Physiology - Gastrointestinal system
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Digestive Process
Motility (mixing and metering)
Secretion (exocrine and endocrine)
Digestion (mechanical and chemical breakdown)
Absorption
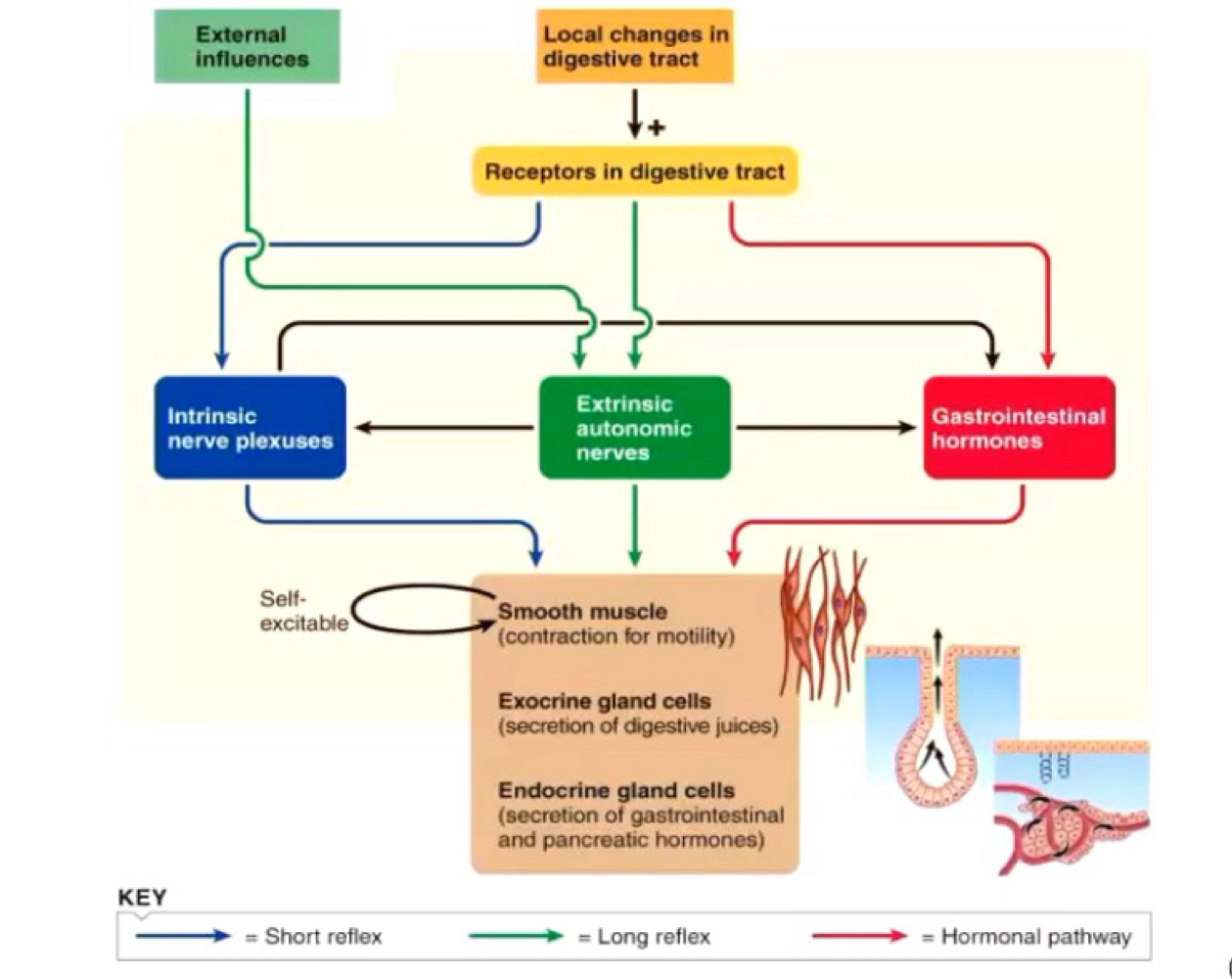
Regultion of GI function
Autonomous smooth muscle function
Intrinsic nerve plexuses
Extrinsic nerves
GI hormone
Phases of Digestion
Inter-digestive: little activity
Cephalic: largely nerves
Gastric: nerve and hormones
Intenstinal: largely hormones
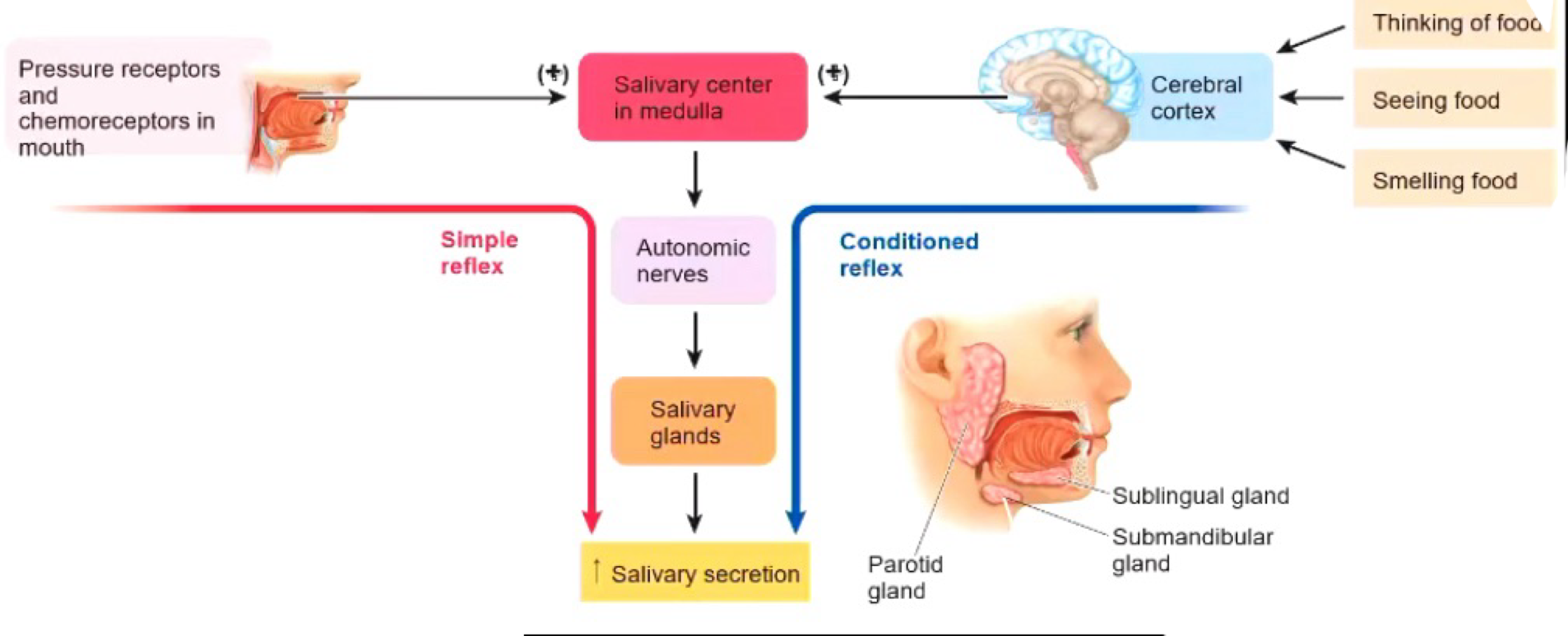
