Overview of the Innate Immune System
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Immunity
Ability to ward off disease
Susceptibility
Vulnerability to a disease
Innate Immunity
Generalized defenses against all pathogens
Adaptive Immunity
Specialized defenses against a specific pathogen
Antigen
A compound that induces an immune response
Antibody
Immuno-protein that binds an antigen
Cytokine
Small proteins involved with short ranged cell signaling
Chemokine
A cytokine that directs cell movement
First line of defense
Intact skin, mucous membranes and their secretions, normal microbiota (barriers)
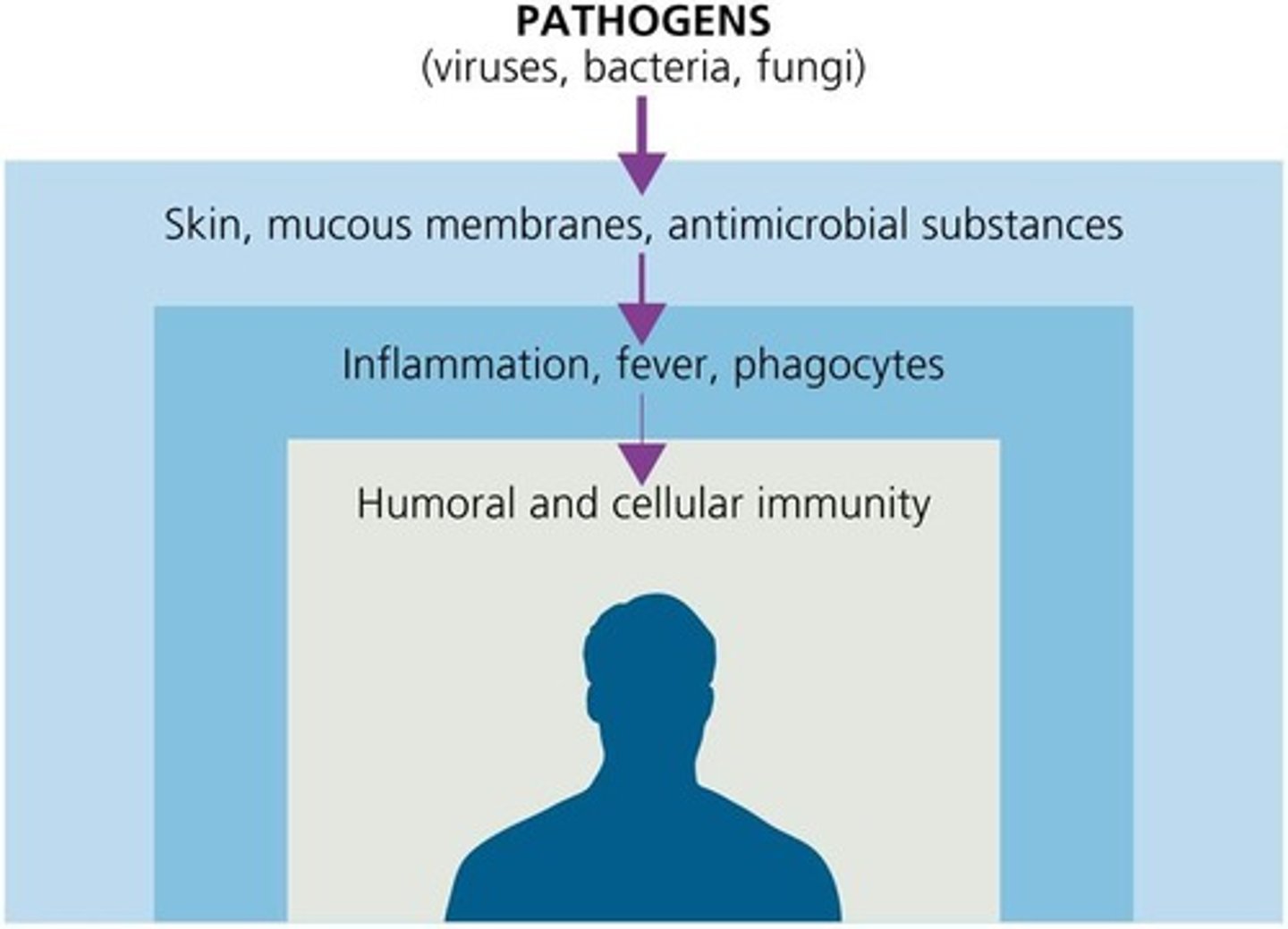
