Bio 20A Final/Midterm 3--Guido Bordignon Winter 2023
1/260
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
261 Terms
Interphase includes which of the following stages of the cell cycle? Check all that apply
A. S
B. G2
C. M
D. G1
A. S
B. G2
D. G1
What would happen when a cell undergoing mitosis is fused with a cell in G1?
A. The G1 cell would immediately enter mitosis
B. The M cell would immediately enter G1
C. Both cells would enter S phase
D. The M cell would enter G1, the G1 cell would enter mitosis
E. Both cells would enter interphase
A. The G1 cell would immediately enter mitosis
Cell cycle checkpoints ensure that:
A. a cell has grown sufficiently prior to division
B. DNA damage is repaired prior to DNA replication
C. sister chromatids are properly aligned on the metaphase plate prior to anaphase
D. DNA has been replicated prior to division
E. All of the above
E. All of the above
A cell that does not divide for an extended period is in _______
A. S
B. G0
C. G1
D. G2
E. Big Trouble
B. G0
A eukaryotic cell in G1 has 10 DNA double helices. If this cell underwent mitosis, how many DNA molecules (i.e. DNA double helices) would be present in the cell during prophase?
A. 5
B. 10
C. 20
D. 40
E. none of the above
C. 20
During mitosis, spindle microtubules attach to the ________ of chromosomes.
A. centrosomes
B. telomeres
C. nucleosomes
D. kinetochores
E. axonemes
D. kinetochores
A mutation prevents the destruction of cyclin during the cell cycle. The most likely effect of this mutation would be:
A. rapid, unregulated cell division
B. cancer
C. the cell would not exit mitosis
D. all of the above
E. none of the above
C. the cell would not exit mitosis
Which of the following kinds of cells divide by binary fission?
A. bacteria
B. human cells
C. plant cells
A. bacteria
The term "chromatid" refers to:
A. the complex of proteins that assembles at the centromere during mitosis
B. DNA and associated proteins
C. a highly condensed chromosome that is visible during mitosis or meiosis
D. the ends of a chromosome
E. DNA wrapped around an octamer of histone proteins
C. a highly condensed chromosome that is visible during mitosis or meiosis
One difference between cancer cells and normal cells is that cancer cells __________.
A. are unable to synthesize DNA
B. are arrested at the S phase of the cell cycle
C. continue to divide even when they are tightly packed together
D. cannot function properly because they are affected by density-dependent inhibition
C. continue to divide even when they are tightly packed together
Meiosis I produces:
A. Diploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
B. Diploid cells with replicated chromosomes
C. Haploid cells with replicated chromosomes
D. Haploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
E. gametes
C. Haploid cells with replicated chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes are separated during ___________
A. anaphase of meiosis II
B. anaphase of meiosis I
C. anaphase of mitosis
D. telophase of meiosis II
E. prophase of meiosis I
B. anaphase of meiosis I
Independent assortment occurs during
A. metaphase of meiosis I
B. metaphase of meiosis II
C. metaphase of mitosis
D. anaphase of meiosis I
E. anaphase of meiosis II
F. anaphase of mitosis
A. metaphase of meiosis I
Sister chromatids are separated during ___________ (check all that apply)
A. anaphase of mitosis
B. anaphase of meiosis II
C. anaphase of meiosis I
D. binary fission
A. anaphase of mitosis
B. anaphase of meiosis II
Meiosis II produces
A. haploid cells with replicated chromosomes
B. diploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
C. diploid cells with replicated chromosomes
D. haploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
E. somatic cells
D. haploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
Sources of genetic variation for organisms that reproduce sexually include:
A. independent assortment of chromosomes
B. random fusion of gametes
C. recombination
D. mutation
E. all of the above
E. all of the above
A diploid cell in G1 has 5 pairs of homologous chromosomes. If this cell underwent meiosis, how many DNA molecules (i.e.DNA double helices) would be present in each gamete after the completion of meiosis?
A. 5
B. 10
C. 20
D. 40
E. none of the above
A. 5
Which of the statements about homologous chromosomes are true
A. they carry the same genes in the same order
B. the versions (alleles) of the genes they carry may be different
C. homologous chromosomes are separated during anaphase of mitosis
D. sister chromosomes are homologous
E. they have identical DNA sequences
A. they carry the same genes in the same order
B. the versions (alleles) of the genes they carry may be different
Which of the following statements are false?
A. multicellular organisms are always composed of diploid cells
B. meiosis leads to the production of haploid gametes
C. the fusion of haploid gametes results in the formation of a diploid cell
D. haploid cells can reproduce via mitosis
E. none of the above
A. multicellular organisms are always composed of diploid cells
A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is __________.
A. a sperm
B. an egg
C. a zygote
D. a somatic cell of a male
A. a sperm
You flip a coin three times and it comes up heads each time. A friend flips a coin 3 times and it comes up tails each time. What is the probability that both you and your friend will both come up tails on the next toss
1/4
Black fur in mice (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). Short tails (T) are dominant to long tails (t). Of 32 progeny of the cross BbTt x BbTt, approximately how many will have brown fur and short tails? (assume the genes are not linked)
6
In a cross AaBbCcDd x AaBbCcDd, what is the probability that one of the offspring will have the genotype aaBBCCDd? Assume the genes are unlinked.
1/128
The segregation of alleles occurs during which of the following?
A. anaphase of mitosis
B. anaphase of meiosis II
C. anaphase of meiosis I
D. metaphase of meiosis I
E. telophase of meiosis II
C. anaphase of meiosis I
Given the parents AABBCc x AabbCc, what proportion of the progeny will phenotypically resemble the first parent (assuming the genes involved are on different chromosomes)?
3/4
A male mouse with brown fur is crossed to a female mouse with white fur. All the male progeny have white fur while all the female progeny have brown fur. What is the most likely explanation for these data? Assume that the data are highly reproducible and large numbers of progeny were examined. (Check all the apply)
A. The brown allele is dominant
B. The brown allele is recessive
C. The coat color gene is autosomal
D. The coat color gene is X-linked
E. The female parent is homozygous for the white allele
A. The brown allele is dominant
D. The coat color gene is X-linked
E. The female parent is homozygous for the white allele
The purple (P) allele of a flower color gene is dominant to the white (p) allele. If two heterozygous plants are crossed, __________ of their progeny will have purple flowers.
75%
Consider the following cross:
P: AABBCC x aabbcc
F1: AaBbCc
Genes A, B and C are linked. In the absence of recombination, what gametes can be produced by the F1 progeny? Hint: draw out the chromosomes of the parents and their progeny before answering this question.
A. No answer text provided.
B. AAA, BBB, CCC, aaa, bbb and ccc
C. ABC, abc, ABc, abC, AbC, aBc, aBC and Abc
D. ABC and abc
E. not enough information to tell
D. ABC and abc
Which of the following could account for incomplete dominance?
