Induction and intubation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are Guedel’s 4 stages of anaesthesia?
Stage I = induction (analgesia)
Stage II = delirium (excitement)
Stage III = surgical anaesthesia
Stage IV = respiratory and medullary paralysis/depression

Properties of propofol, including side effects
lipid soluble
hypnotic
hepatic and extra hepatic metabolism
inhibits GABA receptors
neuroprotective
may cause excitation on induction
respiratory depression
cyanosis
hypotension
vasodilation
does not maintain0 baroreceptor reflex
Properties of alfaxalone, including side effects
hepatic metabolism
similar onset and duration to propofol
respiratory depression depends on dose
moderate vasodilation
hypotension
maintains baroreceptor reflex - less CV depression than propofol
inhibits GABA
less drug accumulation than propofol
needs to be given after sedatives, otherwise agitation, stiffness, dysphoria
Properties of ketamine, including side effects
liver metabolism
give alongside mucle relaxant as increases muscle tone
norketamine metabolite accumulation may occur
dysphoria
hypersensitivity to noise, light and handling
respiratory depression, apneustic breathing
hypersalivation
increased cerebral blood flow
increased heart rate, cardiac output and blood pressure (careful with heart disease)
Avoid in cats with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Characteristics of Etomidate
human drug
preserves cardiovascular function
suppression of adrenal function can lead to Addisons crisis
Discuss usage of thiopental
no longer licenced
causes tissue necrosis if peri-vascular injection
can occasionally be given to horses to top up
List 3 drugs used for co-induction of anaesthesia
midazolam
ketamine
fentanyl
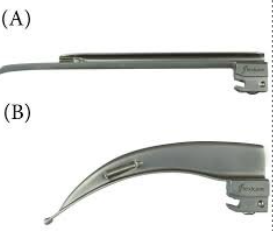
Name these 2 laryngoscopes
A - straight Miller blade
B - curved Macintosh blade
How to confirm correct placement of ET tube? (5)
visualisation with laryngoscope
capnography to check adequate ETCO2
condensation inside ET tube
movement of reservoir bag
squeeze reservoir bag and watch for chest movement
4 limitations of supraglottic airway devices
risk of aspiration not eliminated
hard to completely seal
,may be harder to ventilate
easier to dislodge
List 5 alternative intubation techniques and when they may be used
nasotracheal = common in large animal
pharyngotomy = if having oral surgery
retrograde intubation = if hard to open oral cavity
one lung intubation = for specific thoracic surgeries
tracheostomy = if obstructed upper airway
Considerations when intubating ruminants and camelids
Large ruminants need a bite block, as hand must be placed into mouth
All have regurgitation risk
Considerations when intubating pigs
Difficult due to S-shape larynx, so use a stylet to help
Considerations when intubating birds
use uncuffed tubes due to complete tracheal rings