4.1.6 restrictions on free trade
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
reasons for restrictions on free trade
protect new firms
being reliant on other countries for energy,defence,agriculture creates vulnerabilities
protect jobs
to protect against dumping
correct imbalances in balance of payments
ban certian goods
raise tax revenue
response to recession/low AD
arguement against recession
risk of retaliation
market distortions
higher price for consumers
regressive effect on income inequality
bypassing import controls
higher costs for exporters
dumping
occurs when foreign frims sell products at unfairly low prices in foreign markets
what are type of restrictions on trade
tariffs
quotas
subsidies to domestic producers
non-tariff barriers
protectionism
any attempt to impose restrictions on trade in goods and services
effect of the trade war between USA and the rest of the world
decrease stock markets as low business confidence
long term is beneficial for us production so high economic growth
decrease consumption as increased prices as higher costs due to tariffs so decrease in standard of lving
decrease FDI
structural and cyclical unemployment
what is a tariff
tax on imported goods/services
how do tariffs work
Domestic producers/retailers have to pay the tariff when the good/service crosses the border into the country
This raises the cost of production for domestic firms
Firms often pass on the increased costs to consumers in the form of higher prices
These higher prices allow some domestic firms to increase their output (law of supply)
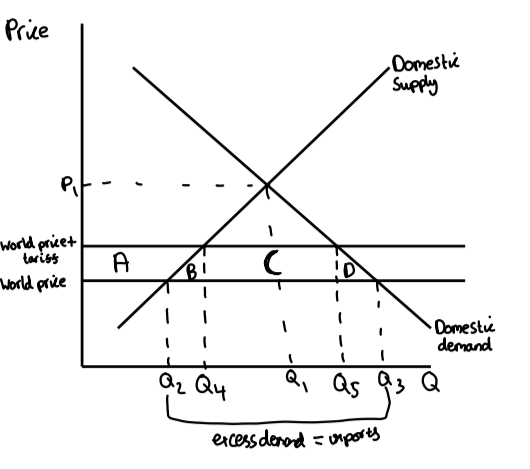
tariff diagram
closed economy (p1 Q1)
open economy - lower price(world price),fall in DS Q1 to Q2 rise in DD Q1 to Q3
increase imports Q1 to Q3
tariff increases domestic supply but decreases domestic demand so less imports
A= increase in producer surplus
ABCD loss in consumer surplus
B and D deadweight welfare loss
C gov revenue from tariff
quota
quantitative limit on the number of imports
what is the effect of a quota
creates excess demand for imports for a givene level of domestic demand
the quota pushes up the market prices
this incentives dometic producers to increase their supply
uk quota example
in June 2022 the UK extended their quota on steel imports for a further two years in order to protect employment in the domestic steel industry
japan quota example
quota on 770,000 tonnes of rice per year imported tariff free and any more are subject to high tariffs
domestic subsidy
any form of financial help given to domestic producers to lower their costs and help them compete in international markets
how domestic subsidies help
subsidy given to domestic suppliers causes a right shift in the domestic supply
the extent of the reduction in costs depends on the size of subsidy
They can increase output and lower prices
With lower prices their goods/services are more competitive internationally
The level of exports increases
The increased output may result in increased domestic employment
non tariff barriers
health and safety regulation
product specifications
environmental regulations
intellectual property laws-patents,copyright
preferential state procurement policies-government favour local producers when finalising contracts for state spending
financial-banks favourdomestic firms to loan
managed exchnage rates
example of health and safety regulation
in 2017 the EU put a new health regulation in place regarding the permitted level of aflotoxins in nuts. Aflotoxin levels are naturally higher in southern hemisphere countries and it effectively blocked the import of southern hemisphere nuts
example of environmental regualtion
in November 2021 new regulations were put in place in the EU and the USA to limit the amount of imports of 'dirty steel' - predominantly this is steel produced using coal fired power stations which are prevalent in China
impact of tariff on domestic producers
lead to higher prices for imported foods so will supply more and receive more demand
but other industries may have higher costs as imports more expensive
impact of tariff on domestic consumers
higher prices so less consumption
impact of tariff for foreign producers
lead to higher costs so have to charge higher prices and so lower demand
but could become more efficient as try to lower costs
impact of tariff for government
igher tax revenus
impact of tariff on standard of living
The standards of living for consumers worsen as the value of their income is eroded as they are paying higher prices
Domestic firms who benefit from increased production may increase employees' wages
This would increase the standard of living for employees
impact of tariff on equality
Workers in industries that have been experiencing structural unemployment due to foreign competition will feel that the tariff results in them being treated more fairly
impact of quota on domestic producers
Increases their output
Raises the selling price
Increases their revenue
but it may encourage domesitc firms to be less productively efficient,may be affected by scarce supply of higher quality overseas imports
impact of quota on foreign producers
Decreases their output
Compared to a tariff, those firms who manage to export in the quota receive a higher price for their sales
impact of quota on consumers
Results in higher prices and less choice
but consumers who work for domestic firms may benefit from higher employment and import cap might stimulte icreased investment
impact of quota on government
they do not receive any tariff revenue (as there is no tariff)
They may receive higher tax revenue at the end of the financial year when domestic firms pay their corporation tax
improved external balance from the reduction in imports and an expansion of GDP from the increase in domestic proudction
impact of quota on standard of living
Reduces for consumers as higher prices erode the purchasing power of their income
impact of quota on equality
Improves for domestic firms but worsens for foreign firm
impact of subsidies on domestic producers
Decreases costs of production
Increases output
Increases international competitiveness
but risk of dependency culture
impact of subsidies on foreign producers
Makes it harder for them to compete with domestic firms
impact of subsidies on consumers
lowers prices but may face higher taxes
impact of subsidies on government
This costs the government the amount of the subsidy
There is an opportunity cost associated with every subsidy provided
impact of subsidies on standard of living
Improves for consumers as they benefit from lower prices - their income goes further
impact of subsidies on equality
Domestic firms can compete more equally
impact of non tariff barriers on domestic producers
Limits foreign competition
Protects levels of outputs
May increase selling price and revenue
impact of non tariff barriers on foreign prodcuers
Acts as a disincentive to sell into foreign markets
Costs of meeting the non-tariff barriers may significantly reduce profit margins
impact of non tariff barriers on consumers
May reduce choice/variety in a market
impact of non tariff barriers on government
They may lose some credibility with the WTO
Enforcing the non-tariff barriers may be difficult or expensive
impact of non tariff barriers on standards of living
Less choice and higher prices erode standards of living
Product labelling information may improve decision making and quality of life
impact of non tariff barriers on equality
May help improve equality e.g. environmental standards help create equal production inputs which results in equality in the costs of production
examle of tarriffs and quotas
In many cases, tariffs and quotas arise from geopolitical factors between countries. For example, the World Trade Organisation (WTO), an intergovernmental organisation that regulates international trade, settled a decade-long argument between the EU and America regarding subsidies. The US was accused of illegal subsidies to Boeing, an American aerospace corporation. By providing subsidies, the firm’s costs of production were reduced, which meant they were able to lower prices to consumers. This had adverse impacts for the competitiveness of Airbus, the European-owned counterpart to the aviation duopoly. The EU therefore took the issue up with the WTO, and was permitted to add tariffs to $4 billion worth of US imports to compensate for the loss of profits to Airbus