Chapter 8: Transport Across Membranes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Passive, simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, channel, carrier, active, primary, direct, secondary, indirect
2 Main Types of Membrane Transport:
___ transport that moves down the [] gradient and no energy
___ ___
___ ___ by ___ and ___ proteins
___ transport that moves against the [] gradient and needs energy
___ or ___ transport
___ or ___ transport
![<p>2 Main Types of Membrane Transport:</p><ol><li><p>___ transport that moves down the [] gradient and no energy</p><ul><li><p>___ ___</p></li><li><p>___ ___ by ___ and ___ proteins</p></li></ul></li><li><p>___ transport that moves against the [] gradient and needs energy</p><ul><li><p>___ or ___ transport</p></li><li><p>___ or ___ transport</p></li></ul></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/595ae45f-5358-4d00-a2f0-555ee0a027cd.png)
Gases, nonpolar, small, free energy, osmosis, solute [], hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic
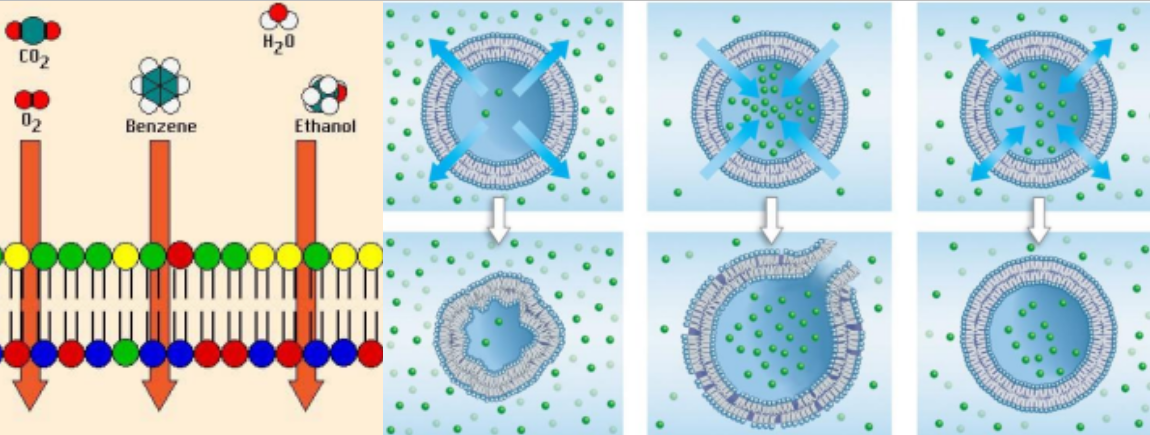
Passive Transport: Simple Diffusion:
Happens with ___, ___, or ___ molecules
Minimized ___ ___
___ is a subtype with water across a selectively permeable membrane
Determined by ___ ___
___ solution with more solutes outside the cell
___ solution with less solutes outside the cell
___ solution with equal solutes across the cell
Transmembrane, channels, carrier, transporters, pumps
Transport Proteins:
Are ___ proteins that transport molecules
3 Classes:
___ for facilitated diffusion
___ or ___ for facilitated diffusion
___ for active transport
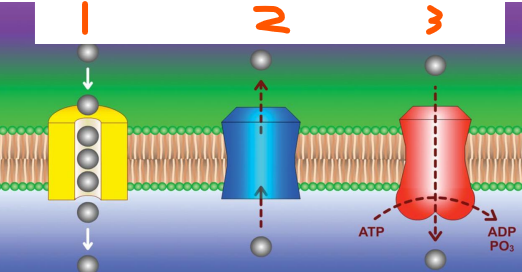
Hydrophilic, ions, sugars, AA, vitamins, carrier, channel proteins, [] gradient, number, transport proteins
