BIOL 1108 Lab Week 5: Plant Anatomy & Growth
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Three organs of the plant body
Stems, roots, and leaves
What is the "shoot" of a plant?
The stem and its leaves
Key features of leaf
-cuticle
-stomata (opened and closed by guard cells)
-columnar mesophyll cells
-spongy mesophyll cells
Cuticle
A water-impermeable, thin waxy layer which covers both the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf.
What is just to the inside of the cuticle?
A single layer of epidermis cells.
Stomata
The openings in leaves that allow moisture and gases to be exchanged with the environment.
Guard Cells
Open and close stomata
Columnar Mesophyll Cells
Long upright orientation of the cells near the upper surface. They are responsible for absorbing light
Spongy Mesophyll Cells
Below the columnar mesophyll cells and closer to the bottom surface of the leaf and have much larger air gaps positioned around them. Allows CO2 to easily spread throughout the leaf tissue
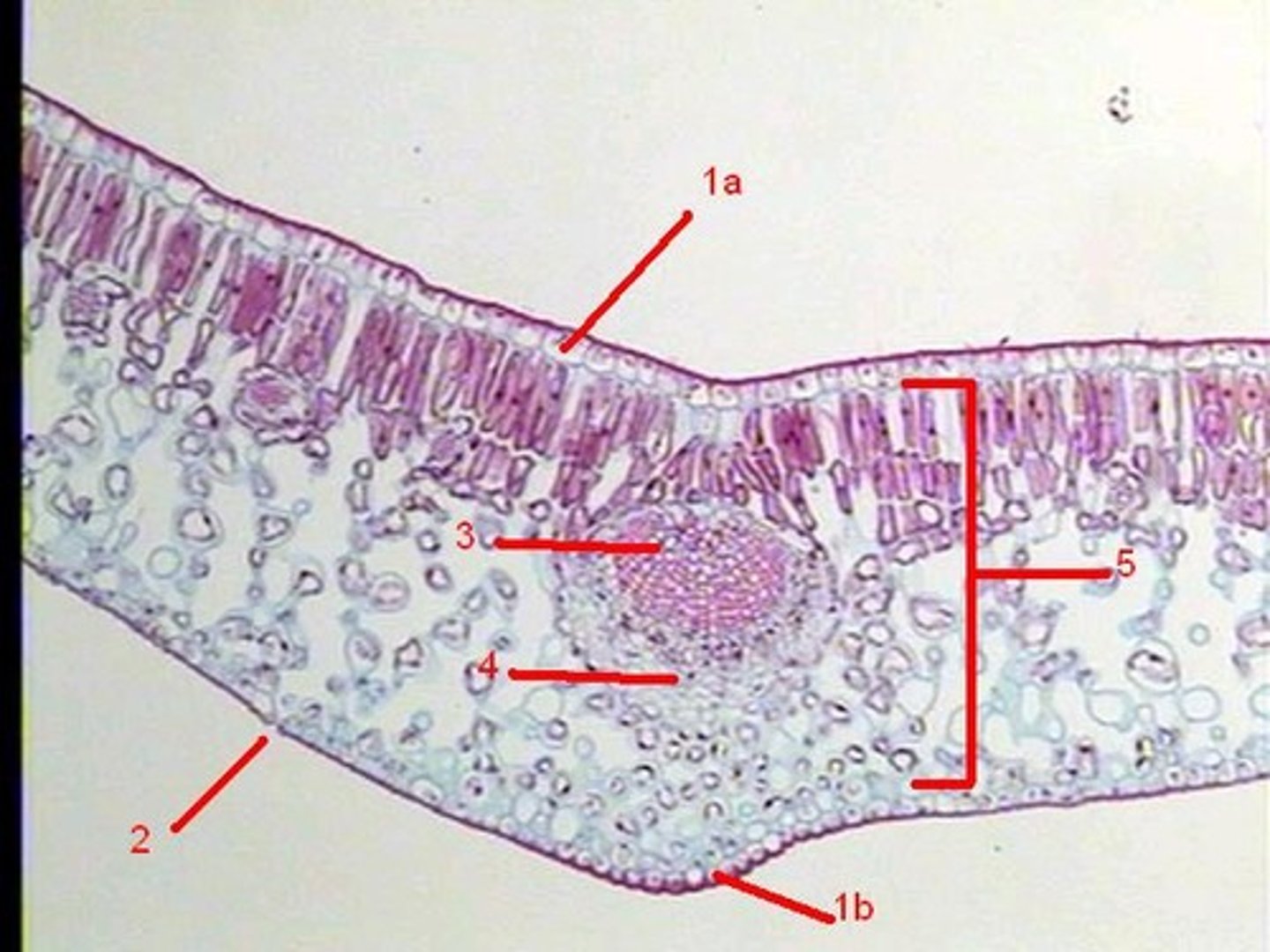
Key features of a privet leaf cross section
-upper epidermis
-mesophyll
-lower epidermis
-central vein/vascular bundle
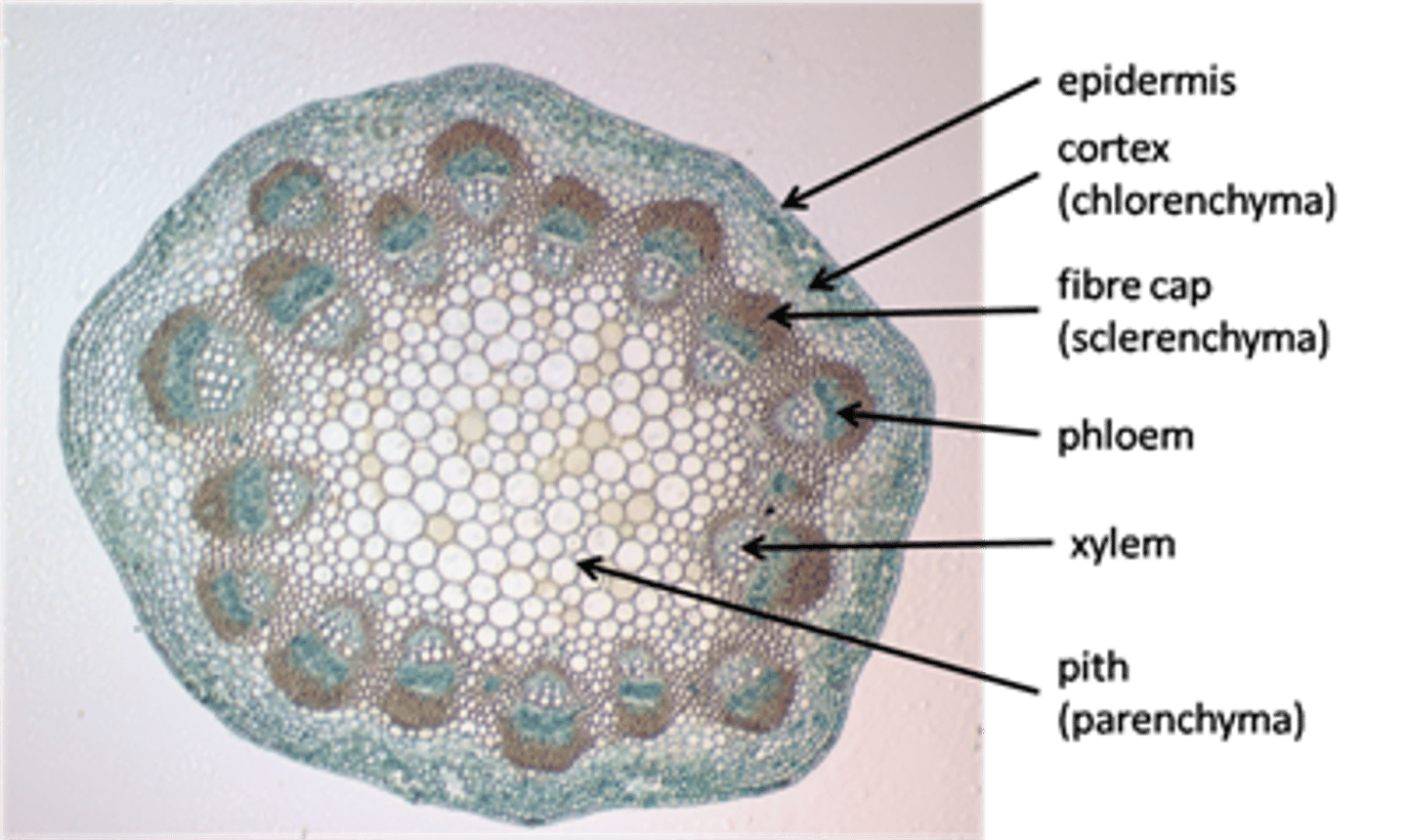
Key features of stem
-epidermis
-cortex
-vascular bundles
-xylem
-phloem
-pith
Epidermis
Outermost layer of cells
Cortex
A layer of cells just beneath the epidermis
Vascular Bundles
Found distributed at regular intervals around the stem. Comprised of xylem and phloem tissues.
Xylem of stem
Has lignin, a rigid substance that helps physically support the plant (stains red). Transports water throughout the entire plant, pulling water from soil.
Phloem of stem
Adjacent to the xylem but on the side of the vascular bundle closest to the outside of the stem. It transports carbohydrates to the non-photosynthetic portions of the plant.
