Gene Regulation in Bacteria: The lac Operon
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Gene regulation
The level of gene expression can vary under different conditions.
Constitutive genes
Genes that have essentially constant levels of expression.
Benefit of regulating genes
Coded proteins will be produced only when required.
Gene expression always 'on'
Constitutive expression.
Gene expression sometimes 'on'
Regulated expression.
Importance of gene regulation
It is important for cellular processes such as metabolism, response to environmental stress, and cell division.
Regulation during transcription
Regulation can occur as the gene is copied into mRNA during transcription.
Feedback inhibition
The product of a metabolic pathway inhibits the first enzyme in the pathway.
Covalent modifications
Changes to the structure of a protein that can alter its function.
Transcriptional regulation
The most common way to regulate gene expression in bacteria by influencing the initiation of transcription.
Regulatory transcription factors (RTFs)
Proteins that influence the rate of RNA synthesis.
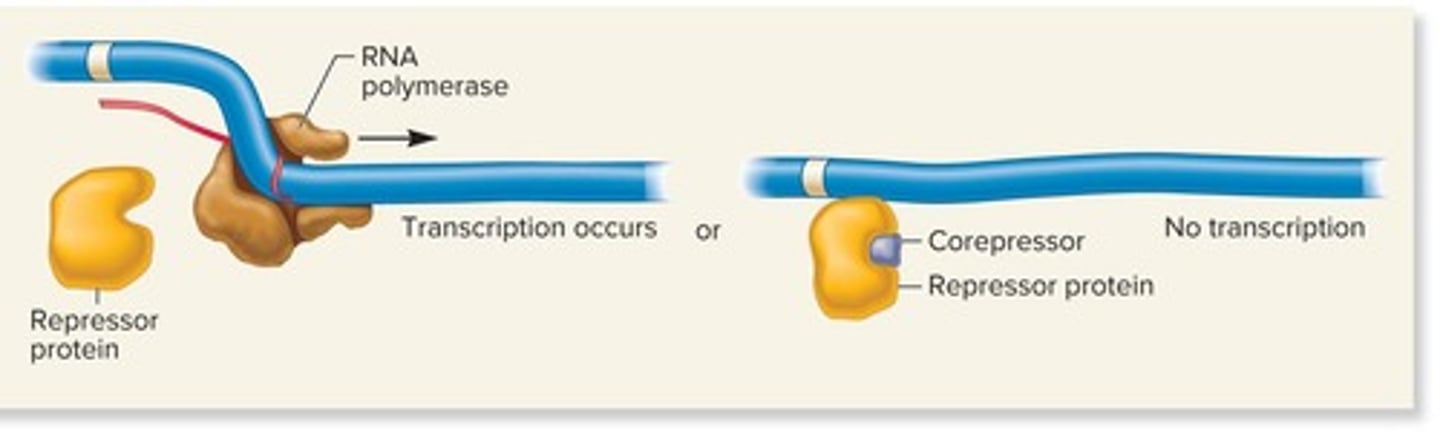
Repressors
Proteins that bind to DNA and inhibit transcription.
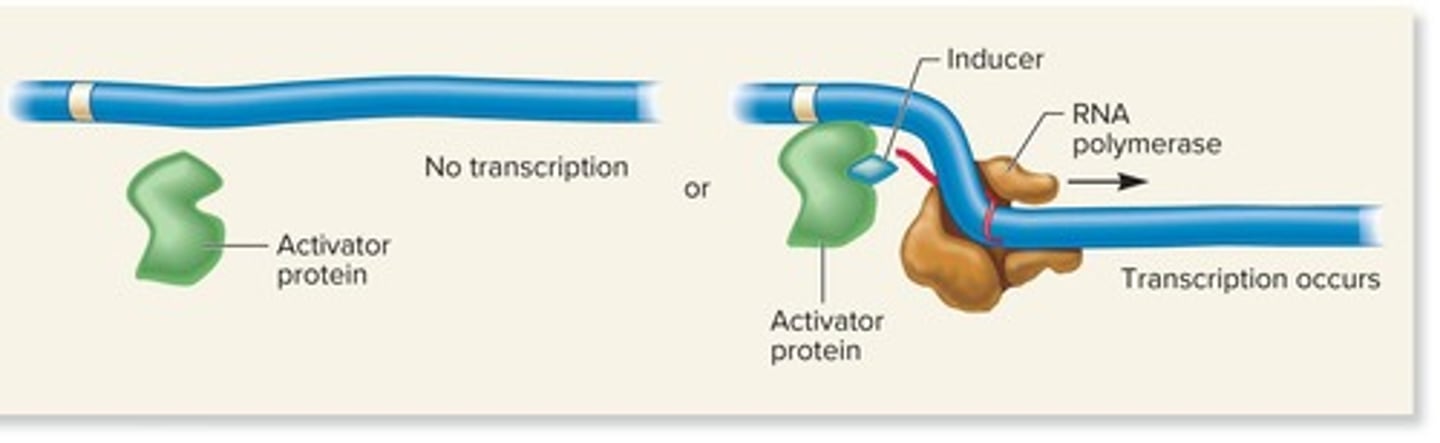
Activators
Proteins that bind to DNA and promote transcription.
Negative control
Transcriptional regulation by repressor proteins.
Positive control
Regulation by activator proteins.
Inducers
Small effector molecules that increase transcription by binding to activators or preventing repressors from binding to DNA.
