusion criteria
how were results presented
generalizability
if results are consistent across studies (even with different demographics) then results are generalizable
Qualitative study appraisal
authors must demonstrate
clear study aims
choice of appropriate methodology
justification for who was included and who was not
what is relationship between researcher and researched
Non-reactive studies
participant is unaware that they are beign studies
has no opportunity to react to researcher
use of information from stats canada to emasure food insecurity
Non-reactive study research designs
comparative studies
secondary data analysis
content analysis
observational field studies
comparative studies
examine similarities and differences between groups
cross-cultural research
Challenges:
hard to confirm equivalence of data
what if japan and canada use different scales to measure food security in each country
hard to confirm Equivalence of concepts
some cultures will have different meanings of ideas
even within cultures
equivalence of indivators
measurement of appitite as an indicator of nutritional status
hard to measure as there is no official definition
need to operationally define this indicator
use of a proxy
questionaires may be the best way but then they must confirm that the two palces conducting studies are measuring variables in similar ways
selecting evidence
ensuring the evidence upon which comparisons are based is equivalent between groups
Sampling
ensurign that the selection of analysis units is careful so that meaningful comparisons can be made
Language
make sure that data is collected in different languages is still equivalent
Secondary data analysis
analysis of published material
analysis of data which was collected by others
strengths and limits of secondary data analysis
cost effective
limitations:
missing or incomplete information
can only analyze the data whcih is available
you do not get to determine what to analyze
Content analysis
technique for making inferences by objectively and systematically identifying specified characteristics of messages
Textual analysis
compare contrast and categorize data
Data: written, visual, verbal
qualitative and quantitative
Data analysis
categorizing data
interpretive
counting frequencies
Basic descisions of content analysis
unit of analysis
how are units selected
what is measured and how
how is information going to be recorded
coefficient of reliability - asses similarity and differences among raters
how is informtion analyzed
Observational field studies
field experiments
no interaction with participants
how many ppl run stop signs?
Methodologies for qualitative research
ethnography
grounded theory
phenomenology
Ethnography
generatign cultural or contextual description
consideration of the values and practices of cultural group
studies behaviour of culture sharing group
learn from people rather than studying them
Grounded theory
exploration of social processes
generation of explinations
consideration of experiences over time
generation of theory grounded in data
Phenomenology
study of phenomena
focuses on the meanign attached to lived experiences
purpose is to describe the essence of lived experiences
provides rich descriptions
meaning of a concept or phenomenon
Reflexivity
researchers position and background can effect
what they choose to study
how they choose to study it
most appropriate methods
interpretation or framing of results
recognize that all knowledge is partial and situated
qualitative data collection
participant observation
in-depth interviews
focus groups
Participant observation
researcher is an active participant
gains entery and builds rapport with the group
data collection: field notes, memos, reflective notes
reporting: descriptive narrative with attention to context
exiting the field in a way that does not abandon the subjects of the study
In depth interviews
interview guide
emergent design
one on one or groups
verbatum interview transcripts for analysis
objective rich descriptions of phenomenon from participant perspectives
Focus groups
roots in 40s, marketing in the 70s, academics in the 80s
Researcher is group facilitator
6-12 participants
group dynamic encourages discussions of issues that would not be raised in 1-1 interviews
collection of data from audio, video, notes etc
Strengths and limits of focus groups
strengths
group dynamic
understanding process of dealign wiht issues
pilot work (needs assessment studies)
cost effective vs 1-1 interviews
Limitations
influence of the group dynamic
dominant voice over quiet or shy participants
not generalizable
Qualitative data analysis
code: apply conceptial label to event, action or intervention
identification of patterns: cluster codes
identification of themes: things that stand out, have evidence from data, confirmed by several participants
Ethnograph - data analysis software
computer program to import text qualitative data
helps to search note segments or interests within data
marks them with code words so they can be retrieved for inclusion in reports or further analysis
Heierarchy of evidence based medicine
systematic reviews are at the top
then RCT
Bottom is expert opinions and case/time series
SLR process
systematic search
critical appraisal
synthesis of the literature
Systematic search
identify a topic
develop clear primary research question
can include intervention, population of interest, outcomes and a time reference
clear question should be searchable
Establish study selection criteria
inclusion and exclusion (type of intervention, population etc)
formal literature search strategy
online databases must be selected (done in duplicate by 2 researchers)
document formal search strategy
list online databases that are searched
terms used
results retrieved
date searches were completed
Critical reading
highlight the main steps of research process
record questions
record key study variables
highlight new terms and significant sentences
definitions of unfamiliar terms
Critical appraisal
appraise the article by assessing the scientific quality of the paper
included its design, methods and analysis
10 criteria for appraising research studies
review of previous research
how closely is literature cited in the study related to previous research
how recent is the review
are there key findings that you are aware of that ahve been omitted?
problem and purpose
is it clear? tied to reviewed literature?
hypothesis
clear and testable?
method/study design
variables defined
operationalized
methods transparent?
Sample population
who is in the sample?
is it clear where the sampel came from?
how were they selected?
Results
are they consistent with study question?
discussion
link to initial hypothesis?
mention limitations?
Significant findings
are the results meaningful
References
overarching evaluation