Second line of defense (first responders)
Phagocytes, such as neutrophils, eosinophils, dendritic cells, and macrophages, inflammation, fever, antimicrobial substances
Third line of defense
Specialized lymphocytes: T cells and B cells, antibodies (adaptive immunity)
Physical Factors
Skin, mucosal membranes and washing action
Chemical Factors
Sebum, wax, low pH, enzymes and gastric juice
Normal Microbiota
Presence of normal microbiota inhibits pathogens by competing for nutrients, producing bacteriocins, altering the environment
Skin
Largest organ of the body; outer most layer composed of dead keratinized cells, high salt concentration, A pH3-5
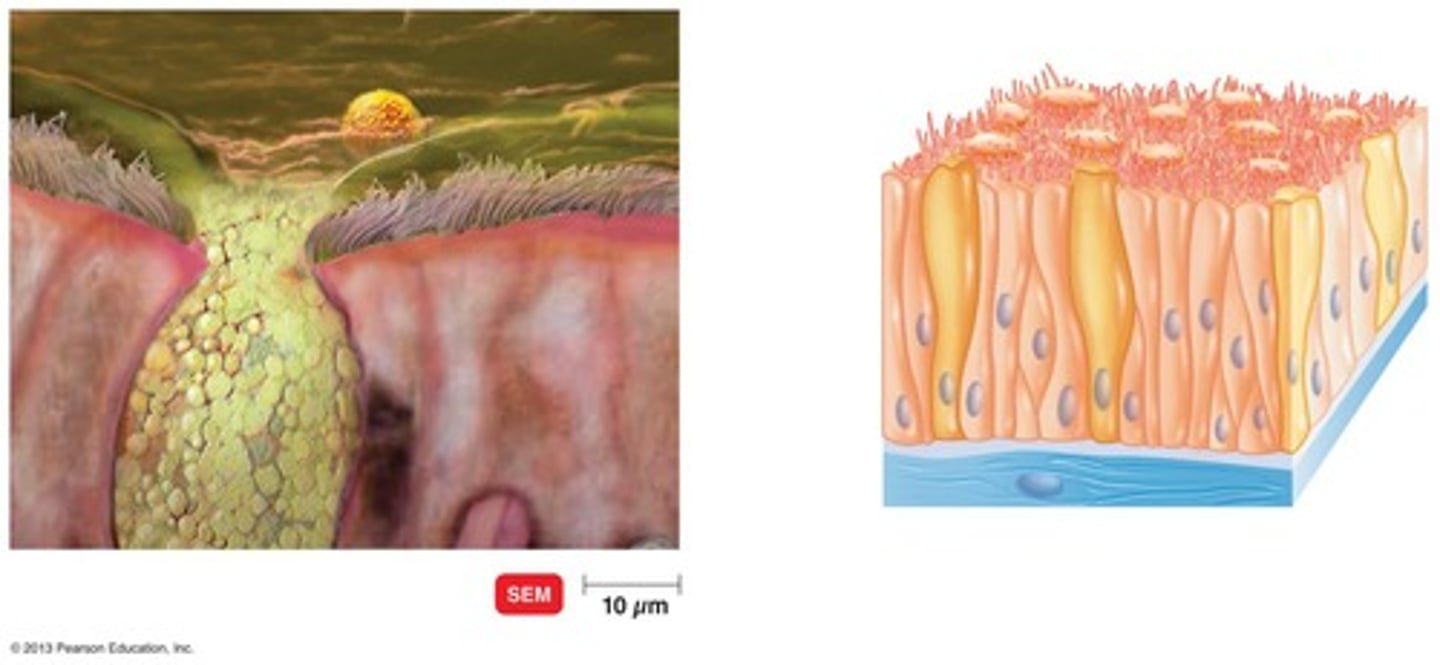
Mucosal Membranes
Found in respiratory, gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts
Goblet cells
Specialized cells that secrete mucus (glycoprotein)
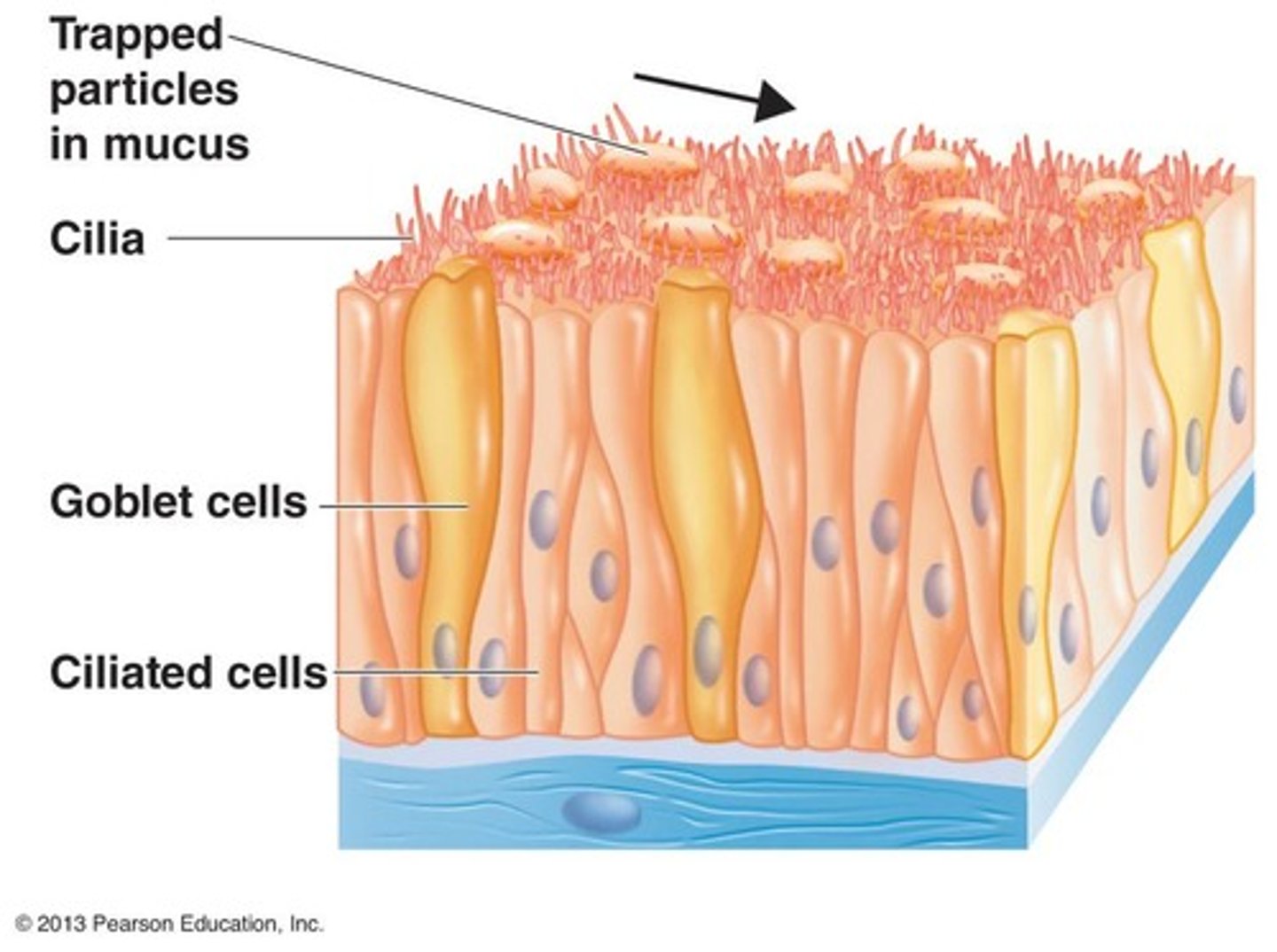
Ciliary Escalator
Ciliated cells transport mucus
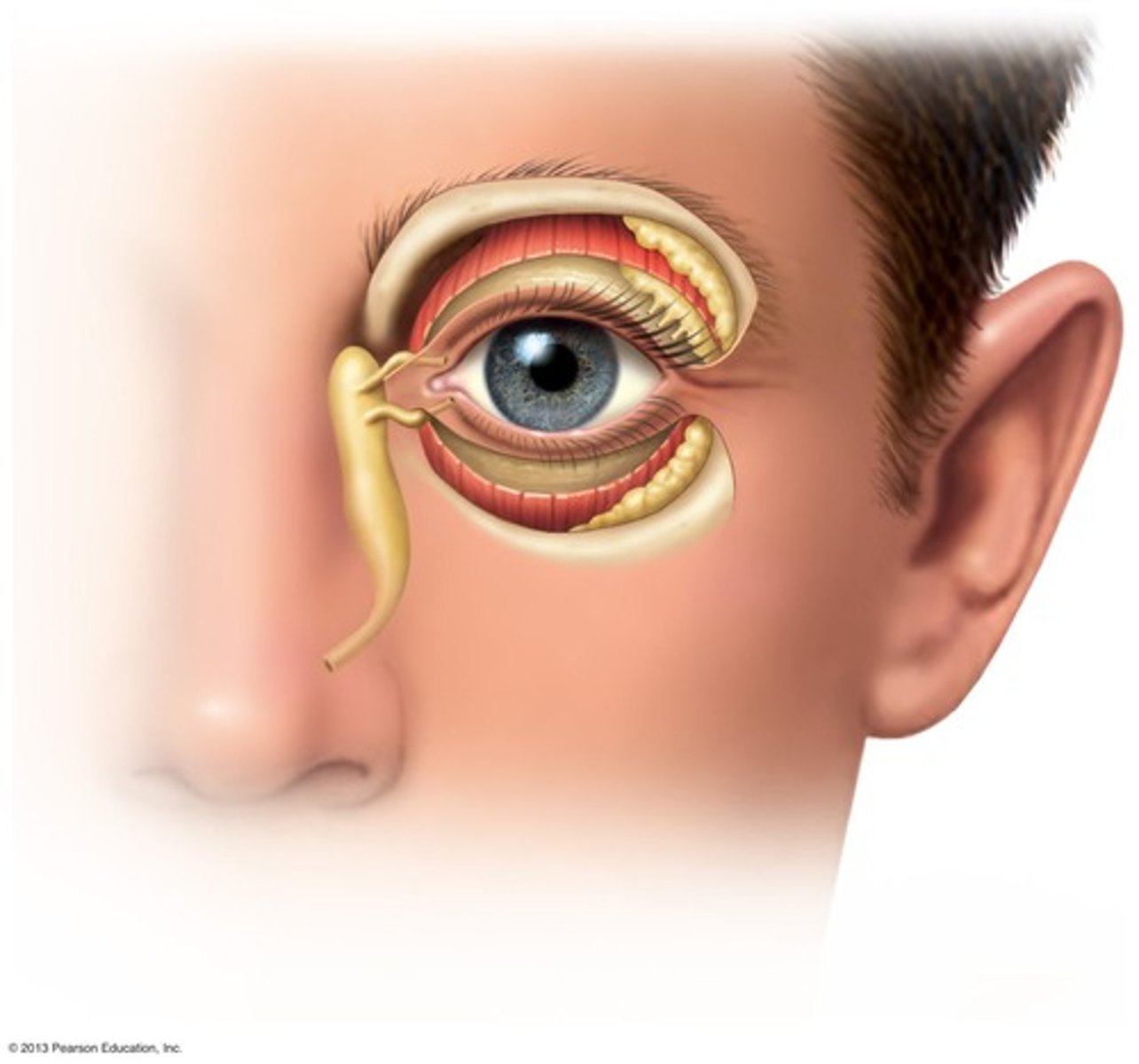
Lacrimal Apparatus
Continually washes away microbes and debris; ex) urination, defecation, vomiting
Lysozyme
Breaks down peptidoglycan of cell wall, found in mucosal layers, saliva, tears, perspiration
Amylase
Enzyme in saliva that breaks down starches
IgA