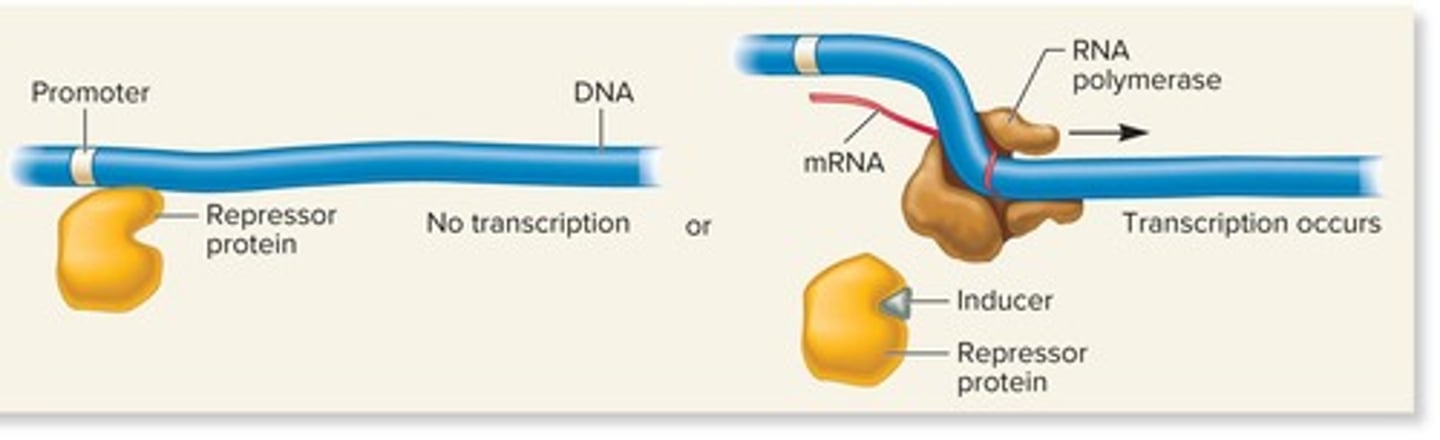
Repressible genes
Genes that are regulated by corepressors binding to repressors.
Corepressors
Molecules that bind to repressors and cause them to bind to DNA.
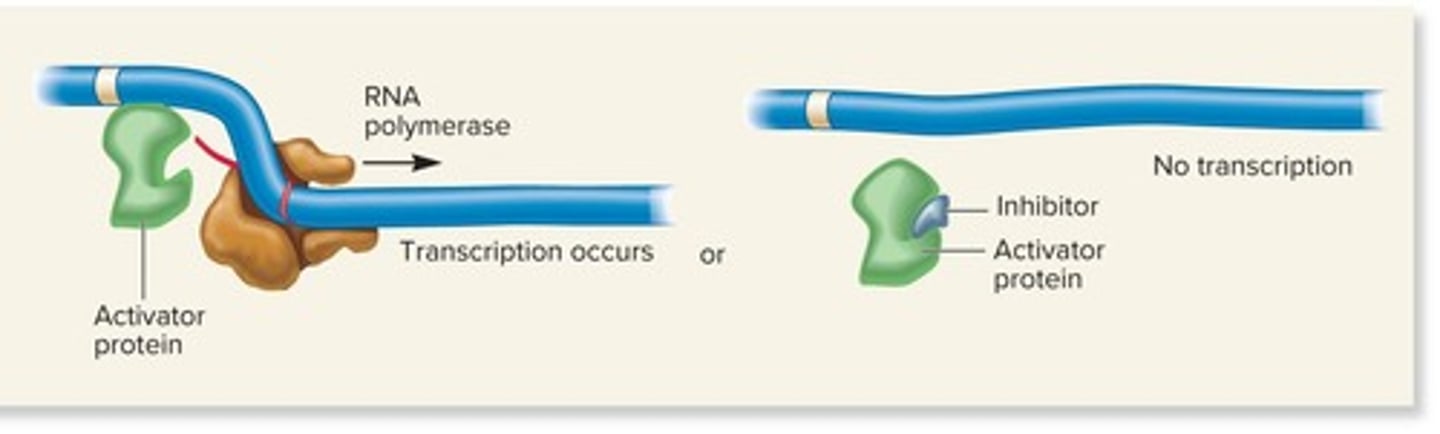
Inhibitors
Molecules that bind to activators and prevent them from binding to DNA.
Regulated expression
Gene expression that is controlled and can be turned on or off.
Transcription
The process of copying a gene into mRNA.
Small effector molecules
Molecules that affect transcription regulation by binding to regulatory transcription factors.
Conformational change
A change in the shape of a protein that can affect its function.
Repressor protein
A protein that inhibits transcription by binding to the DNA.
Inducer molecule
A molecule that binds to an activator protein, enabling it to bind to DNA and activate transcription.
Inducible gene
A gene that can be turned on in response to an inducer molecule.
Activator protein
A protein that increases transcription of a gene when it binds to DNA.
Corepressor molecule
A molecule that binds to a repressor protein, enabling it to bind to DNA and inhibit transcription.
Repressible gene
A gene that can be turned off in response to a corepressor molecule.
Inhibitor molecule
A molecule that causes a conformational change in an activator protein, inhibiting its ability to bind to DNA.
Operon
A regulatory unit consisting of a few protein-coding genes under the control of one promoter.