Pith
In the center of the stem, are large, thin walled cell and store water inside of their vacuoles
Cross section of Medicago stem
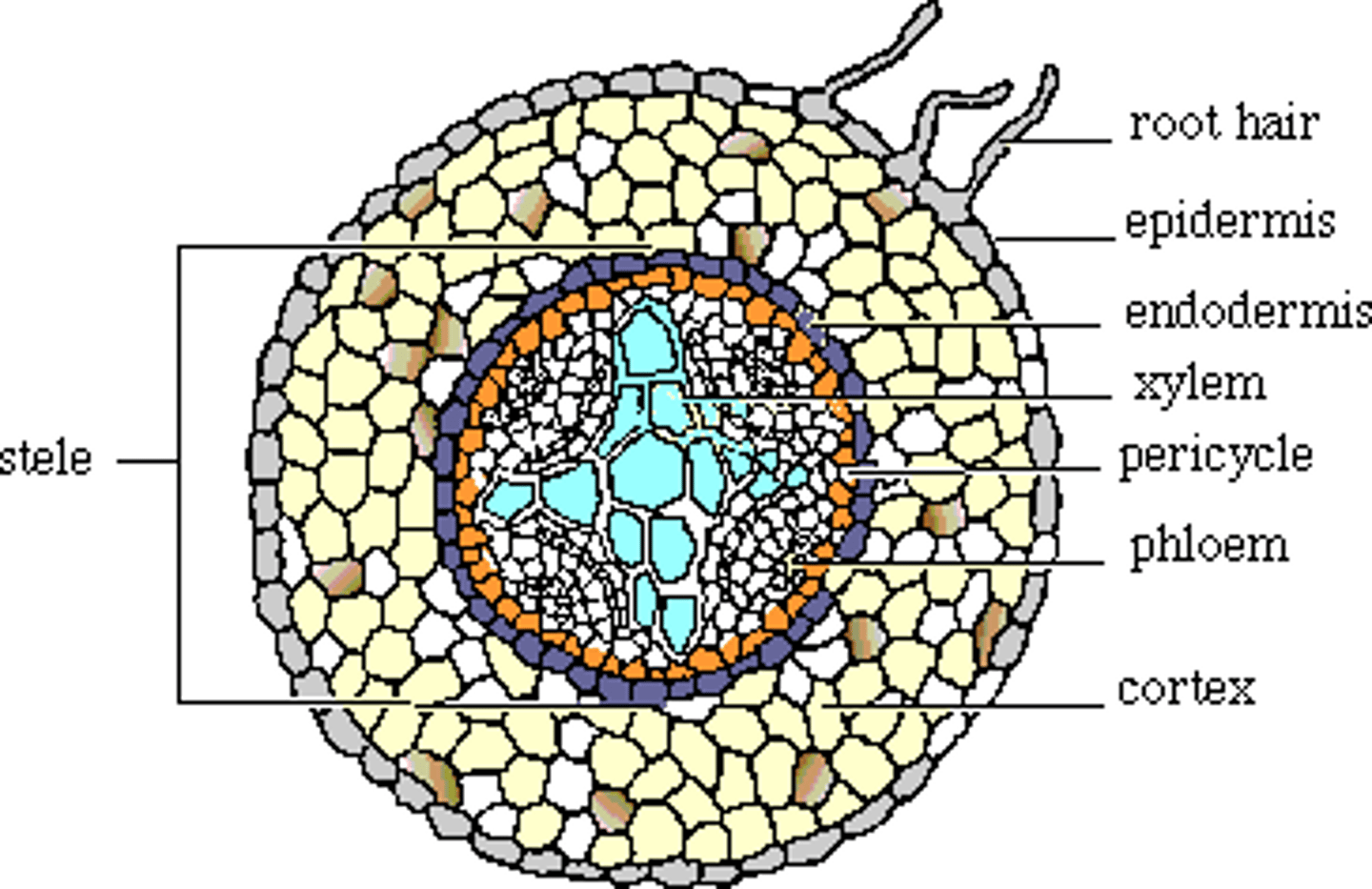
Key features of root anatomy
-epidermis
-cortex
-endodermis
-stele
-pericycle
-xylem
-phloem
Epidermis of root
Outermost layer of the cell. It bears root hairs, which hold the root in place and increase the surface area available for absorption
Endodermis
Circular band of cells that surround the central vascular tissues. Suberin prevents water and minerals from diffusing out of the vascular bundles.
Stele
All the tissue inside the endodermis including the pericycle, xylem, and phloem
Pericycle
The layer of undifferentiated cells directly inside the endodermis.
Xylem of root
Forms cross shaped mass in the center of the root.
