Module 8 - Reverse Transcriptase DNA Viruses
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Reverse-transcribing dsDNA viruses use
an RNA intermediate and reverse transcriptase during genome replication
Non-reverse-transcribing dsDNA viruses replicate their genomes…
directly from DNA without an RNA stage
Hepatitis has an unusual genome because
it is typically circular but partially double stranded. Small RNA pieces bound to one end and reverse transcriptase at the other end.
Reverse transcriptase creates new viral genomes from
pre-genomic RNA within the viral core
Hepatitis B genome and icosahedral capsid together from the
nucleocapsid, enclosed within a lipid envelope studded with viral surface proteins
Unlike retroviruses, all hepadnaviral DNA is produced by
reverse transcription
Hepatitis B basic replication scheme
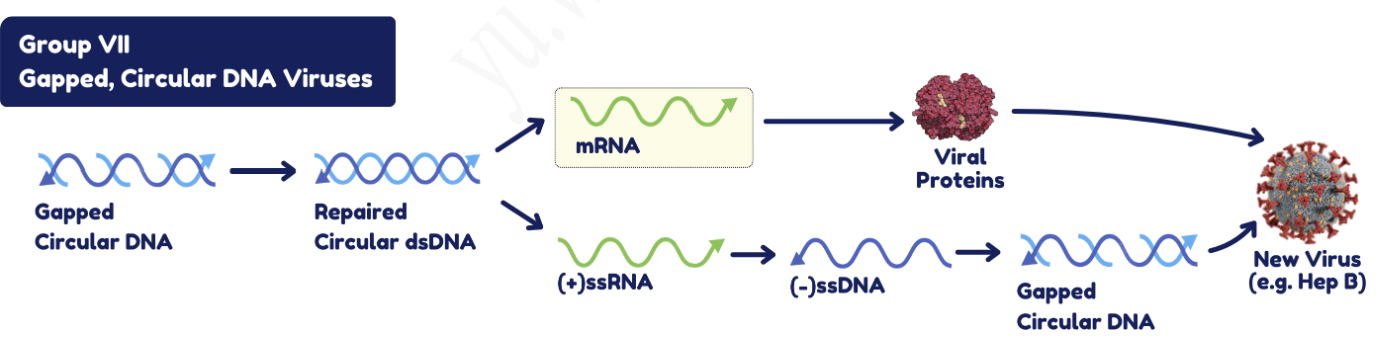
All RNA molecules in hepatitis B replication scheme are produced by
host polymerases
RNA molecules in hepatitis B divide into two groups:
pre-genomic RNA (pgRNA) and mRNA
Pre-genomic RNA in hepatitis B
provides template for new genome production. About 3.4 kb, longest RNA generated by host cellular polymerases
mRNA in hepatitis B
come in various lengths, frameshifts allows for production of multiple overlapping mRNA molecules
pgRNA encodes
capsid protein (HBcAg) and polymerase
Overlapping transcripts allow hepatitis B to generate multiple
cultural and regulatory proteins from its compact genome
Hepatitis B infects hepatocytes in the
liver
Replication cycle of hepatitis B
virus binds to heparan sulfate proteoglycans as attachment factors
then binds to sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP)
after receptor binding, virus enters via receptor-mediated endocytosis and travels to the nucleus
at nucleus, viral core binds nuclear pore proteins
virus releases the genome into the nucleus
host enzymes fill in the gap, forming ds, circular DNA called covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA)
host nuclear polymerases acts on the cccDNA to make pgRNA and mRNAs
hepatitis B DNA is copied in the cytoplasm because it has pre-packaged reverse transcriptase (P protein)
pgRNA and mRNA is exported from nucleus to cytoplasm
in cytoplasm, pgRNA joins with capsid proteins and reverse transcriptase (p protein)
RT binds pgRNA and capsid forms around this complex
Within the capsid, RT produces a gapped, circular, ds DNA copy of pgRNA
In the replication cycle for hepatitis B, creation of new, partially ds, circular genomes from pgRNA occurs in
the viral core
pgRNA transcribed in the nucleus becomes enclosed within
the forming viral capsid along with polymerase (P protein)
In hepatitis B, the polymerase has multiple domains. Terminal protein (TP) domain initiates _______, while RT domain carries out _________
priming; DNA synthesis