eukaryotic cell growth and death
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
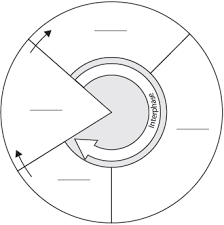
describe the cell cycle
process that starts when a new cell forms, and ends when the cell divides
G1 → S → G2 → M
G0 phase - cells that do not divide stay here
why do cells divide?
to compensate for growth and division - smalls have small surface area to volume ratio
repair and renewal ; replace damaged/dead cells ensuring constant cell number
reproduction; gamete cells producing offspring
cell cycle in diff cell types
some cells divide continuously replacing lost cells eg stem cells
others do not divide eg mature muscle and nerve cells
some cells only divide when stimulated eg hepatocytes
cell cycle divisions
can be divided into
interphase
mitotic phase
interphase
consists of g1, s phase, g2
growth phase
increase in mass, synthesis of cell contents
cells stay here majority of the time
mitotic phase ( m phase)
cellular division via mitosis ( nuclear divison ) and cytokineses ( cytoplasmic divison)
interphase : G1
g= gap
synthesis of RNA, proteins & organelles
but NOOOO!!! chromosomes
cell increases in mass
depenidng on cell type, duration varies
typically 8-10 hours, but a few minutes to hours in faster cells
decide if cell should through cellular divisions
to G0 or stay in G1
centromere
denotes the number of chromosome, holds sister chromatids together
interphase : G2
cell double checks for errors
DNA repair
prepares cell for mitosis ( cell growth + protein synthesis )
typically 4-6 hours
interphase S-phase
s= synthesis
replication of DNA ( in prep for cellular division)
relatively short ( like 5 hrs.)
mitotic (m) phase
m phase : mitosis ( nuclear) + cytokinesis ( cytoplasmic)
results in 2 genetically identical cells
typically 30 - 45 minutes
VERYYYY SHORT
cell cycle regulation
checkpoints ensure proper progression, error free division
if conditions are met cell progresses further
using cyclins & cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks)
if conditions are not met, cell will not continue
how do check points regulate regulation
ensure appropriate timing of cell cycle phases
ensures phase completion before transition to next phase
able to respond to external conditions eg growth factors + nurtients
cyclins & cyclin dependent kinases
remember kinases are enzymes that transition phosphate groups through hydrolysis of atp/gtp
cyclins - proteins that bind to cylin-dependant kinases ( Cdks)
cyclin dependant kinases - enzymes that bind to proteins that activate proteins required for the cycle
name given due to fluctuating concentrations during diff stages
Cdk-cylin complex allows cell to pass checkpoint to the next stage
cyclins
protiens that bind to Cdks
form cyclin-Cdk complexes which allow cells to pass the checkpoint to the next phase
cyclin dependant kinases
bind to cyclin formng Cdk-cylclin, passingg checkpoint, letting cells transition to next stage
cylin dependant kinases activate proties required to progess the cycle
active mitotic cdk-cyclin stimulates
nuclear envelope breakdown
chromosome condensation
mitotic spindle formation
targeted protein degradation
main checkpoints
3 main checkpoints
metaphase- anaphase transition control
G1-S transition control
G2- M transition control
G1-S check point
occurs towards the end of G1
checks whether cell is ready for DNA replication @ S-phase
cell is big enough
has the necessary proteins
is the dna damaged
if all the conditions r not met, cell goes through resting period (g0) until ready to divide
G0 phase
cell exits from cell cylce if cell is not progressing to S-phase
G0 cells are dormant
non-dividing cells undergo terminal differentiation ( eg nerve cells)
can be triggered to re-enter g1 if theres a signal ( eg hepatocytes)
G2-M transition control
occurs @ the end of g2 ( boundary of g2 - m)
checks whether the cell is ready for m phase ( cellular division)
cell is big enough
DNA replication complete
have necessary proteins
if conditions unmet here, arrest of cel can occur here if division is not necessary
metaphase-anaphase checkpoint control
occurs in the mitotic phase ( specifically metaphase and anaphase)
checks whetehr mitosis process is going well
ensures chromatids are properly attached to spindle fibers pro
ensures daughter cells receive complete set of chromosomes
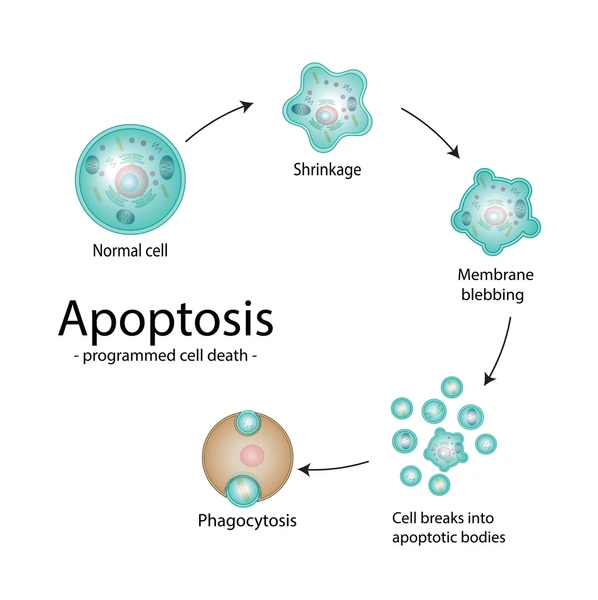
apoptotic cell death process
chromosomes condense, cytoplasm shrinks
nucleus becomes fragmented, bleb formations
apoptotic bodies are ingested by phagocytic cells
what if a cell makes an irreparable mistake
p53 proteins triggers apoptosis ( programmed cell death)
necrosis
premature death where cells swell and rupture, releasing cellular contents
result of external factors ( disease, injury, hypoxia)
apoptosis
programmed cell death
part of development and growth ( healthy process)
triggered by DNA damage by UV, xrays and chemotherapeuatic agents
apoptic vs necrosis