Comprehensive Guide to Server Computers: Types, Roles, and Characteristics
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Server Computer
A powerful machine that provides services, resources, or data to other computers (called clients) over a network.
Server Computer
Unlike personal computers (PCs), servers are designed to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, manage heavy workloads, and run continuously without interruption.
Server Computer
Server provides the foundation for all the critical tasks of any business operations.
Server Computer
Unlike a standard desktop PC, as server offers significantly greater processing power, expanded memory capacity, and advanced storage capabilities to support the simultaneous demands of multiple users and applications.
Client-Server Model
The relationship where servers provide services to clients.
Operating System
Server PC vs. Regular PC
Operating systems such as Windows Server and Linux Server that are specifically designed for servers.
Processors
Server PC vs. Regular PC
Servers often use multiple CPUs or multi-core processors for parallel processing.
Memory
Server PC vs. Regular PC
Servers have more RAM, often error-correcting (ECC) memory for stability.
Storage
Server PC vs. Regular PC
Servers use RAID arrays, SSDs, or SAN (Storage Area Network) for faster and safer data handling.
Power Supply
Server PC vs. Regular PC
Servers have redundant power supplies where uninterrupted power is essential.
Network
Server PC vs. Regular PC
Servers are equipped with multiple high-speed network interfaces for redundancy and faster connectivity.
Advantages of Server Computers
Centralized management of data and resources, high performance for handling multiple users at once, and strong security features for sensitive data, and scalability to grow with business needs.
Disadvantages of Server Computers
Expensive to set up and maintain; requires technical expertise for management; improper maintenance can lead to server failure affecting many users.
Can a simple desktop PC be a Server?
Yes, but it may not be suitable for handling heavy workloads or multiple users.
ECC Memory
Error-correcting memory used in servers for stability.
RAID
A storage technology that combines multiple disk drive components into a single unit for data redundancy and performance.
SAN
Storage Area Network, a dedicated network that provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage.
Characteristics of Server Computers
Features that protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Store and manage data
Functions of Servers
Server hardware provides secure storage for vast amounts of information, such as business emails and social media posts
Run applications
Functions of Servers
Whether it's an e-commerce platform or a complex database, server hardware provides the processing power to keep these applications running smoothly
Deliver resources
Functions of Servers
Printers, scanners, and other network devices rely on server hardware to connect and share resources with other users.
Data storage
Functions of Servers
Servers act as repositories for information that authorized users or applications can access.
Computation
Functions of Servers
Servers perform computations on behalf of clients, offloading processing demands from individual devices.
Communication facilitation
Functions of Servers
Servers act as a gateway between different computers within a network, allowing communication and bridging gaps like middleware.
Tower Servers
Types of Server Computers
- Enclosed in a standalone, vertical cabinet; budget-friendly; suitable for small businesses with basic tasks.
- Low component density allows for more efficient airflow and simpler cooling, reducing costs for advanced or expensive cooling systems.
Rack Servers
Types of Server Computers
- Built to be mounted in standardized server racks; compact and space-efficient; suitable for demanding workloads.
- Modular design makes them highly scalable (additional servers can be added to the rack with ease as the business grows or needs evolve.)
Blade Servers
Types of Server Computers
- Inserts multiple slim, modular blades (each containing its own processor, memory, and network interface) into a single shared chassis; provides maximum space efficiency and scalability.
- Each blade can be hot-swapped for maintenance or upgrades without shutting down the entire system. Reducing downtime and maintain continuous operations.
Hyperconverged Infrastructures (HCI)
Types of Server Computers
- Integrates computing, storage, and networking into a single, unified system for simplified deployment and improved scalability.
- Typically comes as pre-configured appliance or software-defined solution, offering simplified deployment, centralized management, and improved scalability.
Mainframes
Types of Server Computers
- Pioneers of server technology in the IT industry (since 1950s), delivering exceptional processing power and unmatched security, ideal for mission-critical operations.
- Especially well-suited for large financial institutions, government agencies, and other organizations that manage vast amounts of data and essential transactions.
Domain Controller
Roles of a Server Computers
Manages user accounts, passwords, and permissions in a network, verifying credentials and controlling access.
Ex: In a school computer lab, a student logs in their username and password. This verifies if the credentials are correct and decides what files or printers the student can access.
DHCP Server (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
Roles of a Server Computers
Automatically assigns IP addresses to computers and devices in a network.
Ex: When you connect your laptop or phone to Wi-Fi, you don't manually type an IP address. This provides one instantly so you can access the internet.
DNS Server (Domain Name System)
Translates and provides the local mapping of fully qualified domain names (like www.google.com) into IP addresses (like 142.250.190.14), allowing computers to communicate using IP addresses, not names.
Ex: When you type facebook.com, the DNS server finds the correct IP address of Facebook's servers so your browsers can connect.
File Server
Roles of a Server Computers
Stores and manages files in a central location for multiple users to access or share.
Ex: In an office, employees save reports on a shared file server so everyone in the team can open, edit, and store documents in one place.
Print Server
Roles of a Server Computers
Manages printers and handles print requests from multiple users in a network.
Ex: In a school, instead of each computer being connected to a separate printer, all print jobs go through a print server that sends documents to the correct printer.
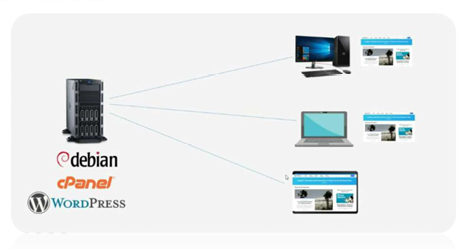
Web Server
Roles of a Server Computers
Hosts websites and delivers web pages to users through a browser.
Ex: When you visit www.wikipedia.org, a wen server is sending the pages to your browser. Popular web servers include Apache, Nginx, and Microsoft IIS.
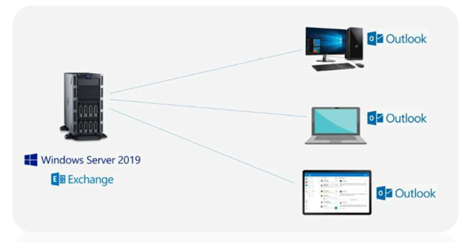
Mail Server
Roles of a Server Computers
Sends, receives, and stores emails, often combined with web servers.
Ex: When you send an email through Gmail, a mail server is responsible for delivering your message to the recipient's mail server so they can read it.
Application Server
Roles of a Server Computers
Hosts and runs specific applications for users, usually business or enterprise apps.
Ex: A bank's online system runs on an application server that processes transactions when clients log in, check balances, or transfer funds.
Database Server
Roles of a Server Computers
Stores, manages, and provides access to databases, allowing multiple users and applications to query and update data.
Ex: When you log in to an e-commerce site like Shopee or Lazada, a database server retrieves your account details, purchase history, and product information.
Server
A computer or system that provides data, resources, or services to other computers, known as clients.
Tower Server
Types of Server Computers

Rack Server
Types of Server Computers

Blade Server
Types of Server Computers

Hyperconverged Infrastructures (HCI)
Types of Server Computers
Mainframes
Types of Server Computers

Web Server
Mail Server