Passive Transport: Facilitated Diffusion:
For ___ molecules like ___, ___, ___, ___
Needs ___ or ___ ___ to facilitate transport which are specific for 1 type of molecule
Transport rate depends on ___ ___ and ___ of ___ ___
Selective, ions, small, regulated, ligand, mechanically, voltage, open, [] gradient, electrochemical potential, aquaporins
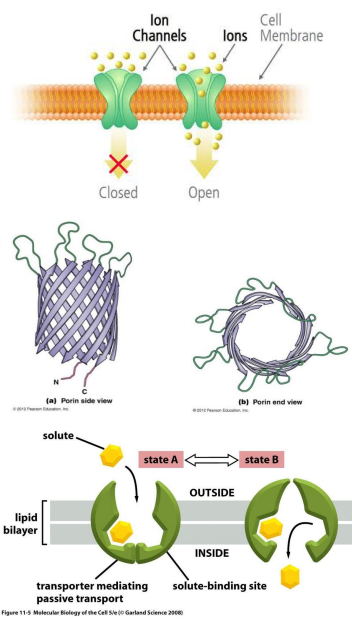
Passive Transport: Facilitated Diffusion: Channel Proteins:
Are ___ for ___ or ___ molecules
Are tightly ___ or gated by being ___-gated, ___-gated, ___-gated, or ___
Transport by ___ ___ and ___ ___
EX: ___ for water
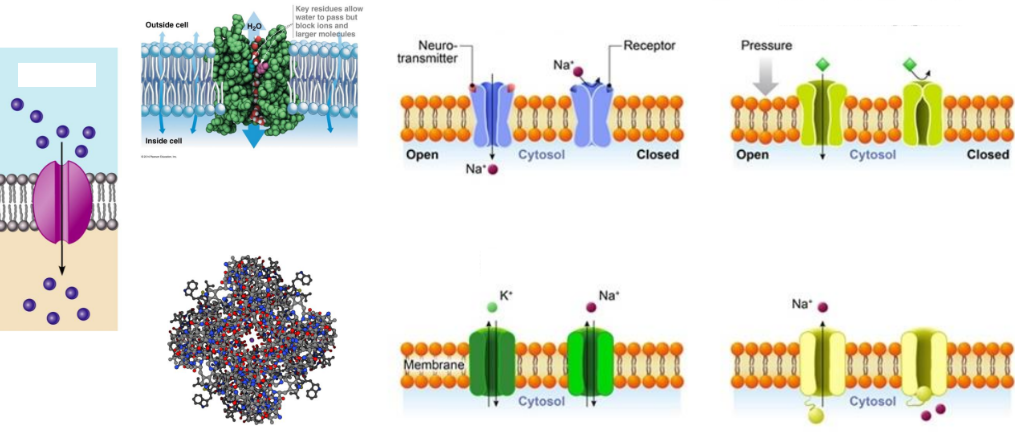
Selective, larger, glucose, AA, regulated, uniport, coupled, symport, antiport
Passive Transport: Facilitated Diffusion: Carrier Proteins:
Are ___ for ___ molecules like ___ or ___
Are tightly ___ or gated
2 Types:
___ for 1 solute
___ for 2 solutes and is dependent on both
Can be ___ in the same direction or ___ in opposite directions
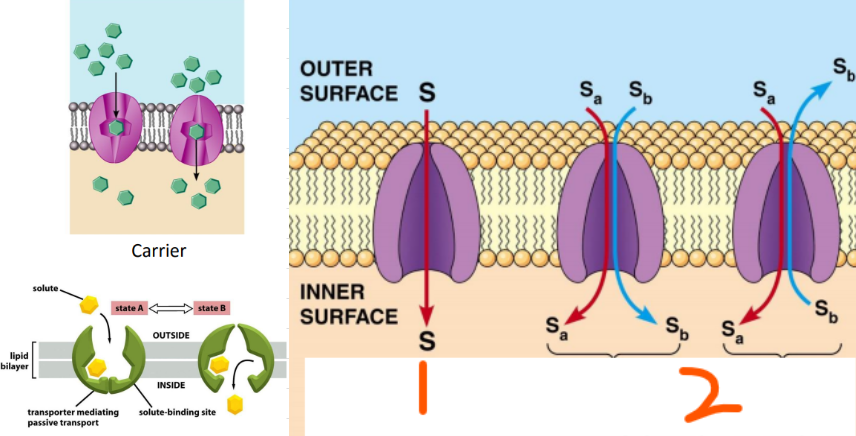
Erythrocyte, glucose, uniport, GLUT1, glucose, GLUT1, outside, T1, T2, inside, glucose, second conformational change, T1
Example of Carrier Proteins:
___ uptake of ___ by a ___ carrier called ___
Steps:
___ binds to ___ that is open to the ___ of the cell or in ___ conformation
Binding triggers ___ conformation that is open to the ___ of the cell
___ is released and protein undergoes a ___ ___ ___
Protein returns to ___ conformation
Exergonic, specific, regulated, faster, saturated, hyperbolic, linear
Facilitated Diffusion Kinetics:
Is an ___ process
Proteins are ___ and can be ___
Transport by channels is ___ than carrier proteins
Carrier proteins can become ___ as solute [] increases