Phloem in root
Found in bundles around the periphery of the star shaped xylem
Cross section of root
-endodermis
-pericycle
-xylem
-phloem
-cambium
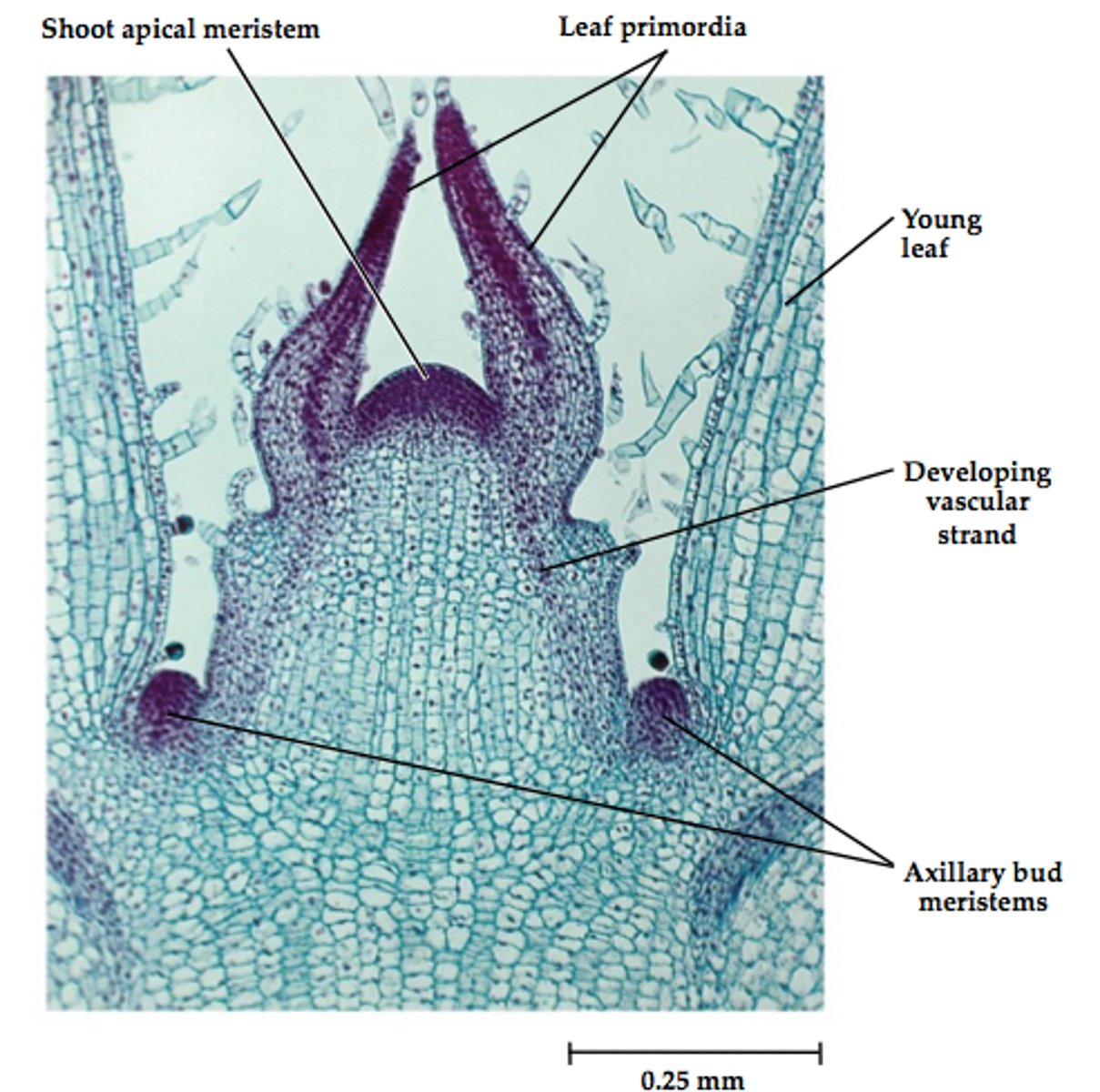
Key features of the shoot apical meristem
The shoot apical meristem is a relatively small dome-shaped mass of cells at the apex of the stem.
The leaf primordial (developing leaves) occur in pairs on opposite sides of the stem and protect the apical meristem
The axillary bud primordia are lumps of small, dark cells that will become the apical meristems for lateral shoots.
