Flashcards: Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is a calorie?
Specific heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1°C.
What is latent heat?
Heat stored or hidden during phase changes (undetected heat).
What happens during evaporation?
Liquid changes to gas, requiring 600 cal/g.
What happens during condensation?
Gas changes to liquid, releasing latent heat.
What is the latent heat of melting?
80 cal/g, when solid changes to liquid.
What is latent heat of fusion?
Heat released when liquid changes to solid.
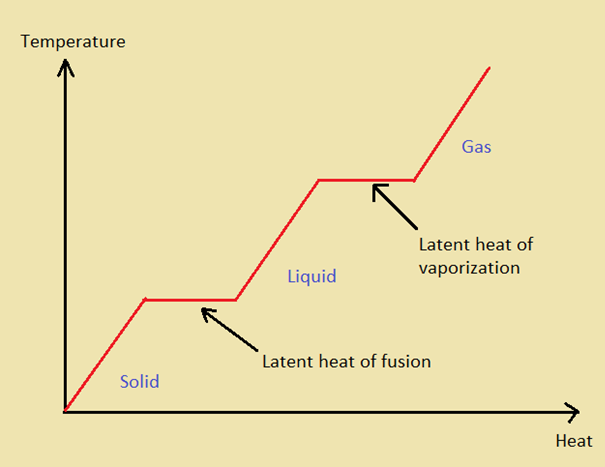
What is sublimation?
Solid changes to gas, requiring 680 cal/g.
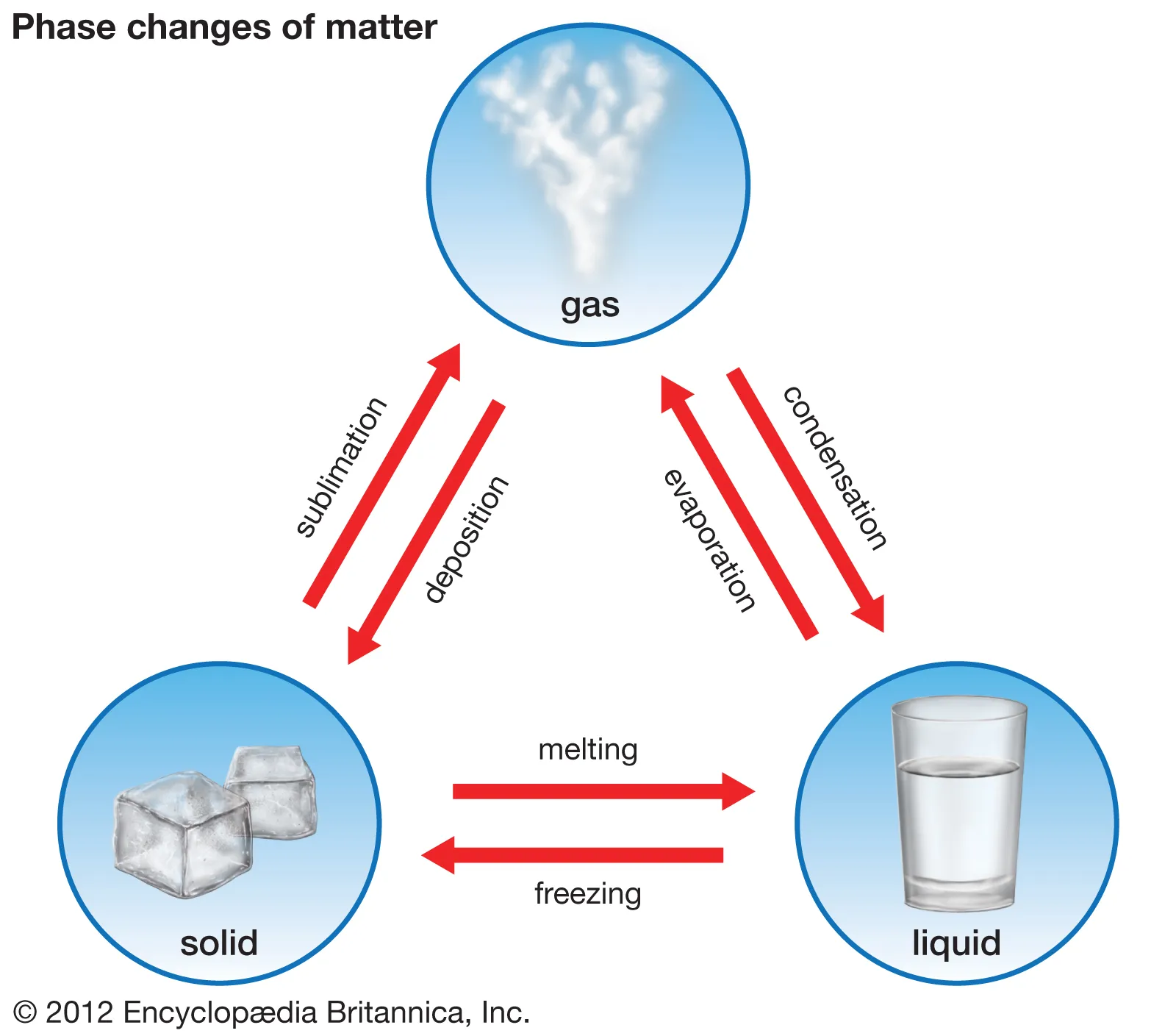
What is deposition?
Gas changes to solid.
Why does water have high thermal inertia?
Due to strong molecular bonds that resist heat flux.
What is saturated air?
Air filled with water vapor to capacity, dependent on temperature.
What is relative humidity?
Ratio of actual water vapor to the amount needed for saturation at a given temperature.
What is 100% relative humidity?
Saturation (dew point reached).
How does temperature affect relative humidity?
High temperature = low RH; low temperature = high RH.
What is the dry adiabatic rate?