If graphed, facilitated diffusion plot is ___ vs simple diffusion plot is ___
![<p>Facilitated Diffusion Kinetics:</p><ul><li><p>Is an ___ process</p></li><li><p>Proteins are ___ and can be ___</p></li><li><p>Transport by channels is ___ than carrier proteins</p></li><li><p>Carrier proteins can become ___ as solute [] increases</p></li><li><p>If graphed, facilitated diffusion plot is ___ vs simple diffusion plot is ___</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/155a6e35-3198-48f6-8738-491dfd2a9ebd.png)
Against, energy, endergonic, exergonic, ATP hydrolysis, directionality, direct, indirect, nutrients, wastes, ion nonequilibrium []
Active Transport:
Solutes move ___ the [] gradient
Needs ___
Couples ___ transport to an ___ process, usually ___ ___
___ of solute transport in 1 direction
Can involve ___ or ___ active transport
3 Functions:
Uptake of ___
Removal of ___
Maintenance of ___ ___ ___
Exergonic, ATP hydrolysis, H+, electrochemical [], solute, ions, H+, solute, H+
Active Transport: Direct vs Indirect:
Direct couples transport with ___ processes like ___ ___ that can transport solutes like ___ to establish an ___ ___
Indirect couples transport of ___ with ___ or ___, the ___ goes against its [] gradient and ___ goes down its [] gradient
![<p>Active Transport: Direct vs Indirect:</p><ul><li><p>Direct couples transport with ___ processes like ___ ___ that can transport solutes like ___ to establish an ___ ___</p></li><li><p>Indirect couples transport of ___ with ___ or ___, the ___ goes against its [] gradient and ___ goes down its [] gradient</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0eb73d2e-4626-4c64-ba4c-bed30cb900c0.png)
P, phosphorylation, V, vacuole, F, factor, ABC, ATP-binding cassette