The Mouth functions
Teeth: mastication (smaller pieces) → increases surface area
Salivary Glands: secrete saliva → salivary amirayse, antibacterial and mucus.
Function of the stomach - Gastric Filling
Weak peristaltic waves move food into the body of the stomach
Receptive relaxation
Can accomodate about 1 litre of contents
Function of the stomach - Gastric Storage
storage in the body of the stomach
Thin smooth muscle layer, so little mixing of food
Function of the stomach - Gastric Mixing
occurs in the antrum of the stomach
Strong peristaltic waves mixes ingested food with gastric secretions
Chyme is pushes towards the pyloric spinchter.
Functions of the stomach - Gastric Motility
emotions can influence gastric motility
Irritation to digestive tract can lead to repulsion of food (abdominal smooth muscle contracts).
Triggers of Gastric Emptying
Factors in the stomach
Aount of chyme and degree of fluidity = increased rate of GE
Factors in the duodenum
Fat, acid, hypertonicity and distention decrease rate of GE via enterogastric reflux).
Gastric digestion and absorption
protein digestion (antrum)
Little carbohydrate digestion (body)
Some fat digestion
Absorption of alcohol and aspirin
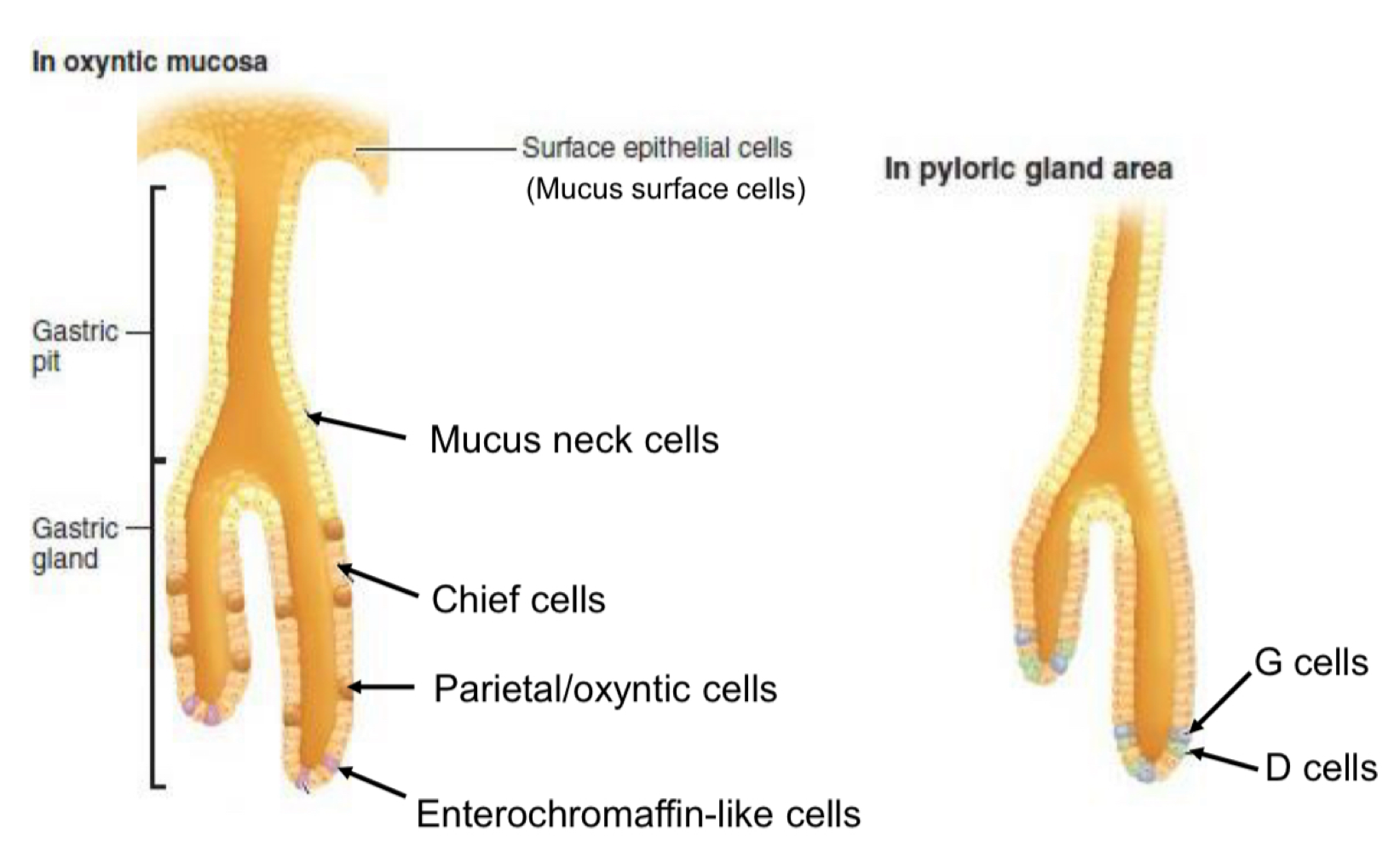
Secretory Cells - Endocrine/exocrine
Exocrine
Mucus neck sells
Chief cells
Parietal/oxyntic cells
Endocrine
enterochromaffin-like cells
G cells
D cells
Mucus surface and neck cells
exocrine
Mucus and bicarbonate-rich secretion
Stomach = hostile environment
Protects surface
Chief ( or zymogen-secreting) cells:
Exocrine
Secretes pepsinogen, when reacted with HCl → pepsin
