Cell Membrane Structure, Permeability, and Osmosis Principles for Biology
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What is the date of the first mini-exam?
Tuesday, 9/16 during the first 40 minutes of class.
What topics are covered in the mini-exam?
Macromolecules and organelles, Polarity and Water, Membranes, Osmosis and diffusion.
How many questions will be on the mini-exam?
25 questions.
What is the allowed material for the mini-exam?
One sheet of handwritten notes (front and back, 8.5x11 standard sheet of paper).
What is the permeability scale for small nonpolar molecules like O2, CO2, and N2?
100 cm/sec.
What is the permeability scale for small uncharged polar molecules like H2O and glycerol?
10-2 to 10-4 cm/sec.
What happens to water during osmosis in relation to solute concentration?
Water moves towards regions of high solute concentration.
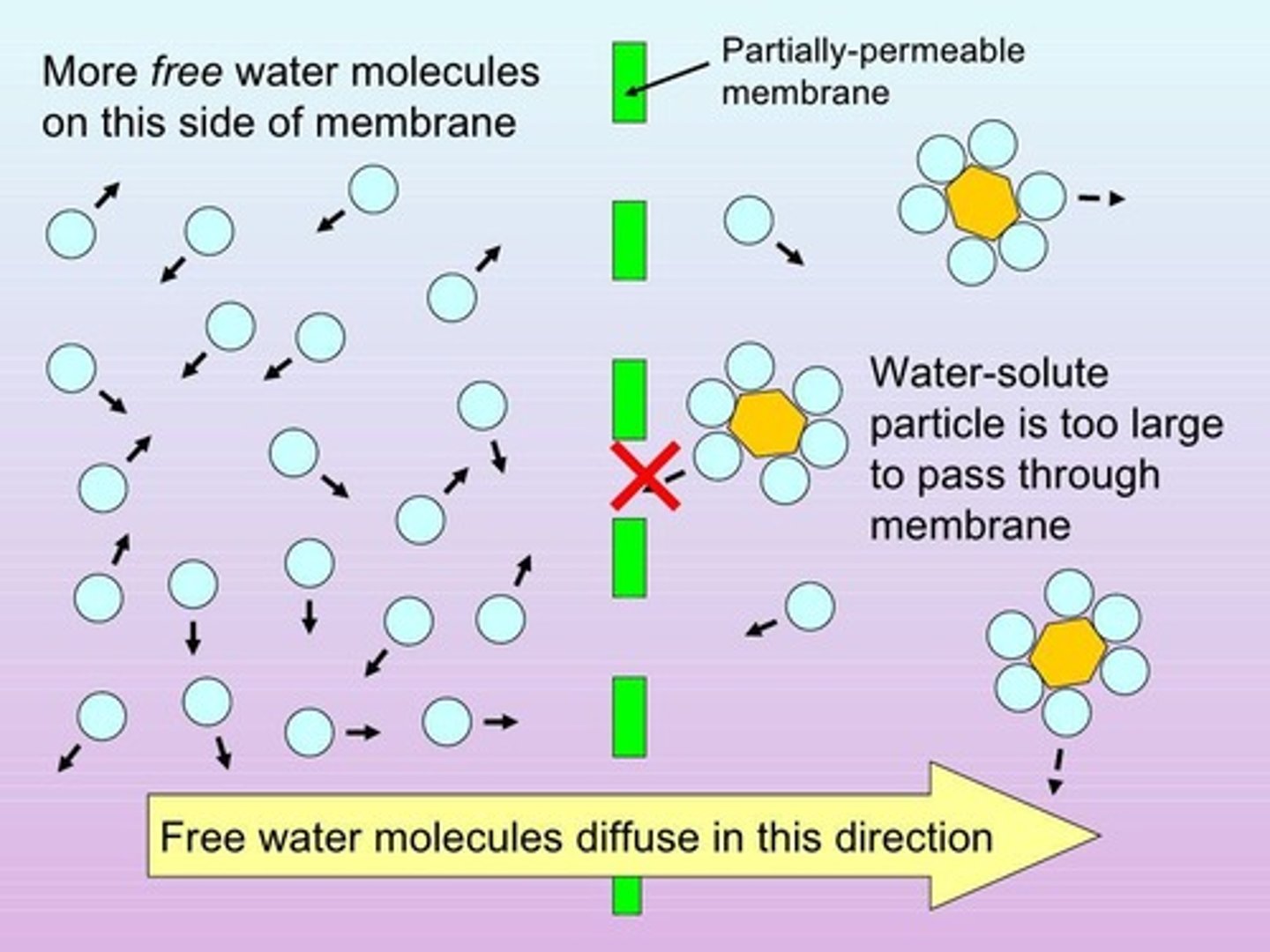
What is the permeability of large uncharged polar molecules like glucose and sucrose?