Active Transport: Direct Transport:
4 Types of ATPases
___-type ATPases (___)
___-type ATPases (___)
___-type ATPases (___)
___-type ATPases (___)
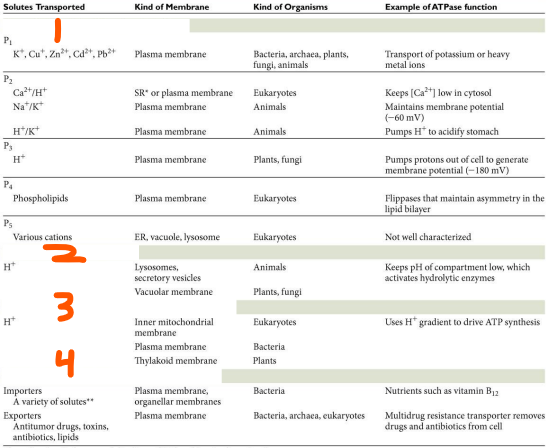
Na+/K+ ATPase, P-ATPase, inside, E1, 3 Na+, E1, phosphorylation, alpha subunits, ATP, E2, outside, 2 K+, E2, dephosphorylation, alpha subunits, E1, 2 K+, inside
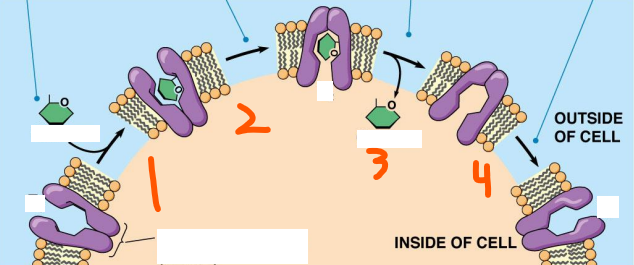
Example of Direct Transport:
The ___/___ ___ which is a type of ___-___ in animal cells
Initial state has protein open to the ___ of the cell and is in ___ conformation
___ (#) ___ binds to ___
Binding triggers ___ of ___ ___ by ___
The rxn causes a conformational change to ___ that releases the solute to the ___ of the cell
___ (#) ___ binds to ___
Binding triggers ___ of ___ ___ to return to ___ conformation
The ___ (#) ___ are released to the ___ of the cell
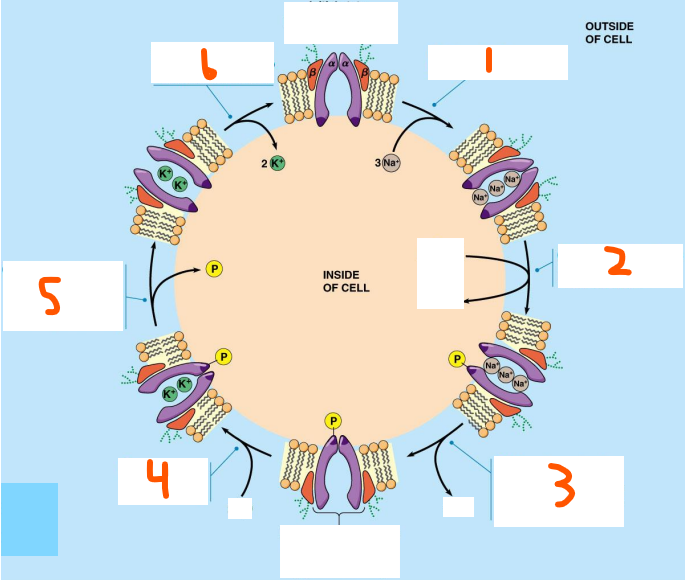
Na+/glucose symporter, outside, E1, 2 Na+, E1, glucose, inside, E2, 2 Na+, Na+/K+, outside, Na+, glucose, inside, E1
Example of Indirect Transport:
The ___/___ ___
Initial state is open to the ___ of the cell and is in ___ conformation
___ (#) ___ binds to ___
Binding triggers ___ to bind and a conformational change
Opens to the ___ of the cell and is in ___ conformation
___ (#) ___ are released but are pumped by the ___/___ pump to the ___ of the cell
Release of ___ is followed by ___ release to the ___ of the cell
Returns to ___ conformation
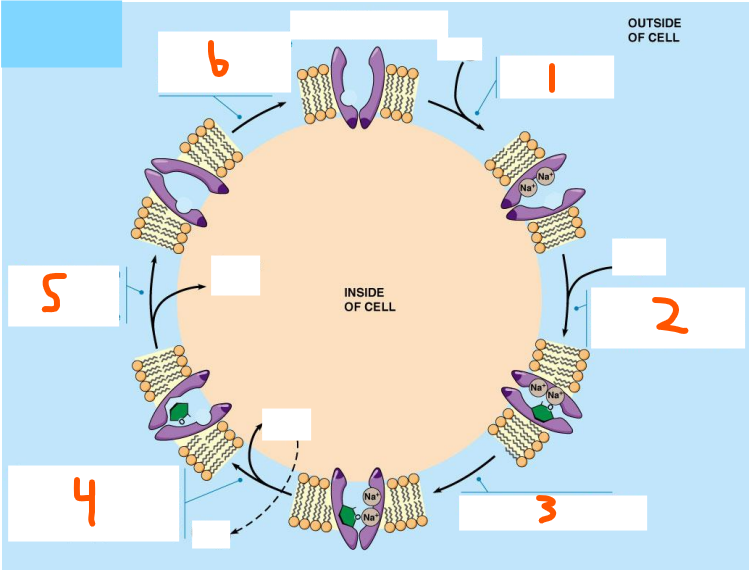
Small polar, small polar, large polar, ions, large polar, ions
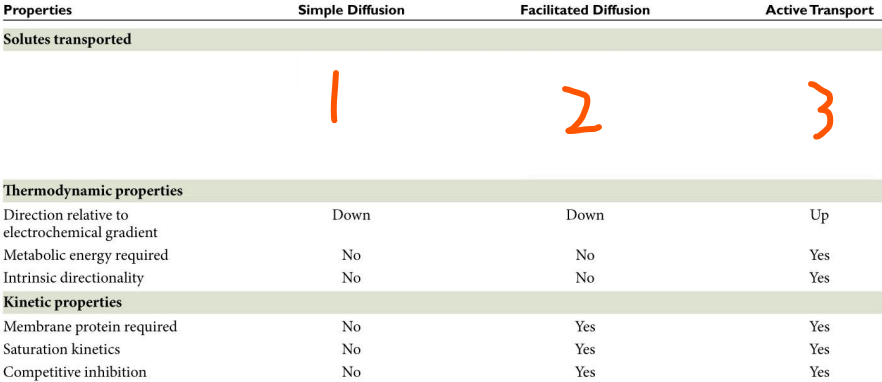
Transport Types:
Simple Diffusion: ___ ___
Facilitated Diffusion: ___ ___, ___ ___, and ___
Active Transport: ___ ___ and ___