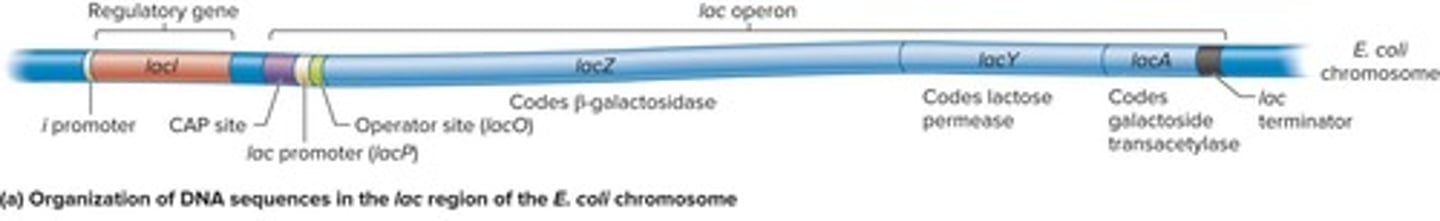
Polycistronic mRNA
An mRNA that contains the coding sequences for multiple protein-coding genes.
Beta-galactosidase
An enzyme produced by E. coli that is involved in lactose metabolism.
Enzyme adaptation
The phenomenon where a particular enzyme appears in the cell only after exposure to its substrate.
E. coli
A type of bacteria used to study lactose metabolism and gene regulation.
Transcription
The process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA.
Lactose metabolism
The process by which E. coli breaks down lactose into simpler sugars.
Regulatory transcription factors
Proteins that regulate the transcription of genes by binding to nearby DNA.
Signal for food
The indication that triggers the production of enzymes in response to the presence of nutrients.
Common functional goal
The coordinated regulation of genes that code for proteins with a shared function.
Promoter
A region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene.
Gene regulation
The process of controlling the expression of genes.
Lactose
A sugar that E. coli can metabolize when present in the environment.
Jacob and Monod
Scientists who studied gene regulation in bacteria, particularly in relation to lactose metabolism.
Pasteur Institute
A research institute in Paris known for its studies in microbiology and immunology.
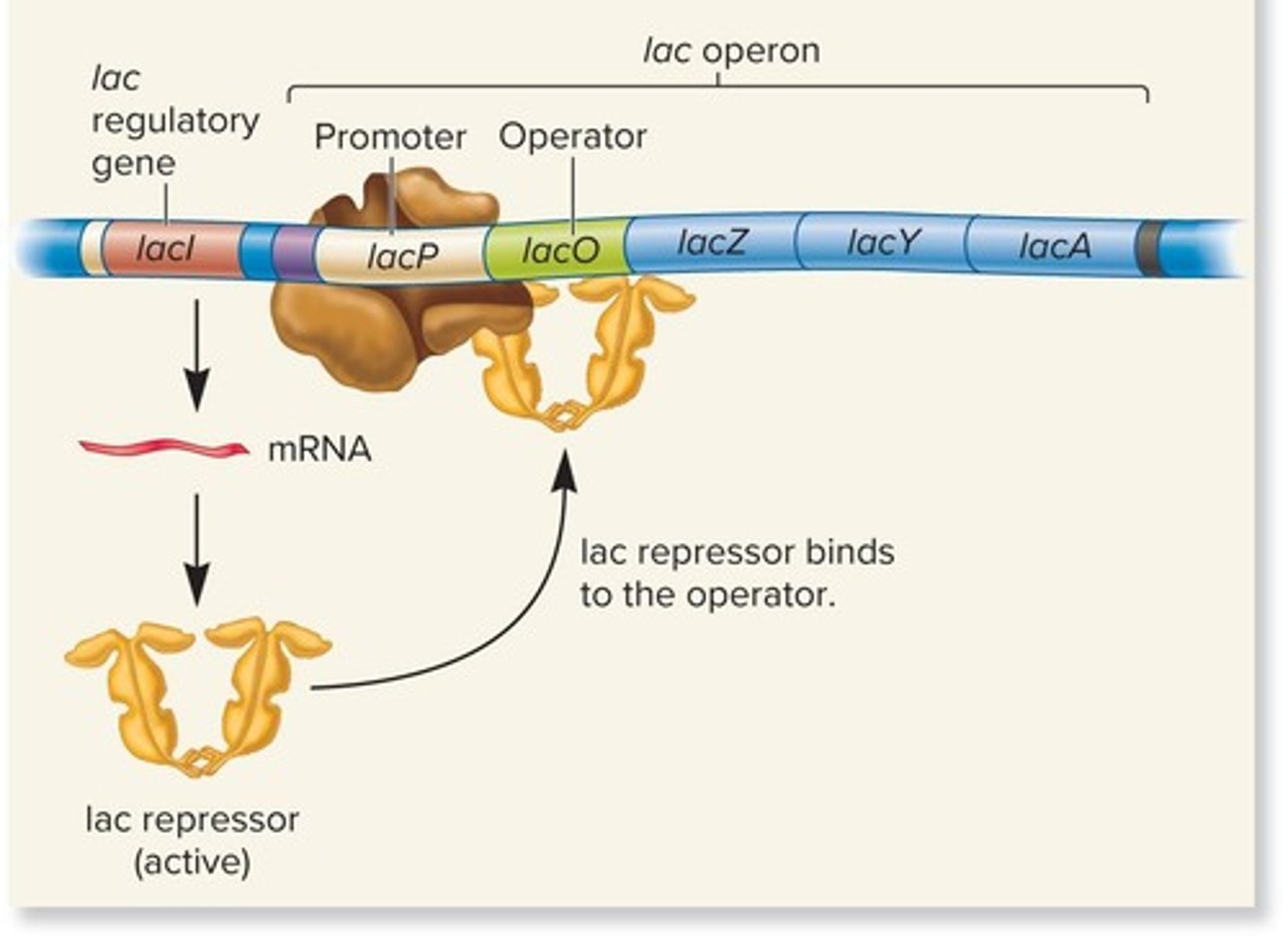
lac operon
A set of genes and their regulatory elements involved in lactose utilization.
lacI gene
A gene that codes for the lac repressor protein and is not considered part of the lac operon.
