organic chem + relative atomic mass etc
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
relative atomic mass Ar
the average of the relative isotopic masses of all the naturally occurring isotopes of an element compared to 1/12 of a carbon-12 atom. The relative percentage abundance of these isotopes are taken into account.
Since it is an average, it is not necessarily a whole number when calculated
no units
relative isotopic mass
the mass of an isotope of an element compared to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom
mass spectrometer
measures the abundance and relative mass of each isotope in an element
relative molecular mass Mr
how heavy a molecule of compound is compared to an atom of carbon-12
the relative atomic masses of each atom in the molecule
mole
amount of substance
can be used to count atoms, molecules or ions
symbol:n
unit:mol
avogadro’s number
represents the number of atoms of carbon-12 in 12 grams of carbon-12
carbon-12 is used as a standard
molar mass
the mass of one mole of pure substance
symbol : M
unit: g mol^-1
molar mass of a pure element or compound= relative atomic/ molecular mass
but relative atomic mass has no units
empirical formula
shows the simplest ratio of atoms or ions in a compound
give the mole ratio of each element present in a compound
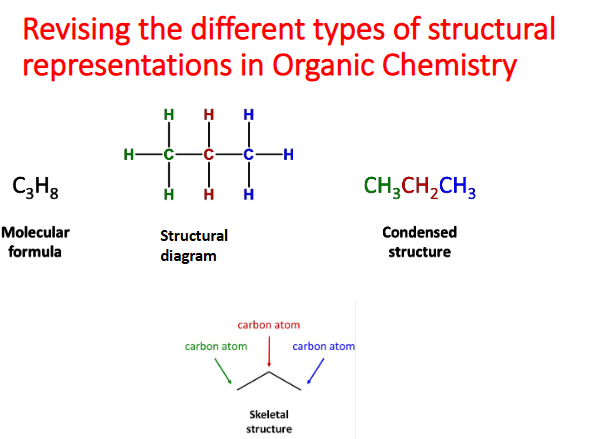
molecular formula
gives the actual number of atoms of each element present
hydrocarbons
molecules containing carbon and hydrogen
alkanes
the series of saturated hydrocarbons containing only single carbon-carbon bonds
molecules are non-polar
general formula CnH2n+2
properties of alkanes
methane
ethane
propane
butane
= gas in room temp
pentane
hexane
heptane
octane
nonane
decane
= liquid in room temp
increases in boiling/ melting point
does not dissolve in water
all are non polar
saturated
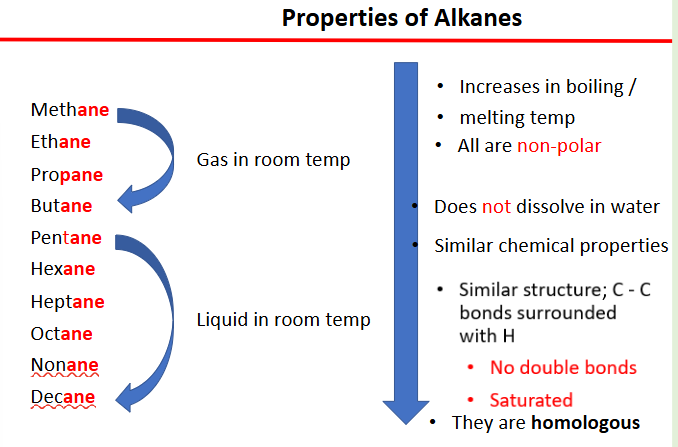
physical properties
larger = higher melting point
larger molecules have more electrons and more instantaneous dipoles
dispersion forces
dispersion forces operate over a greater area for longer molecules
therefore stronger dispersion forces exist between larger molecules
e,g butane (C4H10) higher boiling point than ethane (C2H6)
alkyl group
side groups
shown in brackets in condensed structural formulas
structural isomers
molecules with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms
reactions of alkanes
generally unreactive but can be used as fuel
they burn and react with oxygen
combustion reaction
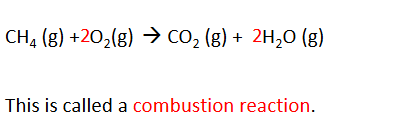
alkenes
the series of unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a double carbon-carbon bond
homologous series
general formula CnH2n
homologous series
a group of organic compounds that
have the same functional group
show a gradual trend in physical properties
have similar chemical properties
saturated
all carbon-carbon bonds are single bonds
the molecules contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible
alkene reactions
more reactive than alkanes
can undergo addition reactions
where a double bond is broken and other atoms are added to the hydrocarbon y bonding with a carbon atom
haloalkanes
side group halogen
halo side chain is considered of equal rank as alkyl side chain
follow alphabetical order for prefixes when naming
F = fluoro-
Cl= chloro-
Br= Bromo-
I = iodo-
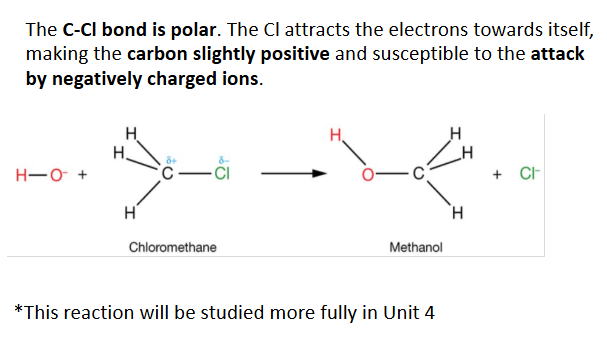
polarity in haloalkanes
all haloalkanes are polar
halogen atoms are electronegative and they pull/ draw electron density towards themselves.