Unsaturated air cools at 1°C per 100 meters when rising, warms at the same rate when descending.
What is the wet adiabatic rate?
Air cools more slowly (0.5°C to 0.9°C per 100 meters) due to latent heat release.
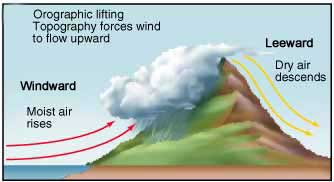
What is orographic lifting?
Air forced upward by elevated terrain, causing rainshadow deserts.
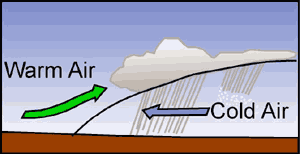
What is frontal wedging?
Warm air rises over cool air, part of storm systems.
What is convergence?
Air flows together and rises due to low pressure.
What is localized convective lifting?
Unequal surface heating causes air to rise due to buoyancy.
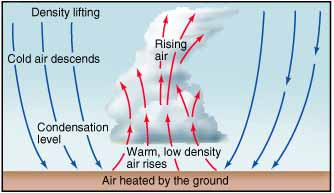
What is absolute stability?
Cooler, denser air that resists vertical displacement; results in fair weather.
What is absolute instability?
Warmer, less dense air that continues to rise; results in heavy cloud formation and bad weather.
What is conditional instability?
Stable for unsaturated air, unstable for saturated air.
What is condensation?
Water vapor changes to liquid, forming dew, fog, or clouds.
What surfaces are needed for condensation?
Plants, windows, dust, etc.
What is the main requirement for condensation to occur?
100% relative humidity.
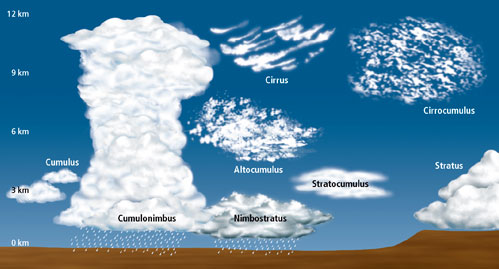
What are cirrus clouds?
