Nerve cells and excitability 3: Synapsws and neurotransmission
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is a synapse?
The point at which electrical signals move from one nerve cell to another
What are the 2 types of synapses and explain them
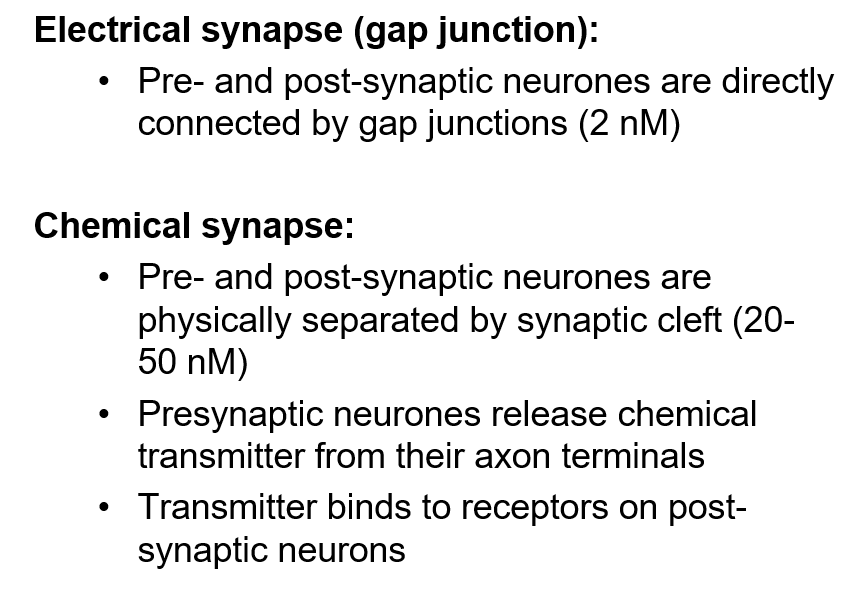
How are electrical synapses formed?
By connexons in both cell membranes, direct passage of ions and small molecules through channel and permit is very rapid signals