This results in a partial negative charge on the halogen atoms and leaves carbon atoms with a partial positive charge.
This creates a polar covalent bond
haloalkanes are more reactive than alkanes
reacitons of haloalkanes
substitution reaction
alcohols
have a functional group -OH
called the hydroxyl functional group
name end in ol
properties
small chain alcohols have a higher boiling point than their corresponding alkanes
due to hydrogen bonding between alcohol molecules
explaination of this trend
alcohol molecules have polar hydroxyl groups which allows the molecules to attract each other by hydrogen bonding ( as well as weaker dispersion forces between molecules)
non polar alkane molecules only attract each other by weak dispersion forces
therefore, less energy is required to overcome the intermolecular forces between corresponding alkane molecules
when the alcohols are too big however
alcohols with small moleucles dissolve in water
e,g water and ethanol
hydrogen bonds break between water molecules
hydrogen bonds break between ethanol molecules
new hydrogen bonds form between alcohol and water molecules
why larger are not
although it has a polar hydroxy group, the large hydrocarbon portion of this molecule is non polar
the dispersion forces between the long hydrocarbon section of the molecule is stronger than any potential hydrogen bonding between the molecule and water molecules
isomers
same molecular formula but differnet strucutral formula
same empirical formula but differ from each other by the way in which the atoms are arranged
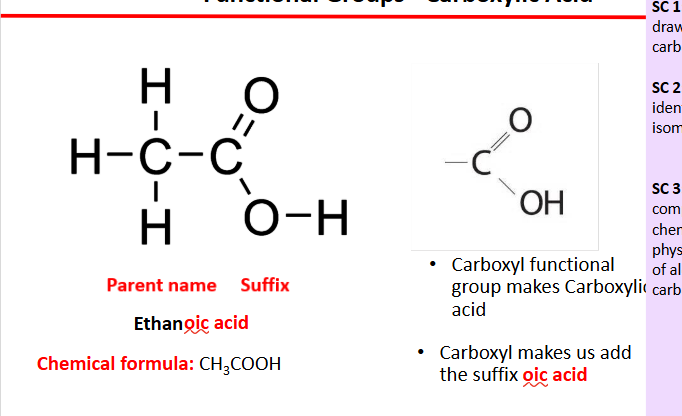
carboxylic acids
have a carboxyl functional group
COOH
end in oic acid
examples in nature
methanoic acid- bee sting
ethanoic acid- vinegar
propanoic acid - preservative
properties
sour
weak acids with relatively high boiling point
sting and cause irritation e.g methanoic acid in ant bites irritates the skin
small carboxylic acids are soluble in water
as they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
they for dimers
where carboxylic acid molecules form two hydrogen bonds with each other causing the hydrogen bonding between carboxylic acids to be stronger than their corresponding alcohols
results in high boiling points
✅ Carboxylic acids contain both:
An –OH group (like alcohols)
A C=O (carbonyl) group
Each of these can participate in hydrogen bonding:
The –OH can donate an H-bond (via H)
The C=O can accept an H-bond (via the O)
🔁 So two hydrogen bonds can form between two acid molecules — often forming dimers in non-polar solvents.
❌ Alcohols only have:
An –OH group
→ So they can donate or accept one H-bond, but not both simultaneously like acids do.
VCE relevance: This explains why carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than alcohols of similar molar mass — stronger intermolecular forces (2 H-bonds per molecule).
Representation | Description |
|---|---|
Molecular formula | Shows the number of each type of atom. E.g. C₂H₆O |
Condensed formula | Shows grouping but not bonding. E.g. CH₃CH₂OH |
Structural formula (semi-structural) | Shows the arrangement of atoms and groups. E.g. CH₃–CH₂–OH |
Displayed (full structural) formula | Shows all atoms and all bonds |
Lewis dot structure | Shows valence electrons and lone pairs |
Skeletal formula | Simplified — carbon atoms are implied, hydrogen atoms on C are omitted |
Feature | Lewis Dot Structure | Structural Diagram (Displayed formula) |
|---|---|---|
Shows electron pairs? | ✅ Yes (lone pairs & bonding pairs) | ❌ No (just bonds) |
Shows actual atoms? | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
Focus | Electron distribution and bonding | Atom connectivity and shape |
Example (H₂O) | :O: with two lone pairs and 2 bonds to H | H–O–H |