Reproductive 5 - Uterine cycle, Fertilization, Implantation
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
How long is the menstrual phase
5 days
What occurs to the uterus during the menstrual phase
Blood flow to tissue decreases, causing tissue death and slough into vagina causing menstrual flow.
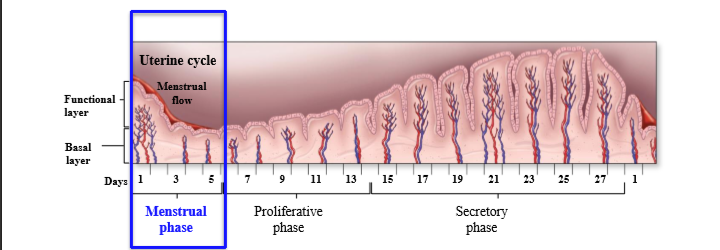
Hormonal control of menstruation
Menstruation triggered by decreased estrogen and progesterone. Hormone decreases when corpus luteum degenerates
What occurs to the uterus in the proliferative phase
Endometrial lining develops and grows, endometrial layer grows and glands enlarge. Smooth muscle layer thickens and cervical glands secrete a thin mucus
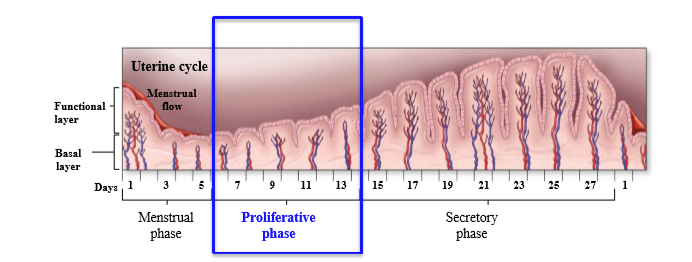
Hormonal control of proliferative phase
Estrogens stimulate development of uterine lining
What occurs to the uterus during the secretory phase
The endometrium prepared for implantation: blood supply increased, glands enlarge and secrete glycogen-rich fluids, and cervical secretions more sticky forming a plug
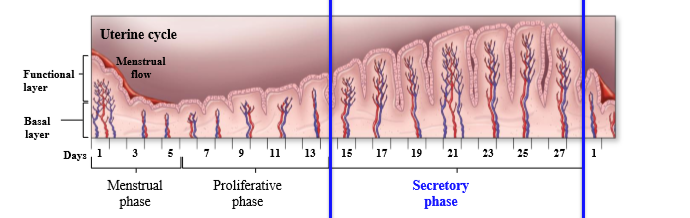
How to contraceptives effect the cervical plug
Increased progesterone forms a thicker cervical plug
Hormonal control of secretory phase
Progesterone + Estrogen
Effects of estrogen on the ovary
Increased growth of follicles, increased receptors for estrogen, progesterone, FSH, LH
Effects of progesterone in the ovary
Decreased FSH-induced E production, decreased receptors for estrogen
Effects of estrogen on the fallopian tube
Increased growth, contractility, cilia activity, secretions
- Contractility and cilia activity for ovum movement
Effects of progesterone on the fallopian tube
Decreased contractility, secretions, cilia number
Effects of estrogen on the uterus
Grows endometrium and myometrium, increase contractility. Contractions don't allow ovum to sit on the uterus
Effects of Progesterone on the uterus
Increase endometrial secretions, decrease contractility, decreased sensitivity to oxytocin (less contractions to prevent loss of ovum)
Effects of estrogen on the cervix
Produces sperm friendly mucus - abundant, watery, alkaline
Effects of progesterone on the cervix
Sperm unfriendly mucus produciton - small, viscous, cellular
Effects of estrogen on the vagina
Proliferation and cornification (keratinization) of epithelium
Effects of progesterone on the vagina
WBC infiltration, decreased cornification
Effects of estrogen on the breasts
Increased duct growth, fat deposition, increased size and pigmentation of areola
Effects of progesterone on the breasts
Increased alveolar growth
What is fertilization
Fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote
Use of male and female external genetalia for mating
Sperm deposited into female to fertilize the ovum
What is the fertilized zygote called in the first two months of gestation
Embryo
what is the zygote called after 2 months of gestation
Fetus
What is parturition
Child birth
Site of fertilization
Female oviduct (fallopian tube)
How long are sperm viable for
5 days
How long is an ovum viable for
12-24 hours
Sperm are initially incapable of fertilization. What do they requires?
Capacitation
Only a few hundred sperm make it to the uterine tubes of the initial 200-300 million. Why?
- Damage due to acidic pH of female tract
- Some loss due to cervix leakage
- Loss of energy
Only the best sperm gets access to the oocyte. What would be the best sperm?