Promoter
The DNA element that binds RNA polymerase to initiate transcription.
Operator
The DNA element that binds the lac repressor protein to inhibit transcription.
C A P site
The DNA element that binds the Catabolite Activator Protein (C A P) to regulate transcription.
Terminator
The DNA element that signals the end of transcription.
lacZ
A protein-coding gene that codes for β-galactosidase, which cleaves lactose and converts it to allolactose.
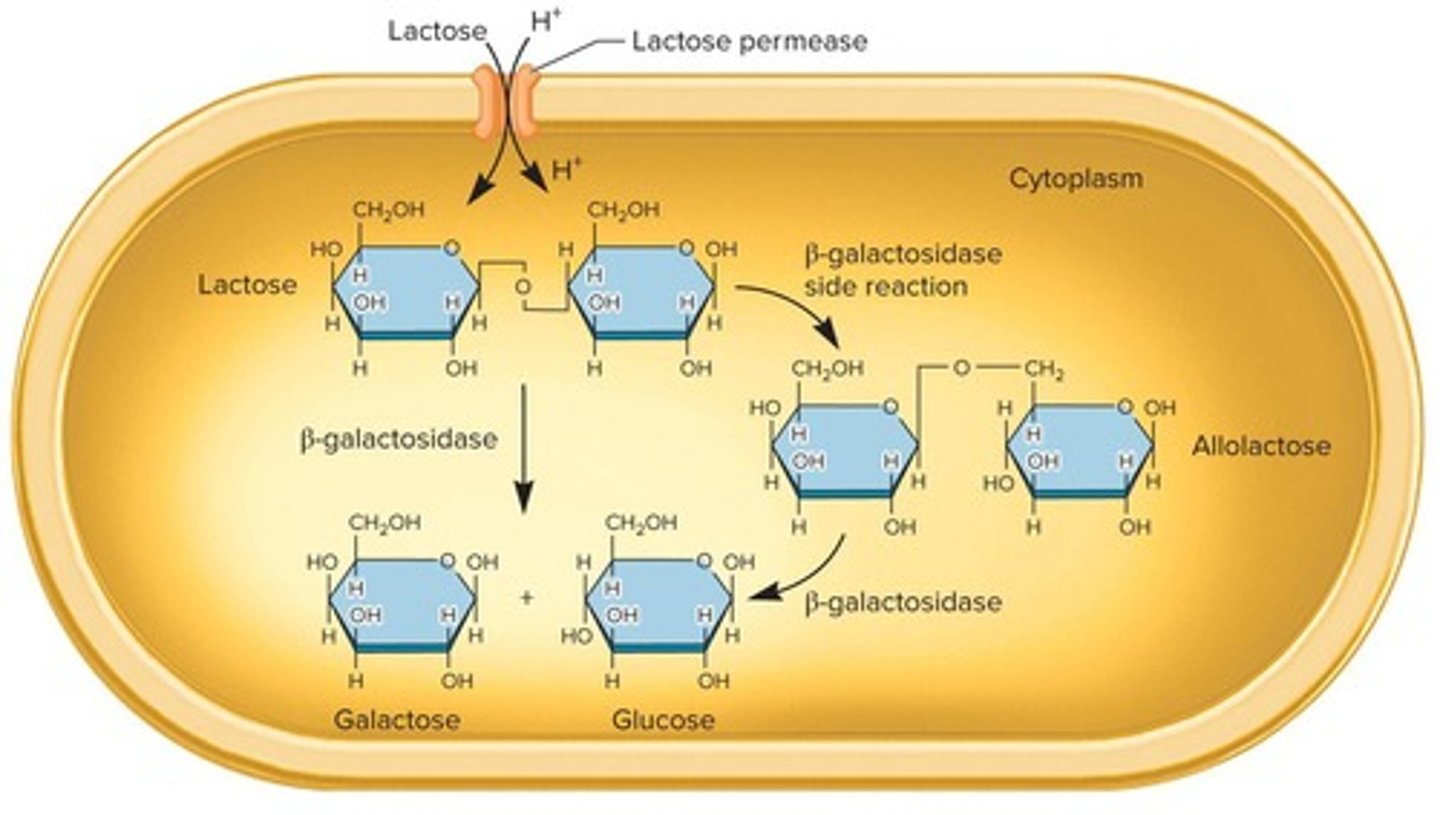
β-galactosidase
An enzyme that enzymatically cleaves lactose and lactose analogs, and converts lactose to allolactose.
lacY
A protein-coding gene that codes for lactose permease, a membrane protein required for lactose transport.
lactose permease
A membrane protein required for the transport of lactose and its analogues.
lacA
A protein-coding gene that codes for galactoside transacetylase, which modifies lactose and prevents toxic buildup.
galactoside transacetylase
An enzyme that covalently modifies lactose and its analogues to prevent toxic buildup.
lac repressor
A protein coded by the lacI gene that inhibits the lac operon by binding to the operator.
inducer
A molecule that binds to the lac repressor and inactivates it, allowing transcription of the lac operon.