Active proteolytic enzyme → breaks down proteins into amino acids/peptides
Begins protein digestion
Parietal (oxyntic) cells
Exocrine
Secretes HCl
denature protein
Activates pepsinogen
Kills most ingested microorganisms
Solublizes Fe3+, assisting absorption
Secretes Intrinsic factor
Binds vitamin B12
Triggers absorption in ileum (endocytosis)
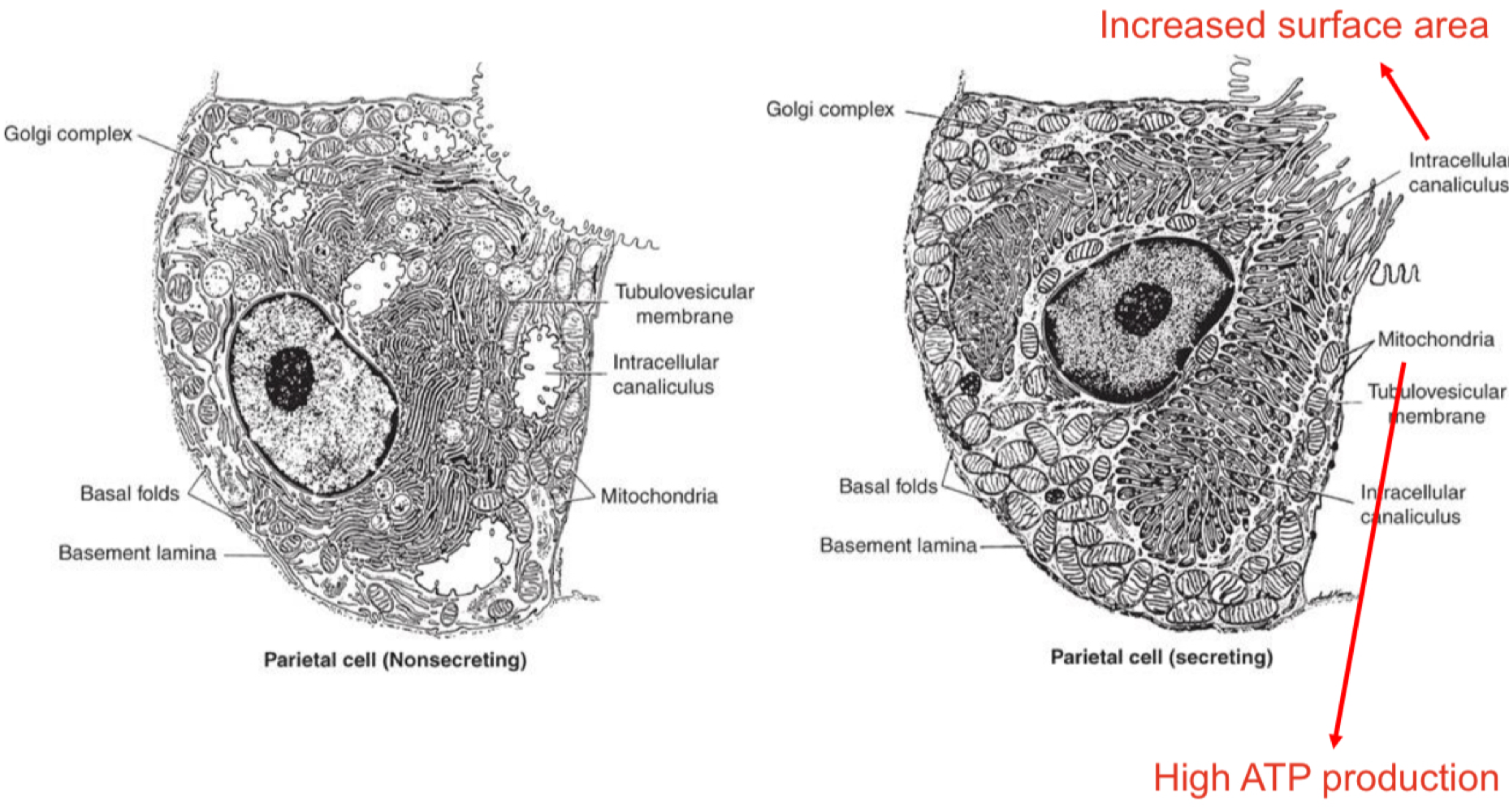
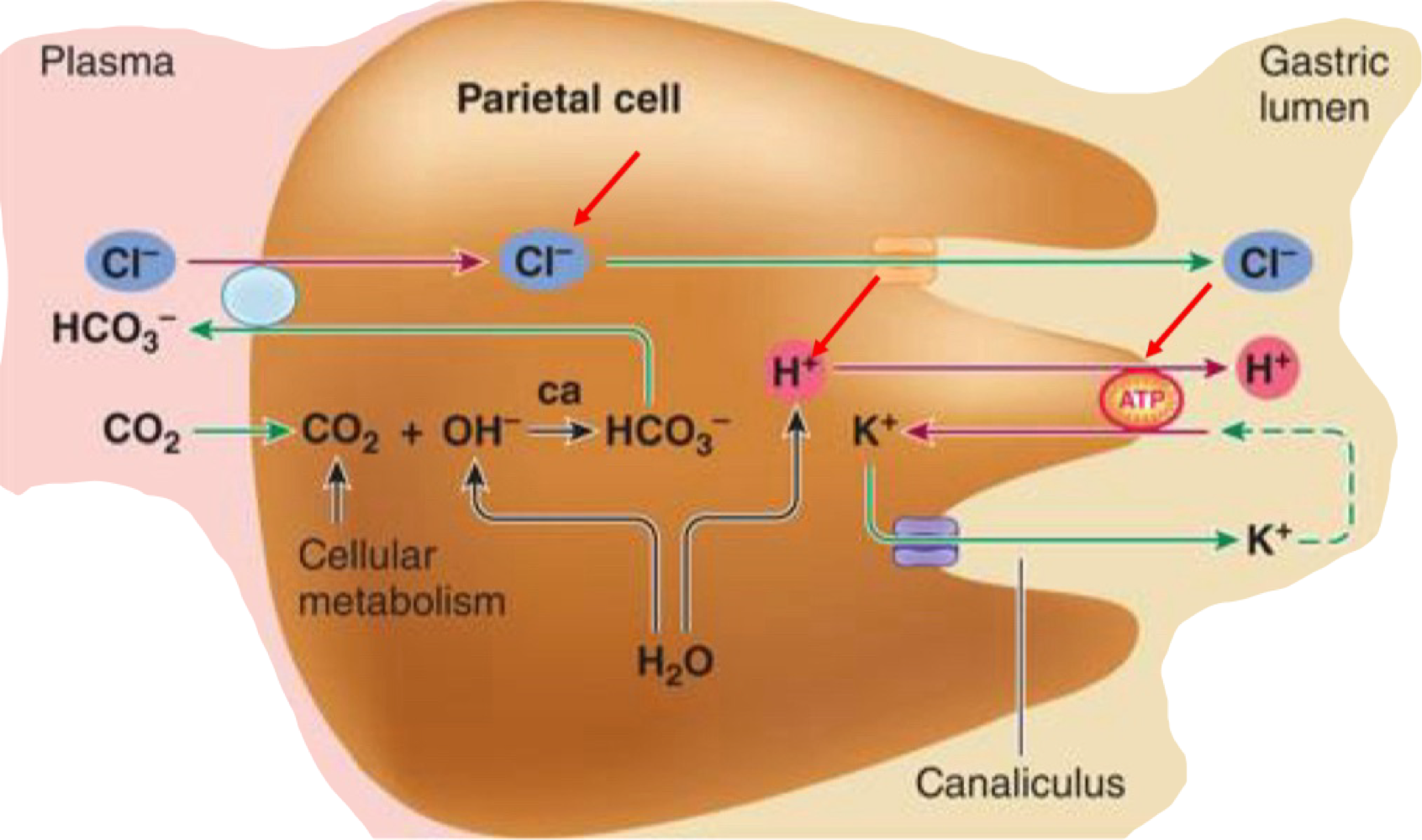
H+ Generation and Secretion - Parietal cells
acid is secreted vis a proton pump, K+ and Cl- channels and ATPase