A. sex-linkage
B. linkage
C. the product of a gene is present in limited quantities
D. polygenic inheritance
E. environmental effects
C. the product of a gene is present in limited quantities
What is asexual reproduction?
The production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent
What is a clone?
a genetically identical copy of a gene or organism
What is binary fission?
A form of asexual reproduction in which the parent divides into two approximately equal parts
What is the cell cycle?
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
what is a chromosome?
a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
What is chromatin?
the material of which the chromosomes of organisms other than bacteria (i.e., eukaryotes) are composed. It consists of protein, RNA, and DNA.
What are histones?
any of a group of basic proteins found in chromatin.
What are nucleosomes?
DNA and histone molecules which together form a bead-like structure.
What is metaphase?
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
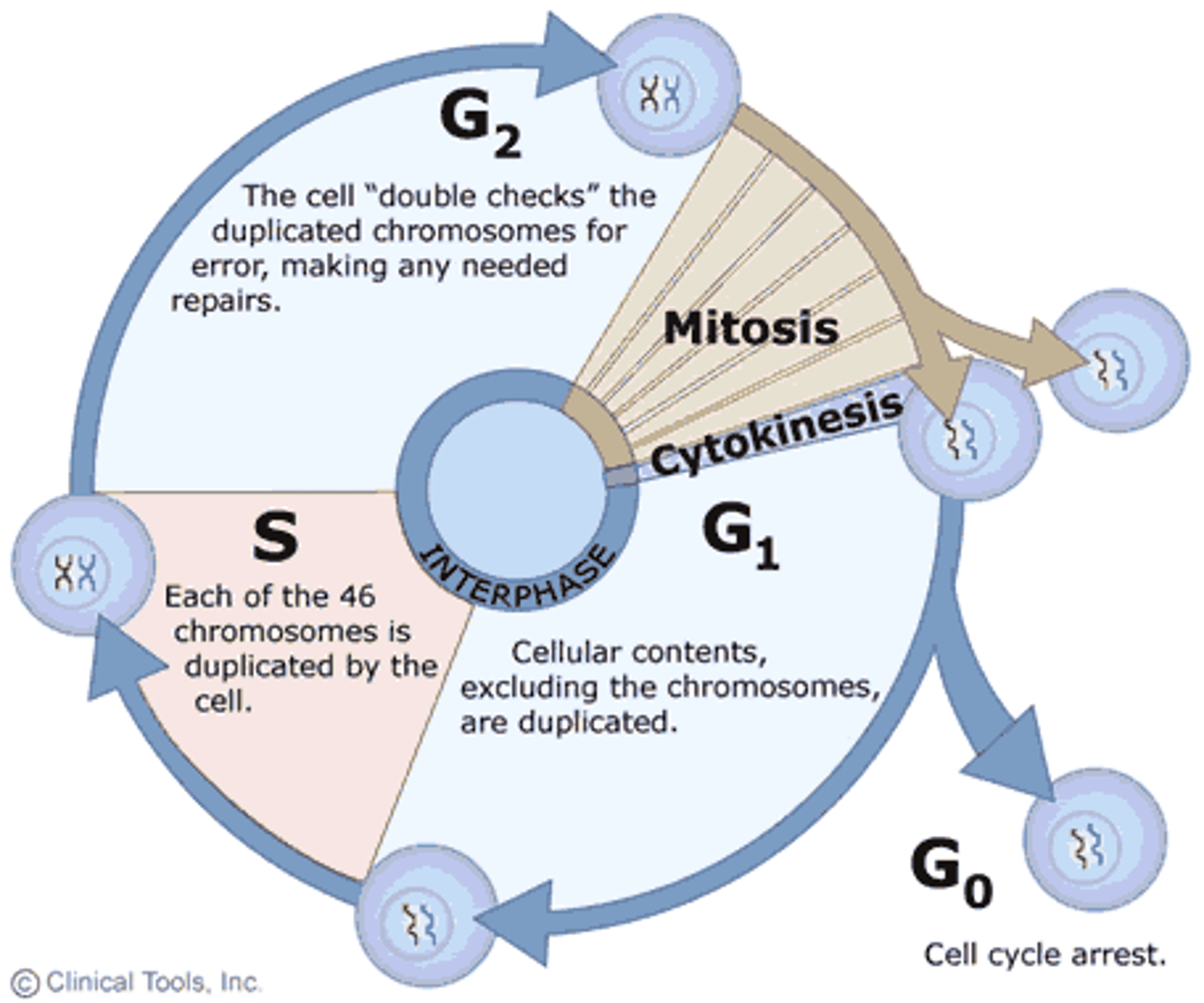
What is interphase?
period of the cell cycle between cell divisions
What is the G1 phase?
Cell growth
What is the G0 phase?
If the cell does not receive the go ahead for G1, it goes to G0 where it does not replicate.
What is the G2 phase?
The period of the interphase where the cell produces proteins and organelles for the cell division.
What is the S phase?
DNA synthesis
What is mitosis?
Cell division that generates new cells for growth and repair. The division of one cell into two genetically identical daughter cells
What is prophase?
DNA and proteins condense into lightly coiled chromosomes in a nuclear envelope
What is prometaphase?
Nuclear envelope breaks down. Microtubules contact chromosomes at kinetochores.
What is anaphase?
Spindle fibers pull each chromatid to opposite sides
What is telophase?
Two new nuclei form
Chromosomes appear as chromatin (threads rather than rods)
Mitosis ends
What is cytokinesis?
the cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis, bringing about the separation into two daughter cells.
what is the nucleolus?
a small dense spherical structure in the nucleus of a cell during interphase. makes ribosomes.
what is a chromatid?
one half of a duplicated chromosome
What are sister chromatids?
2 identical copies of DNA held together by a centromere
what is a telomere
the ends of linear chromosomes
What is a centromere?
the point on a chromosome by which it is attached to a spindle fiber during cell division.
What is the mitotic spindle?
a structure made of microtubules that controls chromosome movement during mitosis
What is the metaphase plate?
an imaginary structure at the midway point between the spindle's two poles
what is a contractile ring?
ring of actin and myosin II filaments built at the equator of a cell at the end of mitosis and causes furrowing during cytokinesis
What is a clevage furrow?
A pinch in the cell when it is about to divide.
What is a cell plate?
A cell plate is a arrangement of vesicles that fuse in the middle of a plant cell.
What is CDK and what does it do?
A cyclin dependent kinase. Regulates the cell cycle.
what is a M-promoting factor?
Maturation or M phase-promoting factor (MPF) is the universal inducer of M phase common to eukaryotic cells. MPF was originally defined as a transferable activity that can induce the G2/M phase transition in recipient cells.