High, thin clouds (>6000m).
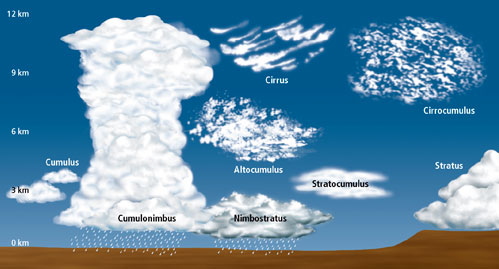
What are cumulus clouds?
Mid-level, globular clouds (2000-6000m), usually associated with fair weather.
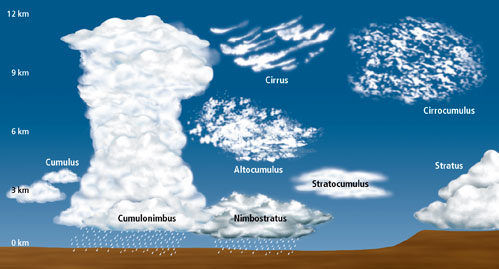
What are stratus clouds?
Low-level, sheet-like clouds (<2000m).
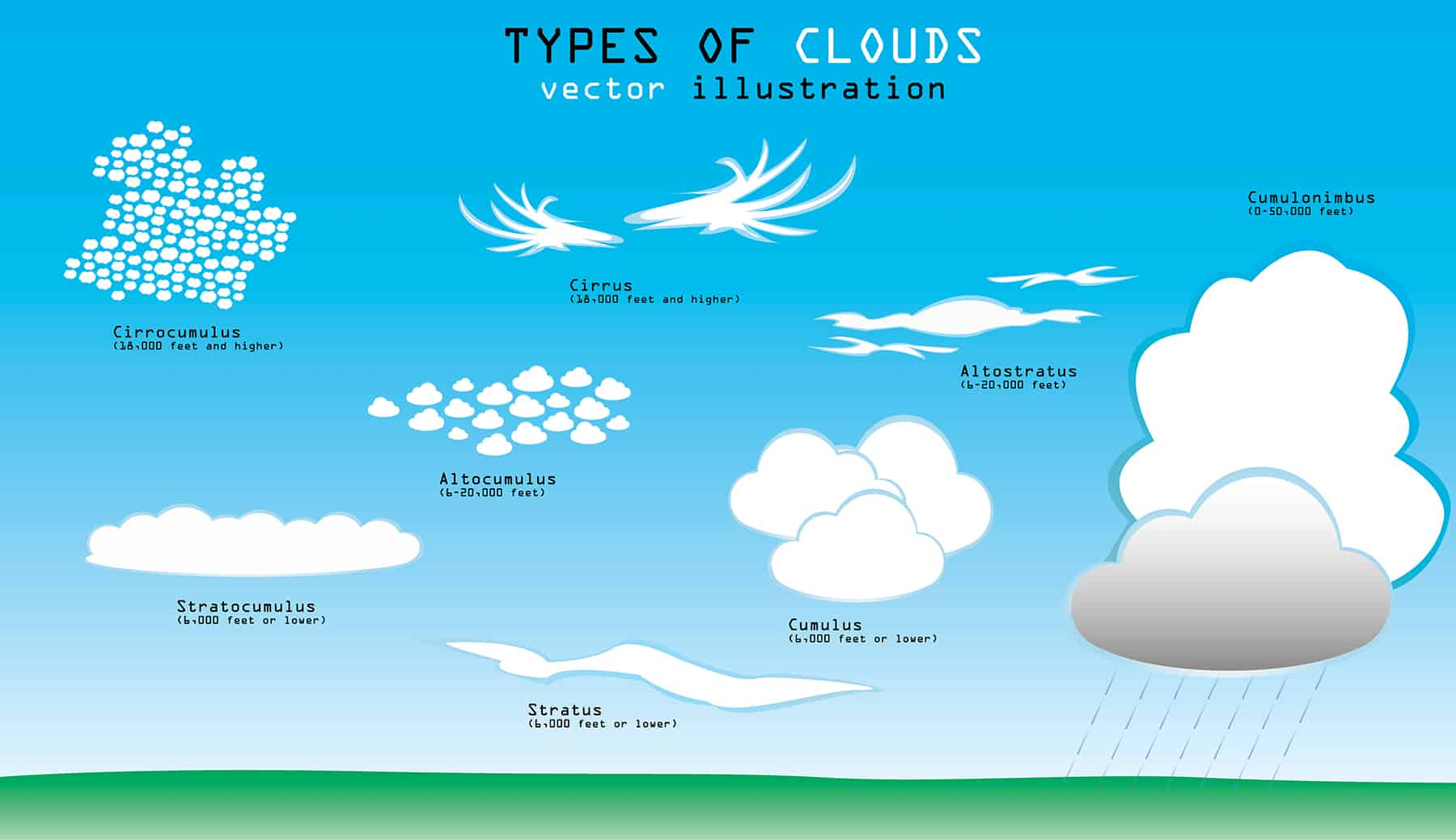
What is a cumulonimbus cloud?
Strong vertical development, storm clouds.
What causes advection fog?
Warm, moist air moves over a cool surface.
What causes radiation fog?
Earth cools rapidly on cool, clear nights.
What causes upslope fog?
Humid air moves up a slope and cools due to adiabatic cooling.
What causes steam fog?