inhibits bacterial attachment
Lowering pH of skin or mucosal membranes
May lead to opportunistic infections
blood
consists plasma and formed elements (cells and cells fragments including erthyrocytes, platelets, and leukocytes)
Leukocytes
White blood cells
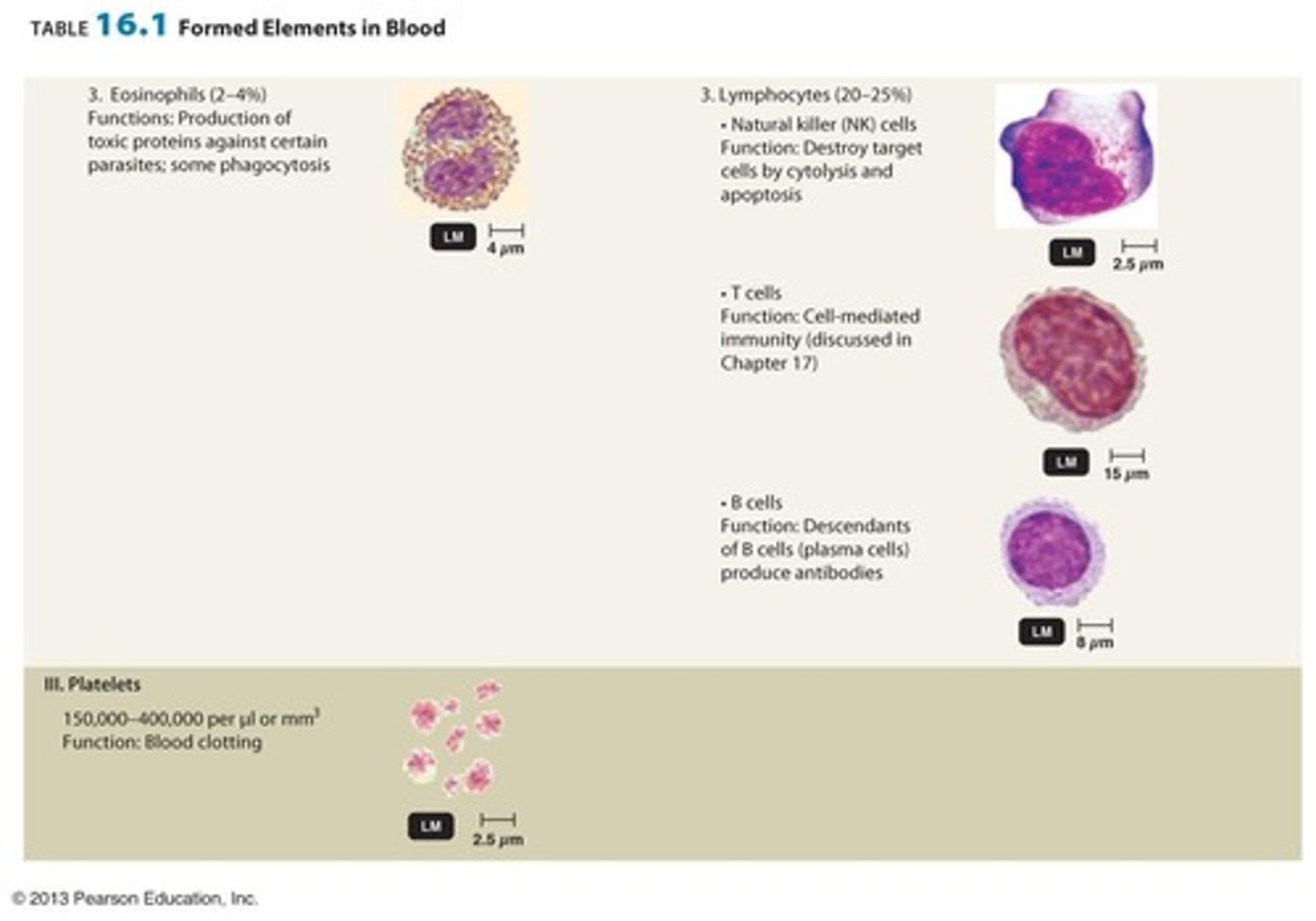
Granulocytes Include
Neutrophils, Basophils and Eosinophils
Eosinophils
Produce toxic proteins which are good at taking them out, 3%, dark pink to orange granules, 3x bigger than red blood cells, bi lobe nucleus
Neutrophils
Phagocytosis, most common white cell 70%, has 4-5 multi cat poop lobe nucleus, dark blue granules, 2x size of blood cells
Basophils
Release histamine, least common< 1%, dark purple granules, bi(2) lobe nucleus, small (about the size of red blood cell),
Sometimes lobes are not visible due to the granules
Granulocytes
contain visible granules when theyre stained
Agranulocytes Include
Monocytes (Macrophages, Dendritic cells) & Lymphocytes (T-cells, B-cells & Natural killer cells)
Natural killer cells
kills cancer cells and virus infected cells
B-cells
recognizes antigens and produces antibodies
T-cells
play a central role in cell-mediated immunity, mature in the thymus and help the immune system identify and destroy infected or abnormal cells.