Gastric juice - 155mM HCl + 15mM KCL
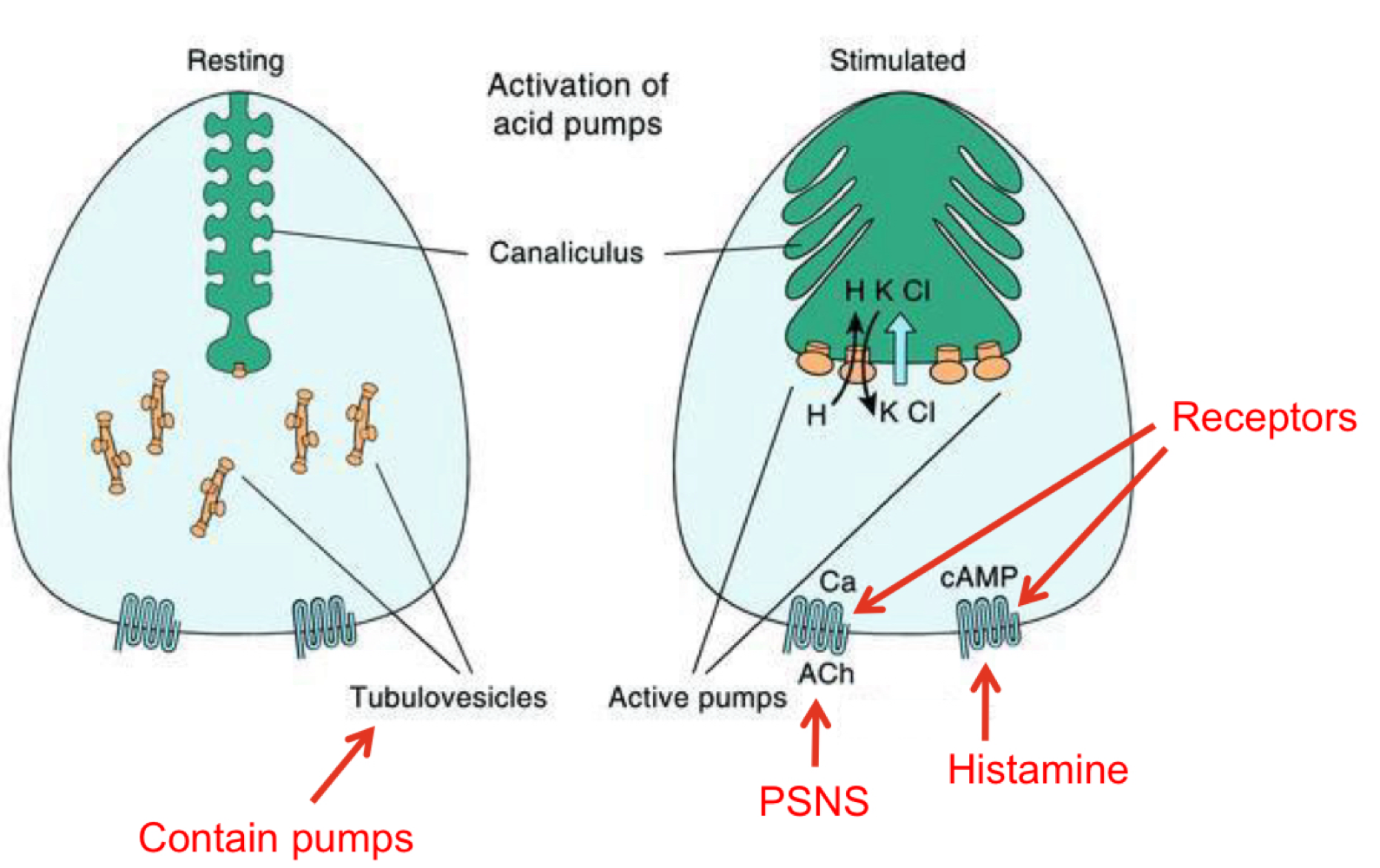
Stimulation of Acid Secretion
Enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells
endocrine
Present in oxyntic gland (body of stomach)
Releases histamine (paracrine) → stimulates acid secretion (parietal cells)
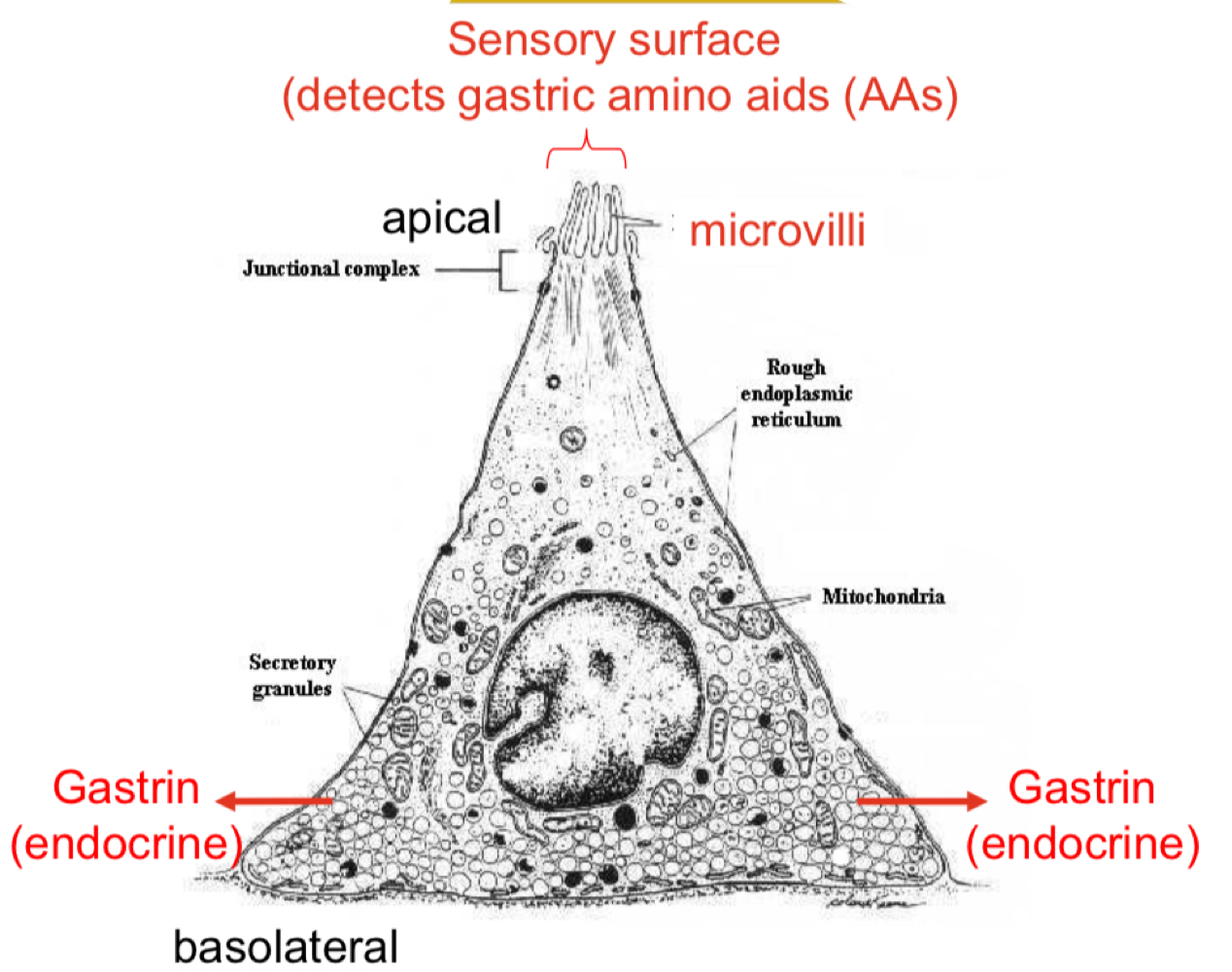
G cells
endocrine
Present in pyloric gland (antrum)
Secretes gastrin → stimulates parietal, chief and ECL cells
D cells
endocrine
Present in the pyloric gland (not rum)
Secrete somatostatin → negative feedback