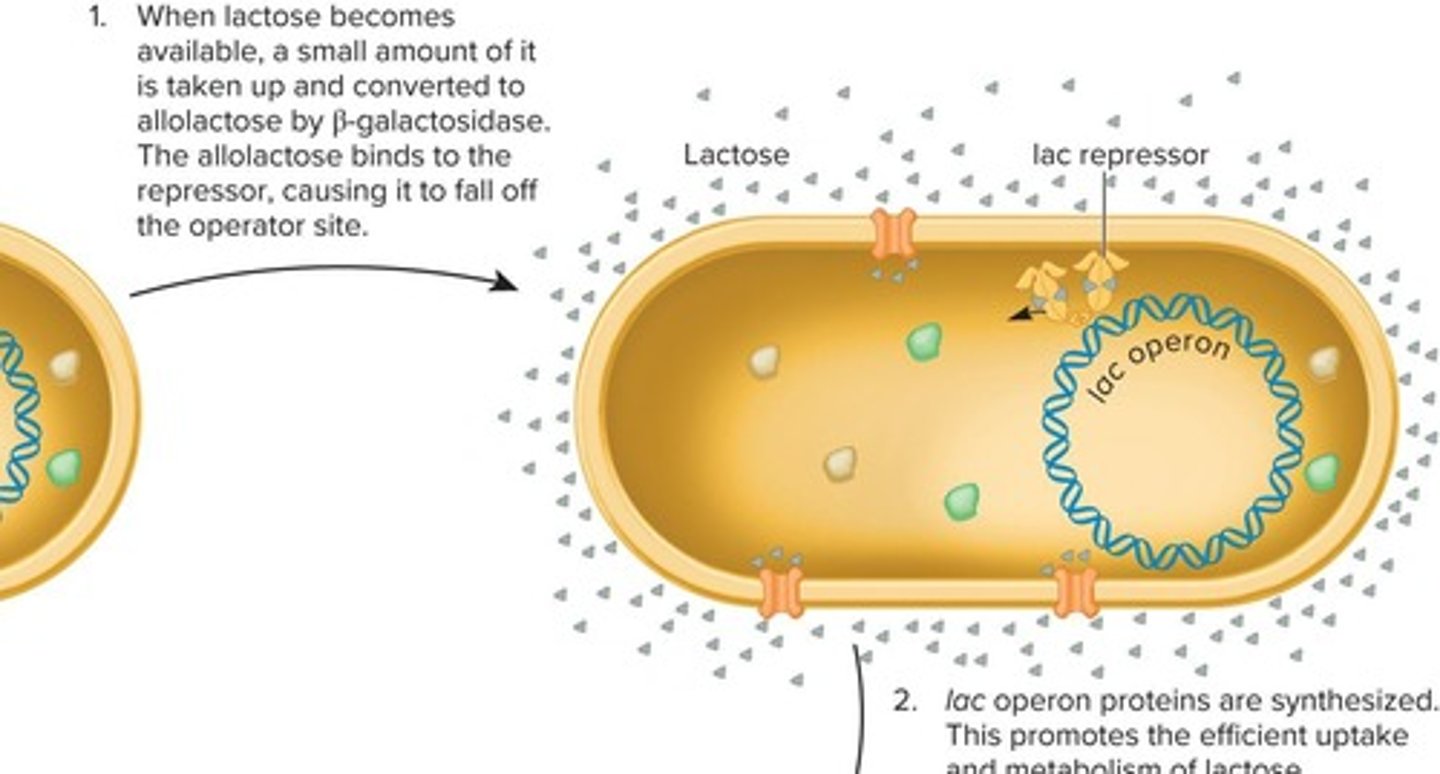
allolactose
An isomer of lactose that acts as an inducer by binding to the lac repressor.
transcriptional regulation
The process by which the expression of a gene is controlled, in this case by a repressor and an activator protein.
negative control mechanism
A regulatory mechanism where a repressor protein inhibits gene expression.
induction of the lac operon
The process by which the presence of allolactose leads to the transcription of the lac operon.
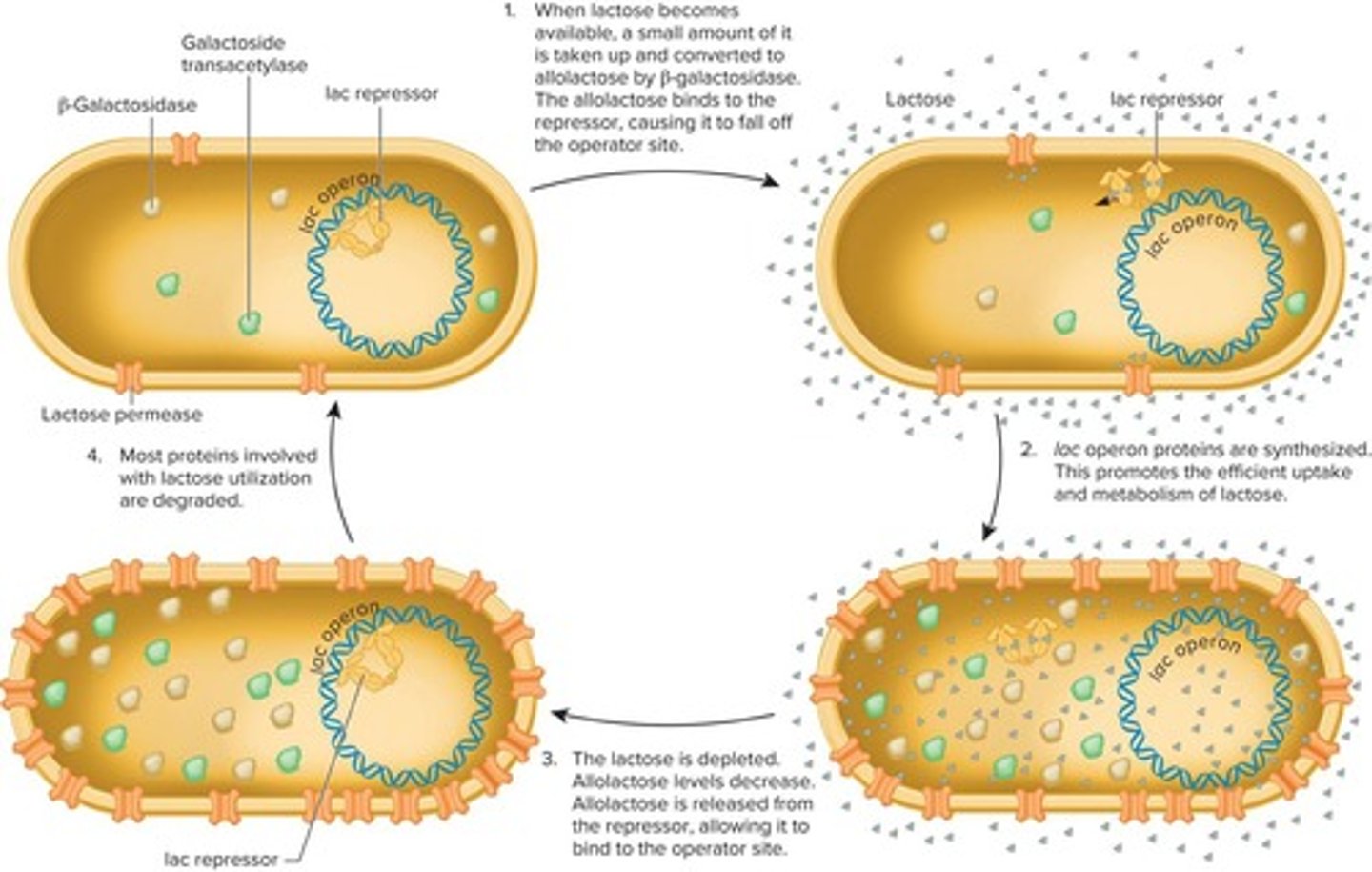
cycle of lac operon induction and repression
The process where lactose is taken up, converted to allolactose, and regulates the expression of lac operon proteins.