T cells consist of
memory t cells, regulatory t cells, helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells
Lymphocytes
natural killer cells , second most common, 20%, have large nucleus,
Contain B&T natural killer cells
Cytolysis
the breaking or bursting (lysis) of a cell
Dendritic cells
Foster communication system between innate and adaptive system
Monocytes
phagocytosis, kidney bean shape, 3-5%
Agranulocytes
do not contain visible cytoplasmic granules (but are present)
Lymphatic System
Defense against infection and disease
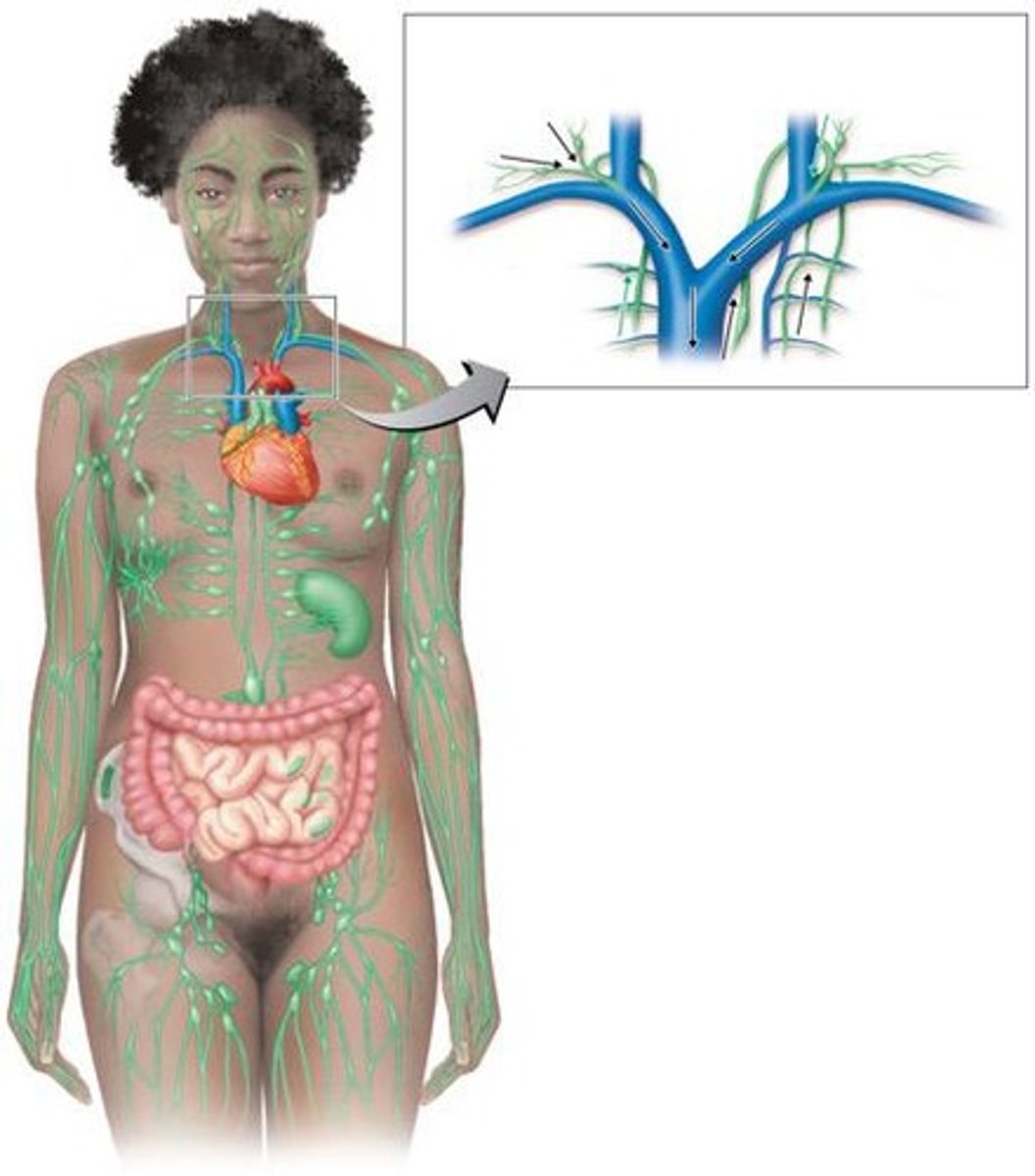
lymphatic system steps
1. Collects fluid from tissues (called lymph) that leaks out of blood vessels.
2. Lymph enters tiny tubes called lymphatic capillaries.
3. Lymph flows through bigger lymph vessels.
4. Passes through lymph nodes, where germs and bad stuff are filtered out.
5. Lymph drains into large lymphatic ducts.
6. Finally, lymph joins the bloodstream near the heart through veins.
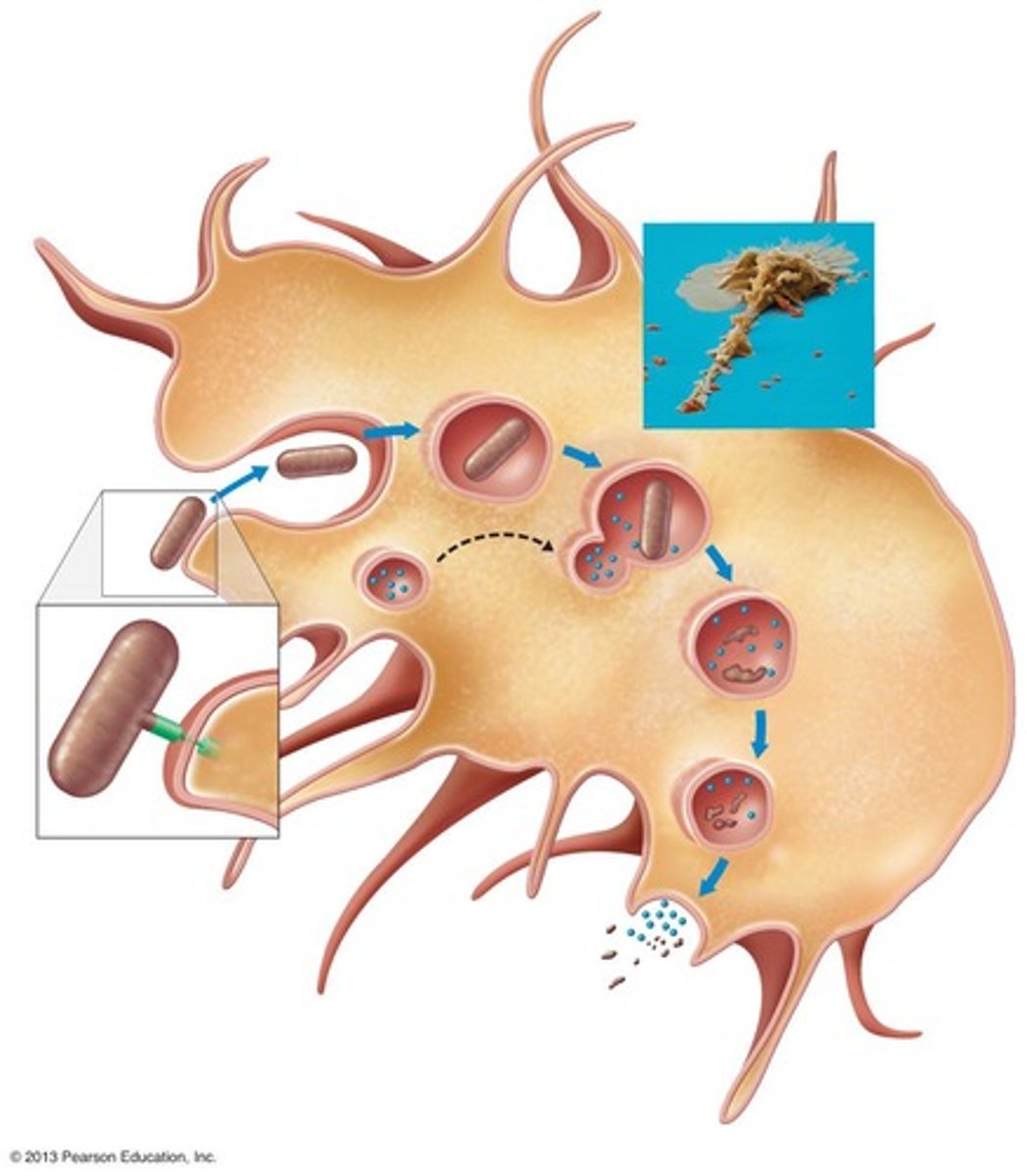
Phagocytosis
Ingestion and destruction of foreign material by cells such as Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Dendritic cells and especially Macrophages
lymph nodes
Bean-shaped filters that cluster along the lymphatic vessels of the body. They function as a cleanser of lymph as wells as a site of T and B cell activation
lymph node pathway
•Enters via afferent lymphatic vessels
-Encounters nodules, Immune cells (like B and T cells) check the lymph for germs or harmful stuff.