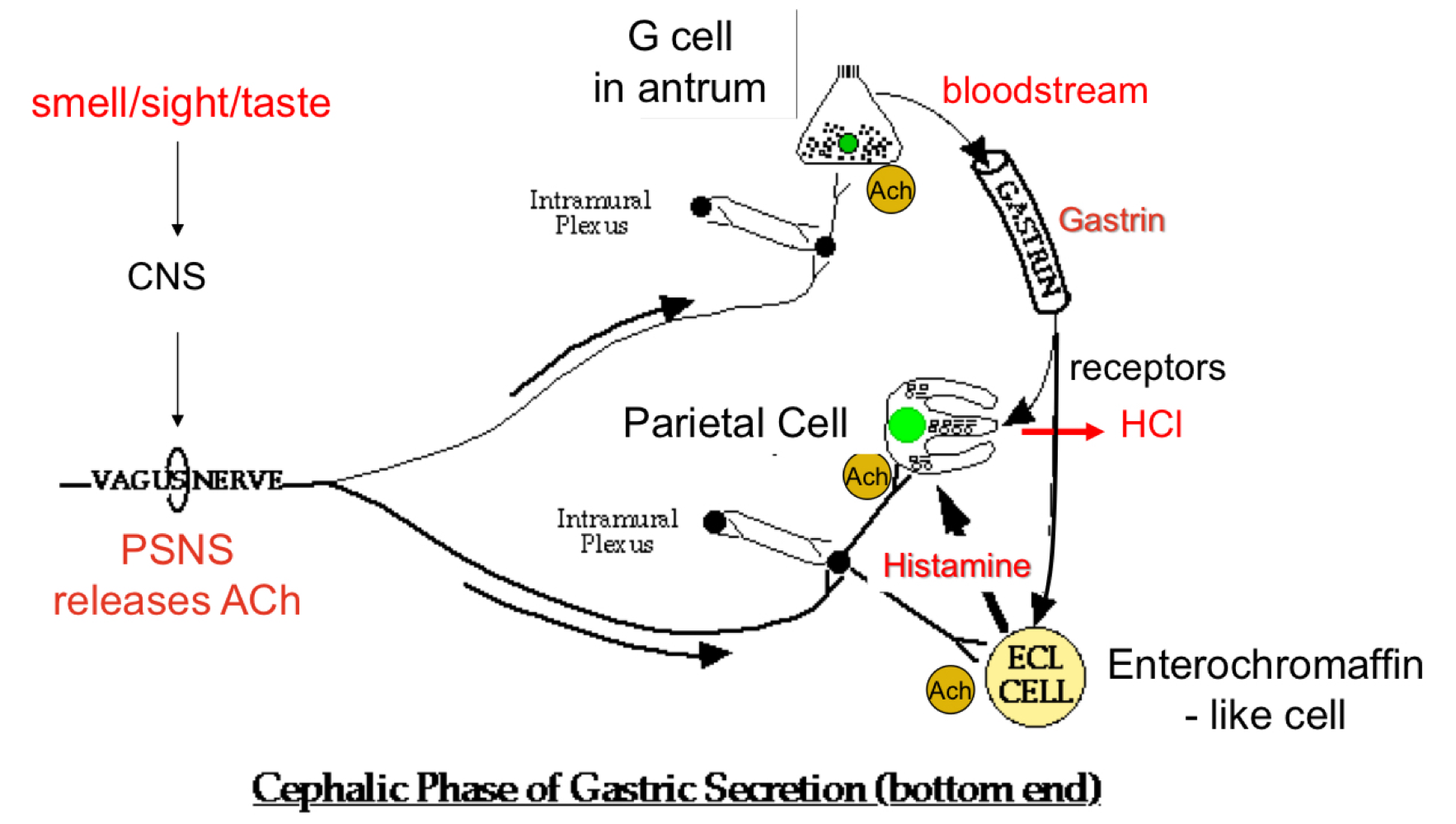
Gatric Secretion - Cephalic Phase
repaired the digestive system for food processing
30% of total gastric secretions
Input: Neural
Output: “predatory” acid and enzyme secretion → increases efficiency of digestion
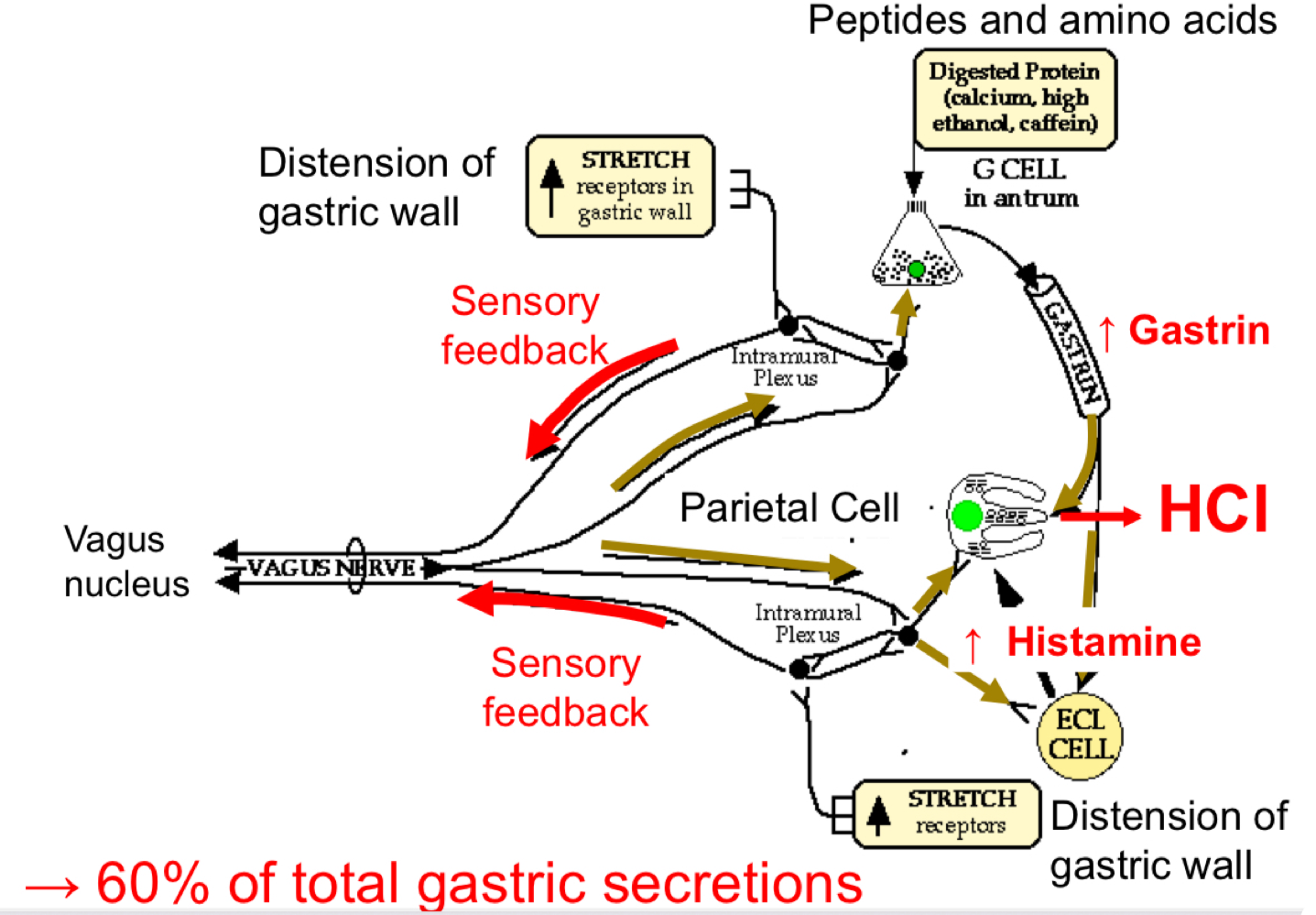
GA Secretion - Gastric Phase
Filling of stomach distends gastric wall
increased sensory feedback → increased parasympathetic output to parietal, ECl and G cells
Presence of amino acids into the antrum stimulates G cells to increase gastrin secretion.
