Thermodynamics chapter 3
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is a pure substance
a substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout
is air a pure substance
yes, air is a mixture of several gasses but is considered to be a pure substance
what is a compressed liquid
a substance that is not about to vaporize
what is a saturated liquid
a liquid that is about to vaporize
what is a saturated liquid-vapor mixture
the state at which the liquid and vapor phases coexist in equilibrium
what is a saturated vapor
a vapor that is about to condense
what is a superheated vapor
a vapor that is not about to condense
when looking at a specific volume vs temperature graph of heating water under constant pressure, what are the phases in order that the liquid will go through
1) compressed liquid
2) saturated liquid
3) saturated liquid-vapor mixture
4) saturated vapor
5) superheated vapor
For a sample of pure water, if we heat the liquid to a superheated vapor, then let that cool back to a compressed liquid, what can be said about the energy of heat between the two processes
they are the same because the cooling will follow the same path as the heating
What is the critical point
the point at which the saturated liquid and saturated vapor states are identical (supercritical fluid)
what is saturation temperature (Tsat)
the temperature at which a pure substance changes phase at a given pressure
what is saturation pressure Psat
the pressure at which a pure substance changes phase at a given temperature
What is latent heat
the amount of energy absorbed or released during a phase-change process
what is latent heat of fusion
the amount of energy absorbed during melting. it is equivalent to the amount of energy released during freezing
what is latent heat of vaporization
the amount of energy absorbed during vaporization and it is equivalent to the energy released during condensation
is latent heat constant across different temperatures and pressures
no, latent heat is dependent of different temperatures and pressures
what is a T-v diagram
it is the specific volume against temperate and it helps show specific characteristics of a substance
what happens to a T-v diagram of water when the pressure is increased
1) water starts boiling at a much higher temperature
2) the specific volume of the saturated liquid is larger
3) the specific volume of the saturated vapor is smaller
4) the horizontal line connecting saturated liquid and saturated vapor states is much shorter
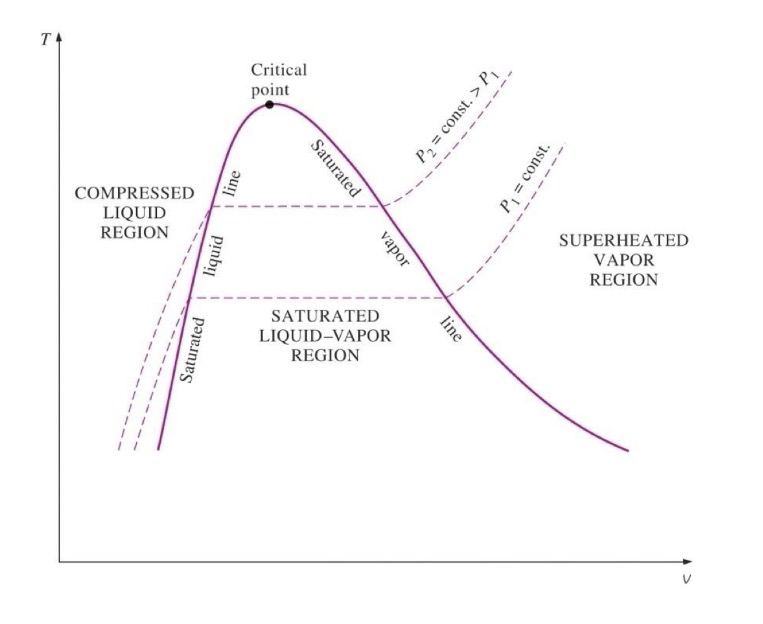
Describe this diagram:
two lines, three regions
1) saturated liquid line
2) saturated vapor line
3) compressed liquid region
4) superheated vapor region
5) saturated liquid-vapor mixture region (wet region)
what is a P-v diagram looking at
it is looking at what happens to the liquid when we keep temperature constant and are changing the amount of pressure on a liquid
What is the triple point
at a specific pressure and temperature the substance exists in three phases in equilibrium
what is the triple point temperature and pressure for water
T= 0.01 C
P= 0.6117kPa
what is the triple point useful for
we can expand it into a P-T diagram to analyze a substance
what are the properties of a P-T diagram
1) no substance can exist in the liquid phase in stable equilibrium and pressure below the triple point
2) substance at high pressure can exist int eh liquid phase at temperature below the triple point temperature
3) at low pressures (below the triple point value) solids evaporate without melting first
what is sublimation
passing from the solid phase directly to the vapor phase
what is another name for enthalpy of vaporization
latent heat of vaporization
what is enthalpy of vaporization
the amount of energy needed to vaporize a unit mass of saturated liquid at a given temperature or pressure