What are the cell cycle checkpoints?
G1, G2, M
what is a cell cycle checkpoint?
A control point in the cell cycle where stop and go-ahead signals can regulate the cycle.
how do eukaryotic cells reproduce asexually?
Asexual reproduction in single-celled eukaryotes involves mitosis, i.e., duplication of chromosomes and cytoplasm to produce "twin cells" in the process of cell division
how do prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually?
binary fission
what are the levels of chromatin packaging?
We can define three levels of chromatin organization in general terms: DNA wrapped around histone proteins (nucleosomes) like "beads on a string". Multiple nucleosomes coiled (condensed) into 30 nm fiber (solenoid) structures. Higher-order packing of the 30 nm fiber into the eventual familiar metaphase chromosome.
how do chromatin protect eukaryotic genomes?
chromatin compaction protects DNA from attack by chemical agents.
what are the steps of mitosis?
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
What happens during interphase?
Typically, this phase accounts for 90% of the cell cycle. It is a time of high metabolic activity. The cell grows by producing proteins and organelles, and chromosomes are replicated.
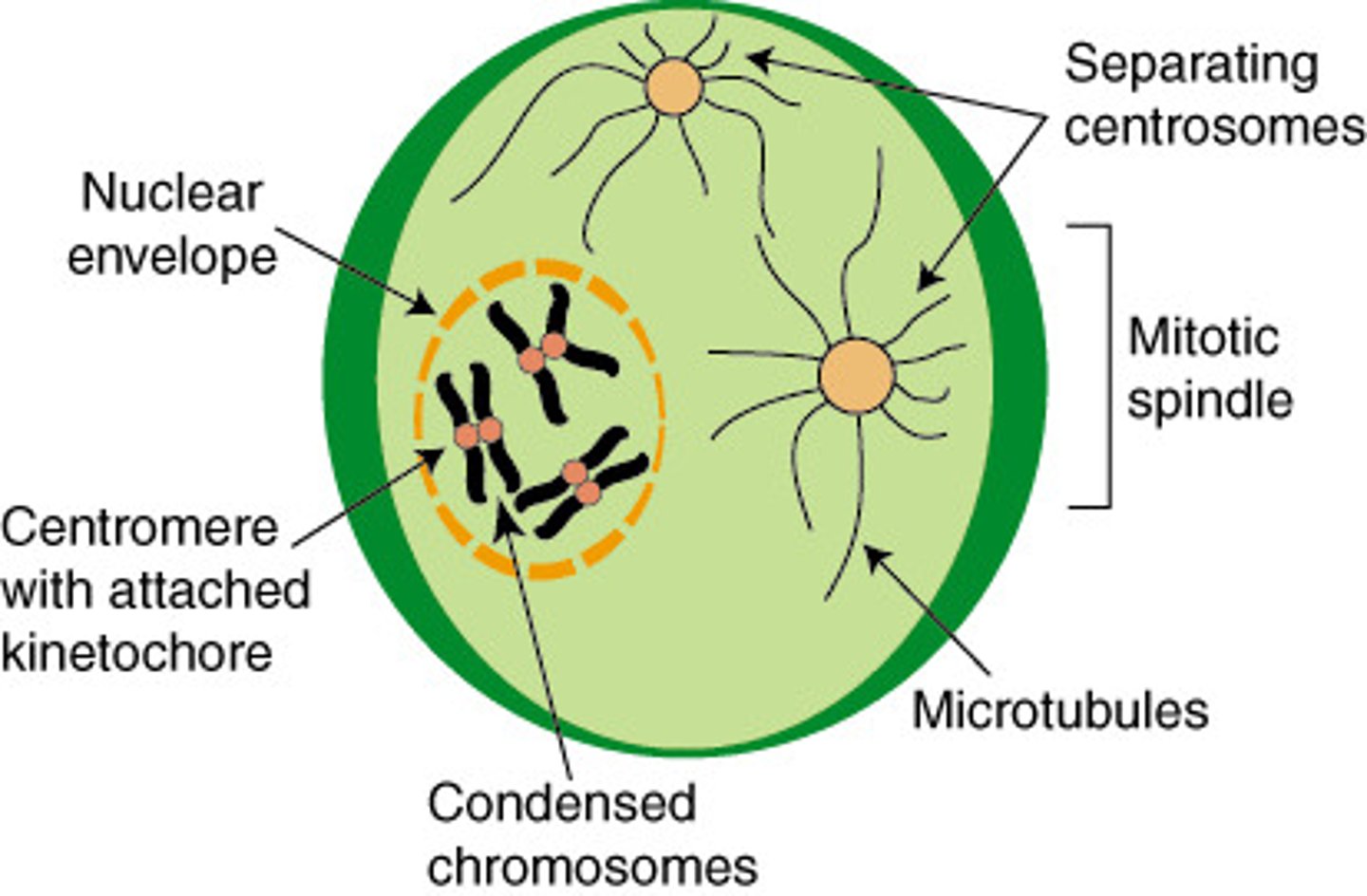
what happens during prophase?