10-6 to 10-8 cm/sec.
What is the permeability of small ions such as Cl-, K+, and Na+?
10-12 cm/sec.
In the context of osmosis, what does hypertonic mean?
A solution with a higher solute concentration compared to another solution.
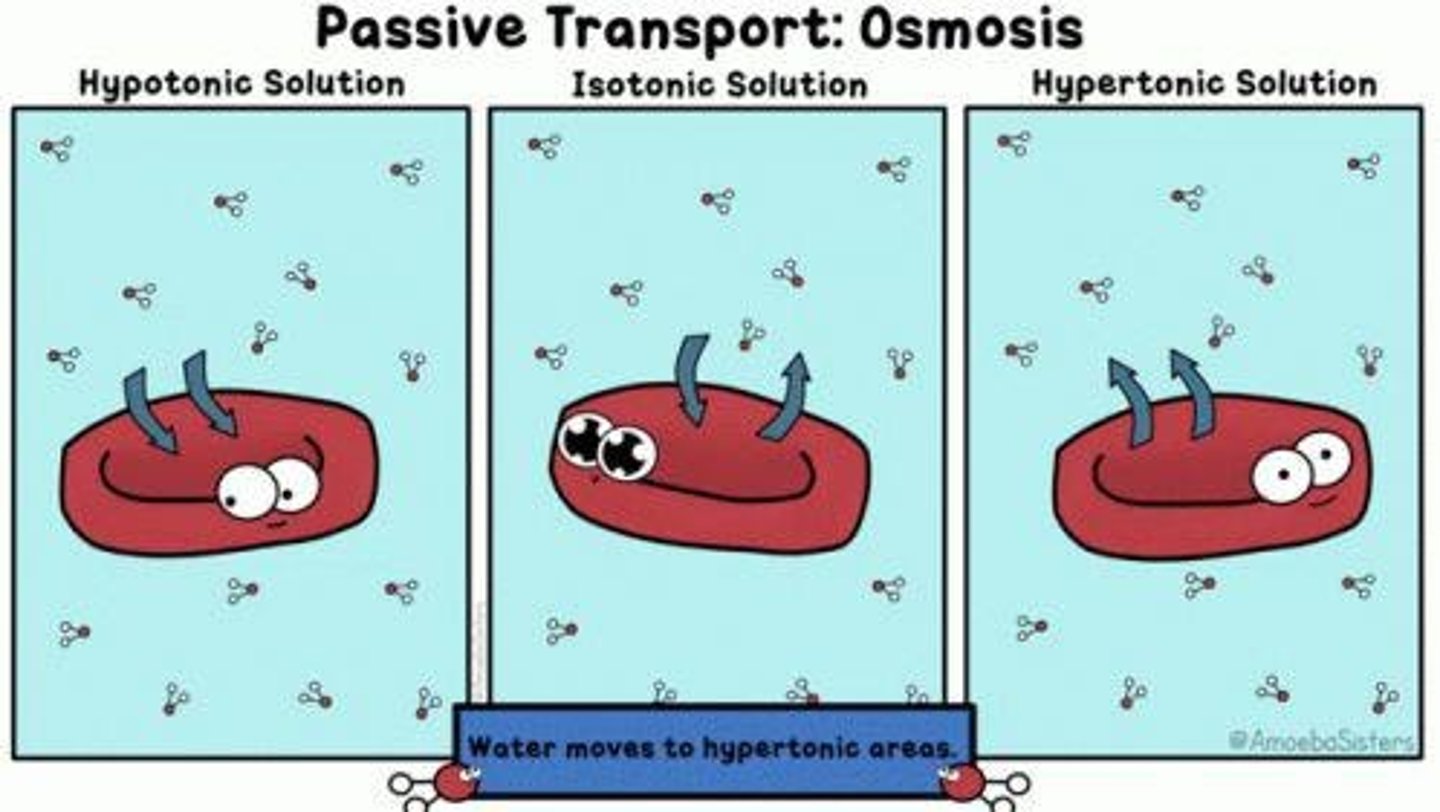
In the context of osmosis, what does hypotonic mean?
A solution with a lower solute concentration compared to another solution.
What will happen to a vesicle in a hypotonic solution?