The sperm that receives capacitation. Altered PM allows for exposure to membrane bound enzymes to make channel through zona pellucida
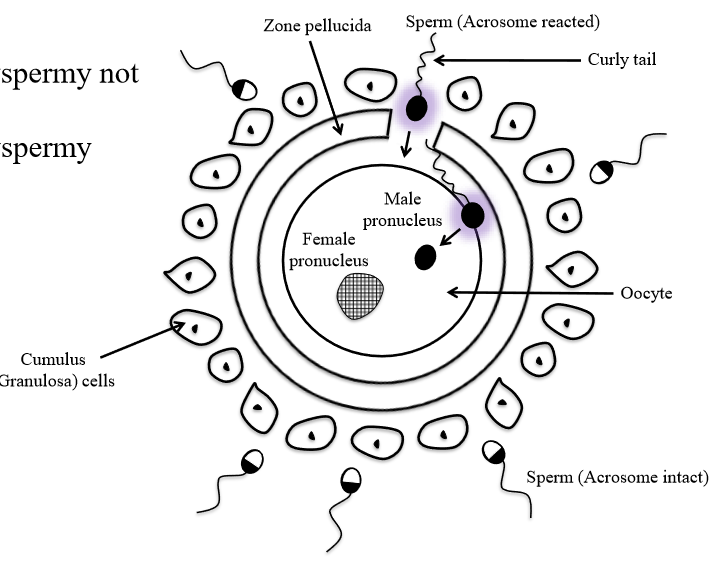
Why does polyspermy not occur?
Chromosome number is not maintained. Embryo has 3 sets of chromosomes
Pronucleus
the nucleus of a sperm or an egg cell during the process of fertilization, after the sperm enters the ovum, but before they fuse
How many sperm undergo acrosomal reaction?
Many sperm can undergo the acrosomal reaction when they bind to zona pellucida
Events of fertilization (steps)
1. Many sperm bind to receptors on the zona pellucida and undergo the acrosome reaction
2. Sperm move through zona pellucida
3. One sperm bind to egg plasma membrane
4. Three things occur
a. Egg releases contents of secretory vesivles into egg plasma membrane and zona pellucida. Enzymes enter zona pellucida and harden the zona to prevent polyspermy
b. Sperm is drawn into egg: egg completes 2nd meiotic division and zygote form
c. Egg enzymes activated when zona pellucida is breached. Zygote begins embryogenesis (zygote divides and forms embryo)
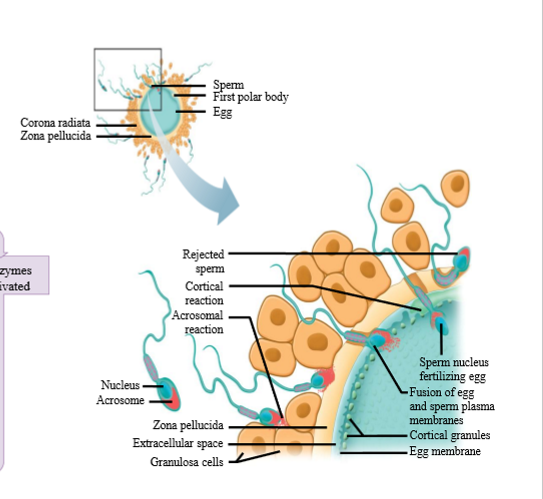
What are the blocks to polyspermy
- Change in membrane potential
- Release of contents from cortical granules
- Enzymes enter and harden zona pellucida
- Enzymes inactive sperm binding receptor
What is the sperm binding receptor on the ovum?
Glycoproteins
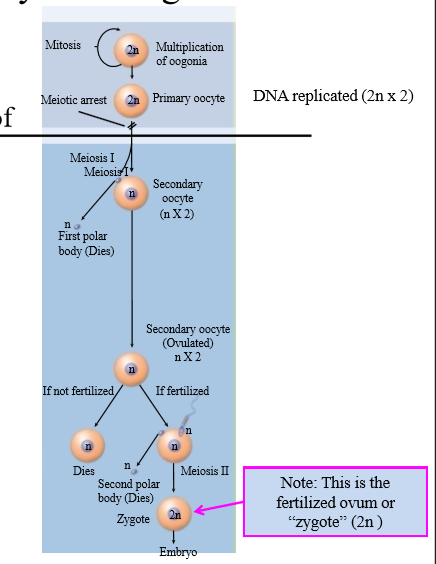
What happens to the oocyte during fertilization?