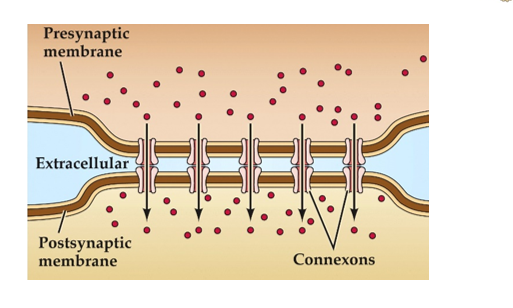
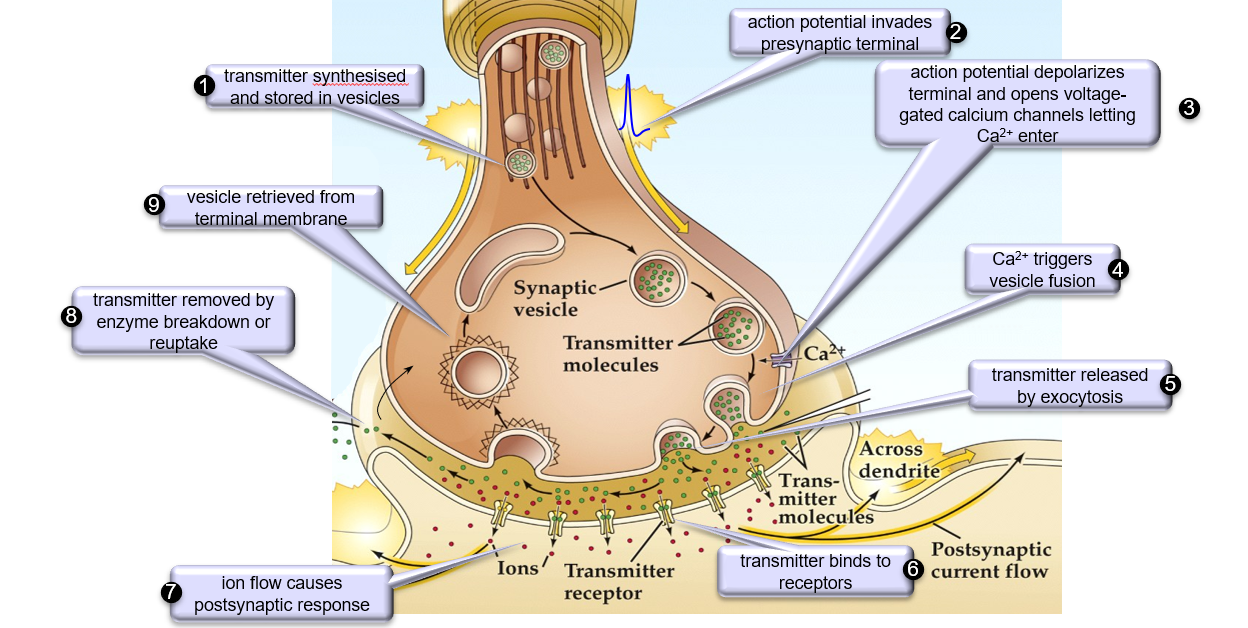
Diagram of a chemical synapse
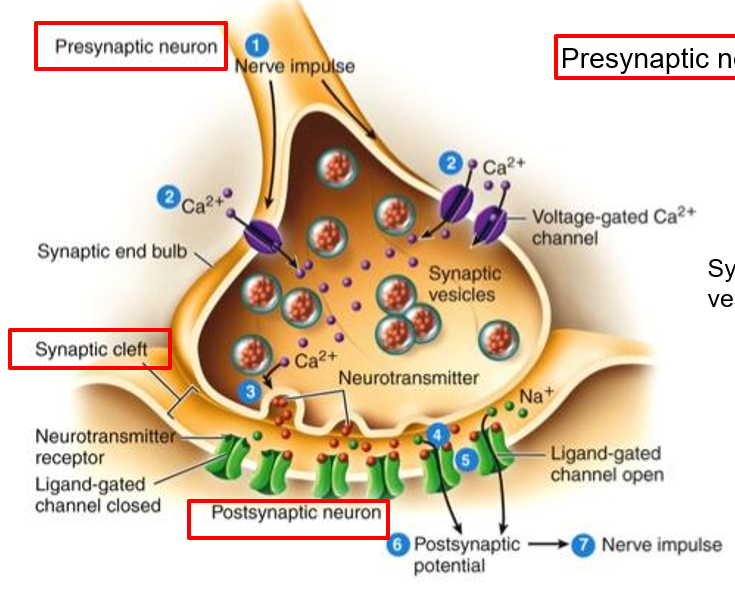
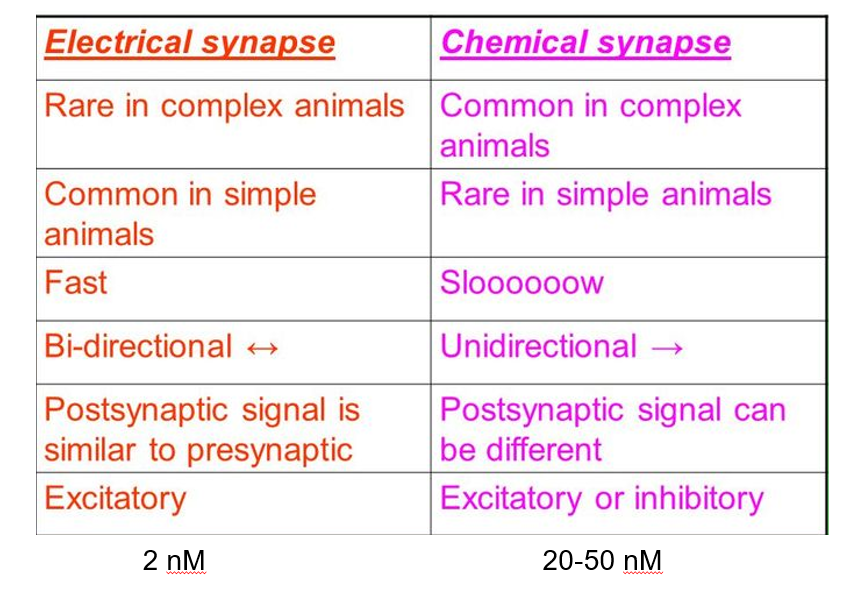
Table of difference between chemical and electrical synapse
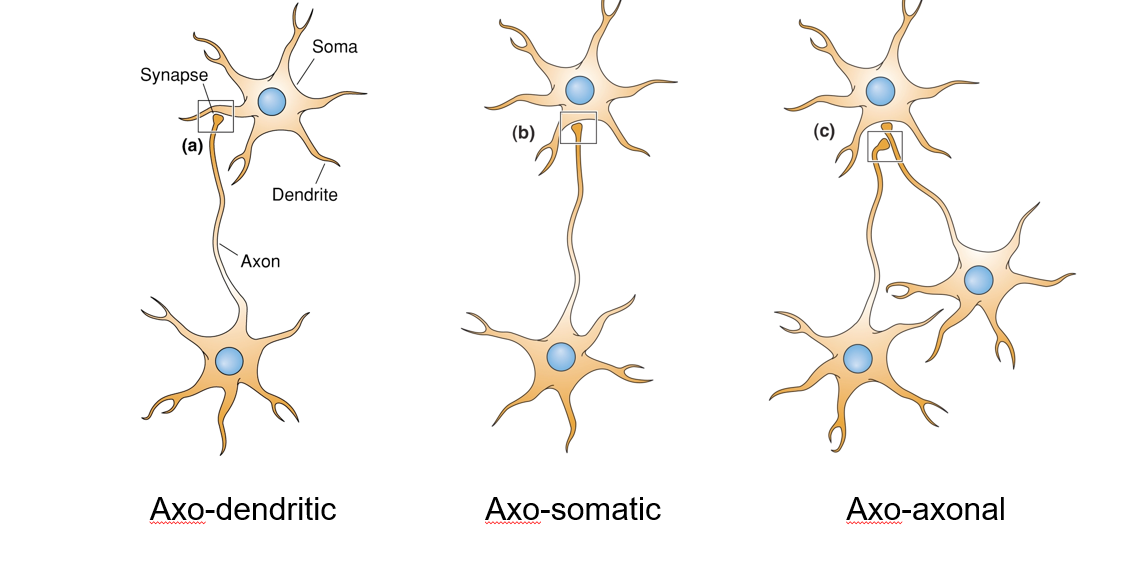
What are the 3 types of synapses in the CNS
Axo-dendritic = most common
Where can neurotransmitters be produced?
Synapses and the cell body (nucleus)