1. Chromatin fibers coil up to become discrete chromosomes.
3. Each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids, joined at the centromere.
4. Microtubules grow out from the centrosomes, initiating formation of the mitotic spindle.
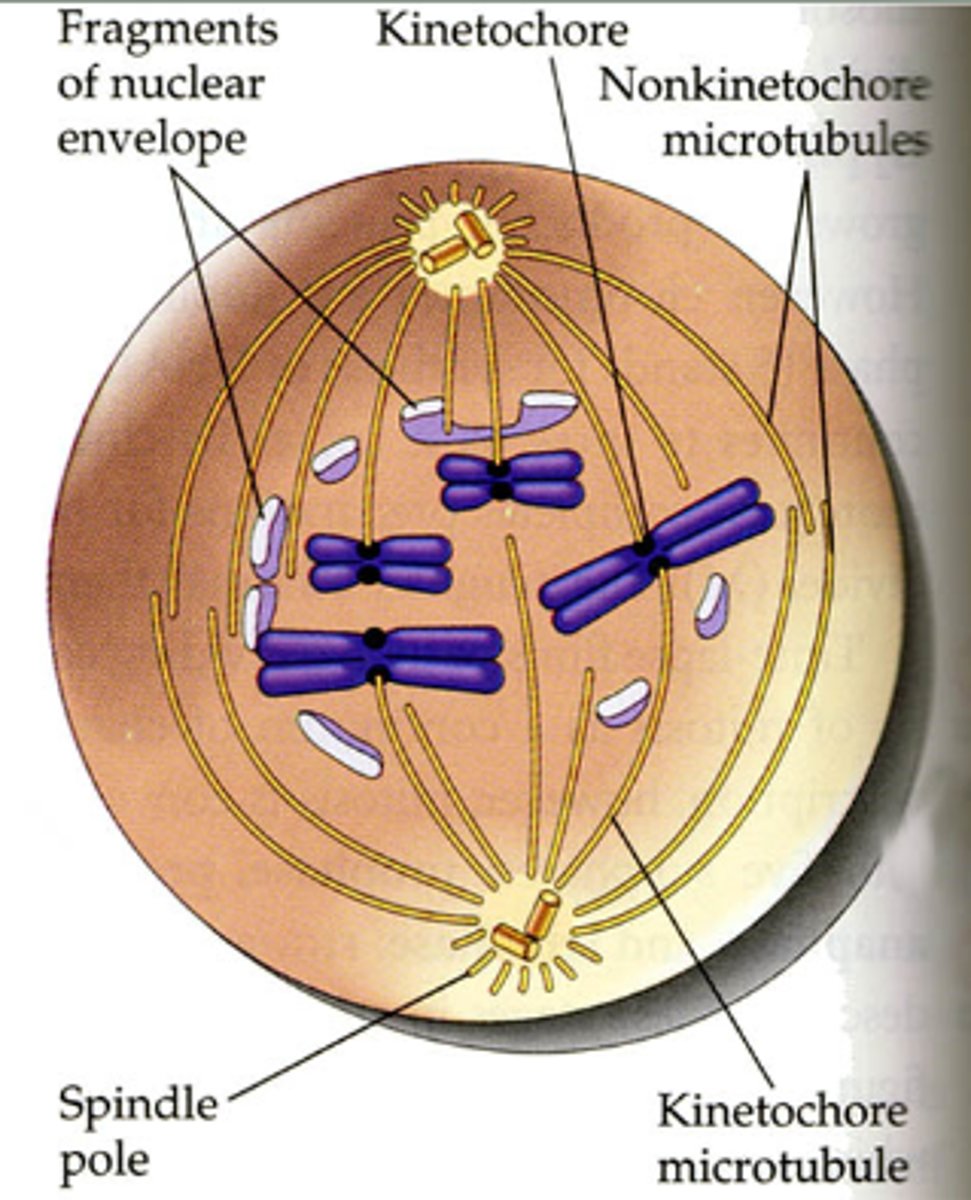
what happens during prometaphase?
1. The nuclear envelope breaks into fragments.
2. Some of the spindle fibers reach the chromosomes and attach to kinetochores, structures made of proteins and specific sections of DNA at the centromeres.
3. Nonkinetochore microtubules overlap with those coming from the opposite pole.
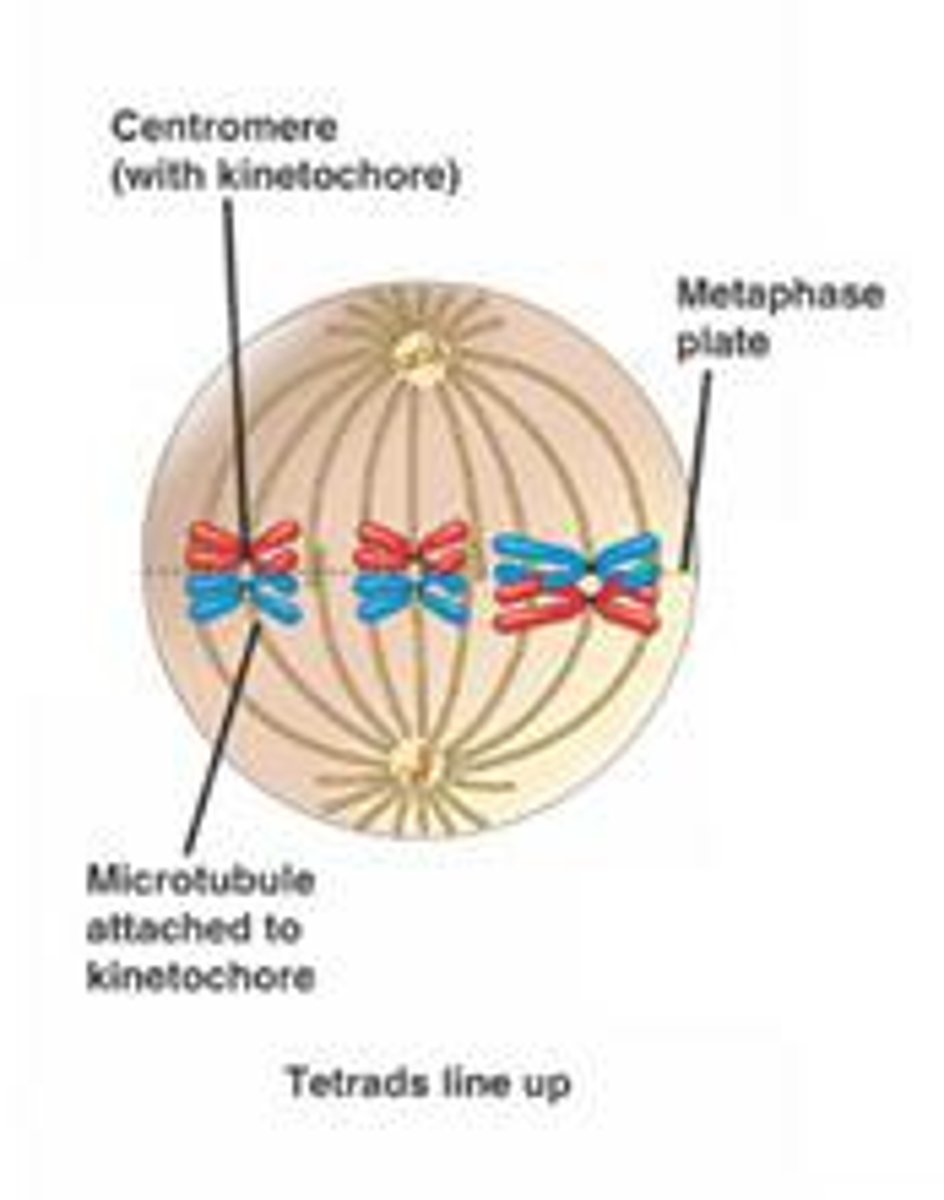
what happens during metaphase?
1. The mitotic spindle is fully formed
2. The microtubules attached to kinetochores move the chromosomes to the metaphase plate, an imaginary plane equidistant from the poles.
What happens during anaphase?
