Biology 🧬 unit 12 lactate (lactic acid) fermentation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration in animals
Glucose → lactic acid + ATP
When does lactate (lactic acid) fermentation occur
Occurs in animals as a means of overcoming a temporary shortage of oxygen
is the ability to produce small amounts of ATP in the absence of oxygen important?
yes → the ability to produce small amounts of ATP in the absence of oxygen has a significant survival value; thus it was selected fro through evolution via natural selection
Where does lactate fermentation mainly occur
Occurs most commonly in muscles as a result of strenuous exercise
When strenuously exercising oxygen is used up rapidly in the process of aerobic respiration. It is used faster than the respiratory and circulatory systems can supply it.
It may be essential that muscles continue to work despite what?
a lack of oxygen
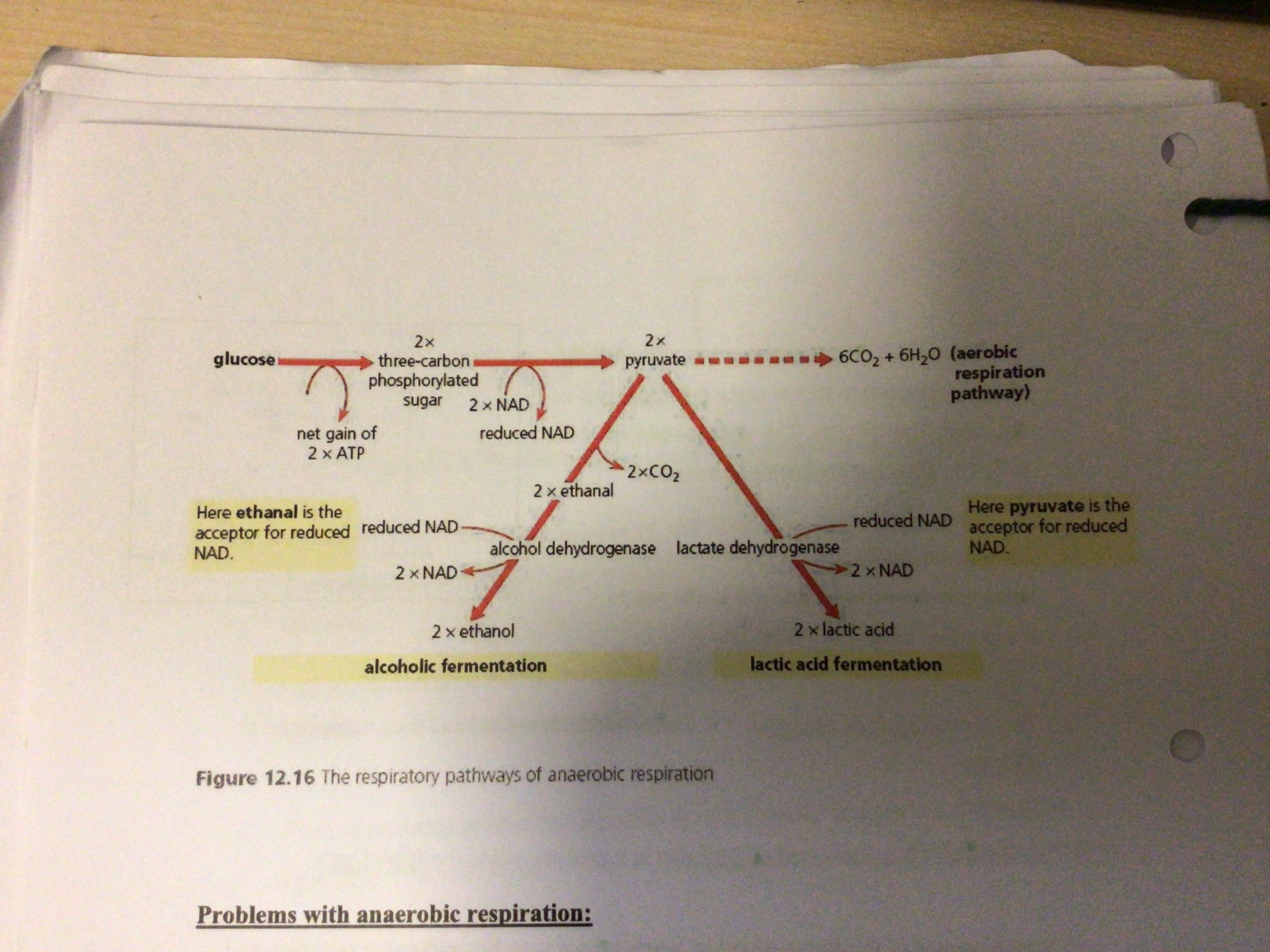
anaerobic respiration in animals 1: In the absence of oxygen what happens in terms of each pyruvate molecule produced
In the absence of oxygen, each pyruvate molecule produced takes up 2 hydrogen atoms from glycolysis to form lactate (lactate dehydrogenase is the enzyme involved)
Pyruvate + NADH → lactate + NAD+

anaerobic respiration in animals 2: the pyruvate is reduced to what? (using the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase) and how is NADH involved?