Key features of the longitudinal section for shoot section
-apical meristem
-leaf primordia
-procambium
-axillary buds
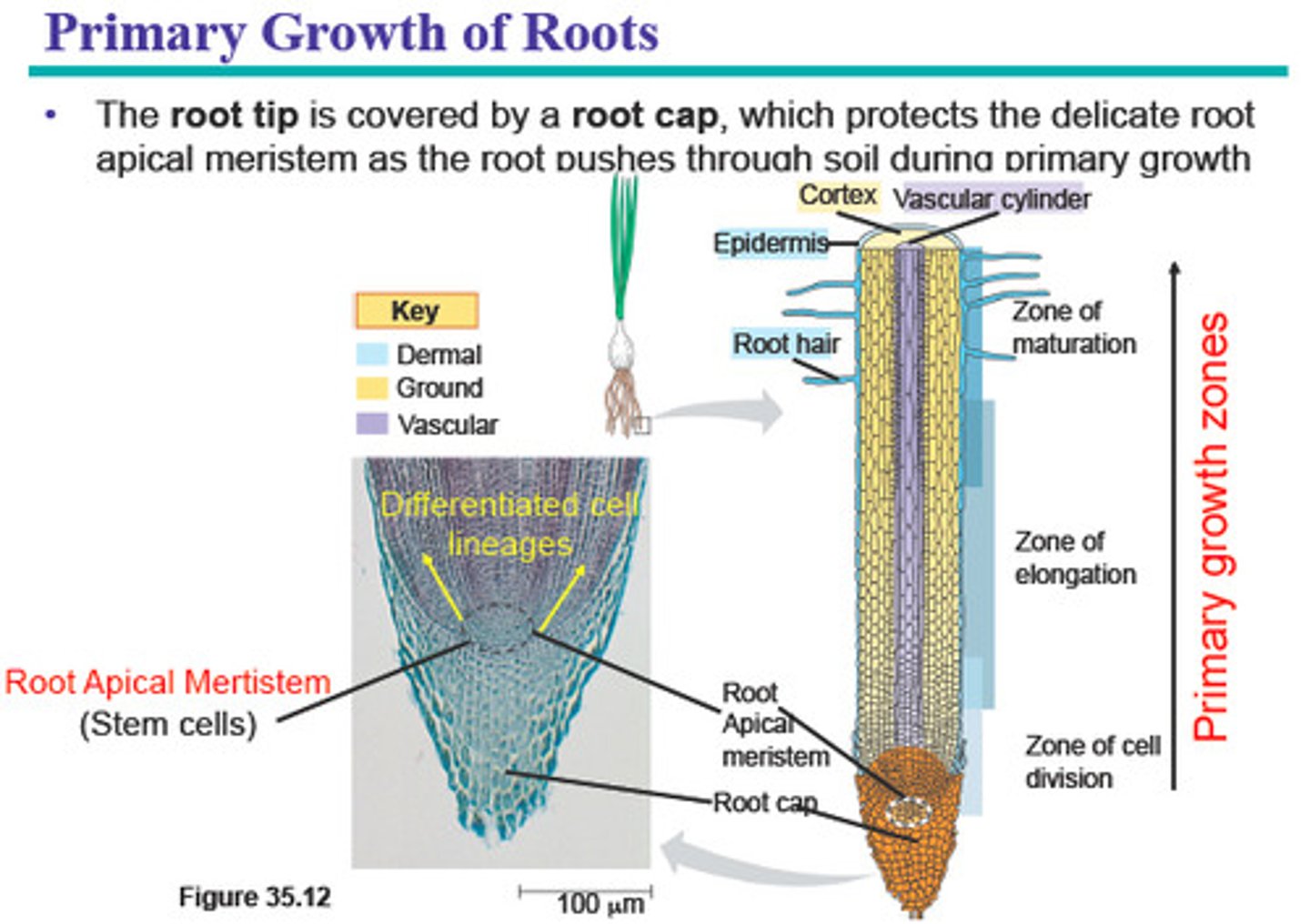
Key features of the root apical meristem
-root cap
-zone of cell division
-zone of elongation
-zone of maturation
Key features of the longitudinal section for root section
-area of maturation
-area of elongation
-area of cell division
-root cap