What are the stages of neurotransmitter release via exocytosis?
How do we know if a molecule is a neurotansmitter?
Depends on which pathway it’s on and the mechanism for removal and/or breakdown must be disposable
What are the 4 ways to remove an unbound neutrotransmitter?

What are the 4 different types of neurotransmitters?
Amines, amino acids, peptides and purines
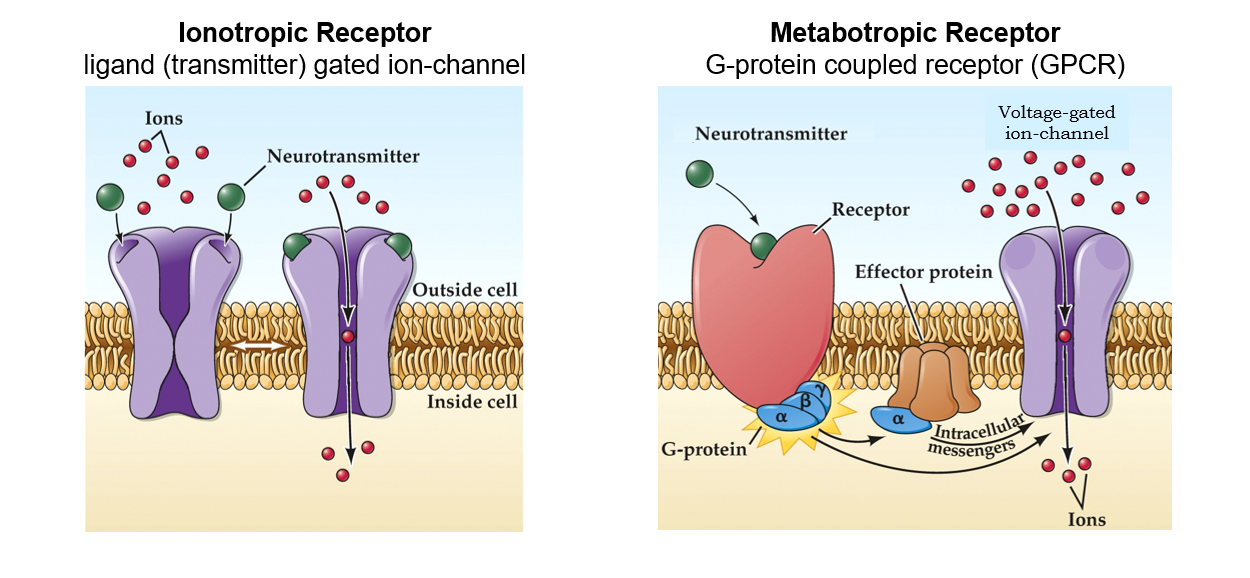
What are the two neurotransmitter receptors?