No, down, energy, driving force, equilibrium, ions, sum, equilibrium
Solute Movement: [] gradient or electrochemical gradient:
[]:
For solutes with ___ +
Simple or facilitated diffusion goes ___ the [] gradient and no ___ needed
[] gradient increases the ___ ___ of the solute
___ when there is no [] gradient
Electrochemical:
For solutes that are ___
Is the ___ of [] and + gradients
___ when chemical and electrical gradients are balanced
2
Which of the following is likely to cross the membrane the slowest?
Glucose
Na2+
Vitamin K (hydrophobic)
Estrogen (large, hydrophobic)
4
Which of the following molecules can enter cells by diffusion in the absence of a transporter protein?
oxygen and K +
K + and H +
carbon dioxide and H +
oxygen and carbon dioxide
3
Celery stalks that are immersed in freshwater for several hours become stiff. Similar stalks left in a 0.15 M salt solution become limp. Which of the following statements is true?
Freshwater and the salt solution are both hypertonic to the cells of the celery stalks
Freshwater and the salt solution are both hypotonic to the cells of the celery stalks
Freshwater is hypotonic and the salt solution is hypertonic to the cells of the celery stalks
Freshwater is hypertonic and the salt solution is hypotonic to the cells of the celery stalks
2
How is facilitated diffusion similar to active transport?
Both involve moving substrates down a concentration gradient.
Both involve specific transport proteins.
Both consume ATP.
Both can involve “pump” proteins.
2
Which if the following is most likely to be transported by a carrier protein?
Tyrosine up its concentration gradient
Ions down their concentration gradient
Alanine down its concentration gradient
Water against its gradient