Net flow of water into the vesicle; the vesicle swells or may burst.
What will happen to a vesicle in a hypertonic solution?
Net flow of water out of the vesicle; the vesicle shrinks.
What is the significance of specifying tonicity?
You must specify what you are comparing and the order matters.
What is the physiological importance of osmosis?
It influences individual cells and organisms as a whole.
What is the expected outcome when starch and iodine mix in a dialysis tubing experiment?
The solution turns blue when they mix, indicating iodine has moved through the membrane.

What should you bring to the mini-exam besides your notes?
A pencil and your student ID.
What is the permeability of the phospholipid bilayer?
Low permeability.
What is the permeability scale for small uncharged polar molecules like glucose?
10-10 cm/sec.
What are the two learning objectives for the class?
3.2 Predict the movement of water based on changes in solute concentrations; 3.3 Propose interventions that would influence movement of water.
What is the role of the interactive demo in the lab?
To illustrate concepts of osmosis and diffusion using starch and iodine.
What should you do to prepare for the medical case study?
Complete both 12 and 13 of the case studies on your in-class guide.
What are the main functions of the plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane allows for a distinct internal environment, facilitates compartmentalization of organelles, separates incompatible chemicals, and concentrates reactants for efficient chemical reactions.
Name at least three organelles that have a membrane.
Nucleus, Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), Golgi, Lysosomes, Vacuoles, Peroxisomes, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts.
What are the two classifications of fatty acids?
Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
What characterizes saturated fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acids have a full set of hydrogens bonded to the carbon chain and are straight in structure.
What characterizes unsaturated fatty acids?
Unsaturated fatty acids have bends in their structure due to double bonds between carbons, which create missing hydrogens.
What effect do cholesterol, temperature, and fatty acid composition have on membranes?
They affect the fluidity of the membrane.
What is the role of organelle membranes?
Organelle membranes allow for compartmentalization within the cell.
How do membranes contribute to the efficiency of chemical reactions?