-apical meristem
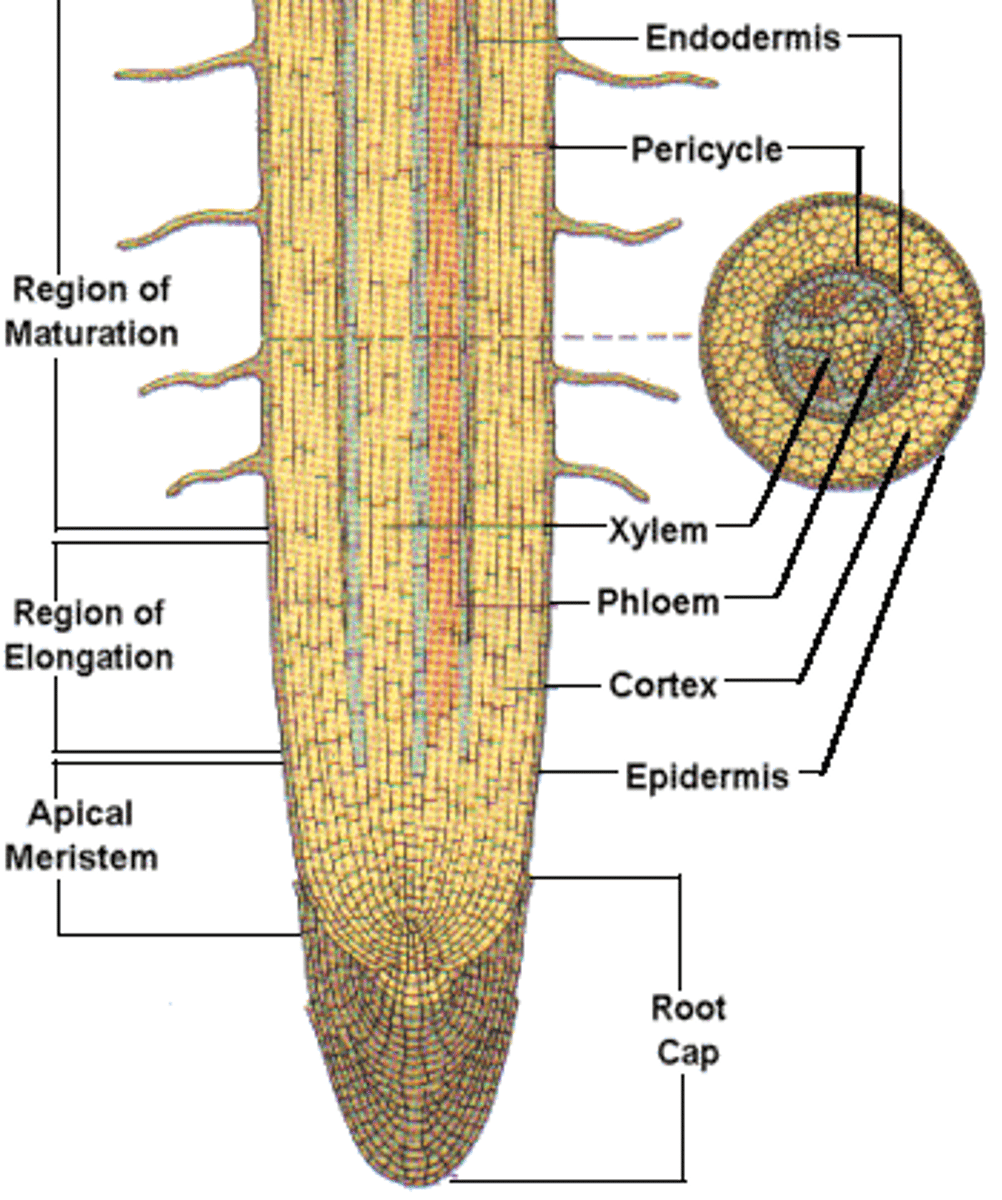
Zones of growth of root apical meristem
-zone of cell division
-zone of elongation
-zone of maturation
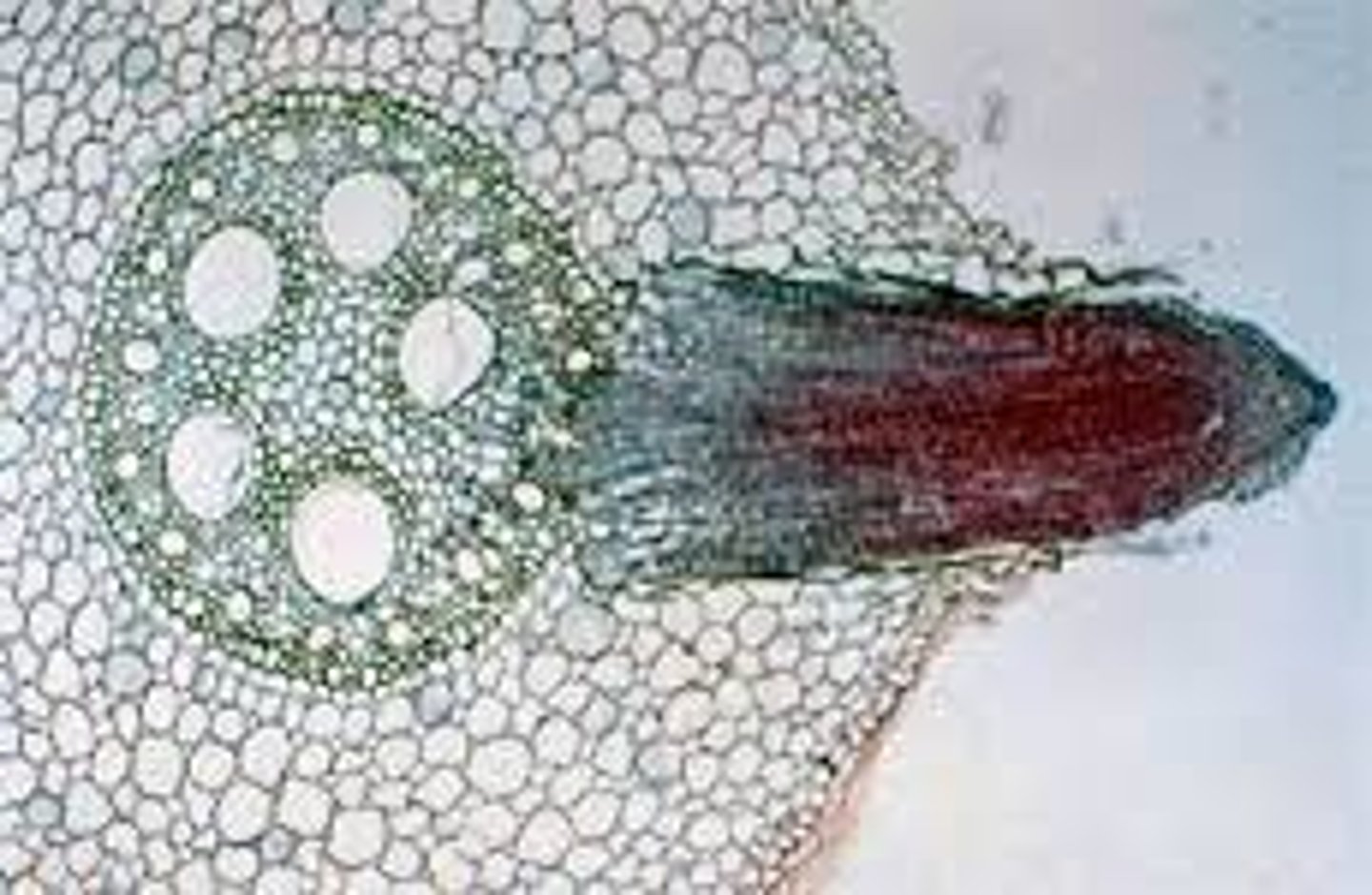
cross section of lateral root formation
-cortex
-epidermis
-pericycle
-endodermis
-developing lateral root
Key features of secondary growth
-Lateral Meristems which are:
-Vascular Cambium
-Cork Cambium
