Using numerical examples, explain absolute and comparative advantage
1/3
Earn XP
Description and Tags
10 marks
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Numerical example of absolute advantage

Paragraph for absolute advantage
Define absolute advantage:
Occurs when a country can produce more output using the same amount of resources than another country
Explanations using the example:
Country A can produce more cars (10 vs 5) and more wheat (20 vs 10) than Country B in the same time period.
This means Country A has an absolute advantage in both goods, as it is more productive in each case.
Country B has no absolute advantage, as it produces fewer goods using the same resources.
Numerical example for comparative advantage
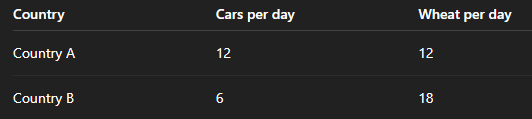
Paragraph for comparative advantage
Define comparative advantage:
Occurs when a country can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country.
Calculate the opportunity costs:
Country A:
1 car=1 wheat
1 wheat= 1 car
Country B:
1 car=3 wheat
1 wheat=0.33 cars
Explanation using the example:
Country A has a lower opportunity cost in car production (1 wheat per car compared to 3 wheat in Country B), so it has a comparative advantage in cars.
Country B has a lower opportunity cost in wheat production (0.33 cars compared to 1 car in Country A), so it has a comparative advantage in wheat.
If each country specialises in the good they have a comparative advantage in and trades, total global output increases, allowing both countries to benefit from trade.