lecture 2a: nervous system
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
2 NS division
CNS and PNS
CNS
brain and spinal cord
PNS
nerves/ganglion
2 divisions: afferent and efferent
afferent (sensory) division of PNS
detects stimuli and transmits information from receptors TO CNS (brain)
2 divisions: somatic and visceral
somatic sensory
sensory input that is consciously perceived from receptors (skin, eyes, ears)
division of afferent peripheral
visceral sensory
sensory input that is not consciously perceived from blood vessels and internal organs (heart)
division of afferent peripheral
efferent (motor) nervous system
initiates and transmits information FROM the CNS to the effectors (body/organ, etc.)
away from brain - to effectors)
division of PNS
somatic motor
motor output that is consciously or voluntarily controlled; effector is skeletal muscle
division of efferent peripheral
visceral motor
motor output that is not consciously or involuntarily controlled; effectors are cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands.
nucleus
aggregation of dendrites and nerve cell bodies in CNS
(like ganglion but in CNS)
ganglion
aggregation of dendrites and nerve cell bodies in PNS
like nucleus but in PNS
some ONLY have cell body
tract
bundle of fibers (axons in CNS)
like nerve but in CNS
imbedded in the spinal cord
nerve
bundle of fibers (axons) in the PNS
like tract but in PNS
commissure
tract in the CNS that crosses from one side to the other (white vs grey)
white matter
areas of myelinated axons
myelinated = highly conductive
grey matter
area of unmyelinated axons, cell bodies, and dendrites
not that schwann cells aren’t involved, they’re giving a side hug
white vs grey matter
in white, schwann cells are bear hugging - wrapped around axon
in grey, schwann are just side hugging
axon hillock
tac guy, info coming in can be exiting or inhibiting
adding up information to see if we’re making a response or not
neurolemmocyte
AKA schwann cell
neurofibril node
AKA node of ranvier: exposed axon (between schwann/neurolemmocyte)
synaptic cleft
space that defines pre-vs-post synaptic
postsynaptic neuron
could be a neuron/muscle/gland, etc.
has receptors for whatever neurotransmitter is there
telodendria
synaptic terminals
how are neuron types classified
by # of extensions coming off of cell body
multipolar neruron
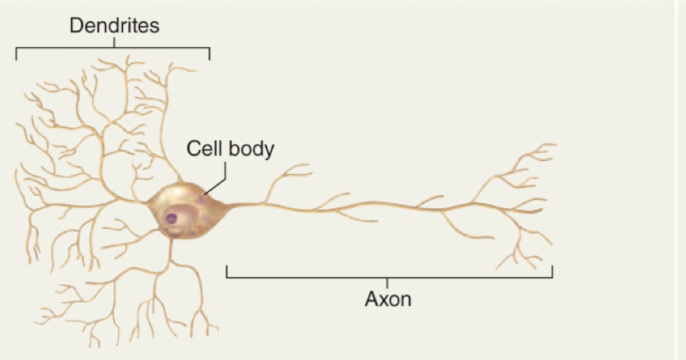
many extensions coming off of the cell body
typically many dendrites and one axon
efferent neurons and interneurons
bipolar neuron
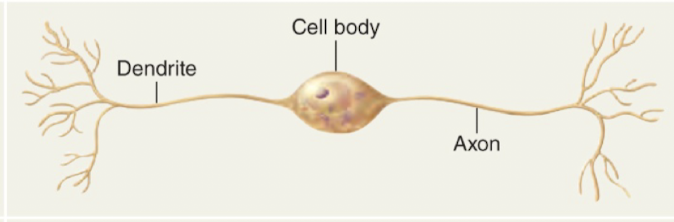
two nerve cell processes extend directly from the cell body: one dendrite and one axon
only in special senses: eyes, ears, nose
unipolar neuron
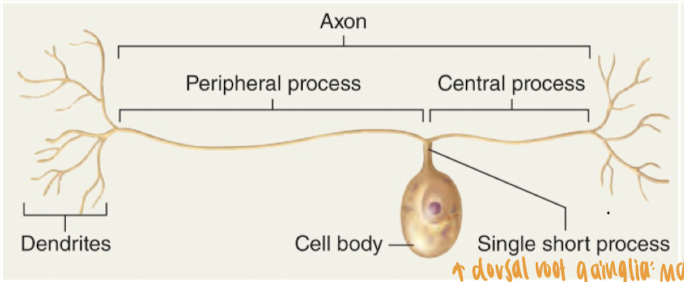
single short cell process extends directly from the cell and looks like a T as a result of the fusion of two processes into one long axon
99% fo sensory (afferent) neurons
dorsal root ganglia: many of these cell bodies
anaxonic neuron
nerve cell processes are only dendrites; no axon present
CNS
spinal reflex arc
receptor → afferent (sensory) neuron → interneuron → efferent (motor) neuron → effector (gland or muscle)
PNS CNS
bundle of fascicles
neuron/nerve
dorsal root ganglia
all the cell bodies from sensory neurons sending info to the CNS
plexuses
nerves; not same as vertebrae
cervical plexus
C1-C4
brachial plexus
C5-T1
enlargement
dilated area of spinal cord because of nerves branching to extremity
cervical enlargement: nerves branching to UE
lumbosacral enlargement: nerves branching to LE
lumbar plexus
L1-L4
where does the spinal cord terminate
conus medullaris
T12-L1
cauda equina
horses tail
bundle of nerve roots in the lower end of the spinal cord
filum terminale
thin, fibrous thread that extends from the conus medularis to the coccyx
continuation of the pia mater
pia mater
anchors spinal cord to coccyx
delicate, innermost membrane enveloping the brain and spinal cord
dura mater
outermost layer of meninges; very rough/thick
spinal meninges and structure of spinal cord
dura mater: (tough mother), outer most layer
subdural space
arachnoid mater (spider mother)
subarachnoid space
pia mater (soft mother)
dorsal/posterior root ganglian
sensory/posteror aspect of the spinal cord
anterior root ganglion
motor
dermatomes
single spinal nerve innervating different branches/segment sof skin
myatomes
nerves that innervate specific muscles