To lactate using hydrogen ions and electrons from NADH
This oxidises NADH back to NAD, allowing glycolysis to continue
anaerobic respiration in animals 3: the lactate (Lactic acid) produced will cause what?
cramps and muscle fatigue if it is allowed to accumulate in muscle tissue
anaerobic respiration in animals 4: how is lactate removed
It is transferred to the blood and then transported to the liver
At the liver, it is converted to glycogen in a process called the Cori Cycle
In the reverse of the equation, some lactate may be oxidised to pyruvate and then enter the Krebs cycle
The individual still, at this point, is incurring an oxygen debt, and like all debts this must be paid off
What is the Cori Cycle
The process where lactate is converted to glycogen at the liver
What is the oxygen debt
The volume of oxygen required to oxidise the lactate built up during anaerobic respiration
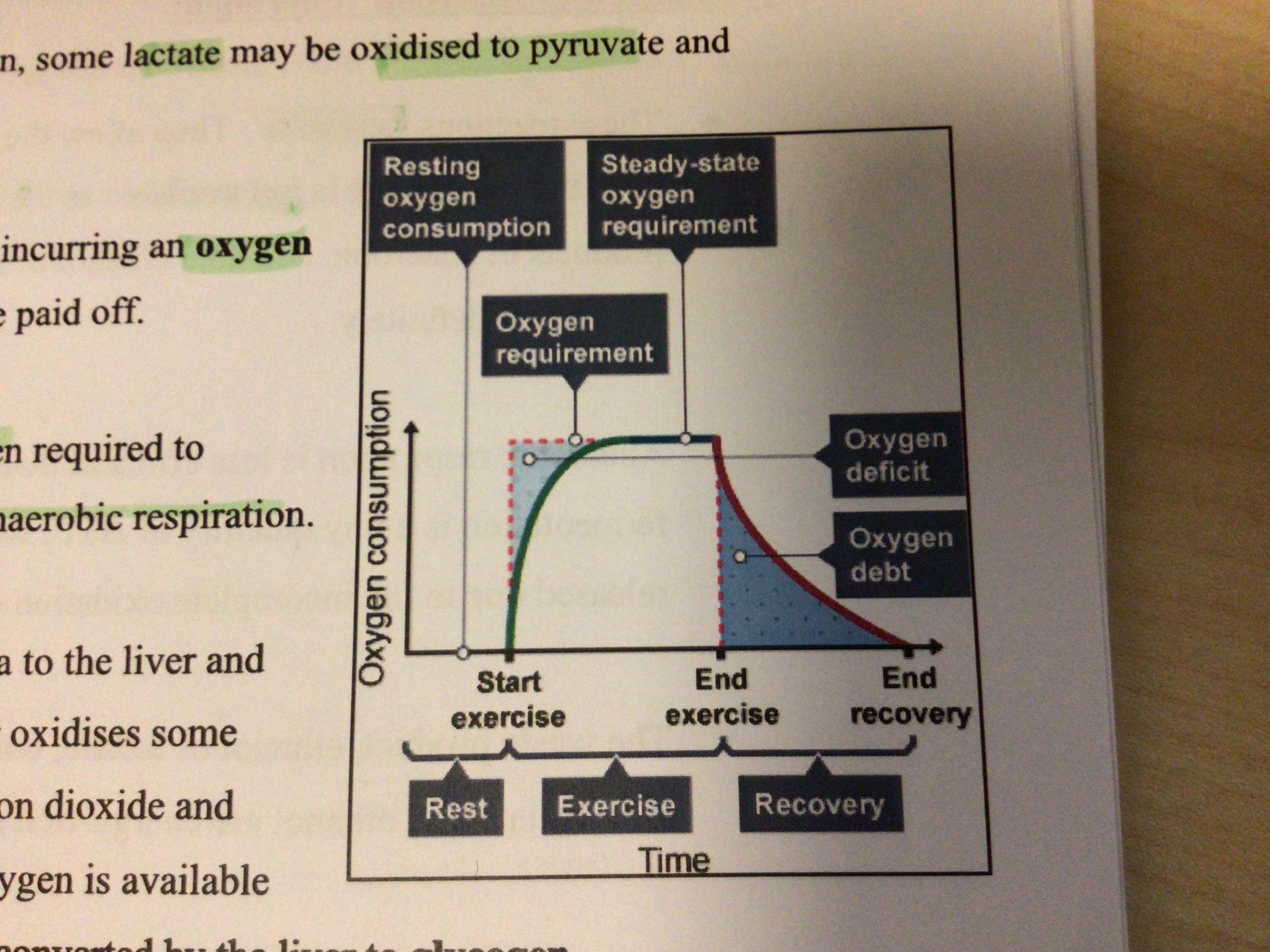
Lactate is carried by the ……… …….. to the …….. and converted back to …………
The liver oxidises some (20%) of the incoming lactate to carbon dioxide and water via ……… ……. when oxygen is available again.
The remainder of the lactate is concerted by the liver to …………
blood plasma, liver
Pyruvate
Aerobic respiration
Glycogen
What are the differences between anaerobic respiration in yeast cells (alcoholic fermentation) and anaerobic respiration in animals (lactate fermentation)