Vascular Cambium
Produces secondary xylem toward the center of the stem and secondary phloem towards the outside. Located in between the primary xylem and primary phloem
Tilia Slide
-cork
-cortex
-secondary phloem
-vascular cambium
-secondary xylem
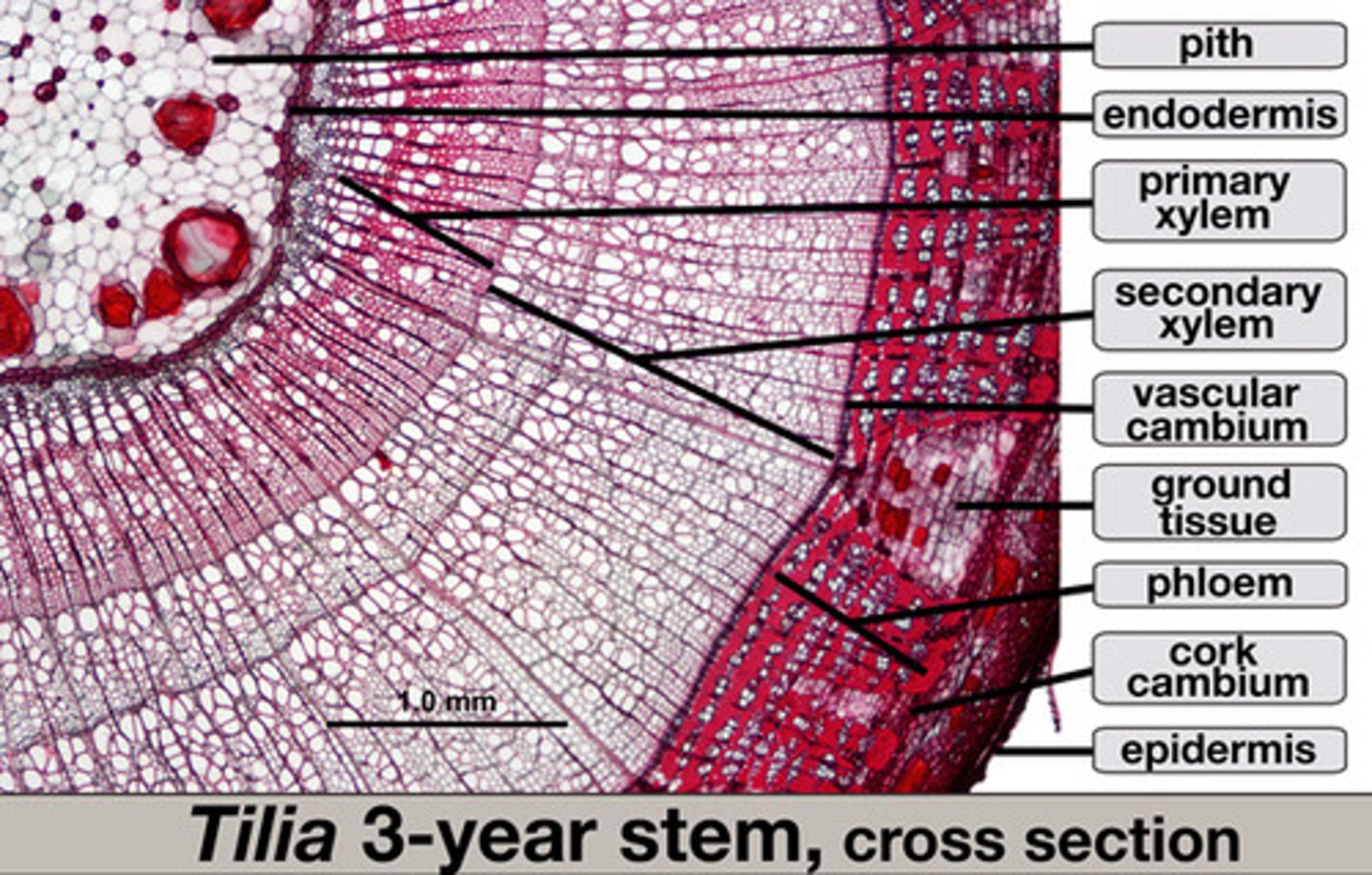
Cork Cambium
Primarily adds cells to the outside of the stem, creating a protective layer. Cork is not the same as bark.