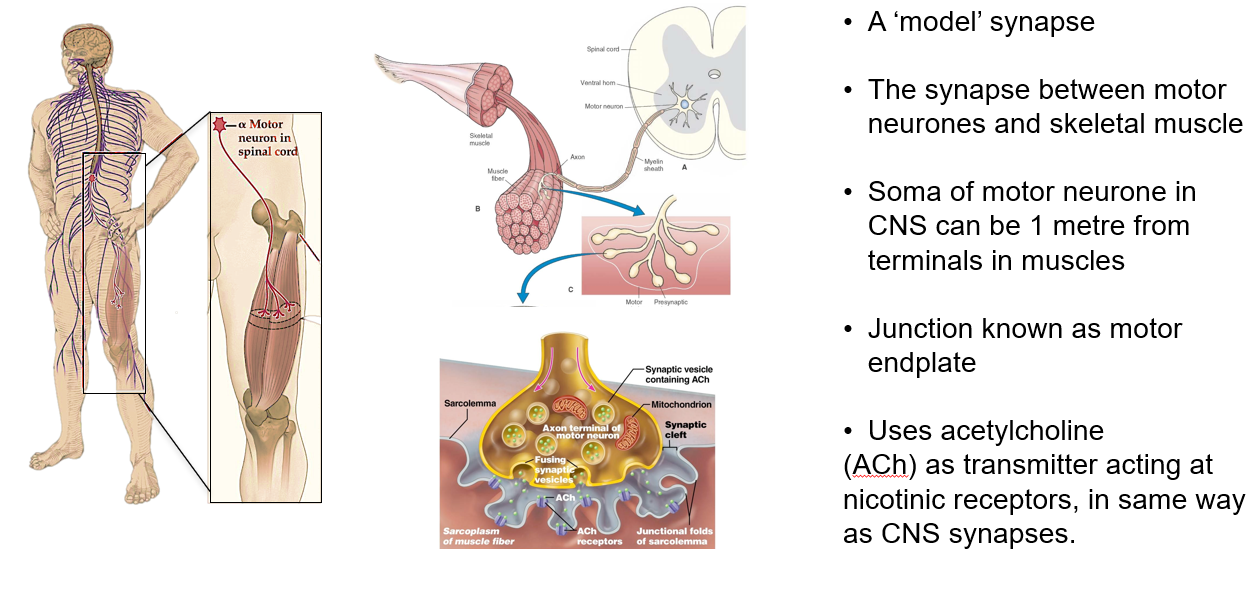
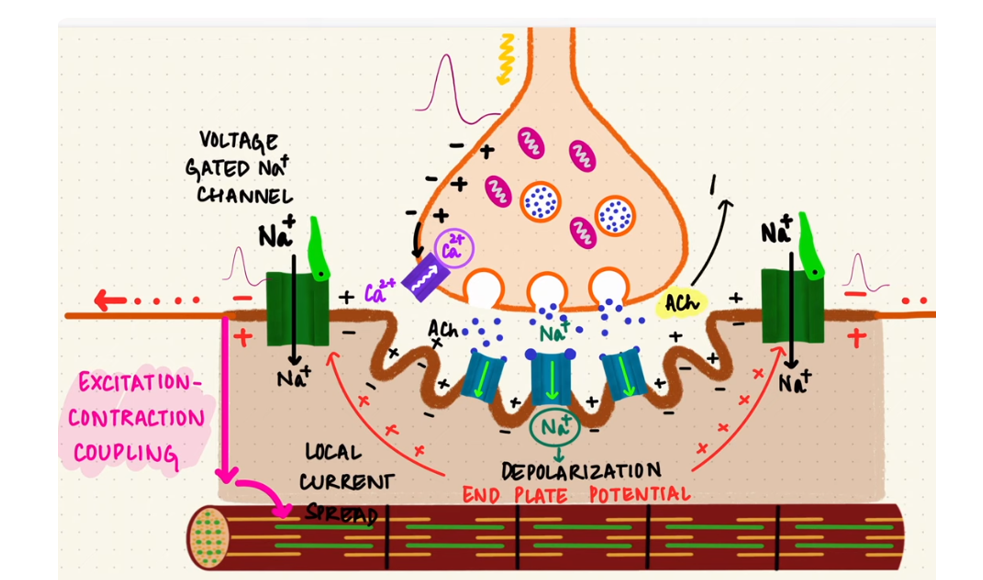
How ACh activates muscle contraction
Neurotransmitter terminology
The suffix -ergic applies to the neuron that releases the neurotransmitter e.g dopamine and the dopamingergic neuron and acetylcholine and the cholinergic neuron