no decarboxylation/CO2 removed in animal cells
Different hydrogen acceptors. In animals, pyruvate is the hydrogen acceptor and in yeast cells, ethanal is the hydrogen acceptor
One is reversible, lactate can (later) be converted back to pyruvate. Whereas in yeast cells, ethanol cannot be converted back to pyruvate
problems with anaerobic respiration:
These reactions ‘buy time’. They allow the continued production of at least some …… even though oxygen is not available as the ……….. acceptor.
However, as the products of anaerobic reaction, ethanol or lactate, are toxic, the reactions cannot continue indefinitely
ATP
hydrogen
Problems with anaerobic respiration:
Anaerobic respiration is …… efficient than aerobic respiration, the useful product of fermentation is a tiny quantity of ……
With anaerobic respiration, much less energy is released due to the incomplete oxidation of glucose (2 molecules of ATP)
Less
ATP
Problems with anaerobic respiration:
The waste product, ……….. or ……….. contains much unused chemical energy. In fact, both lactate and ethanol are energy-rich molecules
ethanol, lactate
Problems with anaerobic respiration:
Oxygen is required to remove lactic acid from the ……….., the amount of oxygen required to do this is known as the ‘oxygen debt’
The reason why people continue to have a high heart rate and breathe heavily after intense (anaerobic) exercise is to pay off this ………. ……
Blood
Oxygen debt