RNA polymerase
The enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template during transcription.
operator site
The specific region on the DNA where the lac repressor binds to inhibit transcription.
lacI gene
A gene that codes for a diffusible repressor protein involved in lactose metabolism.
lacI −
A mutation in the lacI gene that results in the constitutive expression of the lac operon even in the absence of lactose.
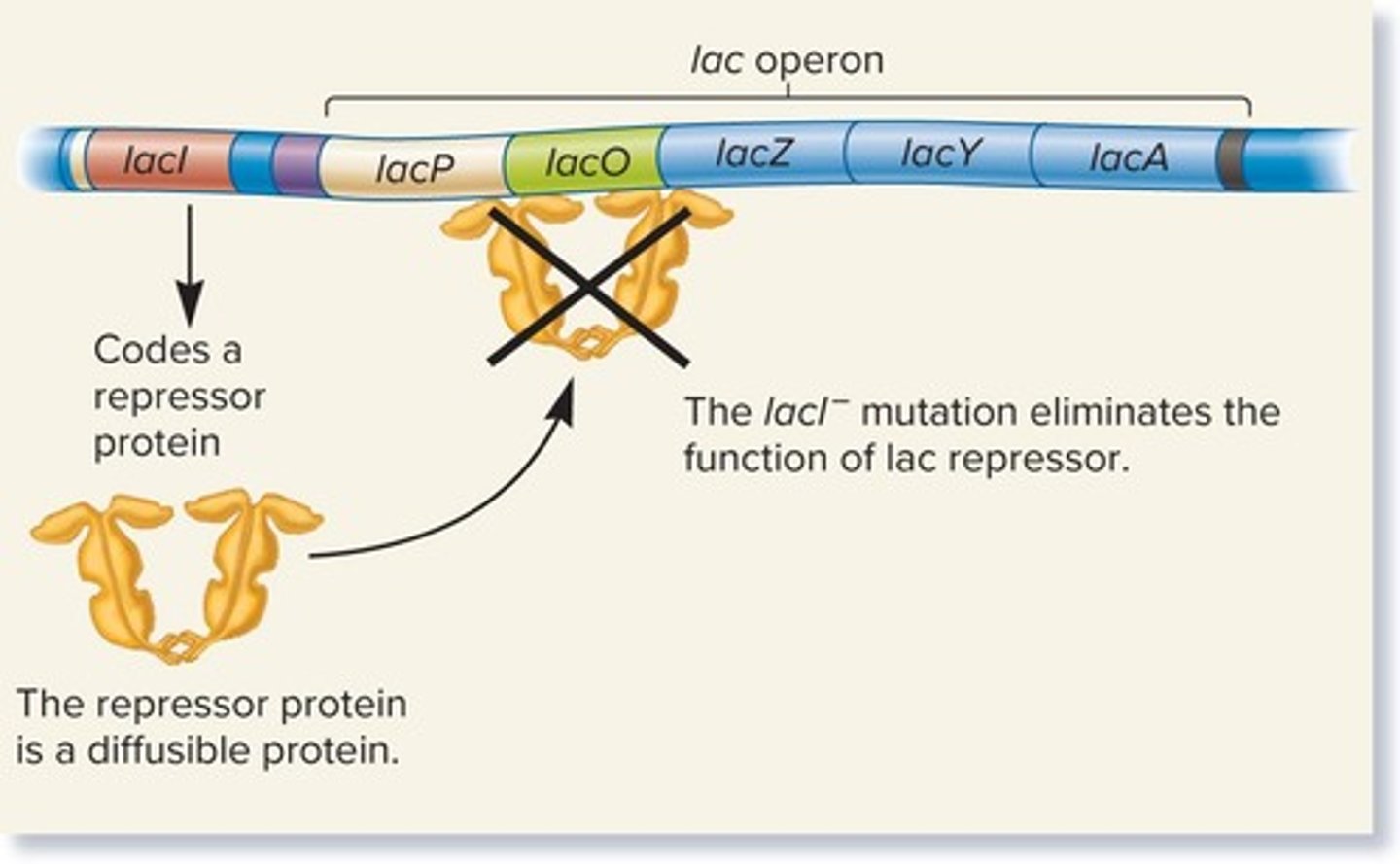
constitutive expression
The continuous expression of a gene regardless of the presence or absence of its substrate.