•Exits via efferent lymphatic vessels
PAMPs
Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns -special markers found on germs immune system sees as red flags to start fighting infection.
PRRs
Pattern Recognition Receptors -like security sensors in immune cells. They detect danger signs (PAMPs) on germs and alert the immune system to fight back.
Chemotaxis
Movement of phagocytes towards the site of infection
Adherence
Binding of phagocyte to microbe
Phagosome
Phagocytic vesicle formed during phagocytosis
Phagolysosome
Fusion of phagosome with a lysosome
Digestive enzymes
Include lysozyme, lipases, proteases, nucleases, and reactive oxygen species generated by oxidative burst
Oxidative Burst
Process where NADPH oxidase produces superoxide to kill bacteria
Superoxide dismutase
Converts superoxide to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
NADPH oxidase
Uses electron from NADPH to produce superoxide (O2•)
Residual body
Contains indigestible material after digestion in phagolysosome
Discharge of waste materials
Final step in phagocytosis where waste is expelled from the cell
Streptococcus pyogenes
Bacterium known for evasion of phagocytosis
Capsules & M proteins
Inhibit adherence of pathogens. (streptococcus progenes, S. pneumoniae)
Leukocidins
Kill phagocytes.
Membrane attack complex
Lyses phagocytes.
Shigella & Rickettsia
Escapes phagosome.
HIV & Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Prevents phagosome-lysosome fusion.
Coxiella burnettii
Survives in phagolysosome.