Cholinergic transmission at neuromuscular junction
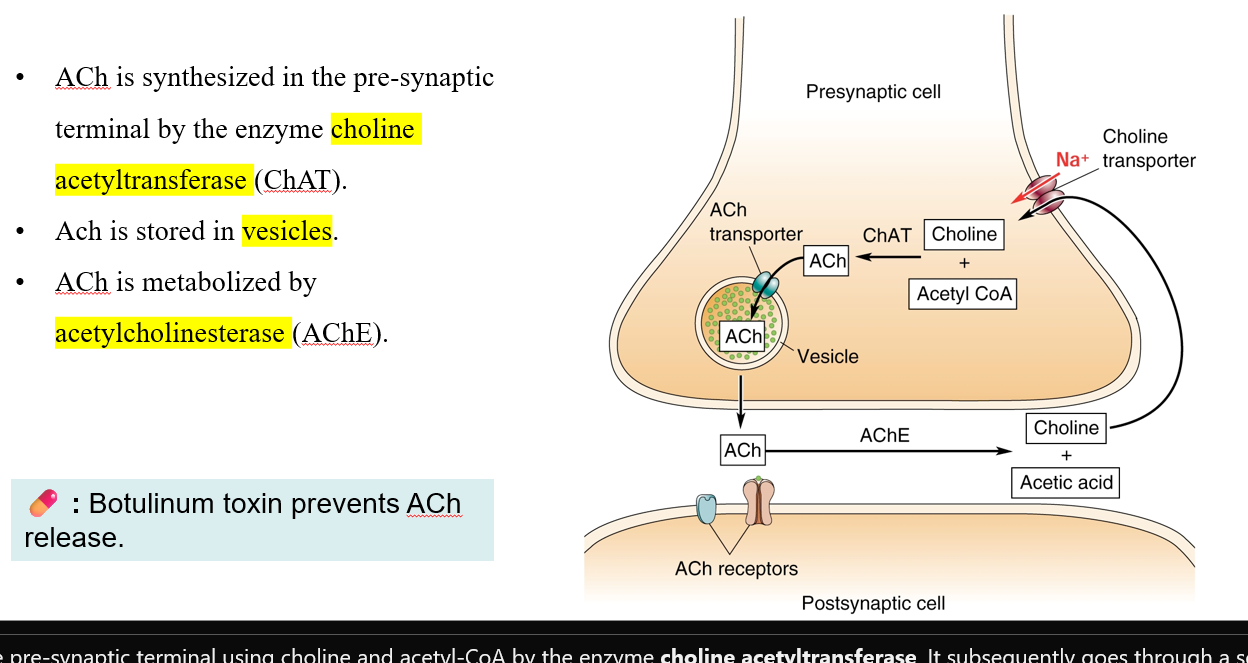
Synthesis and degradation of Ach
Acetylcholine

What are the 2 main brain amino acid neurotransmitters and explain what they do
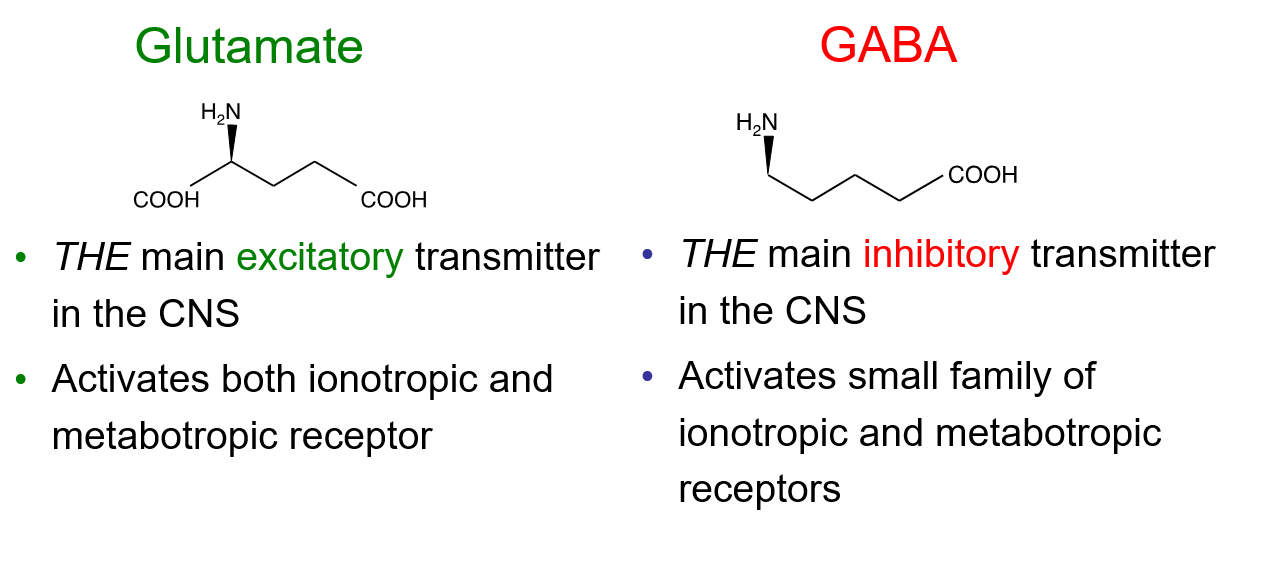
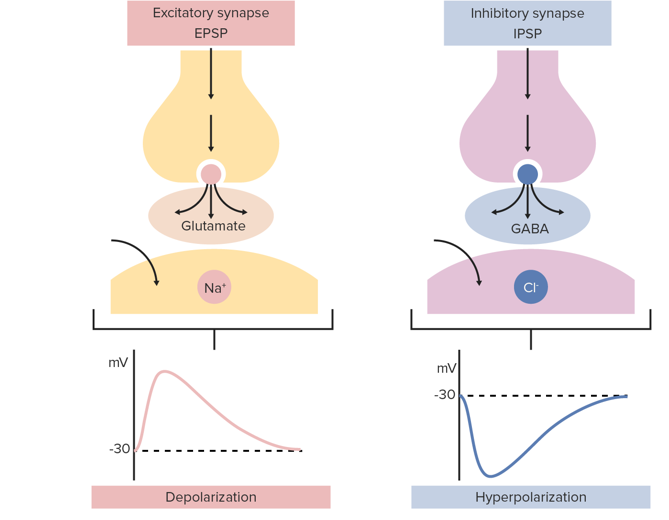
Why do some synapses excite ?
