Lesson 11: Echinodermata (and Deuterostome)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Deuterostomia vs. Protosotmia
bilateria → deuterostome rather than protostome
main differences
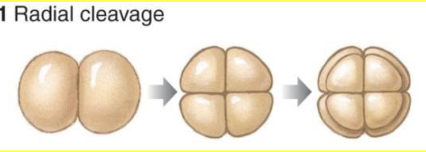
radial cleavage
regulative embryo
blastopore becomes anus, mouth forms secondarily
coelom forms by outpocketing (enterocoelous)
Deuterostome Radial Cleavage
radial four cell embryo cleavage (cut in half, and in half again) compared to the protostome spiral cleavage of the embryo
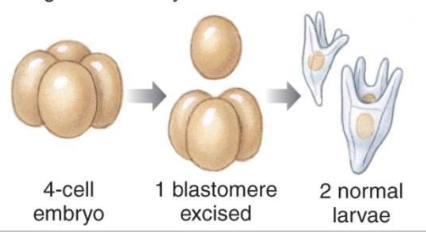
Deuterostome Regulative Embryogenesis
regulative (indeterminate)
4 cell radial cleaved embryo excises one blastomere, to create 2 normal larvae
Deuterostome Fate of Blastopore
blastopore envaginates to form the anus initially
mouth forms secondarily
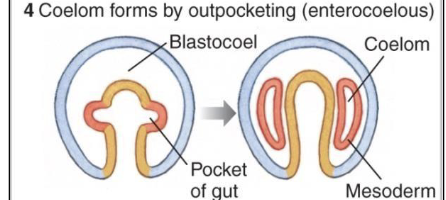
Deuterostome Enterocoelous
outpocketing
coelom forms by outpocketing
Deuterostomia DIvision
Ambulacraria or Chordata
Ambulacraria divides into Echinodermata or Hemichordata
Deuterostome Groups
Ambulacraria
Echinodermata
Hemichordata
Enteropneusta
Pterobranchia
Chordata
Echinodermata
“spiny skin”
exclusively marine
lack cephalization
loss of gill slits
5 unique features:
pentaradial symmetry in adults
calcareous endoskeleton
water vascular system
pedicellariae
dermal branchiae (papulae)
class:
asteroidea
ophiuroidea
echinoidea
holothuroidea
crinoidea
Pentaradial Symmetry
from a bilateral ancestor
mouth side= oral
opposite of mouth= aboral
Madreporite
a perforated plate by which the entry of seawater into the vascular system of an echinoderm is controlled.
Calcareous Endoskeleton
mesodermal porous endoskeleton
meshwork of ossicles form the stereom
connected by mutable “catch collagen”
therefore, can change from liquid to solid
Water Vascular System
hydraulic fluid system
canals and tube feet
only open on one end
specialized coelomic system
functions:
respiration
excretion
locomotion
feeding
medreporite → stone canal → ring canal → radial canal → lateral canal → ampullae → podia (tube feet)
Ambulacra
bands from which tube feet project within Echinodermata
singlular: ambulacrum
Pedicellariae
usually on aboral surfaces (all around in sea urchins)
functions:
cleaning
food capture
defense
Dermal Branchiae (Papulae)
also called skin gills
projections of thin walled coelom
Basic Internal Characteristics
nervous system
no brain or ganglia
nerve ring, radial nerves, and epidermal nerve net
sensory cells; eyespots at the tip of arms
digestive system
feeding mode varies (carnivores, scavengers, herbivores, deposit feeders, suspension feeders)
reproduction
often separate sexes with external fertilization
Larval Development
deuterostome embryology
coloem forms via outpocketing
anus forms before mouth
radial cleavage
regulative
bilateral free-swimming larvae
left side becomes the oral surface
right side becomes the aboral surface
tube feet
metamorphosis to adult form
Regeneration
only need 1/5th of the central disk and 1 arm
able to deliberately shed body parts of appendages
autotomy
used as an escape response to predators, or as a means of replacing infected or damaged appendages
in some cases, fragmentation not regeneration
Linckia
Asteroidea
class of phylum Echinodermata
star form
poster echinoderm
central disc + 5, 7, or 50 arms
two part stomach
can evert cardiac stomach
scavengers and carnivores
can also suspension feed
keystone species
purple intertidal seastar (controls BC mussel populations)
reef seastar
some can be deadly
crown of thorns
pacific sunflower seastar
Seastar Wasting Disease
white lesions form, and water vascular system stops working
leads to fragmentation, and death
associated with warmer temperatures and densovirus
Ophinuroidea
class of phylum echinodermata
“like a serpent”
abundant and can form huge carpets
move with flexible, articulated arms
closed ambulacral grooves
tube feet for feeding, no suckers
no pedicellariae, papulae, or anus
madreporite on oral side
organs inside central disc
cryptic
move away from light
fragile, with remarkable regeneration
Echinoidea
class of phylum Echinodermata
sea urchins, sand dollars, heart urchins
compact body within a test
ossicles as fused plates
some secondarily bilateral
5 ambulacra extends up and around towards anus (aboral)
no arms
tube feet for locomotion with assist from spines in socket joints
short spines on sand dollars
many with venomous pedicellariae (3 jaws)
mostly herbivorous
aristotle’s lantern with 5 teeth
sand dollars deposit feeders
Ecological Impacts of Echinoidea
kelp forest destruction leads to an urchin barren environment
effects surrounding wildlife: otter, etc.
Holothuroidea
sea cucumbers
elongated oral-aboral axis
secondarily bilateral
reduced ossicles
ventral tube feet specialized for locomotion on sole
no arms
benthic crawlers (however, few pelagic species exist)
burrowers, therefore no tube feet. circular and longitudinal muscles instead
oral tentacles are modified tube feet for suspension or deposit feeding
important nutrient cyclers
cloaca
spacious coelomic cavity
hydrostatic skeleton
Cloaca
all purpose orifice via anus of holothuroidea
respiration and excretion
respiration via respiratory tree
amazing self-defence
evisceration of cuvierian tubules
Crinoidea
class of phylum echinodermata
stalk with cirri attached to aboral side of calyx with many arms that branch into pinnules
can move, crawl, sweep, or swim via cirri or feathery arms
sea lillies
flower shaped on top of stalk attached to substrate
feather stars
short stalk with many branched arms
no pedicellariae, spines or madreporite
mouth and anus on oral side
many in deep water
Hemichordata
gill slits
once included in chordates, but notochord is not homologous with the chordate notochord
3 part coelom
2 classes
Enteropneusta
Pterobranchia
Enteropneusta
class of phylum hemichordata
acorn worms
solitary, exclusively marine
deposit and suspension feeders via mucus on proboscis
Pterobranchia
class of phylum hemichordata
small, tube dwelling mostly colonial
suspension feeders via crown of tentacles with coelomic extensions
convergent with the lophophore
Echinodermata Organization
Echinodermata Symmetry
Echinodermata Body Cavity
Echinodermata Development
Echinodermata Segmentation
Hemichordata Organization
Hemichordata Symmetry
Hemichordata Body Cavity
Hemichordata Development
Hemichordata Segmentation