Inflammation
Nonspecific response to tissue injury caused by pathogen/physical trauma.
Cardinal signs of inflammation
Redness (rubor), Warmth (calor), Pain (dolor), Swelling (tumor), Altered function (functio laesa).
Cytokines in inflammation
Regulate and initiate inflammation
results of inflammation being initiated
increases capillary dilation, blood flow, expression of adhesion molecules, and development of fibrin clot to restrict pathogen movement
Histamine
Causes vasodilation and increased permeability of blood vessels.
Kinins
Cause vasodilation and increased permeability of blood vessels.
Prostaglandins
Intensify histamine and kinin effect.
Leukotrienes
Increase permeability of blood vessels and phagocytic attachment.
pathway of inflammation being initiated
injury or infection → chemicals released → blood vessels widen and leak → immune cells arrive → white blood cells cleanup to help heal tissue → inflammation signs appear
diapedesis
the passage of blood cells through the intact walls of the capillaries, typically accompanying inflammation.
Fever
Abnormally high body temperature as a systemic response to infection.
hypothalamus
regulates body temperature at 37'C, may release prostaglandins to raise temp
Interleukin-1 (IL-1)
Released by phagocytes in response to gram-negative endotoxins. causes fever
increased body temperature
increases production of t cells and transferrins, Intensifies effects of antiviral interferons, May inhibit bacterial enzymes (metabolism), Aid in tissue repair
Transferrins
Decrease availability of free iron in the body.
Complement System
30+ serum proteins that defend against bacterial infection and enhance antibody responses. (bridge between innate&adap) -dispose of wastes
mechanisms of action for complement system
opsonization, inflammation, cytolysis
Opsonization
Coating of microbe with serum components to enhance recognition and phagocytosis. (works in conjunction with antibodies)
Cytolysis
Puncture cell membranes causing cell lysis. (membrane attack complex)
C3
Inactivated C3 splits into activated C3a and C3b.
C5a
calls phagocytes to the infection site, helping the body clear out pathogens efficiently.
complement system steps
1. activation of complement proteins
2. C3 splits into C3a (calls immune cells -inflammation) and C3b (sticks to germs -opsonization).
3. C3b helps cut C5 into C5a (another inflammation booster and immune cell attractant) and C5b (starts the formation of a special complex)
4. C5b & other complement proteins help build a hole-making complex (MAC) that bursts the germ and kill it
5. C3a and C5a cause blood vessels to become leaky and attract immune cells like neutrophils and macrophages. (chemotaxis) and clean up everything
Classical Complement Pathway steps
1. Antibodies bind to a pathogen (bacteria, virus).
2. C1 complex binds to the antibodies on the pathogen.
3. C1 activates the inactives C2 and C4, which both split and join C2a & C4b to form C3 convertase.
4. C3 convertase splits C3 into C3a (causes inflammation) & C3b (sticks to the pathogen, tagging it).
5. C3b helps form C5 convertase, which splits C5 into: C5a (attracts immune cells, causes inflammation) & C5b (starts forming the Membrane Attack Complex).
6. C5b binds to C6, forming the C5b6 complex (stabilizing it)
7. C5b, C6, C7, and C8 bind together sequentially and
insert into the microbial plasma membrane, where they function as a receptor to attract a C9 fragment;
8. C9 fragments are added to form a channel. Together, C5b through C8 and the multiple C9 fragments form the
membrane attack complex, resulting in cytolysis. (MAC)
9. Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) forms and creates holes in the pathogen, killing it.
Mast cell
A type of immune cell that releases histamine during allergic reactions.
C3a
A fragment that promotes inflammation and attracts immune cells.
Membrane attack complex (MAC)
A structure formed by C5b, C6, C7, C8, and multiple C9 fragments that disrupts microbial membranes.
Classical Pathway
A complement activation pathway (innate) initiated by antigen-antibody complexes. (adaptive)
Alternative Pathway
A complement activation pathway that does not require antibodies.
Lipid-carbohydrate complex
A structure on the surface of microbes that can activate the alternative pathway.
Lectin Pathway
A complement activation pathway initiated by lectin binding to carbohydrates on microbes.
Interferons
Cytokines produced by macrophages and lymphocytes that are effective against viral infections.
Antiviral Proteins (AVPs)
Proteins that degrade viral mRNA and inhibit protein synthesis to combat viral infections.
Iron-Binding Proteins
Proteins that sequester free iron to limit its availability to pathogens.
Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs)
Short polypeptides that have a broad spectrum of activity against various pathogens.
mode of action for Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs)
inhibition of cell wall synthesis, damage to cytoplasmic membrane, attacking a pathogens DNA/RNA