Cool air moves over warm water, adding moisture to the air.

What causes frontal fog?
Forms when rain evaporates into cool air.
What is the Bergeron Process?
Ice crystals collect water vapor, forming snowflakes that may melt to rain.
What is the collision-coalescence process?
Large droplets form in warm clouds and collide with others, common in the tropics.
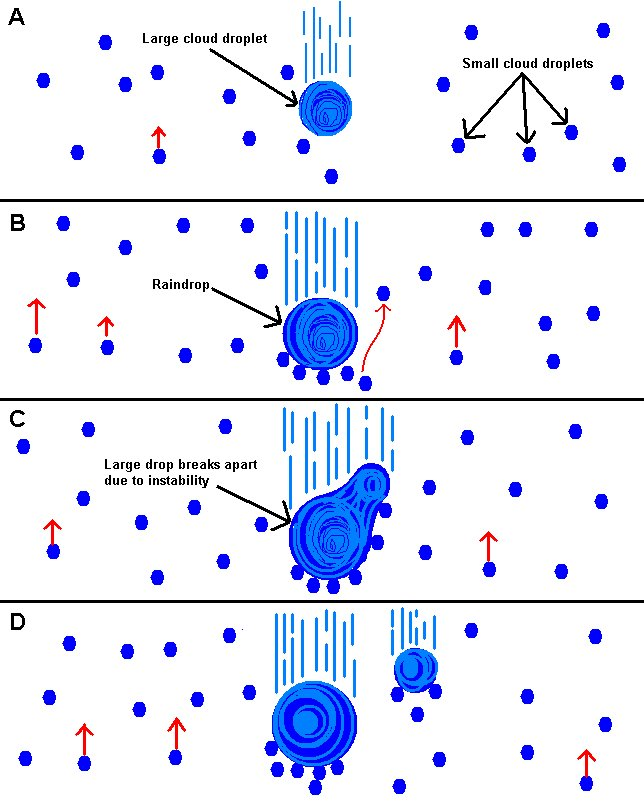
What is rain?
Free-falling water droplets.
What is snow?
Free-falling ice crystals.
What is sleet?
Frozen raindrops.
What is glaze?
Freezing rain.
What is hail?
Ice pellets with concentric ice layers, formed in cumulonimbus clouds with strong updraft