Uplearn electromagnetic radiation from stars
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Quantised
energy levels exist in discrete values
Why are energy levels in an atom negative?
The electrons bound to the atom must gain energy in order to move up to a higher energy level or escape the atom, therefore we write that they have negative energy
The electron has been excited
It has gained sufficient energy to move from one energy level to another that is at a higher energy
electronvolt
The electronvolt is the amount of energy transferred to an electron when it is passed through a potential difference of one volt
An electron undergoes de-excitation within an atom. What happens to the energy it loses?
It is released as a single photon
Luminosity
total radiant power output of a star, measured in W
Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
a graph of log ( L / Lsolar) on the y-axis and log(T) on the x-axis. The log(T) axis runs from high values on the left to low values on the right
Electron energy level
a discrete energy that an electron in an atom is allowed to possess. Energy levels in atoms are negative
Ground state
the lowest electron energy level of an atom
The wavelengths of light emitted by an atom form a unique pattern called an:
Emission spectrum or emission spectra
Which of the following is an emission spectrum?
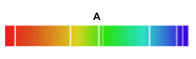
1)Which of the following might be produced by heated metal such as a filament lamp?
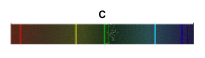
2)What is this type of spectrum called?
1) B
2)continuous spectrum
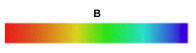
1)Which of the following might be produced by continuous spectrum passing through a cool gas?



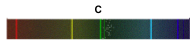
2)What is this type of spectrum called?
1)A
2)absorption spectrum or absorption spectra
Absorption spectra are used to study stars. They can be used to:
Identify the elements within a star
Emission spectrum
A set of electromagnetic frequencies produced by excited atoms and visible as bright lines in spectroscopy. Each atom has a characteristic emission spectrum that represents its unique set of energy levels
Continuous spectrum
A spectrum containing all visible electromagnetic frequencies are present, for example produced by a lamp filament or other heated solid metals
Absorption spectrum
A set of electromagnetic frequencies that are missing from an otherwise continuous spectrum and therefore show as dark lines on the spectrum. The missing frequencies have been absorbed and re-emitted in all directions by atoms or molecules present in between the source and detector. The absorbed frequencies correspond to the energy levels present in the absorbing atoms or molecules
Coherent light incident on a diffraction grating will produce an interference pattern on a screen behind the grating similar to that produced by Young’s Double Slit experiment.
The letter ‘n’ is used to label different fringes.
a) State the value of n for the central (bright) maximum in the fringe pattern
b) State the value of n for the bright fringe adjacent to the central maximum
a) n=0
b)n=1
We have seen the term ‘path difference’ when studying waves earlier in the course. Identify the correct definition of path difference
The difference in the distance travelled by two waves from their source to a specific point
Select the option that completes the statement below.
If ‘n’ is a whole number, then two waves are in phase if they have:
a path difference of nλ or a phase difference that is an even number multiple of 180o (which is the same as an even number multiple of π radians)
Calculate the grating spacing, d, for a diffraction grating that is labelled as having 400 lines per mm
d=2.5×10-6m
equation for maxima
dsin(θ) = nλ
We have just seen that equivalence of two angles, as shown below.
Choose the correct definition for the θ that is positioned just below the dotted line.
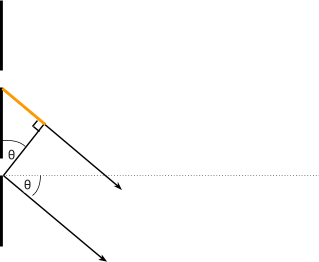
The angle between the line drawn from the grating to the 0th order and the line drawn from the grating to nth order
White light is incident on a diffraction grating and produces an interference pattern of bright and dark fringes on a screen placed behind the grating. Select the statement that correctly describes the bright fringes on the screen.
The central bright fringe is white, the rest are are a spectrum of colours with blue on the side closest to the central fringe, and red on the furthest side
Consider the section of a diffraction grating below. The grating equation is dsin(θ) = nλ, which tells at which grating spacing and θ combinations a maximum occurs: if dsin(θ) is a whole number of wavelengths (i.e nλ), then there is a maximum at this angle.