1. The two centromeres of each chromosome come apart, separating the sister chromatids.
2. The spindle fibers pull apart the chromatids to form two nucleus of the cells.
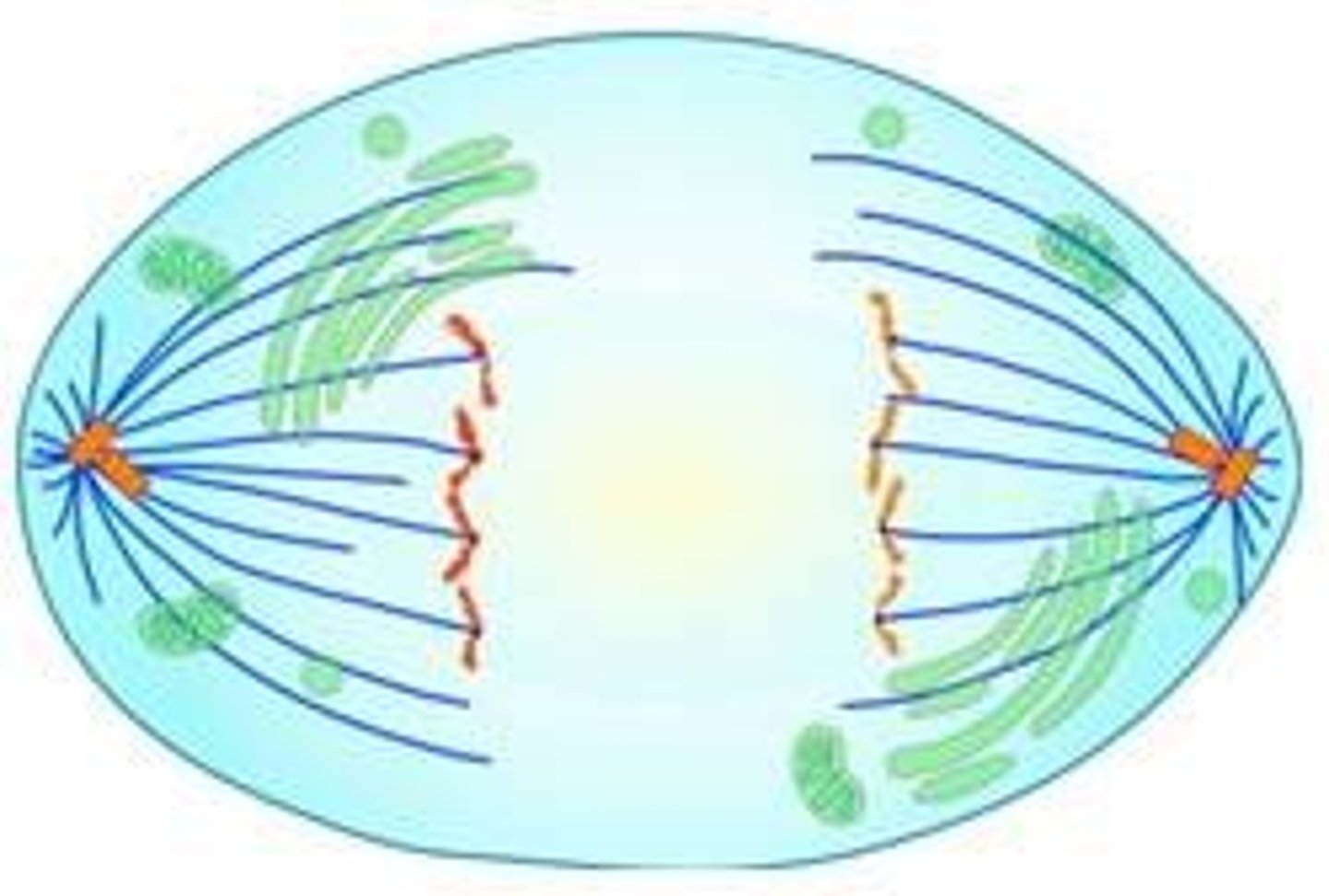
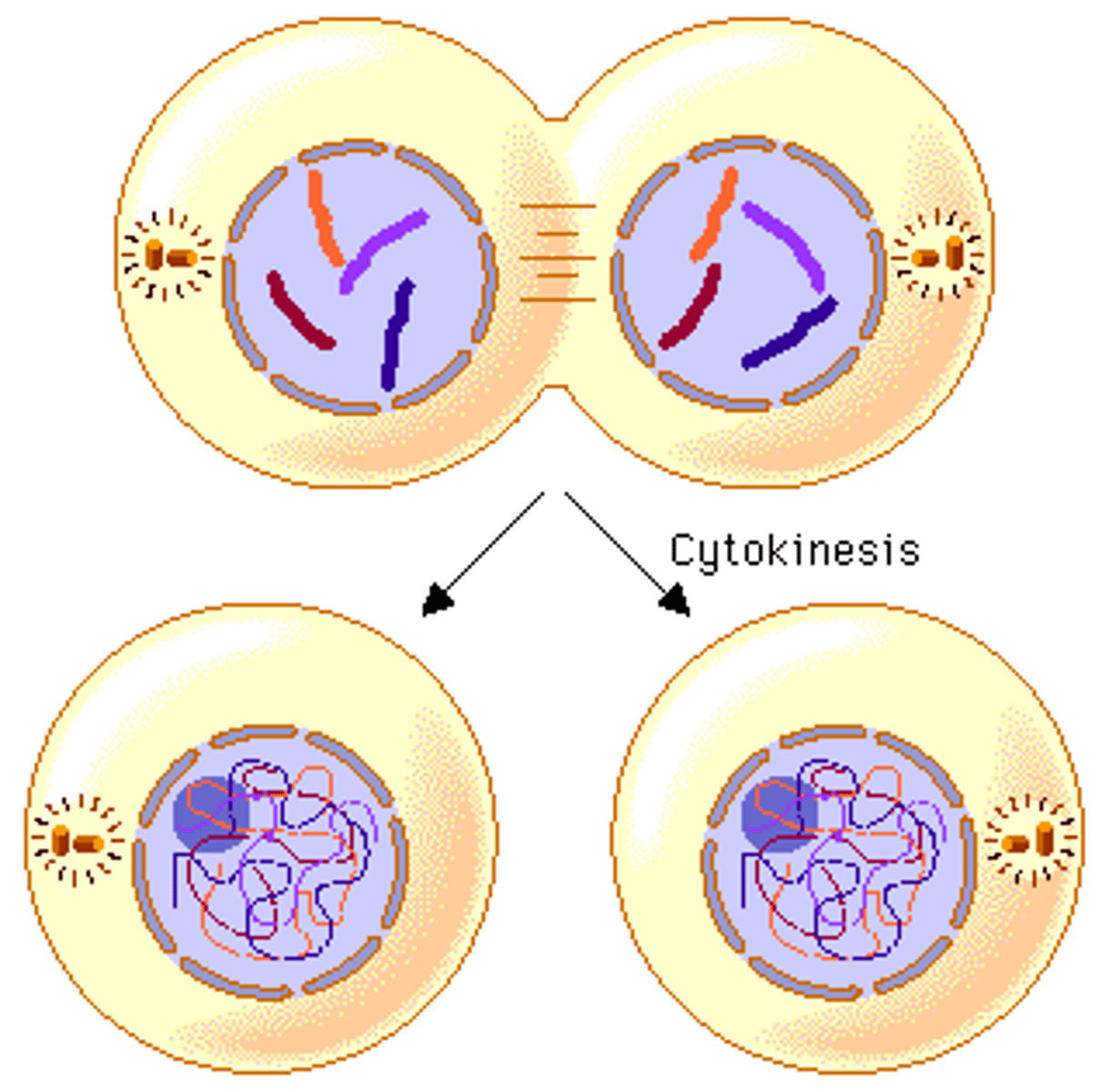
What happens during cytokinesis in eukaryotes?
