biological molecules
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
monomers
small single units that create bigger molecules
polymers
made up of many monomers bonded together
condensation reaction
removal of a water molecule from monomers enables a chemical bond to form (between 2 monomers)
hydrolysis reaction
water molecule added between 2 monomers to break the chemical bond
name the 3 monomers and their polymers
nucleotides → polynucleotide
monosaccharides (glucose) → polysaccharides (starch)
amino acids → polypeptides (proteins)
function of carbohydrates
provide energy and structural support to plant cells
name the 3 monosaccharides and their disaccharides they make
glucose + glucose → maltose
glucose + fructose → sucrose
glucose + galactose → lactose
property & function of monosaccharides
sugars and soluble in water
provide energy or act as building blocks for large molecules
what do all carbohydrates contain
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
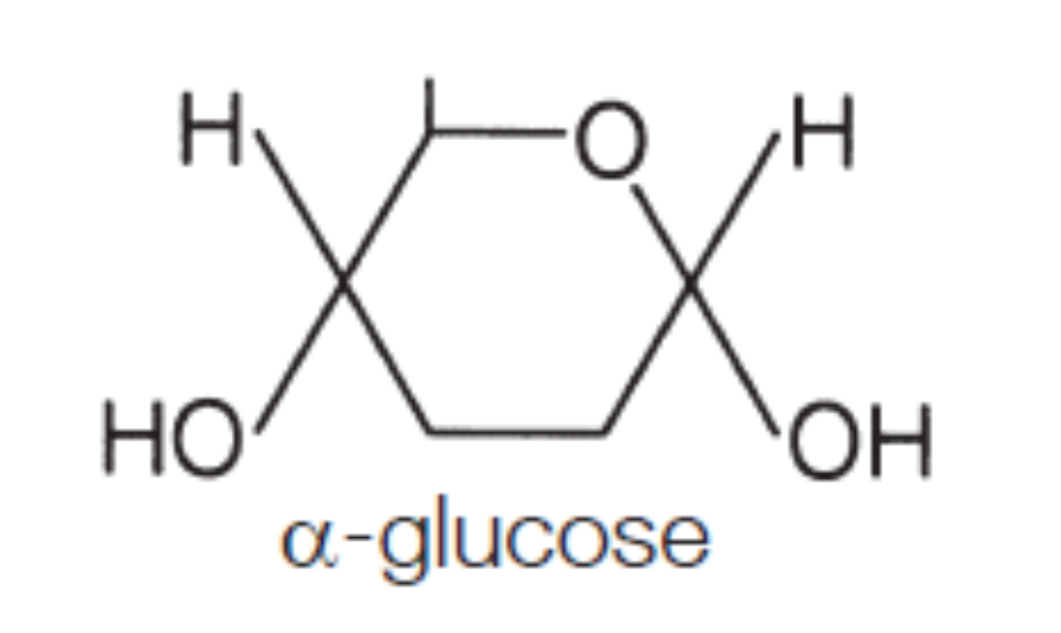
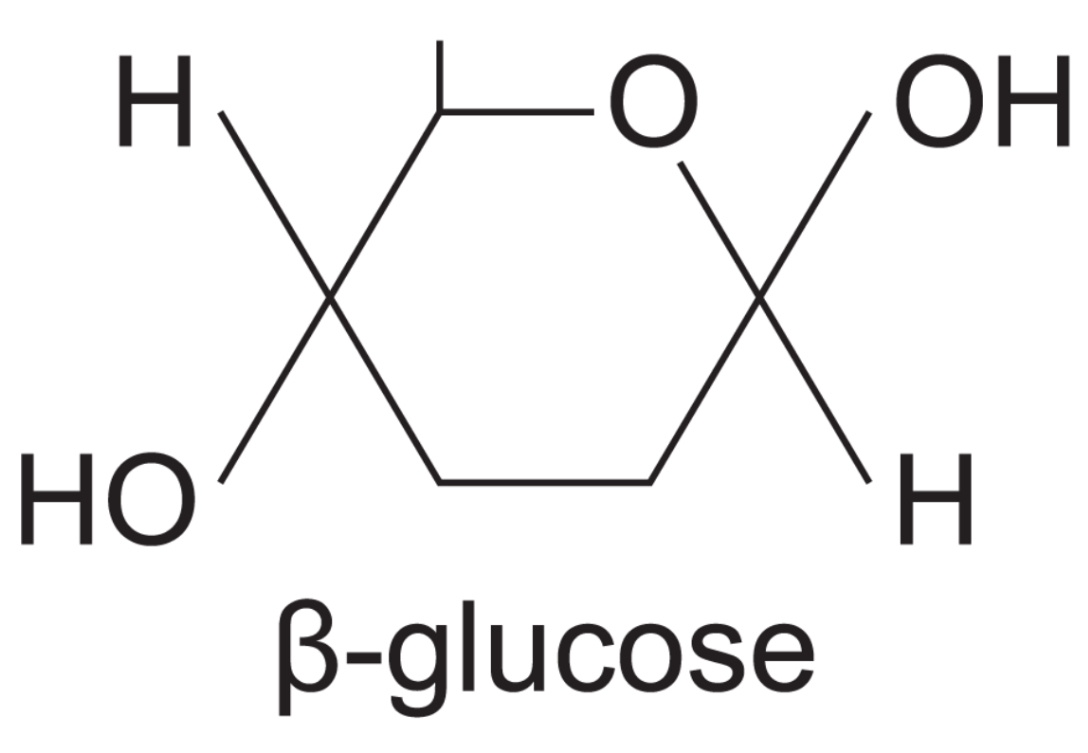
2 isomers of glucose
alpha glucose & beta glucose
alpha glucose
OH group on bottom
beta glucose
OH group on top
what are disaccharides
2 monosaccharides bonded together by glycosidic bond (condensation reaction)
what are polysaccharides
polymers made up of many monosaccharides
made by condensation reactions
3 main polysaccharides
starch, glycogen, cellulose
starch
found in plants, NOT animal cells & is energy store
made from excess glucose from photosynthesis & converted into starch for storage
structure of starch
alpha glucose
joined via condensation reactions
held by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
2 polymers that make up starch
amylose and amylopectin
amylose structure
coiled shape, joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds
amylopectin structure
1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds, branched structure (due to 1,6)
properties of starch (inc. amylose & amylopectin)
insoluble, can be stored within cell and not dissolve & won’t change water potential of cell and osmosis won’t occur
amylose; spiral shaped so compacted
amylopectin; branched so large surface area for enzymes to attach to
starch is readily hydrolysed back into glucose when plant cells running low on glucose for respiration