As for example glutamate generates an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
Why do some synapses inhibit?
As for example GABA generates an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
Diagram showing exitatory and inhibatory synapses
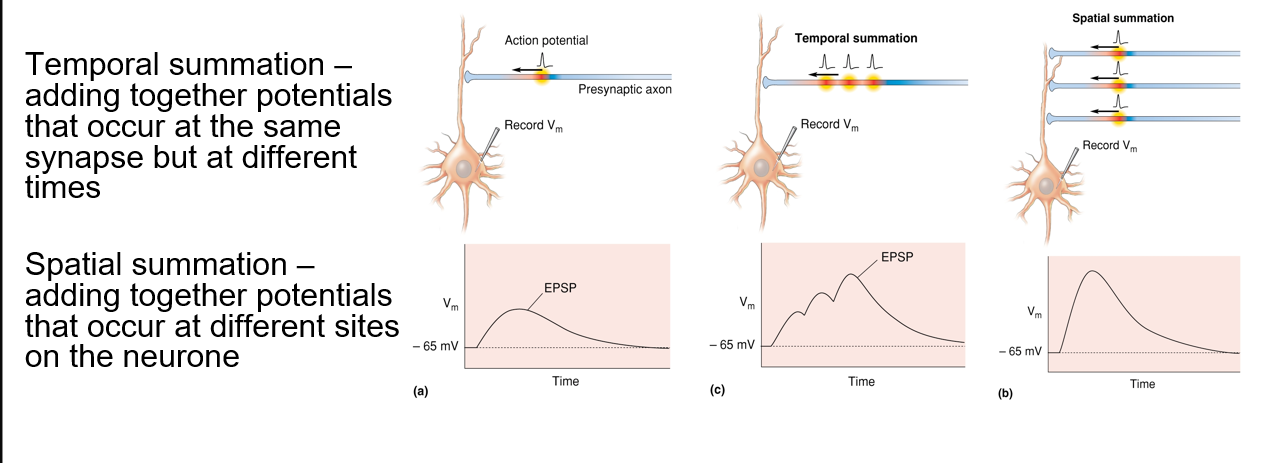
Explain the two different types of summation