F' factors
Plasmids that carry portions of the lac operon used in bacterial conjugation.
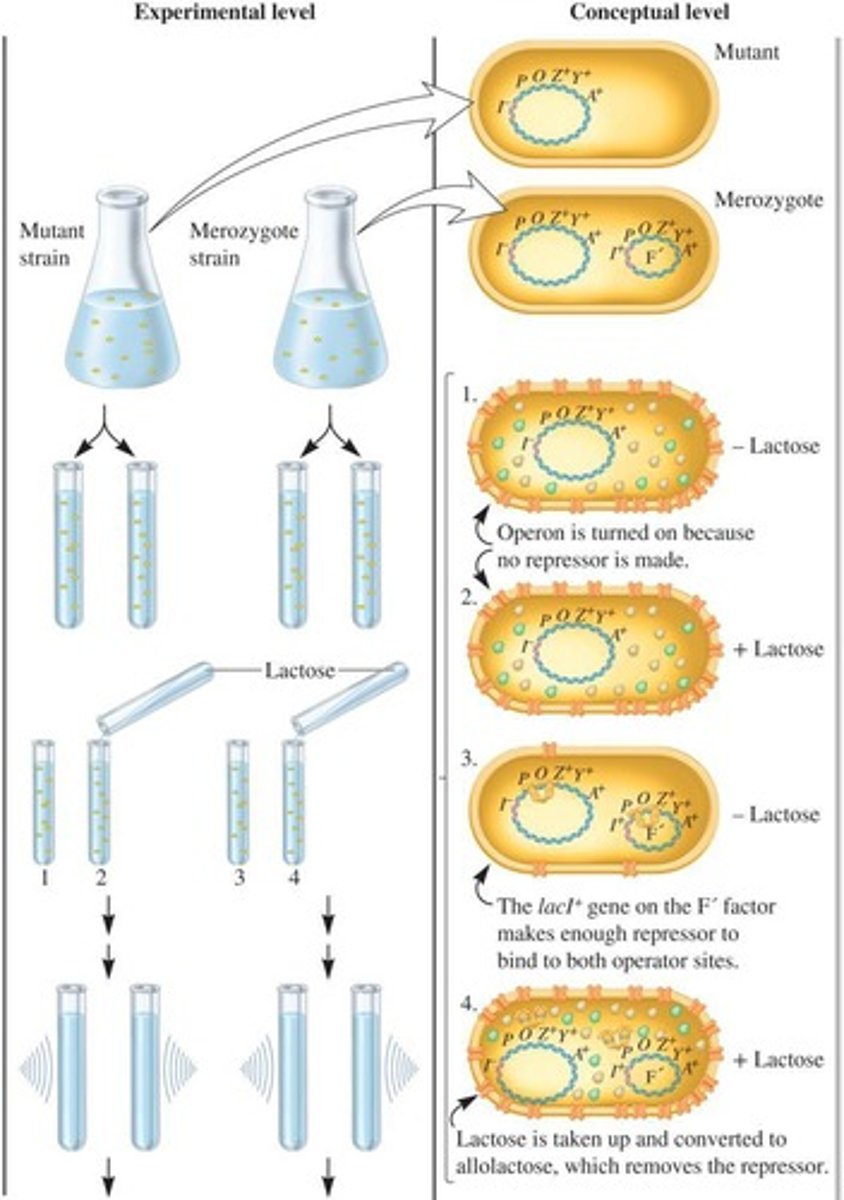
merozygotes
Bacteria that contain two copies of the lacI gene, one on the chromosome and one on the F' factor.
partial diploids
Another term for merozygotes, referring to organisms with two copies of a gene.
alleles
Different versions of a gene that may exist at the same locus on homologous chromosomes.
internal inducer hypothesis
The hypothesis that the lacI- mutation results in the synthesis of an internal inducer that activates the lac operon.
repressor hypothesis
The hypothesis that the lacI- mutation eliminates the function of a lac repressor that can diffuse throughout the cell.
β-galactosidase
An enzyme that cleaves lactose into glucose and galactose, and is used as a marker for lac operon activity.