This is the step in the cell cycle when the cytoplasm divides in two.
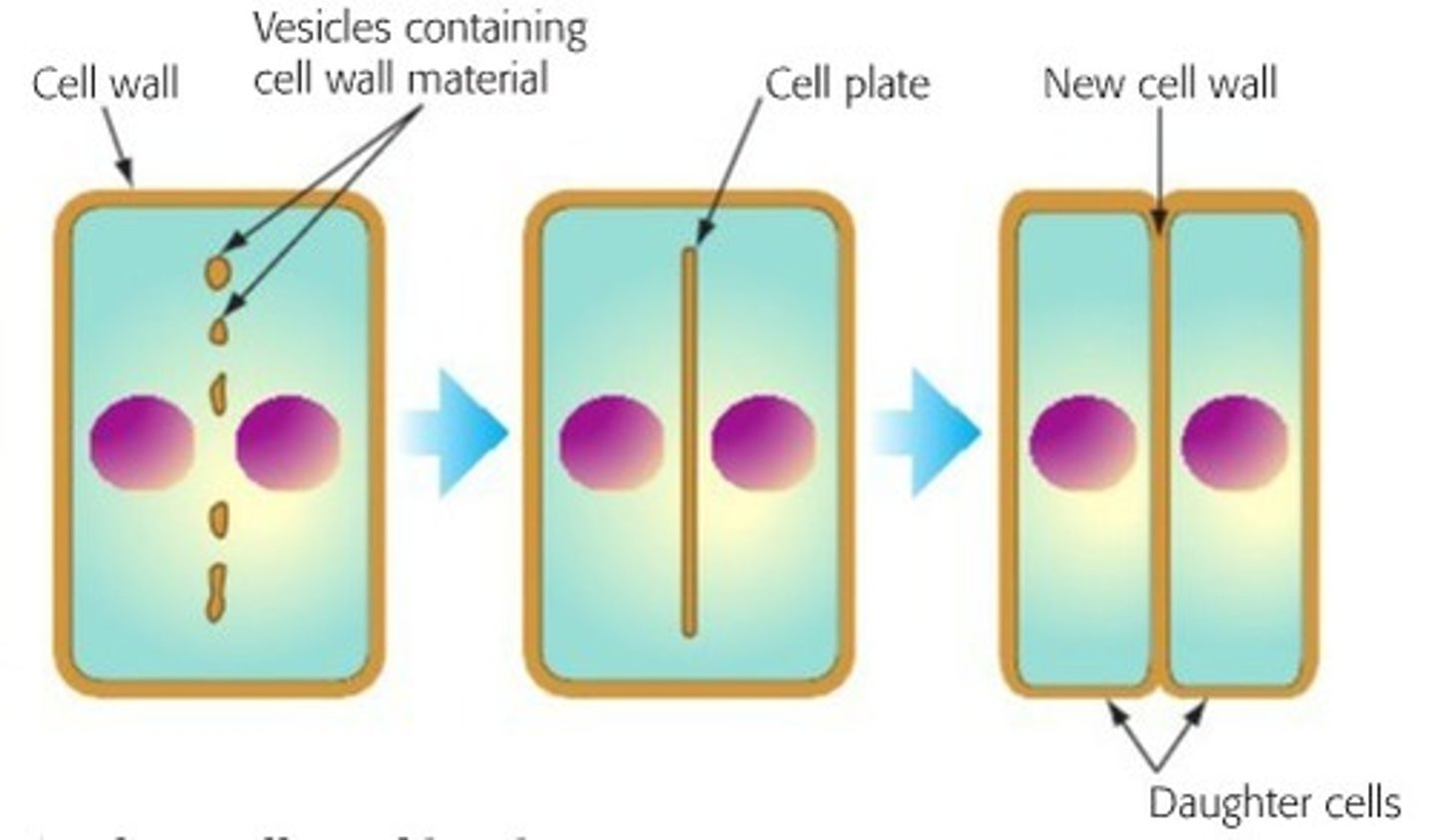
What happens during cytokinesis in plant cells?
a cell plate forms, followed by a new cell membrane, and finally a new cell wall forms
How do cyclins regulate the cell cycle?
1.Cyclins activate cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs), which control cell cycle processes through phosphorylation.
2.When a cyclin and CDK form a complex, the complex will bind to a target protein and modify it via phosphorylation.
3.The phosphorylated target protein will trigger some specific event within the cell cycle (e.g. centrosome duplication, etc.).
4.After the event has occurred, the cyclin is degraded and the CDK is rendered inactive again.
(Cells cannot progress to the next stage of the cell cycle unless the specific cyclin reaches it threshold)
How do CDKs promote cell division?
They phosphorylate proteins that allow passage through cell cycle checkpoints.
how do cell-cycle checkpoints regulate cell division?
Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. These include growth to the appropriate cell size, the replication and integrity of the chromosomes, and their accurate segregation at mitosis.
What is a haploid cell?
a cell that contains one set of chromosomes
What is a diploid cell?
A cell which contains the full number of chromosomes in homologous pairs.
what does homologus mean?
To have the same typical structure and position.
how do prokaryotic cells divide using binary fission?
asexual reproduction
what does non-homologus mean?
To not have the same typical structure and position.
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46 chromosomes
How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have?
23 pairs
what are the human gametes?
sperm and egg cells
Are eggs and sperm haploid or diploid?
haploid
What is the haplotonic life cycle?
a type of life cycle with a dominant haploid stage. Haplontic is a kind of life cycle in Biology where the zygote takes the lead, meaning, zygotes are the only diploid cell. It divides itself mitotically in order to give rise to a brand new plant.