Membranes concentrate reactants of chemical reactions, making these reactions more efficient.
What is the chemical composition of fatty acids?
Fatty acids consist of a carboxylic acid group and a chain of hydrocarbons.
What is the significance of the water/oil interface in membrane studies?
It helps predict how molecules will arrange themselves based on their polarity.
What should students do before starting the interactive demo on the water/oil interface?
Predict how the molecules will arrange themselves and draw their prediction.
What is the purpose of the interactive demo on micelles?
To observe how phospholipids arrange themselves in different environments, such as oil.
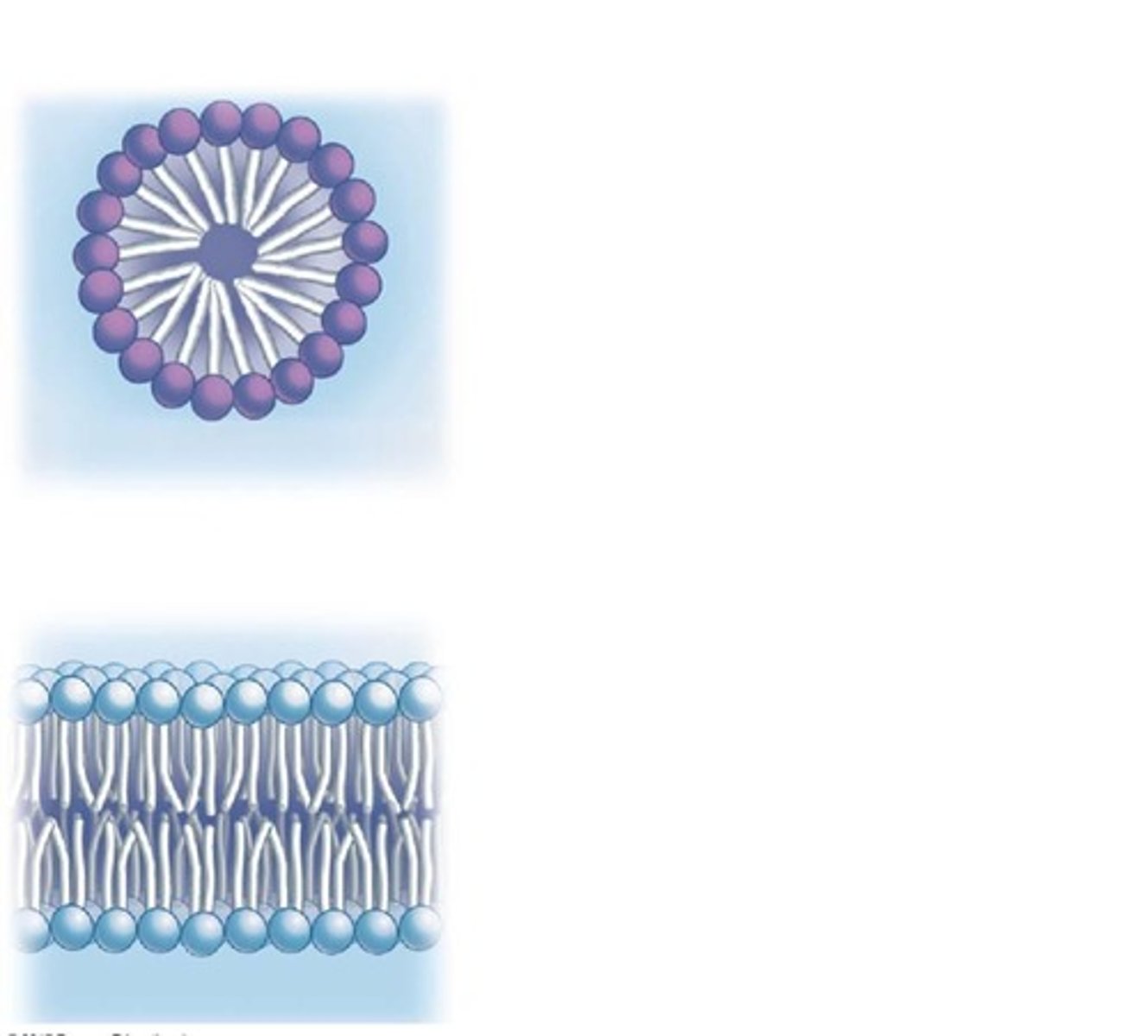
What is the expected arrangement of phospholipids in oil?
Phospholipids would rearrange differently compared to their arrangement in water.
What is the primary learning objective related to cell membranes?
To describe the structure, composition, and chemical properties of a cell membrane.
What is the importance of understanding the permeability of molecules across the plasma membrane?
It helps rank molecules based on size and chemical properties, which is crucial for understanding cell function.
What is the significance of the interactive demos in the lab?
They allow students to visualize and predict molecular behavior in different environments.
What is the role of fatty acids in the cell membrane?
Fatty acids are a key component of the cell membrane, influencing its structure and function.
What does it mean for a fatty acid to be 'saturated'?
It means that the fatty acid has no double bonds between carbon atoms and is fully saturated with hydrogen atoms.
What does it mean for a fatty acid to be 'unsaturated'?
It means that the fatty acid contains one or more double bonds between carbon atoms, resulting in fewer hydrogen atoms.
How do the properties of fatty acids affect membrane fluidity?
The saturation level of fatty acids influences the fluidity; unsaturated fatty acids create kinks that prevent tight packing, increasing fluidity.
What is the expected outcome of the interactive demos regarding predictions?
Students should compare their predictions with actual outcomes and discuss any differences.
What is the significance of membrane compartmentalization in cells?
It allows for specialized environments for different cellular processes, enhancing overall cell function.
What are lipid micelles and bilayers composed of?
Lipid micelles and bilayers are composed of hydrophilic heads that interact with water and hydrophobic tails that interact with one another.