- Fusion of sperm with oocyte stimulates 2nd
meiotic division of oocyte
• oocyte -->ovum
- Sperm plasma membrane disintegrates
- Chromosomes from sperm and ovum migrate
to center
- DNA replicated --> zygote
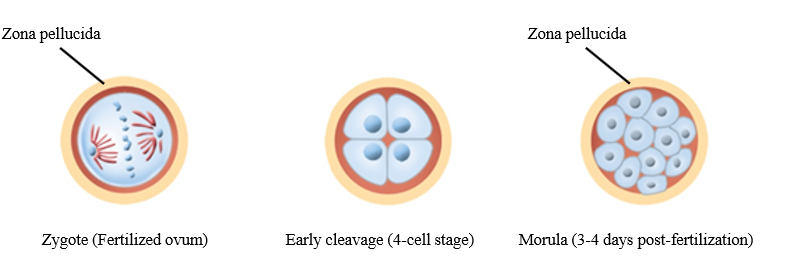
Morula
A solid ball of cells that makes up an embryo; in humans, this stage occurs within four days of fertilization.
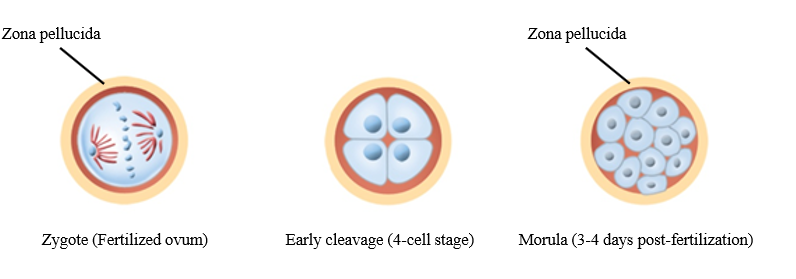
Is there cell division in early embryonic development?
No - only cell cleavage
Totipotent
Stem cells with the potential to differentiate into any type of cell.
How long does the embryo remain totipotent?
Up to 16-32 cell stage
What does the morula proliferate into?
Blastocyst
How are identical twins formed
Division of totipotent morula.
How are fraternal twins formed
Fertilization of two oocytes (released during the same cycle)
When does the blastocyst form
4-5 days after fertilization
What structure in the morula is lost in the blastocyst?
Zona pellucida
Anatomical components of the blastocyst
Outer cell layer is the trophoblast, and there is an inner cell mass. beside the cell mass is a fluid filled cavity blastocoele