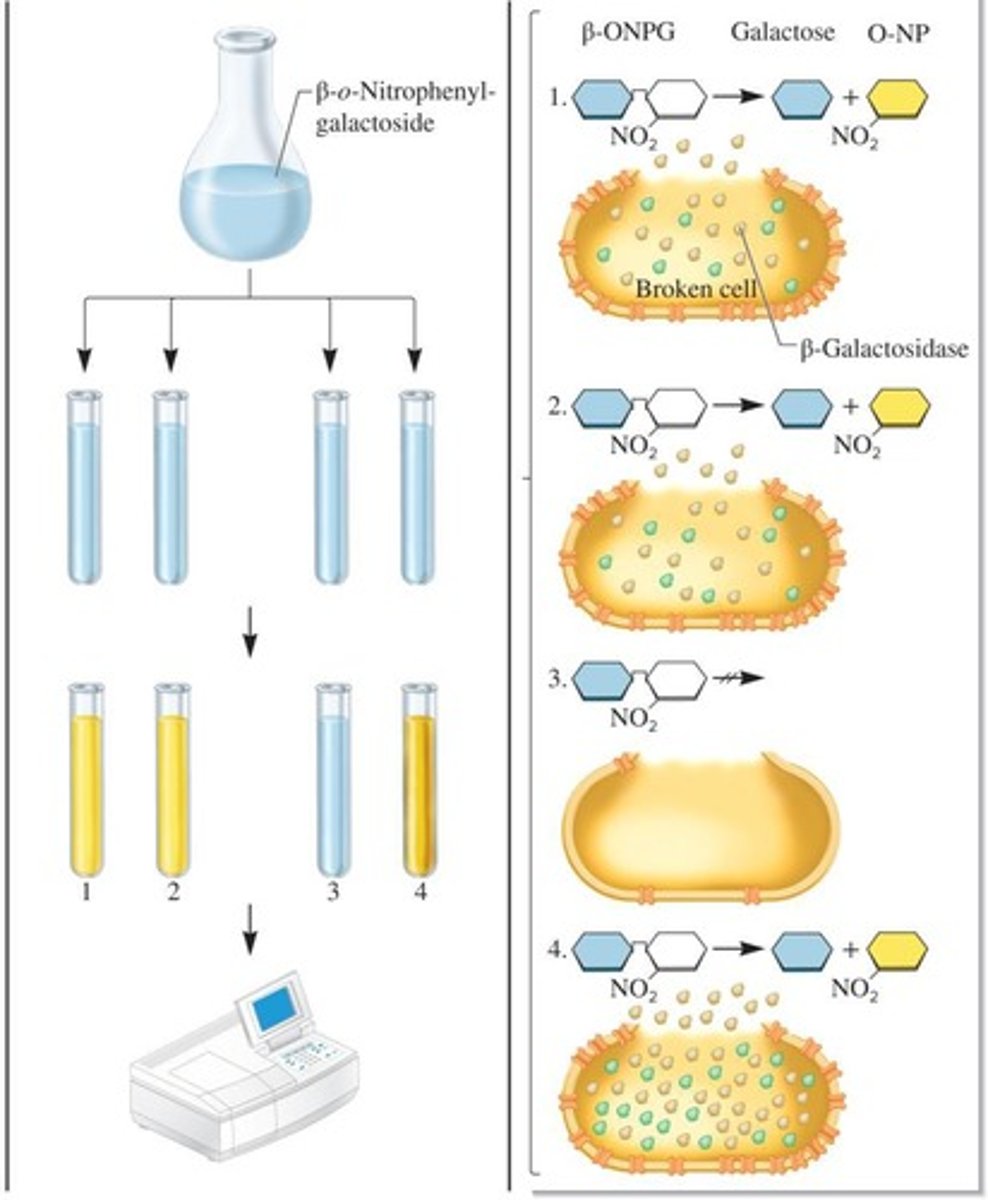
β-o-nitrophenylgalactoside (β-ONPG)
A colorless compound that is cleaved by β-galactosidase to produce a yellow color, indicating enzyme activity.
spectrophotometer
An instrument used to measure the amount of light absorbed by a solution, used to quantify β-galactosidase activity.
mutant strain
A strain of bacteria that carries a mutation, in this case, the lacI- mutation.
incubation
The process of maintaining cells at a specific temperature to allow for growth or biochemical reactions.
sonicator
A device used to lyse cells by applying ultrasonic sound waves, allowing the release of intracellular components.
yellow color measurement
The depth of yellow color produced in the reaction with β-ONPG, which correlates with the amount of β-galactosidase produced.
lactose addition
The process of adding lactose to bacterial cultures to induce the lac operon.
data from experiment
Results showing that mutant strains produce 100% β-galactosidase regardless of lactose addition, while merozygotes produce <1% without lactose and 220% with lactose.
Jacob, Monod, and Pardee
Scientists who conducted foundational research on the lac operon and its regulation.
lact operon
A set of genes involved in the metabolism of lactose in bacteria.
chromosome
The structure that contains the genetic material of an organism.
bacterial conjugation
A process by which bacteria transfer genetic material through direct contact.
mutant strain results
In the experiment, both mutant strains showed 100% β-galactosidase production regardless of lactose presence.
Mutant strains
Express the lac operon at 100% because of constitutive expression in the lacI- strain.
Merozygote
In the absence of lactose, both lac operons are repressed → <1%; in the presence of lactose, both lac operons are induced, yielding a higher level of enzyme activity → 220%.
lacI- mutant
Doesn't make a repressor protein.
lacI+ gene
Makes a repressor protein that can repress the lac operon in the same cell, doesn't have to be on the same piece of DNA as its gene.
Trans-effect
Genetic regulation that can occur even though DNA segments are not physically adjacent, mediated by genes that code regulatory transcription factors.
Cis-effect
A DNA sequence that must be adjacent to the gene(s) it regulates, mediated by sequences that bind regulatory transcription factors.
lac operator
An example of a cis-acting element.
Mutation in a trans-acting factor
Is complemented by the introduction of a second gene with normal function.
Mutation in a cis-acting element
Is not affected by the introduction of another normal cis-acting element.
Wild type lac operon expression
With lactose: 100%; Without lactose: <1%.
lacI- expression
With lactose: 100%; Without lactose: 100%.