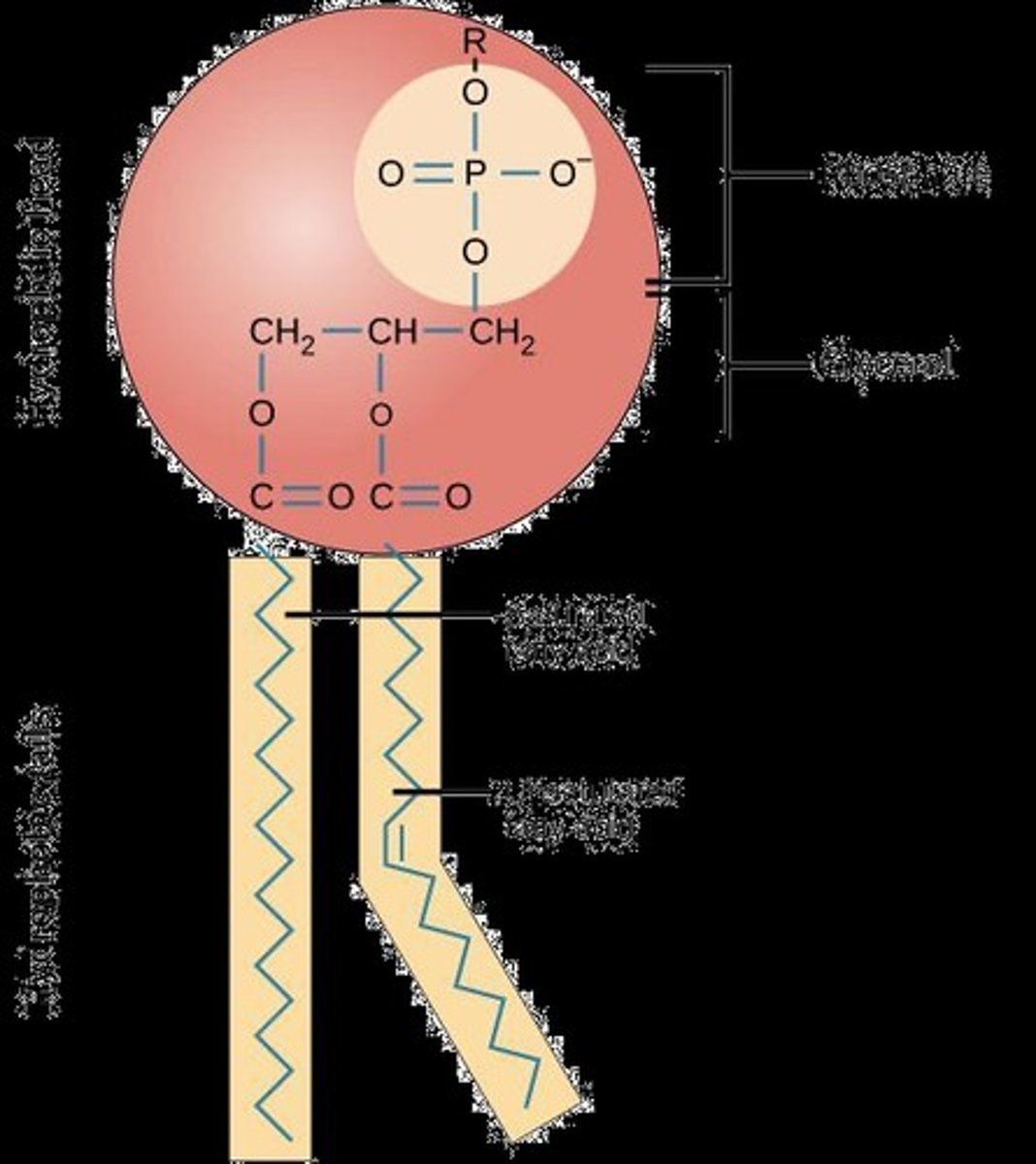
What are phospholipids and their role in cell membranes?
Phospholipids are the main building blocks of cell membranes, consisting of a hydrophilic head (phosphate group, glycerol, carboxylic acid group of fatty acid) and a hydrophobic tail (hydrocarbon chain of fatty acids). They are amphipathic, having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
What factors influence membrane permeability?
Membrane permeability is influenced by size and charge/polarity of molecules.
Which small, nonpolar molecules have high permeability across cell membranes?
O2, CO2, and N2 are small, nonpolar molecules with high permeability.
What is the permeability of small uncharged polar molecules like water and glycerol?
Small uncharged polar molecules like water and glycerol have moderate permeability.
How does the permeability of large uncharged polar molecules compare to small ions?
Large uncharged polar molecules have low permeability compared to small ions.
What is the impact of membrane fluidity on cell function?
Membrane fluidity allows lipids to move within the membrane, affecting how substances are transported and how the membrane functions.
How do saturated and unsaturated lipids affect membrane permeability?
The number of saturated vs. unsaturated lipids impacts membrane permeability; more unsaturated lipids increase fluidity, while more saturated lipids decrease it.
What is the relationship between temperature and membrane fluidity?
Increasing temperature increases membrane fluidity, making it more fluid like olive oil and less fluid like solid butter.