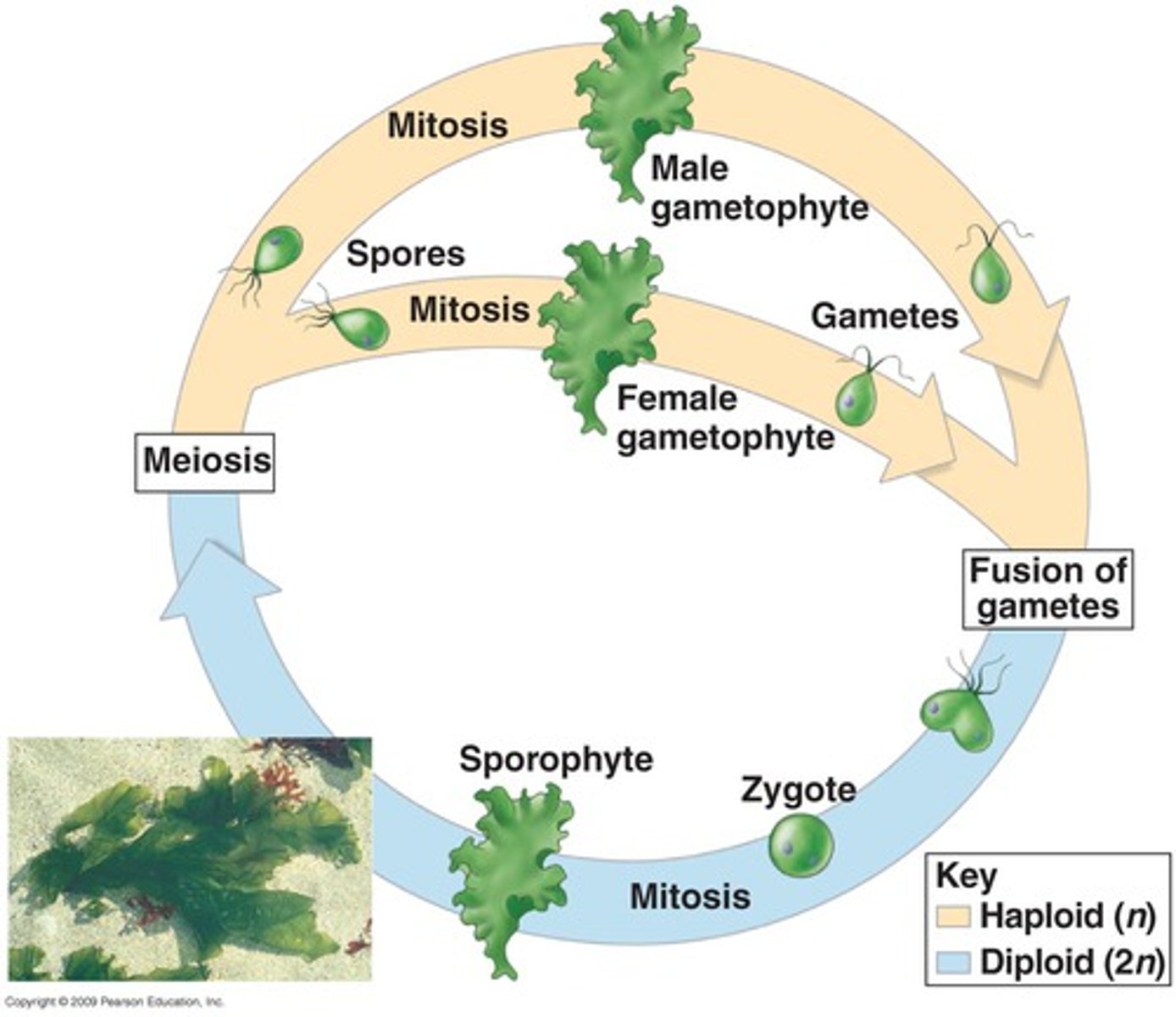
What is the diplotonic life cycle?
the life cycle of organisms, which is dominated by the diploid stage. Plants and algae show alternation of generation. All the plants showing sexual reproduction alternate between two multicellular stages, viz. Haploid gametophyte and diploid sporophytes.
What are the differences between asexual and sexual reproduction?
In sexual reproduction, an organism combines the genetic information from each of its parents and is genetically unique. In asexual reproduction, one parent copies itself to form a genetically identical offspring.
Describe the process of meiosis
Interphase- Cell growth and synthesis of DNA.
Meiosis I
Prophase I- Each replicated chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosome.
Metaphase I- paired homologous chromosomes line up across the center of the cell.
Anaphase I- Spindle fibers pull up each homologous chromosome pair towrad the opposite end of the cell.
Telophase I- a nuclear membrane forms around each cluster of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis- forms two new cells.
Meiosis II
Prophase II- chromasomes-each containing two chromatids- becomes visible.
Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and Telophase two are all the same as in Meiosis I the product is just four Haploid cells.
Describe the process of mitosis
- Start with: Diploid, 2N
- Interphase: DNA replication = Dipoid, 4N
- Prophase: Condensation of chromatin,
appearance of sister chromatids
- Metaphase: Sister chromatids align
- Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate,
centromeres divide
- Telophase and Cytokinesis: Two identical,
diploid, daughter cells: Diploid, 2N
What is independent assortment?
genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
What is recombination?
also called genetic recombination, is the process that introduces genetic diversity into the gametes during meiosis. There are 2 processes that make up recombination: independent assortment and crossing over.
How does independent assortment contribute to genetic variation?
Independent assortment produces new combinations of alleles.
In meiosis I, crossing over during prophase and independent assortment during anaphase creates sets of chromosomes with new combinations of alleles. Genetic variation is also introduced by random fertilization of the gametes produced by meiosis.