What does the trophoblast become
Fetal placenta
What does the inner cell mass become
Embryo
Where in the female reproductive system is the blastocyst found
Uterine site
Which uterine phase does implantation occur?
Secretory phase
Role of glycogen in implantation
helps blastocyst anchor to endometrial lining
What allows trophoblast cells to implant
The trophoblast cells are sticky, and will adhere
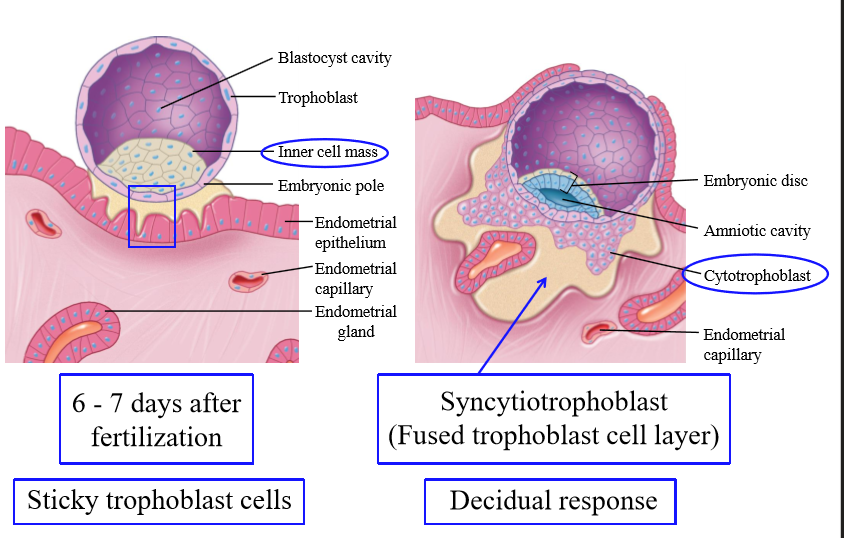
When does implantation occur
6-7 days after fertilization
Syncytiotrophoblast
outer layer of trophoblast that enters the endometrium
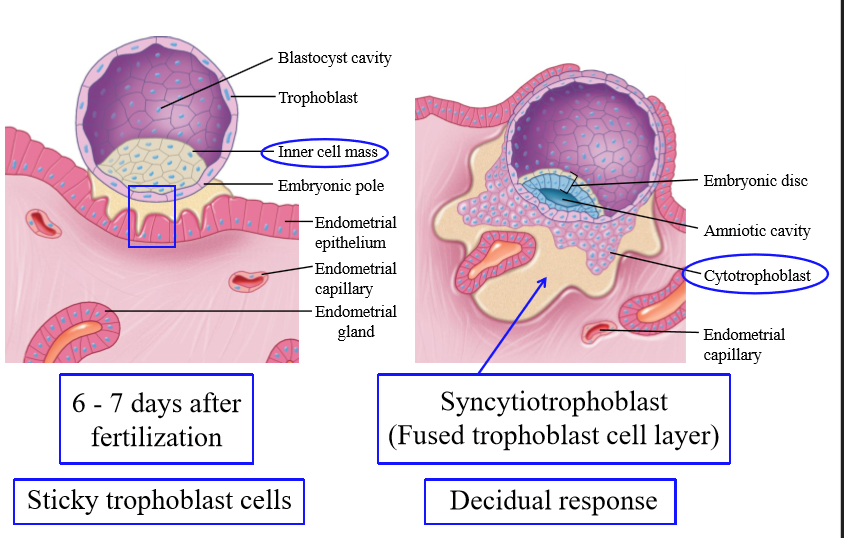
Cytotrophoblast
inner cellular layer of the trophoblast that secrete hormones for growth
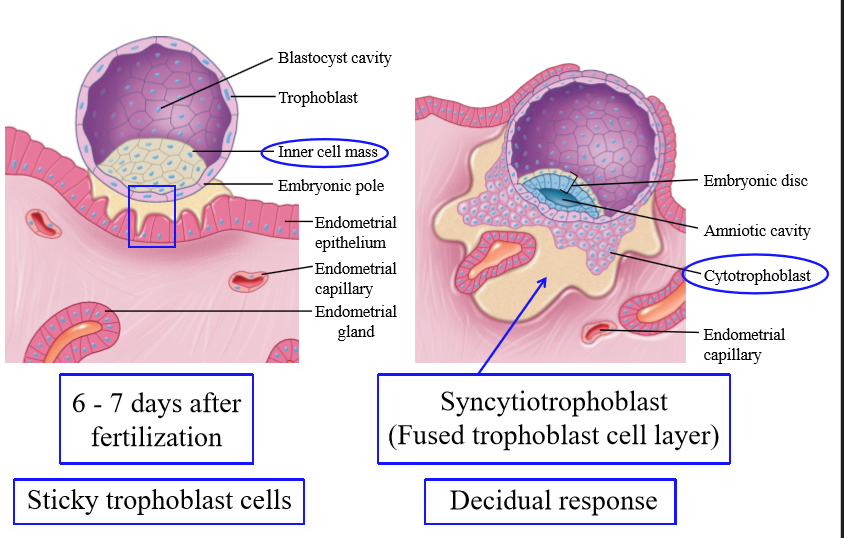
Decidual response
The uterine response to the presence of the embryo. The cells of the endometrium swell and become full of glycogen, lipids and other nutrients. The blood vessels branch and move closer to blastocyst
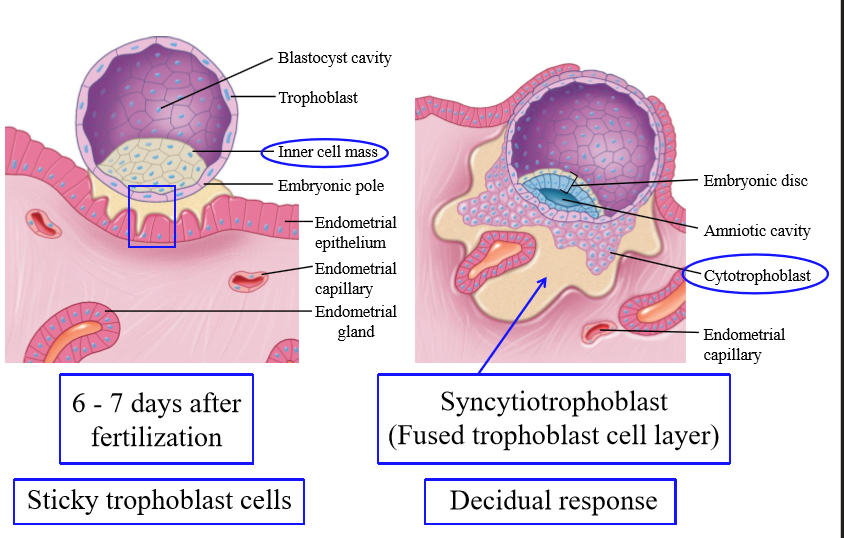
What age does the placenta function and heart beat?
By 5 weeks