60% of total gastric secretions
Protective Barrier
Mucus Surface cells produce a mucosal barrier
High levels of bicarbonate, prevents stomach lining from being digested
Gastric Emptying - Order
Isotonic saline/water
Acidic and caloric fluids
Fatty materials
<2mm solids
Intestinal Motility - Peristalsis
Initiared by nervous and hormonal signals
Spreads out chyme throughout the instestine and propels of towards the ileocecal valve
Intestinal phase of digestion
Requires further digestion → new enzymes required
Secretions:
Pancrease
copious enzymes to further digest food
Bicarbonate to neutralise acid
Liver (biliary system) - secretes bile salts
Pancrease Acinus
Acinar cells: releases, proteases, lipases, amylases and nuclei acid enzymes
Intercalated duct cell: bicarbonate
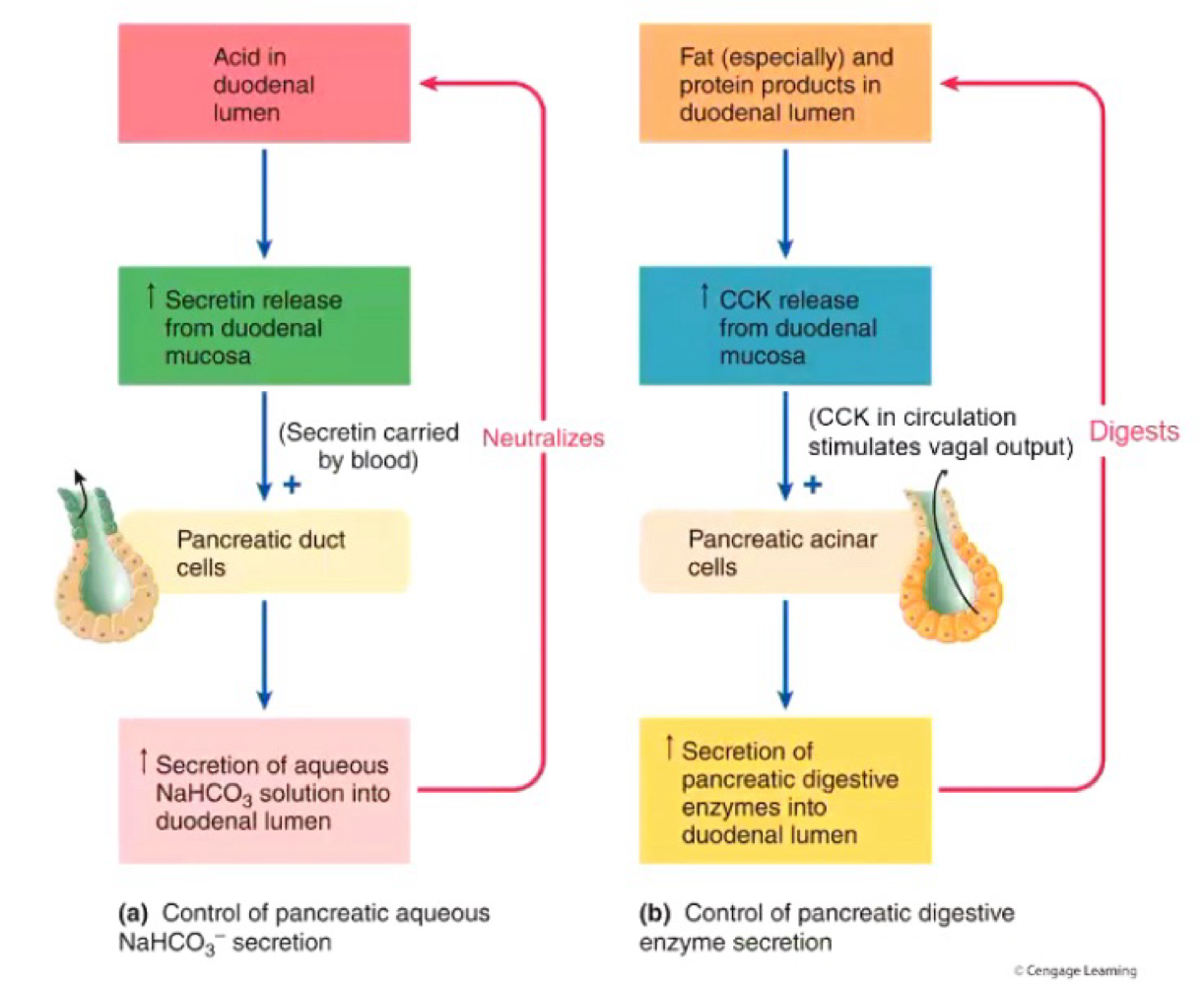
Control of pancreatic Secretion
Vagus (parasympathetic) nerve (via Ach) - controls both enzyme release and bicarbonate release
Cholecystoknin (CCK) - enzyme release only
Secretin - bicarbonate release only
Control of CCK Release
Stimulated by:
digested fat and proteins
CCK-releasing factor
H+
Inhibited by:
Trypsin in lumen
Somatostatin
CCK-RF and Trypsin are continuously released into the duodenal lumen
Secretion of CCK
CC-RF binds to enteroendocrine cells which further stimuleast CCK release
Between meals:
Trypsin binds to and break down CCK-RF
Digested CCK-RF can’t bind to enteroendocrine cells therefore decreased CCK
After meal:
Trypsin preferentially binds to and digest proteins
Therefore no CCK-RF broken down
CCK-RF binds to enteroendocrine cells → triggers CCK secretion (pancreatic enzyme secretion)
CCK Actions on Pancrease
stimulus pancreatic enzyme secretion largely via stimulation of vagal Afferent (sensory)
No CCK receptors on acinar cells
Vagotomy or atropineinhibits pancreatic enzyme secretion
Secretion Action on Pancreas
Secrein released from enterocytes in repsonse to aci d
Acts via vago-vagal pathway and directly via secretin receptors on duct cells
Induces ducts cells to produce bicarbonate