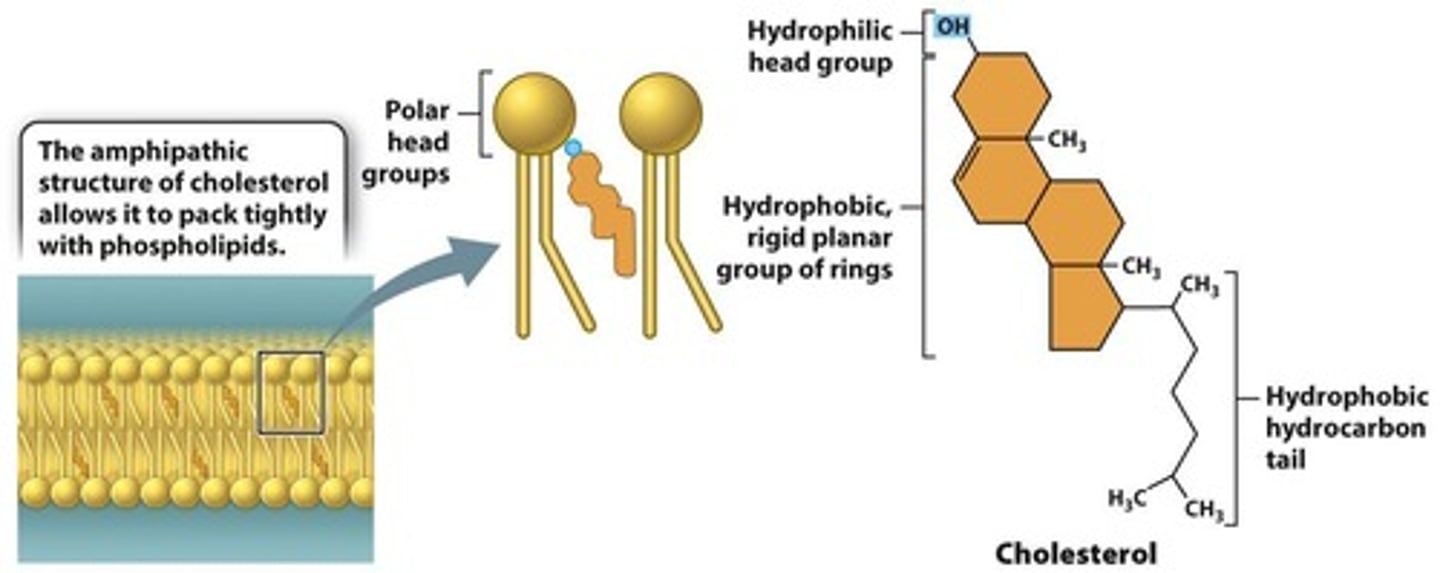
How does cholesterol affect membrane fluidity?
Cholesterol is amphipathic and its effect on fluidity depends on temperature; it fits between lipid tails to prevent tight packing or excessive spreading.
What happens to membrane permeability when cholesterol levels are increased?
Increased cholesterol levels can stabilize membrane fluidity, affecting permeability at different temperatures.
How does plasma membrane thickness affect permeability?
Thicker membranes generally have lower permeability compared to thinner membranes.
What experimental method was used to measure the permeability of membranes of varying thickness?
Membranes of various thicknesses were created by varying lipid tail length, and permeability was measured using two different molecules.
What is the expected trend in permeability as membrane thickness increases?
As membrane thickness increases, permeability generally decreases.
What are the learning objectives related to cell membrane structure?
By the end of class, students should be able to describe the structure, composition, and chemical properties of a cell membrane and graph the effects of temperature and fatty acid composition on membrane fluidity.
What is the significance of amphipathic molecules in membranes?
Amphipathic molecules, like phospholipids and cholesterol, are crucial for forming the bilayer structure of membranes, allowing for selective permeability.
What is the permeability scale for small ions?
Small ions such as Cl-, K+, and Na+ have very low permeability (10^-12 cm/sec) across the phospholipid bilayer.
How does the presence of unsaturated fatty acids affect membrane fluidity?
The presence of unsaturated fatty acids increases membrane fluidity, allowing for more movement within the membrane.
What experimental observations can be made regarding membrane thickness and permeability?
Experiments show that as membrane thickness increases, permeability decreases, which can be graphed to illustrate the relationship.
What role does temperature play in membrane fluidity?
Temperature increases fluidity, making membranes more flexible and allowing for better transport of materials.
How can the effects of temperature and fatty acid composition on membrane fluidity be graphically represented?
The effects can be represented in a graph showing increased fluidity with higher temperatures and varying percentages of saturated fatty acids.
What is the significance of the hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions in phospholipids?
The hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions of phospholipids are essential for forming the bilayer structure of cell membranes, influencing permeability and fluidity.
What is the general trend in permeability for different types of molecules across cell membranes?
Small nonpolar molecules have the highest permeability, followed by small uncharged polar molecules, while large uncharged polar molecules and ions have the lowest permeability.