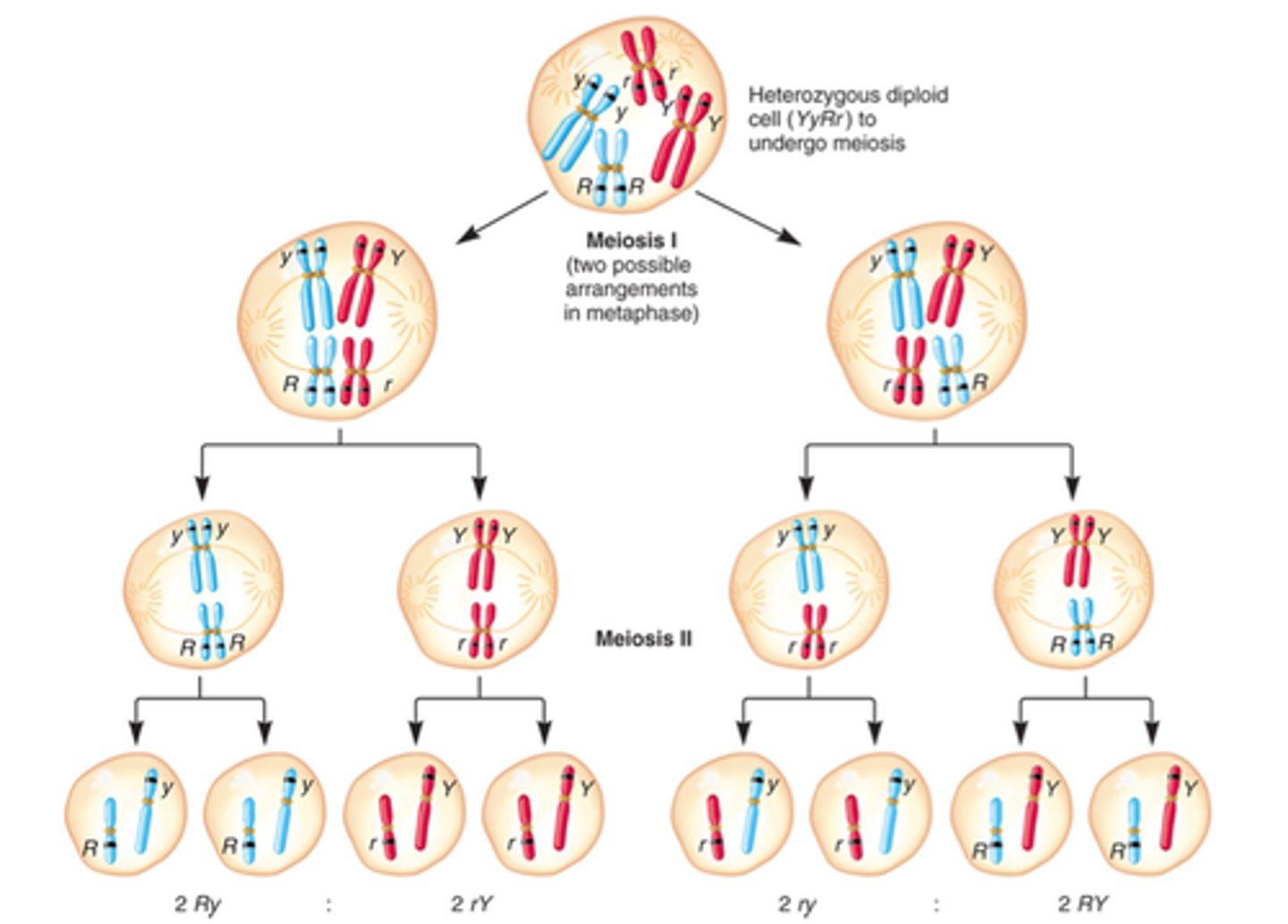
how does recombination contribute to genetic variation?
Recombination effectively 'shuffles' maternal and paternal DNA, creating new combinations of variants in the daughter germ-cells. Figure 2 Recombination contributes to human genetic variation by shuffling parental DNA and creating new combinations of variants.
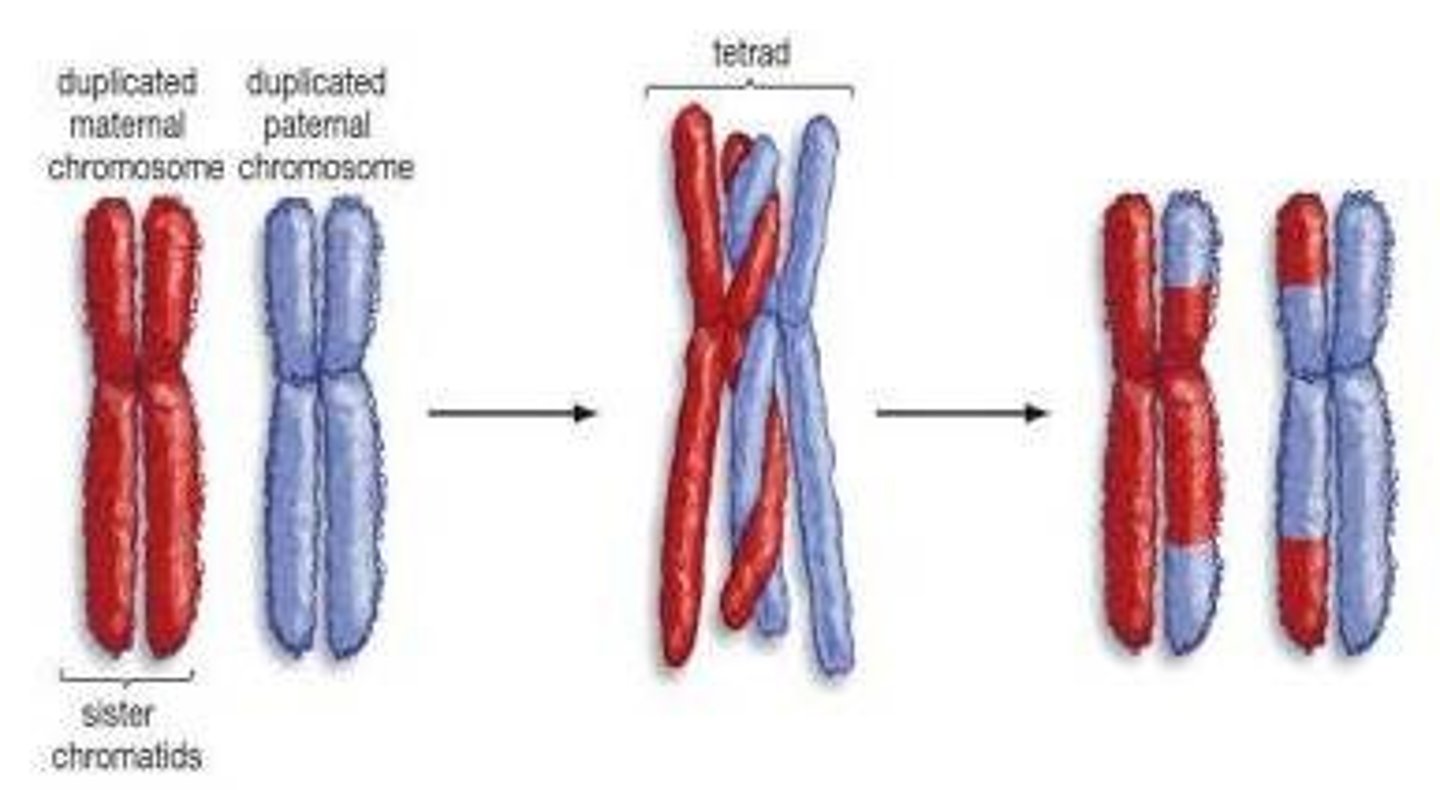
what is the difference between recombination and independent assortment?
Recombination occurs during meiosis to create variation, wherein some genes, that are far from each other on a chromosome, can get exchanged( with respect to alleles) while segregating( meiosis I). This does not follow Mendelian inheritance and we get the parental type offsprings as well as recombinants.
what is an allele?
one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome.
What is a somatic cell?
any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells.
what is a haploid cell?
a cell that contains one set of chromosomes