Bark
Outermost covering of the tree or plant, including everything external to the vascular cambium, including the phloem, cortex, and cork.
Lenticels
Splits in the outer protective layer (bark) allow for gas exchange with the environment.
How does a tree grow?
Primary Growth affects the vertical growth with the production of new leaves, stems, and roots
Secondary Growth increases the girth
The cambial tissues involved are the vascular and cork cambium in secondary growth
The primary vascular tissue includes primary phloem and primary xylem
The secondary vascular tissue includes the secondary phloem, which grows between the secondary xylem and secondary phloem.
Secondary Growth
Occurs by increasing the girth of the plant through the action of the Lateral Meristems, which include the Vascular Cambium and the Cork Cambium
Primary Growth
The production of new leaves, stems, and roots resulting in the vertical growth of the plant. It occurs in specialized regions called apical meristems. These are regions in which cell division and growth occurs continuously.
Cambial Tissues Involved
Vascular Cambium and Cork Cambium
Primary and Secondary Vascular Tissue
The primary vascular tissue includes primary phloem and primary xylem
The secondary vascular tissue includes the secondary phloem, which grows between the secondary xylem and secondary phloem.
Modifications and Variations of Leaves
-needle or scale leaves
-spines
-succulents
-leaf tendrils
-storage organs
-trichome
-floatation
-carnivorous
Needle or scale leaves
Typically seen in plants that keep there leaves all year long, the reduced size and surface area allows for better water retention in dry environments (pines spruce fir juniper cedar)
Spines
Mechanical defense structures that deter herbivores looking to consume the plant for water (cacti, holly)
succulents
Thick fleshy leaves that retain moisture due to a low surface-to-volume ratio (sedum, jade, aloe)
leaf tendrils
spirally coiled structures sensitive to touch. Coil for additional support for the plant body when something touches it (sweet pea, wild pea)
Storage Organs
Thick, fleshy scale-like leaves that store either water or nutrients (onion, tulip, lily)
Trichome
hairlike projections that extend from a plant's epidermis. some are glandular and produce secretions (geranium, tomato, begonia)
floatation
expanded airspaces in mesophyll of the leaf that provide buoyancy (water lily, water hyacinth)
carnivorous
traps insects allowing for plant growth in nitrogen and nutrient poor soil. (Venus fly trap, pitcher plant)
Modifications and Variations of Stems
-stem tuber
-rhizome
-stolon
-bulb
-corm
-stem tendril
stem tuber
fleshy underground stem used as starch storage, grow shallowly in soil (potato, yam)
rhizome
a horizontal, underground stem that produces new shoots and roots from its nodes (hops, ginger, iris)
stolon
shoot that grows along ground, producing roots at its nodes (strawberry)
Bulb
short stem with fleshy leaves or leaf bases that function as food storage organs during dormancy (onion, tulip, lily)
Corm
Short, hard underground stem that serves as storage to help plant survive adverse environmental conditions (crocus, banana)
stem tendril
thin, spiral coiling stem that attaches to nearby surfaces to support the plant body (grape, passiflora)
Modifications and Variations of Roots
-taproot
-fibrous
-aerial
-prop/stilt
-root tuber
taproot
large, central root, tending to be straight and thick. May have smaller roots branching from the large central one (dandelion, welwitschia)
Fibrous
Thin branching roots (grass, ferns, coconut palm)
Aerial
Above ground roots, which may take in water and or nutrients directly from the air (ivy, orchids)
Prop/stilt
Structural roots capable of holding up shoots that might otherwise fall over (corn, sugarcane, banyan tree)
root tuber
similar to a stem tuber, these are thickened storage organs that develop from lateral roots. Tend to grow deeper into the soil than do stem tubers. (sweet potato, dahlia)