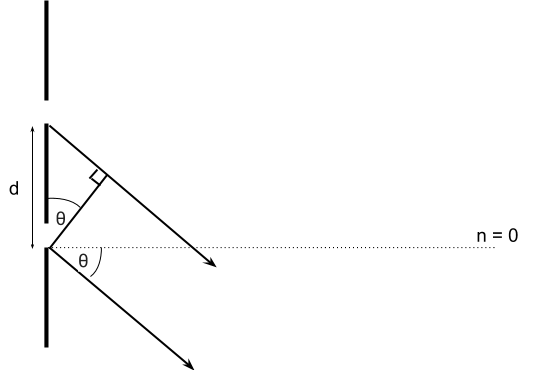
What is the value of θ beyond which maximum fringes can no longer be produced on the screen? You may assume that the screen has infinite length.
Below θ = 90o, maximum fringes are possible
∘∘ At θ = 90o, the light’s path would run parallel to the diffraction grating, and not hit the screen. Beyond 90o, the light’s path would have to go back through the diffraction grating
∘∘ So we say that the maximum angle for a maxima is 90o
Identify the equation for the highest order maxima
n=d/λ
Light of wavelength 520 nm is incident on a diffraction grating that has grating spacing d=2×10-6m. Calculate the highest order maximum that is produced on the screen.
nmax=3
Identify the correct requirement for an object to emit electromagnetic radiation
The temperature must be above, 0 K (zero kelvin)
Identify the correct relationship between the peak wavelength (λmax) and the temperature (T)
λmax∝1/T
Identify the correct definition of Wien’s Law.
λmaxT=constant
Identify the correct statement about the electromagnetic radiation emitted by objects of different temperature
The higher the temperature of an object, the lower the peak wavelength of emitted electromagnetic radiation
properties of a blackbody(2)
A blackbody absorbs all of the electromagnetic radiation that is incident on it.
When in thermal equilibrium, a blackbody emits a characteristic distribution of wavelengths at a given temperature
The graph below shows the typical shape of a blackbody radiation curve.
Choose the correct labels for the x-axis (horizontal) and the y-axis (vertical).
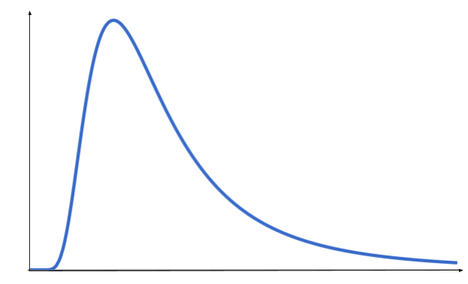
x-axis: wavelength; y-axis: intensity
As the temperature of a blackbody increases the shape of the blackbody curve will also change.
Identify the correct changes to the blackbody curve as temperature increases
Higher temperatures cause the peak of in the intensity-wavelength curve to become sharper and the value of the peak wavelength to reduce
What is meant by the luminosity of a star?
Total power radiated by a star
Stefan’s Law for the luminosity of star of radius r and surface temperature T is given by:
L=4πr2σT4
Stefan’s constant value
5.670 × 10⁻⁸ W m⁻² K⁻⁴
what is wein’s constant?
2.9×10-3mK
Blackbody
a blackbody absorbs all of the electromagnetic radiation that is incident on it and when in thermal equilibrium, emits a characteristic distribution of wavelengths at a given temperature
Peak wavelength (of a blackbody)
The wavelength at which the intensity is maximum for blackbody emission
Wien's law
The peak wavelength is inversely proportional to the absolute temperature of a blackbody
(λmaxT = constant) Constant is 2.90x10-3 m K
Stefan’s Law
The luminosity of a star is related to its surface area, 4πr2, and temperature,T, by: L = 4πr2σT4, where σ = Stefan’s Constant = 5.67x10-8 W m-2 k-4